

 Flow graph is a single-entry,
single-exit directed graph G(N,E) that reflects the structure of a
procedural programming source code.
Flow graph is a single-entry,
single-exit directed graph G(N,E) that reflects the structure of a
procedural programming source code.
 Flow graph example
Flow graph example
PROGRAM main(INPUT,OUTPUT); VAR x,y,z: INTEGER; BEGIN READLN(x,y,z); y := f1(x,y); WHILE (x >= 0) z := f2(x,y,z); IF (y <= 400) OR (y > x) THEN y := f3(y) ELSE x := f4(x) END; WRITELN(z) END. A Pascal source code
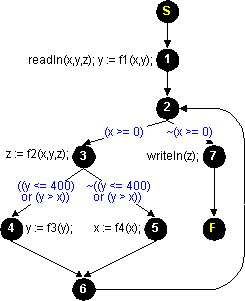 Labeled with statements and expressions | 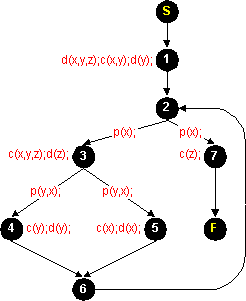 Labeled with defs, c-uses and p-uses |
| Flow graph example | |
 Flow Graph Generator (FGG)
extracts the information from a procedural programming source code to
generate a flow graph ASCII file, which is called flow file
[4] in short.
So far, FGG works only with the Pascal source code using the
programming unit Pasflow [4].
Future development will expand the input domain to cover the specifications
given as an Estelle module or an SDL process.
Flow Graph Generator (FGG)
extracts the information from a procedural programming source code to
generate a flow graph ASCII file, which is called flow file
[4] in short.
So far, FGG works only with the Pascal source code using the
programming unit Pasflow [4].
Future development will expand the input domain to cover the specifications
given as an Estelle module or an SDL process.
 Web
Web