ITI 1121. Introduction to Computer Science II
Laboratory 6
Winter 2013
Objectives
- Creating a hierarchy of classes
- Further understanding of inheritance
- Further understanding of polymorphism
- Creating memory diagrams
Biological Game of Life
This laboratory brings together two problems. One of them is the Game of Life; invented by the Cambridge
mathematician John Conway. The game consists of a two dimensional grid, where each cell is occupied or
not. Based on simple rules, a cell can live, die or multiply. Since this laboratory is about inheritance,
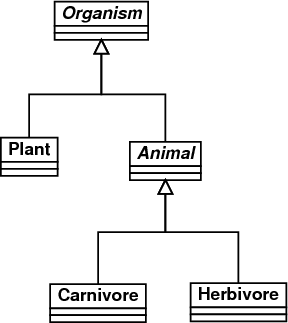
we are introducing a new concept to the game: let the content of a cell be an Organism, where an
Organism can be either a Plant or an Animal. The animals are further divided into herbivores and
carnivores. All the organisms have an update method that determines, based on its neighborhood, if this
Organism will survive to the next generation. The particular survival rules depend on the particular
Organism.
The class Simulation is the heart of this application. A run consists of fixed number of discrete generations. At
the start of the simulation, a two dimensional grid is created and initialized with a population of organisms. At each
generation, the simulation gathers, for each Organism, the list of its neighbors; a cell has a maximum of 8
neighbors. The method update of the Organism receives the list of neighbors and this information is used to
determine if the Organism remains alive or dies. New organisms come to life at each generation, and the dead
organisms are removed from the grid. The simulation ends when the maximum number of generations has been
reached. You will be implementing the classes that determine behavior of the simulation; the class Organism and
its descendants.
1 Organism
Implement an abstract class, called Organism, to represent the characteristics that are common to all the
organisms. Namely,
- An Organism is alive or not; all the organisms are alive at birth;
- It has an instance method, boolean isAlive(), that returns true if this Organism is alive, and false
otherwise;
- It declares an abstract (instance) method, void update( Organism[] neighbors ), that will be
implemented by the subclasses of Organisms.
2 Plant
Create a subclass of Organism to represent the characteristics of all plants. This will be a concrete class called
Plant.
- Give an implementation for the method void update( Organism[] neighbors ),
- A Plant dies when surrounded by 5 or more neighboring organisms;
- A Plant dies if it is surrounded by 2 or more Herbivores.
If none of the above rules apply, a Plant can live forever.
- Implement a method public String toString() to return the String “P” (quotes not included).
3 Animal
Create an abstract subclass of Organism to represent the characteristics of all animals, call this class
Animal.
- All animals have an age. At the birth of the Animal, its age is 0. At every generation (each call to the
method update) the age will be incremented by 1;
- Create an access method that returns the age of this Animal.
4 Herbivore
A Herbivore is an Animal that eats plants (i.e. is a subclass of Animal).
- Implement the method public void update( Organism[] neighbours ), such that,
- A Herbivore dies unless it is surrounded by at least one Plant;
- A Herbivore cannot live more than 20 generations.
- Implement a method public String toString() to return the String “H” (quotes not included).
5 Carnivore
A Carnivore is an Animal that eats other animals.
- A Carnivore must eat regularly. If a Carnivore is not surrounded by at least one Animal for a given
generation, this counts as one fasting generation;
- Implement the method public void update(Organism[] neighbours), such that,
- A Carnivore dies after four consecutive generations of fasting;
- A Carnivore cannot live more than 15 generations.
- Implement a method public String toString() to return the String “C” (quotes not included).
6 Simulation
As explained in the introduction, the Simulation is the hearth of this program. It creates the initial population of
Organisms and orchestrates the simulation. Complete the implementation by creating the following two
methods.
- Implement the method public String toString() that displays the content of the grid. The format
is as follows, the header consists of the label “Generation = ” followed by the current number of
generations. It is followed by a two dimensional grid of cells, where each cell is represented by the
String “[X]”, where X is a blank symbol (space) if the cell is not occupied or a symbol that depends of
the particular Organism that occupies the cell. See below for an example;
- Implement the method public void tabulate() that displays statistics about the current population.
Specifically, it lists the total number of Organisms, Plants, Animals, Herbivores and Carnivores. See
below for an example.
Class diagram
Files
- Organism.java
- Plant.java
- Animal.java
- Herbivore.java
- Carnivore.java
- Simulation.java
7 Quiz (1 mark)
- Draw memory diagrams for all variables and objects created during the execution of the main method
below.
class Singleton {
private int value;
Singleton( int value ) {
this.value = value;
}
}
class Pair {
private Object first;
private Object second;
Pair( Object first, Object second ) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
public class Quiz {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
Singleton s;
Pair p1, p2;
s = new Singleton( 99 );
p2 = new Pair( s, null );
p1 = new Pair( s, p2 );
}
}
Create a file called README.txt containing your name, student id, as well as the answer to the above quiz. Put
all the files that were created for this assignment, including the README file, into a directory called l5_123456,
where 123456 has been substituted by your student id. Create a jar file with the content of that directory (make
sure that it has a top directory named l5_123456). Now submit the archive (l5_123456.jar) using Blackboard
Learn:
- If your TA agrees with this, you can draw the memory diagrams for the quiz on a piece of paper (with
your name and student id) that you will hand in to her (him). You still need to upload the files for the
assignment on the Virtual Campus.
Example of an output
> java Simulation
Generation = 0
[P][ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][P][ ][C]
[P][ ][ ][P][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[P][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][P][ ][ ][ ]
[P][H][ ][P][P][C][H][H][ ][C]
[ ][H][P][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][P]
[ ][H][P][P][ ][H][ ][ ][P][P]
[ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][P][ ][ ]
[P][ ][H][ ][P][ ][H][H][H][ ]
[ ][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ][C][ ][P]
[H][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ][P][ ]
Organisms = 41
Plants = 26
Animals = 15
Herbivores = 11
Carnivores = 4
Generation = 1
[P][ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][P][ ][C]
[P][ ][ ][P][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[P][ ][P][ ][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[ ][H][P][P][P][C][H][H][ ][C]
[ ][H][ ][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][P][P]
[ ][H][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][P][P][P]
[ ][ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[P][ ][H][ ][P][ ][H][H][H][ ]
[ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][ ][C][ ][P]
[ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][ ][ ][P][ ]
Organisms = 43
Plants = 30
Animals = 13
Herbivores = 9
Carnivores = 4
Generation = 2
[P][ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][P][ ][C]
[P][ ][ ][P][P][P][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[P][ ][P][ ][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][ ]
[ ][H][ ][P][P][C][H][H][ ][C]
[ ][H][P][ ][P][ ][ ][P][ ][P]
[ ][ ][P][P][ ][ ][ ][P][P][P]
[ ][ ][P][P][P][ ][ ][ ][P][P]
[P][ ][H][ ][P][ ][ ][ ][H][P]
[ ][ ][P][P][P][ ][ ][C][P][P]
[ ][ ][P][P][P][ ][ ][ ][P][P]
Organisms = 50
Plants = 40
Animals = 10
Herbivores = 6
Carnivores = 4
Last Modified: February 10, 2013