| 10 ton asteroid impact | has average interval time 1 year |  |
| is a kind of asteroid impact |  |
| 100 ton asteroid impact | has average interval time 10 years |  |
| is a kind of asteroid impact |  |
| 1000 ton asteroid impact | has average interval time 100 years |  |
| is a kind of asteroid impact |  |
| 16th century scientist | has definition a scientist born between 1500 and 1600 AD |  |
| is a kind of dead person |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| 17 Leporis | has companion M1 III | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A close binary system (A0 V, M1 III) with a shell-like spectrum indicating that mass transfer may be occurring from the late-type companion onto the A0 primary. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has primary A0 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Lepus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of shell star |  |
| 17th century scientist | has definition a scientist born between 1600 and 1700 AD |  |
| is a kind of dead person |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| 18th century scientist | has definition a scientist born between 1700 and 1800 AD |  |
| is a kind of dead person |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| 19th century scientist | has definition a scientist born between 1800 and 1900 AD |  |
| is a kind of dead person |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| 2-meter Telescope | has altitude 331 m |  |
| has aperture 1.34 m |  |
| has comment can also be used in Cassegrain and coude modes |  |
| has creation date 1960 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.00 |  |
| has has mirror diameter 2 m |  |
| has latitude 50° 59' N |  |
| has location Tautenberg, Germany |  |
| has longitude 11° 43'E |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has mirror type Schott ZK-7 glass |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has owner Karl Schwarzschild Observatorium |  |
| has synonym Tautenberg Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| 2.3-meter Telescope | has altitude 725 m |  |
| has aperture 2.33 m |  |
| has creation date 1985 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.25, 13, 43 |  |
| has latitude 12° 35' N |  |
| has location Kavalur, Tamil Nadu, India |  |
| has longitude 78° 50' E |  |
| has mirror maker Indian Inst. Astrophys. |  |
| has mirror type Zerodur |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Walchandnagar Industries |  |
| has owner Vainu Bappu Observatory |  |
| has synonym Vainu Bappu 2.3 m |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| 20th century scientist | has definition a scientist born between 1900 and 2000 AD |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| 26-inch Equatorial | has altitude 92 m |  |
| has aperture 0.66 m |  |
| has creation date 1873 |  |
| has focal ratio f/15.0 |  |
| has latitude 38° 55' N |  |
| has lens maker Alvan Clark & Sons |  |
| has location Washington, DC, US |  |
| has longitude 77° 04' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Warner and Swasey |  |
| has owner US Naval Observatory |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| 28-inch Visual Refractor | has altitude 47 m |  |
| has aperture 0.711 m |  |
| has comment Dome under repair in 1992 |  |
| has creation date 1894 |  |
| has focal ratio f/11.9 |  |
| has latitude 51° 29' N |  |
| has lens maker Gmbh |  |
| has location Greenwich, London, England |  |
| has longitude 00° 00' |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Ransomes and Sims |  |
| has owner Old Royal Observatory |  |
| has synonym Greenwich refractor |  |
| is an instance of English equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| 2U 1543-47 | is an instance of transient X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| 3 alpha process | has definition A nuclear reaction (3 4He → 12C + γ + 7 MeV) by which helium is transformed into carbon. The process is dominant in red giants. At a temperature of about 2 × 108 K and a density of 105 g cm-3, after core hydrogen is exhausted, three α-particles can fuse to form an excited nucleus of carbon 12, which occasionally decays into a stable carbon 12 nucleus. The overall process can be looked upon as an equilibrium between three helium nuclei and the excited 12C*, with occasional irreversible leakage out of the equilibrium into the ground state of carbon 12. Further capture of α-particles by carbon 12 nuclei produces oxygen 16 and neon 20. (also called the triple-α process) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| 3-kpc arm | has definition A component of the Sagittarius arm with noncircular gas motions. It is seen in absorption against Sgr A with a velocity of -53 km s-1, implying that at least part of the arm is expanding away from the galactic center. The nearest "edge" is presently at a radius of 4 kpc from the Galactic center. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Sagittarius arm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| 3.5-meter Telescope | has altitude 2168 m |  |
| has aperture 3.50 m |  |
| has creation date 1984 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.5, 3.9, 10, 35 |  |
| has latitude 37° 13' N |  |
| has location Calar Alto, Spain |  |
| has longitude 2° 32' W |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss (Ober.) |  |
| has mirror type Zerodur |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Voith, Heidenheim; Zeiss (Ober.) |  |
| has operator German-Spanish Astronomical Center |  |
| has owner Calar Alto Observatory |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| 30 Doradus Nebula | has absolute magnitude Mv = - 19 |  |
| has definition A giant H II region, at least 300 pc across - one of the largest known. It is larger and more luminous than any known in the Galaxy. It is the brightest object in the Large Magellanic Cloud at both optical and radio wavelengths, and contains the densest concentration of W-R stars. (The brightest object near the center is a O+ WN star of Mv = - 10.2.) It is characterized by very rapid, disordered, and complex motions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 170000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym Great Looped Nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 2070 |  |
| has synonym Tarantula Nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| 36-inch Refractor | has altitude 1290 m |  |
| has aperture 0.895 m |  |
| has comment Front surface of crown element refigured in 1987 |  |
| has creation date 1888 |  |
| has focal ratio f/19.7 |  |
| has latitude 37° 20' N |  |
| has lens maker Alvan Clark & Sons |  |
| has location Mount Hamilton, Calif., US |  |
| has longitude 121° 39' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Warner and Swasey |  |
| has owner Lick Observatory |  |
| has synonym 36 inch |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| 3TA-10 Schmidt Telescope | has altitude 1450 m |  |
| has aperture 1.00 m |  |
| has comment three 1 m diameter objective prisms |  |
| has creation date 1961 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.13 |  |
| has latitude 40° 20' N |  |
| has location Mount Aragatz, Armenia |  |
| has longitude 44° 30' E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.5 m |  |
| has mirror maker LOMO |  |
| has mounting manufacturer LOMO |  |
| has owner Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory |  |
| has synonym Byurakan Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| 4-kpc arm | has definition A component of the Sagittarius arm with noncircular gas motions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Sagittarius arm |  |
| 40 Eridani | has definition A nearby triple system, 5 pc distant. Component A is K0 V; component B is a DA white dwarf; component C is M5e V. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Eridanus |  |
| is an instance of triple star |  |
| 47 Tucanae | has definition A metal-rich globular cluster. It has roughly one-quarter the solar metal abundance. It has a high galactic latitude and low reddening. It is a member of the thick-disk population. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 15000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Tucana |  |
| is an instance of unclassified globular cluster |  |
| 4N nucleus | has definition Nuclei possessing equal and even numbers of neutrons and protons. 4N nuclei are formed in supernova envelopes at temperatures of at least 2 × 109 K and are very stable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym even-even nucleus |  |
| is a kind of Bose-Einstein nucleus |  |
| 53 Arietis | has definition Runaway star which diverges from a comparatively small area in Orion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Aries | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of runaway star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| 61 Cygni | has definition The first star other than the Sun to have its parallax, and hence distance, measured. The star is a double orange dwarf. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 11.4 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cygnus | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high proper motion star |  |
| [O III] line | is a kind of forbidden line |  |
| [WR] star | has definition WR star that is the central object of a planetary nebula. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Wolf-Rayet |  |
| A band | has definition One of about a dozen of the strongest Fraunhofer lines seen in the Solar spectrum, the A band at 7600 angstoms is due to telluric lines of molecular oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. (originally thought to originate in the Sun by Fraunhofer) |  |
| has species O2 |  |
| has wavelength 7600 Å |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| occurs in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| A ring | is a kind of ring |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| A star | has absorption line H I |  |
| has color white |  |
| has definition Star with spectral type A in which the spectrum of the Balmer lines of hydrogen attain their greatest strength. Helium lines can no longer be seen. Some metallic lines are present; in late A stars the H and K lines of ionized calcium appear. A0 stars have a color index of zero. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 10000 K |  |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| ablation | has definition Removal of material from a solid by heating, vaporization or collisions | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has example Erosion of a meteorite by the friction generated when it passes through the Earth's atmosphere. The material passes from solid to gas phase. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has final phase gas |  |
| has initial phase solid |  |
| has inverse process condensation |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| absolute magnitude | has definition A measure of the intrinsic brightness of a star or galaxy. Absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude the star or galaxy would have if it were 32.6 light-years (10 parsecs) from Earth. The lower an object's absolute magnitude, the greater its intrinsic brightness. For example, the Sun has an absolute magnitude of +4.83, while Sirius, whose intrinsic brightness is greater, has an absolute magnitude of +1.43. A star that is one absolute magnitude brighter than another (e.g., +4 versus +5) is 2.5 times intrinsically brighter; a star that is 5 absolute magnitudes brighter is 100 times intrinsically brighter; and a star that is 10 absolute magnitudes brighter is 10000 times intrinsically brighter. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The absolute magnitude (g) of a solar-system body such as an asteroid is defined as the brightness at zero phase angle when the object is 1 AU from the Sun and 1 AU from the observer. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of magnitude |  |
| absolute temperature | has definition Temperature measured on the Kelvin scale: 0 Kelvin = -273.15 ° Celsius. Absolute temperature is directly related to (kinetic) energy via the equation E = kBT, where kB is Boltzmann's constant. So, a temperature of 0 K corresponds to zero energy, and room temperature, 300 K = 27 °C, corresponds to an energy of 0.025 eV. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| absolute zero | has definition The lowest possible temperature, attained when a system is at its minimum possible energy. The Kelvin temperature scale sets its zero point at absolute zero (-273.15° on the Celsius scale, and -434.07° on the Fahrenheit scale). | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature |  |
| absorption | has definition Decrease in the intensity of radiation, representing energy converted into excitation or ionization of electrons in the region through which the radiation travels. As contrasted with monochromatic scattering (in which reemission occurs in all directions at the same frequency), the inverse process of emission refers to radiation that is reemitted in general in all directions and at all frequencies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has inverse process emission |  |
| is a kind of radiation intensity modification |  |
| absorption edge | has definition Sudden rises superposed on the smooth decrease of the curve of the attenuation coefficient, which cause the curve to have a typical sawtooth aspect. They generally occur at the limit of spectral lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral feature |  |
| absorption line | has antonym emission line |  |
| has definition Dark line in a spectrum, produced when light or other electromagnetic radiation coming from a distant source passes through a gas cloud or similar object closer to the observer. Like emission lines, absorption lines betray the chemical composition and velocity of the material that produces them. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Dark line superposed on a continuous spectrum, caused by the absorption of light passing through a gas of lower temperature than the continuum light source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| abstraction | has definition a general concept formed by extracting common features from specific examples |  |
| is a kind of kbTop |  |
| acceleration unit | has definition meter per second squared |  |
| has symbol m·s-2 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| accretion | has definition A process by which a star accumulates matter as it moves through a dense cloud of interstellar gas; or, more generally, whereby matter surrounding a star flows toward it (as in close binaries). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Collection of material together, generally to form a single body. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of contraction |  |
| accumulating oceanic element | has ocean concentration depth indenpendent |  |
| has ocean residence time 105 years or greater |  |
| is a kind of oceanic element |  |
| accumulation theory | has definition The theory by which planetesimals are assumed to collide with one another and coalesce, eventually sweeping up enough material to form the planets. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planetary theory |  |
| acetaldehyde | has symbol CH3CHO |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Achernar | has B-V magnitude -0.16 |  |
| has declination -57 14 12 |  |
| has distance 35 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 1 37 42.9 |  |
| has spectral type B3Vpe |  |
| has spectral type B5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha Eridani | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 472 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.46 |  |
is a part of Eridanus  |  |
| is an instance of B star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif) |
| Achilles | has asteroid number 588 |  |
| has definition Trojan asteroid (60°) ahead of Jupiter. It was the first Trojan to be discovered. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1906 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.15 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 10°.3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 11.98 yr | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 5.2 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Trojan asteroid |  |
| is an instance of Trojan asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| achromatic lens | has definition Lens (or combination of lenses) that brings different wavelenghts within a ray of light to a single focus, thus overcoming chromatic aberration. It was first successfully made by Joseph von Fraunhofer. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of lens |  |
| achromatic objective | has definition A lens of two or more components with different refraction indices (e.g., crown glass and flint glass), used to correct for chromatic aberration. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of achromatic lens |  |
| actinide | has atomic number 89 to 103 |  |
| has definition Element with atomic number between 89 (Actinium) and 103 | ![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has filling orbital 5f |  |
| is a kind of inner transition metal |  |
| is a kind of inner transition metal |  |
| is a kind of metal | ![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:23.0](facet.gif) |
| actinium | has abundance minute traces in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance n.a. in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance nil in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 383.312 nm for Ac II |  |
| has atomic emission line 408.844 nm for Ac II |  |
| has atomic emission line 450.720 nm for Ac II |  |
| has atomic emission line 591.085 nm for Ac II |  |
| has atomic emission line 416.840 nm for Ac II (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 438.641 nm for Ac II (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 89 |  |
| has atomic radii 188 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 3470 ± 300 K |  |
| has chief source uranium ore contain 0.2 p.p.m. |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 531.1 pm |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. |  |
| has daily dietary intake nil |  |
| has definition soft, silvery-white, radioactive metal which glows in the dark |  |
| has density 10060 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Andre Debierne |  |
| has discovery date 1899 |  |
| has discovery location Paris, France |  |
| has electron configuration [Rn]6d17s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.1 Pauling |  |
| has hazard never encountered normally, dangerous because it is a powerful source of α-radiation, element found only inside nuclear facilities or research laboratories |  |
| has heat capacity 20.84 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 27.2 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 14.2 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of sublimation 51.9 ± 0.5 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 418 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image 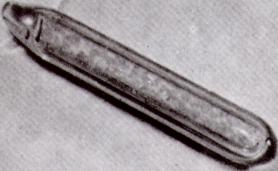 |  |
| has ionic radii 118 pm for Ac3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 209 to 232 |  |
| has level in humans nil |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 14.9 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope actinium 227 |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass of element in person nil for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1320 ± 50 K |  |
| has molar volume 22.6 cm3 |  |
| has name origin aktinos from Greek word for 'ray' |  |
has number of isotopes 26  |  |
| has number of protons 89 |  |
| has pronunciation ak-tin-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7440-34-8 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 227.0728 for 227Ac in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has space group Fm3m |  |
| has specimen not commerecially available |  |
| has symbol Ac |  |
| has symbol Ac |  |
| has synthesis mechanism bombardment of radium 236 with neutrons |  |
| has synthesis mechanism decay of uranium 235 |  |
| has term symbol 2D3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 12 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has world production probably less than a gram |  |
| is a kind of actinide |  |
| is a kind of radioactive element |  |
| reacts with water to release hydrogen gas |  |
| actinium 224 | has atomic mass 224.021685 |  |
| has decay mode α (6.323 MeV) 9.1% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.397 MeV) 90.9% |  |
| has half life 2.9 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = |  |
| has number of neutrons 135 |  |
| has number of nucleons 224 |  |
| has symbol 224Ac |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| actinium 225 | has atomic mass 225.023205 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.935 MeV) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 10.0 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 136 |  |
| has number of nucleons 225 |  |
| has symbol 225Ac |  |
| has uses tracer |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| actinium 226 | has atomic mass 226.026084 |  |
| has decay mode α 6 × 10-3% |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.117) 83 % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.635 MeV) 17% |  |
| has half life 29 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1- |  |
| has number of neutrons 137 |  |
| has number of nucleons 226 |  |
| has symbol 226Ac |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| actinium 227 | has atomic mass 227.027750 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.043 Mev) 1.380% |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.0410 Mev) 98.620% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay products radium 223 |  |
| has decay products thorium 227 |  |
| has half life 21.773 years |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 3.5 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has NMR frequency 13.1 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.1 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 1.7 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 138 |  |
| has number of nucleons 227 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 227Ac |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 515 barns |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| actinium 228 | has atomic mass 228.031015 |  |
has decay mode β- (2.142 MeV)  |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 6.15 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 139 |  |
| has number of nucleons 228 |  |
| has symbol 228Ac |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| actinium 229 | has atomic mass 229.032980 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.0410 MeV) 99% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 62.7 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 140 |  |
| has number of nucleons 229 |  |
| has symbol 229Ac |  |
is an instance of actinium  |  |
| active galaxy | has definition Active galactic nuclei are very luminous. Their energy output is in two forms: nonthermal continuum and thermal emission line. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any galaxy which is emitting large quantities of non-thermal radiation. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity 1043 to 1046 ergs s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| active optics | has definition Controlling the shape of a telescope mirror at a relatively slow rate. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| active satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| active Sun | has definition The Sun during its 11-year cycle of activity when spots, flares, prominences, and variations in radiofrequency radiation are at a maximum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 11 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of periodic celestial event |  |
| is an instance of solar event |  |
| adaptive optics | has definition Compensating for atmospheric distortions in a wavefront by high-speed changes in the shape of a small, thin mirror. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| advance of the perihelion | has definition The slow rotation of the major axis of a planet's orbit in the same direction as the revolution of the planet itself, due to gravitational interactions with other planets and/or other effects (such as those due to general relativity). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| AE Aurigae | has definition Runaway star which diverges from a comparatively small area in Orion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O9.5 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Auriga | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| is an instance of runaway star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| Ae star | has definition A-type star with emission in one or several Balmer lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line one or several Balmer lines |  |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| aeon | has definition In astronomical terms, 1000 million years. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym eon |  |
| is an instance of time unit |  |
| aether | has definition In Aristotelian physics, the fifth element, of which the stars and planets are made. |  |
| has definition In Classical physics, an invisible medium that was thought to suffuse all space. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| AI Velorum star | has definition A class of dwarf Cepheids. They are all RR Lyrae stars with periods shorter than 0.25 days. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf Cepheid |  |
| airborne telescope | is a kind of telescope |  |
| airglow | has definition Light in the nighttime sky caused by the collision of atoms and molecules (primarily oxygen, OH, and Ne) in Earth's geocorona with charged particles and X-rays from the Sun or outer space. The airglow varies with time of night, latitude, and season. It is a minimum at zenith and maximum about 10° above the horizon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym nightglow |  |
| is a part of geocorona |  |
| alchemy | has definition Art of bringing parts of the universe to the perfect state toward which they were thought to aspire - e.g., gold for metals, immortality for human beings. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| Aldebaran | has B-V magnitude 1.54 |  |
| has declination +16 30 33 |  |
| has definition A K5 III subgiant (a foreground star in the Hyades). It has a faint M2 V companion. It is now known to be slowly and irregularly variable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 21 parsecs | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 4 35 55.2 |  |
| has spectral type K5III |  |
| has synonym alpha Tau | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 1457 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.85 |  |
is a part of Taurus  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Algol | has definition An eclipsing system of at least three components (B8 V, K0, Am). Period of components A and B is about 68.8 hours; period of components A, B, and C is about 1.9 years. Long term observations also indicate a massive, unseen fourth component with a period of about 190 years. Algol is also an erratic radio source of about 0.5 AU diameter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The most famous eclipsing binary, Algol was probably the first variable star discovered. It lies in the constellation Perseus and consists of two stars that orbit each other every 2.87 days. When one star passes in front of the other, the light of the system dims. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 25 pc |  |
| has synonym beta Per |  |
| has synonym Demon star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Perseus |  |
| is an instance of beta Persei star |  |
| alkali earth metal | has definition Element in the second column of the periodic table (from the left) |  |
| alkali Earth metal | has group 2 |  |
| alkali earth metal | has hardness malleable, extrudable and machinable |  |
| alkali Earth metal | has synonym group II element |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| alkali earth metal | is a kind of metallic element |  |
| alkali metal | has appearancee silvery except for francium |  |
| has definition Metal in the first column of the periodic table | ![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has group 1 |  |
| has hardness soft |  |
| has synonym group I element |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| reacts with water vigorously |  |
| Alpha Andromedae | has B-V magnitude -0.11 |  |
| has declination +29 05 26 |  |
| has right ascension 00 08 23.2 |  |
| has spectral type B8IVpMnHg |  |
| has synonym HR 15 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.06 |  |
is a part of Andromeda  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Antliae | has B-V magnitude 1.45 |  |
| has declination -31 04 04 |  |
| has right ascension 10 27 09.1 |  |
| has spectral type K4III |  |
| has synonym HR 4104 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.25 |  |
is a part of Antlia  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Apodis | has B-V magnitude 1.43 |  |
| has declination -79 02 41 |  |
| has right ascension 14 47 51.6 |  |
| has spectral type K2.5III |  |
| has synonym HR 5470 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.83 |  |
is a part of Apus  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Arietis | has B-V magnitude 1.15 |  |
| has declination +23 27 45 |  |
| has right ascension 02 07 10.3 |  |
| has spectral type K2IIIabCa-I |  |
| has synonym HR 617 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.00 |  |
is a part of Aries  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Caeli | has B-V magnitude 0.34 |  |
| has declination -41 51 50 |  |
| has right ascension 4 40 33.6 |  |
| has spectral type F2V |  |
| has synonym HR 1502 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.45 |  |
is a part of Caelum  |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Cassiopeiae | has B-V magnitude 1.17 |  |
| has declination +56 32 15 |  |
| has right ascension 0 40 30.4 |  |
| has spectral type K0III |  |
| has synonym HR 168 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.23 |  |
is a part of Cassiopeia  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| alpha Centauri | has B-V magnitude 0.71 |  |
| has declination -60 50 07 |  |
| has definition A binary star whose components have G2 V and K5 V spectral types. The nearest star system to the Sun and the third brightest star in the night sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4.35 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 80 years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has proper motion 3'.68 per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 14 39 36.2 |  |
| has spectral type G2V |  |
| has synonym HR 5459 |  |
| has synonym Rigil Kent | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has V magnitude -0.01 |  |
is a part of Centaurus  |  |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Cephei | has B-V magnitude 0.22 |  |
| has declination +62 35 08 |  |
| has right ascension 21 18 34.7 |  |
| has spectral type A7V |  |
| has synonym HR 8162 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.44 |  |
is a part of Cepheus  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Chamaeleontis | has B-V magnitude 0.39 |  |
| has declination -76 55 11 |  |
| has right ascension 08 18 31.7 |  |
| has spectral type F5III |  |
| has synonym HR 3318 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.07 |  |
is a part of Chamaeleon  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Circini | has B-V magnitude 0.24 |  |
| has declination -64 58 31 |  |
| has right ascension 14 42 30.3 |  |
| has spectral type ApSrEuCr: |  |
| has synonym HR 5463 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.19 |  |
is a part of Circinus  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Columbae | has B-V magnitude -0.12 |  |
| has declination -34 04 27 |  |
| has right ascension 05 39 38.9 |  |
| has spectral type B7IVe |  |
| has synonym HR 1956 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.64 |  |
is a part of Columba  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Comae Berenices | has B-V magnitude 0.00 |  |
| has declination +17 31 46 |  |
| has right ascension 13 09 59.2 |  |
| has spectral type F5V |  |
| has synonym HR 4969 |  |
| has V magnitude 5.22 |  |
is a part of Coma Berenices  |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| Alpha Coronae Autralis | has B-V magnitude 0.04 |  |
| has declination -37 54 16 |  |
| has right ascension 19 09 28.2 |  |
| has spectral type A2V |  |
| has synonym HR 7254 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.11 |  |
is a part of Corona Australis  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Coronae Borealis | has B-V magnitude -0.02 |  |
| has declination +26 42 53 |  |
| has right ascension 15 34 41.2 |  |
| has spectral type A0V |  |
| has synonym HR 5793 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.23 |  |
is a part of Corona Borealis  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| alpha decay | has definition Spontaneous emission by a heavier element (such as uranium) of positively charged helium nuclei - alpha particles - comprising 2 protons and 2 neutrons. The result of this radioactive decay is that the original element is very gradually converted into another element, with a decreased atomic number and mass. Alpha particle emission may be simultaneous with beta particle decay. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The disintegration of an atomic nucleus, in which the final products are an alpha particle and a nucleus with two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the original. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nuclear decay |  |
| Alpha Doradus | has B-V magnitude -0.10 |  |
| has declination -55 2 42 |  |
| has right ascension 4 33 59.8 |  |
| has spectral type A0IIISi |  |
| has synonym HR 1465 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.27 |  |
is a part of Dorado  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Equulei | has B-V magnitude 0.53 |  |
| has declination + 5 14 52 |  |
| has right ascension 21 15 49.3 |  |
| has spectral type G0III+A5V |  |
| has synonym HR 8131 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.92 |  |
is a part of Equuleus  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Fornacis | has B-V magnitude 0.52 |  |
| has declination -28 59 14 |  |
| has right ascension 03 12 04.2 |  |
| has spectral type F8V |  |
| has synonym HR 963 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.87 |  |
is a part of Fornax  |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Gruis | has B-V magnitude -0.13 |  |
| has declination -46 57 40 |  |
| has right ascension 22 8 13.9 |  |
| has spectral type B7IV |  |
| has synonym HR 8425 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.74 |  |
is a part of Grus  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Horologii | has B-V magnitude 1.10 |  |
| has declination -42 17 40 |  |
| has right ascension 04 14 00.1 |  |
| has spectral type K1III |  |
| has synonym HR 1326 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.86 |  |
is a part of Horologium  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Hydrae | has B-V magnitude 1.44 |  |
| has declination -8 39 31 |  |
| has right ascension 9 27 35.2 |  |
| has spectral type K3II-III |  |
| has synonym Alphard |  |
| has synonym HR 3748 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.98 |  |
is a part of Hydra  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Indi | has B-V magnitude 1.00 |  |
| has declination -47 17 29 |  |
| has right ascension 20 37 34.0 |  |
| has spectral type K0IIICNIII-IV |  |
| has synonym HR 7869 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.11 |  |
is a part of Indus  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Lacertae | has B-V magnitude 0.01 |  |
| has declination +50 16 57 |  |
| has right ascension 22 31 17.4 |  |
| has spectral type A1V |  |
| has synonym HR 8585 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.77 |  |
is a part of Lacerta  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Leonis | has B-V magnitude -0.11 |  |
| has declination +11 58 2 |  |
| has right ascension 10 8 22.3 |  |
| has spectral type B7V |  |
| has synonym HR 3982 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.35 |  |
is a part of Leo  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Leporis | has B-V magnitude 0.21 |  |
| has declination -17 49 20 |  |
| has right ascension 05 32 43.7 |  |
| has spectral type F0Ib |  |
| has synonym HR 1865 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.58 |  |
is a part of Lepus  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Lupi | has B-V magnitude -0.20 |  |
| has declination -47 23 17 |  |
| has right ascension 14 41 55.7 |  |
| has spectral type B1.5III |  |
| has synonym HR 5469 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.30 |  |
is a part of Lupus  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Lyncis | has B-V magnitude 1.55 |  |
| has declination +34 23 33 |  |
| has right ascension 9 21 3.2 |  |
| has spectral type K7IIIab |  |
| has synonym HR 3705 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.13 |  |
is a part of Lynx  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Mensae | has B-V magnitude 0.72 |  |
| has declination -74 45 11 |  |
| has right ascension 06 10 14.6 |  |
| has spectral type G6V |  |
| has synonym HR 2261 |  |
| has V magnitude 5.09 |  |
is a part of Mensa  |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| Alpha Monocerotis | has B-V magnitude 1.02 |  |
| has declination -09 33 04 |  |
| has right ascension 07 41 14.8 |  |
| has spectral type K0III |  |
| has synonym HR 2970 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.93 |  |
is a part of Monoceros  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Muscae | has B-V magnitude -0.20 |  |
| has declination -69 08 08 |  |
| has right ascension 12 37 11.0 |  |
| has spectral type B2IV-V |  |
| has synonym HR 4798 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.69 |  |
is a part of Musca  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Ophiuchi | has B-V magnitude 0.15 |  |
| has declination +12 33 36 |  |
| has right ascension 17 34 56.0 |  |
| has spectral type A5III |  |
| has synonym HR 6556 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.08 |  |
is a part of Ophiuchus  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| alpha particle mass | applies to particle alpha particle |  |
| has symbol mα |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000052 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 6.64465598 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| Alpha Pavonis | has B-V magnitude -0.20 |  |
| has declination -56 44 07 |  |
| has right ascension 20 25 38.8 |  |
| has spectral type B2IV |  |
| has synonym HR 7790 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.94 |  |
is a part of Pavo  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Persei | has B-V magnitude 0.48 |  |
| has declination +49 51 41 |  |
| has right ascension 3 24 19.3 |  |
| has spectral type F5Ib |  |
| has synonym HR 1017 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.79 |  |
is a part of Perseus  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of supergiant |  |
| alpha Persei cluster | has definition A young open cluster with a high mean rotational velocity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Perseus |  |
| is an instance of open cluster |  |
| Alpha Phoenicis | has B-V magnitude 1.09 |  |
| has declination -42 18 22 |  |
| has right ascension 0 26 17.0 |  |
| has spectral type K0III |  |
| has synonym HR 99 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.39 |  |
is a part of Phoenix  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Pictoris | has B-V magnitude 0.21 |  |
| has declination -61 56 29 |  |
| has right ascension 06 48 11.4 |  |
| has spectral type A7IV |  |
| has synonym HR 2550 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.27 |  |
is a part of Pictor  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Pyxidis | has B-V magnitude -0.18 |  |
| has declination -33 11 11 |  |
| has right ascension 08 43 35.5 |  |
| has spectral type B1.5III |  |
| has synonym HR 3468 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.68 |  |
is a part of Pyxis  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Reticuli | has B-V magnitude 0.91 |  |
| has declination -62 28 26 |  |
| has right ascension 04 14 25.5 |  |
| has spectral type G8II-III |  |
| has synonym HR 1336 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.35 |  |
is a part of Reticulum  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Sculptoris | has B-V magnitude -0.16 |  |
| has declination -29 21 28 |  |
| has right ascension 0 58 36.3 |  |
| has spectral type B7IIIp |  |
| has synonym HR 280 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.31 |  |
is a part of Sculptor  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Scuti | has B-V magnitude 1.33 |  |
| has declination -08 14 39 |  |
| has right ascension 18 35 12.3 |  |
| has spectral type K3III-IIIb |  |
| has synonym HR 6973 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.85 |  |
is a part of Scutum  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Serpentis | has B-V magnitude 1.17 |  |
| has declination +6 25 32 |  |
| has right ascension 15 44 16.0 |  |
| has spectral type K2IIIbCN1Fe414 |  |
| has synonym HR 5854 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.65 |  |
is a part of Serpens  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Sextantis | has B-V magnitude -0.04 |  |
| has declination -0 22 18 |  |
| has right ascension 10 7 56.2 |  |
| has spectral type A0III |  |
| has synonym HR 3981 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.49 |  |
is a part of Sextans  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Telescopii | has B-V magnitude -0.17 |  |
| has declination -45 58 06 |  |
| has right ascension 18 26 58.3 |  |
| has spectral type B3IV |  |
| has synonym HR 6897 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.51 |  |
is a part of Telescopium  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Alpha Trianguli Australis | has B-V magnitude 1.44 |  |
| has declination -69 01 40 |  |
| has right ascension 16 48 39.9 |  |
| has spectral type K2IIb-IIIa |  |
| has synonym HR 6217 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.92 |  |
is a part of Triangulum Australe  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Tucanae | has B-V magnitude 1.39 |  |
| has declination -60 15 35 |  |
| has right ascension 22 18 30.1 |  |
| has spectral type K3III |  |
| has synonym HR 8502 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.86 |  |
is a part of Tucana  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Alpha Vulpeculae | has B-V magnitude 1.50 |  |
| has declination +24 39 54 |  |
| has right ascension 19 28 42.2 |  |
| has spectral type M0III |  |
| has synonym HR 7405 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.44 |  |
is a part of Vulpecula  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of M star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| alpha-particle | has definition Nucleus formed by the α-process (q.v.) (see even-even nuclei). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle first discovered in radioactive α decay, and later identified as helium nuclei (two protons and two neutrons bound together). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The nucleus of a 4He atom, consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Mass of α-particle 4.00260 amu. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of 4N nucleus |  |
| alpha-process | has definition A hypothetical process of nucleosynthesis, which consisted of redistributing α-particles in the region from neon 20 to iron 56 (and perhaps slightly higher). The α-process has been replaced by explosive and nonexplosive C, O, and Si burning occurring in rapidly evolving or even explosive stages of stellar evolution which at higher temperatures and densities becomes the e-process. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| alpha2 CVn | has definition A spectrum variable with spectrum showing strong, profuse lines of rare earths, iron-peak elements, and Si. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 5.469 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Canes Venatici |  |
| is an instance of spectrum variable |  |
| Altair | has apparent magnitude mv = 0.78 |  |
| has B-V magnitude 0.22 |  |
| has declination +08 52 06 |  |
| has definition A bright A7 V star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4.8 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 19 50 46.9 |  |
| has spectral type A7 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha Aql |  |
| has synonym HR 7557 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.77 |  |
is a part of Aquila  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| altazimuth telescope | has definition A form of mounting similar to that of a radar which allows the telescope tube to be moved horizontally (by rotation in azimuth or compass direction) and vertically (by rotation in altitude or elevation). To follow a star the telescope must be adjusted simultaneously in both axes. (also called alt-az) | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has mounting altazimuth | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Earth based telescope |  |
| aluminium | has abundance 0.13 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.3 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.3 × 106 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 5.2 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 82000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 9.7 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 308.215 nm for Al I |  |
| has atomic emission line 309.271 nm for Al I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 309.281 nm for Al I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 394.401 nm for Al I |  |
| has atomic emission line 396.152 nm for Al I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 13 |  |
| has atomic radii 143 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 2740 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 75.2 GPa |  |
| has chief source bauxite |  |
| has covalent radii 125 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 404.959 pm |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. |  |
| has daily dietary intake 2.45 mg |  |
| has definition soft and malleable metal |  |
| has density 2390 kg m-3 for liquid at 933.52 K melting point |  |
| has density 2698 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Oersted |  |
| has discovery date 1825 |  |
| has discovery location Copenhagen, Denmark |  |
| has electrical resistivity 2.6548 × 108 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 44 kJ mol-1 from Al to Al- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.61 Pauling |  |
| has hazard accumulates in the body from daily intake, compounds are used as food additives and in indigestion tablets |  |
| has heat capacity 21.38 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 24.35 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 10.67 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 293.72 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 57 pm for Al3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 22 to 31 |  |
| has level in human blood 0.39 mg dm-3 |  |
| has level in human bone 4 - 27 p.p.m. |  |
| has level in human liver 3 - 23 p.p.m. |  |
| has level in human muscle 0.7 - 28 p.p.m. |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 23.03 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope aluminium 27 which is stable |  |
| has main mining area Surinam, Jamaica, Ghana, Indonesia, Russia |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 48.6 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 5.16 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility 7.7 × 109 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 60 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 933.52 K |  |
| has mineral bauxite, boehmite, diaspore, gibbsite, andalusite, corundum, sillimanite, topaz |  |
| has molar volume 10.00 cm3 |  |
| has name origin alumen = alum from latin |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.3449 × 10-12 cm |  |
has number of isotopes 11  |  |
| has number of protons 13 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 150 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.345 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation al-oo-min-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7429-90-5 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 26.981539 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 6 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 26.2 GPa |  |
| has space group Fm3m |  |
| has specimen foil, granules, ingots, pellets, powder, rod, shot or wire. Safe. Aluminum powder can react dangerously with other materials. |  |
| has symbol Al |  |
| has term symbol 2P1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 237 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has toxic intake 5 g |  |
| has uses vehicle, aircraft and construction industries |  |
| has van der Waals radii 205 pm |  |
| has world production 15 × 106 tonnes per year |  |
| has young's modulus 70.6 GPa |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of group III element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| reacts with air to produce a thin protective oxide layer |  |
| stable isotope aluminium 27 |  |
| aluminium 26 | has atomic mass 25.986892 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.005 Mev) 82% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 18% |  |
| has decay product magnesium 26 |  |
| has diagnostic role if decay products found in a solid then solid must have condensed within the first million years after the creation of Al 26 |  |
| has half life 7.2 × 105 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 13 |  |
| has number of nucleons 26 |  |
| has symbol 26Al |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of aluminium  |  |
| is an instance of supernova produced radioactive element |  |
| aluminium 27 | has atomic mass 26.9885386 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 6.9704 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has NMR frequency 26.057 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 1.17 × 103 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 3.641504 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.1403 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 14 |  |
| has number of nucleons 27 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.21 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 27Al |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.231 barns |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of aluminium  |  |
| aluminium 28 | has atomic mass 27.981910 |  |
| has decay mode β- (4.642 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.25 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 3.24 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 15 |  |
| has number of nucleons 28 |  |
| has symbol 28Al |  |
is an instance of aluminium  |  |
| aluminium 29 | has atomic mass 28.980446 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.68 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 6.5 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 16 |  |
| has number of nucleons 29 |  |
| has symbol 29Al |  |
is an instance of aluminium  |  |
| Am star | has definition A-type or F-type object to which no unique spectral type can be assigned. Usually the classifier provides a classification according to the hydrogen, metallic and calcium lines. Also call metallic-line stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Peculiar star whose metallic lines are as strong as those of the F stars but whose hydrogen lines are so strong as to require that they be classed with the A stars. They are generally short-period (<300d) spectroscopic binaries with high atmospheric turbulence and variable spectra, and are slower rotators than normal A stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| is a kind of peculiar star |  |
| Amalthea | has definition The innermost satellite of Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 140 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Barnard | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1892 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0028 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 0°.4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 0.498 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Barnard's satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| americium | has abundance nil in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance nil in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 367.312 nm for Am I |  |
| has atomic emission line 377.750 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 392.625 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 408.929 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 428.926 nm for Am I |  |
| has atomic emission line 450.945 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 457.559 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 466.279 nm for Am II |  |
| has atomic emission line 605.464 nm for Am I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 95 |  |
| has atomic radii 173 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 2880 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 346.80 pm for α phase |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 489.4 pm for β phase |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. for β phase |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for α phase |  |
| has daily dietary intake nil |  |
| has definition radioactive silvery metal which does not occur naturally |  |
| has density 13670 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Glen T. Seaborg, R.A. James, L.O. Morgan, and A. Ghiorso |  |
| has discovery date 1944 |  |
| has discovery location Chicago, Illinois, US |  |
| has electrical resistivity 68 × 10-8 Ω m |  |
| has electron configuration [Rn]5f77s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.3 Pauling |  |
| has hazard intense α-radiation, maximum permissible body burden of 241Am is 0.03 μCi - it targets bone. γ radiation is a problem in gram amounts. |  |
| has heat of fusion 14.4 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of sublimation 34.2 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 284 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 107 pm for Am3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 80 pm for Am6+ |  |
| has ionic radii 86 pm for Am5+ |  |
| has ionic radii 92 pm for Am4+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 227 to 247 |  |
| has level in humans nil |  |
| has longest lived isotope americium 243 |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +5 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 |  |
| has mass of element in person nil for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1445 K |  |
| has mineral none |  |
| has molar volume 17.78 cm3 |  |
| has name origin america from English |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.83 in 10-12 cm units |  |
| has number of isotopes 23 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 95 |  |
| has phase changed temperature 1347 K at α to β phase crystal transition |  |
| has pronunciation amer-is-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7440-35-9 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 243.0614 for americium 243 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has space group Fm3m for β phase |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for α phase |  |
| has symbol Am |  |
| has term symbol 8S7/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 10 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 75.3 barns |  |
| has uses source of radiation for γ-radiotherapy |  |
| has world production probably a few kilograms per year |  |
| is a kind of radioactive element |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| reacts with air, steam and acids, but not alkalis |  |
| americium 237 | has atomic mass 237.050050 |  |
| has decay mode α (6.20 Mev) 0.02% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.6 Mev) 99.98% |  |
| has half life 1.22 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 142 |  |
| has number of nucleons 237 |  |
| has symbol 237Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 238 | has atomic mass 238.051980 |  |
| has decay mode α (6.04 Mev) < 0.1% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (2.26 MeV) |  |
| has half life 1.63 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 143 |  |
| has number of nucleons 238 |  |
| has symbol 238Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 239 | has atomic mass 239.053016 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.924 Mev) 0.01% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.800 MeV) 99.99% |  |
| has half life 11.9 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 144 |  |
| has number of nucleons 239 |  |
| has symbol 239Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 240 | has atomic mass 240.055278 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.592 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.38 MeV) |  |
| has half life 2.12 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3- |  |
| has number of neutrons 145 |  |
| has number of nucleons 240 |  |
| has symbol 240Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 241 | has atomic mass 241.056823 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.637 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 432.2 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.61 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 146 |  |
| has number of nucleons 241 |  |
| has specimen commercially available, under licence |  |
| has symbol 241Am |  |
| has synthesis mechanism 241Pu subjected to neutron bombardment over a period of years |  |
| has uses research, medical therapy, medical diagnosis |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 242 | has atomic mass 242.056541 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.663 Mev) 83% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.750 Mev) 17% |  |
| has half life |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.388 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1- |  |
| has number of neutrons 147 |  |
| has number of nucleons 242 |  |
| has symbol 242Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 242m | has decay mode α (5.62 Mev) 0.5% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode IT (0.48 Mev) 99.5% |  |
| has half life 141 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5- |  |
| has number of neutrons 147 |  |
| has number of nucleons 242 |  |
| has symbol 242mAm |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 243 | has atomic mass 243.061375 |  |
| has decay mode α (5.438 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 7370 years |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.54 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has NMR frequency 5.76 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.61 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +4.210 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 148 |  |
| has number of nucleons 243 |  |
| has specimen commercially available, under licence |  |
| has symbol 243Am |  |
| has synthesis mechanism 239Pu subjected to neutron bombardment |  |
| has uses research, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 244 | has atomic mass 244.064279 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.427 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 10.0 hours |  |
| has number of neutrons 149 |  |
| has number of nucleons 244 |  |
| has symbol 244Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| americium 245 | has atomic mass 245.066444 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.894 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.05 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 150 |  |
| has number of nucleons 245 |  |
| has symbol 245Am |  |
is an instance of americium  |  |
| ammonia | has symbol NH3 |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| amount of substance unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of amount of substance |  |
| amount-of-substance concentration unit | has definition mole per cubic meter |  |
| has symbol mol·m-3 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| ampere | has consequence fixes the magnetic constant (permeability of vacuum) at exactly 4 × 10-7 H · m-1 |  |
| has definition constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 × 10-7 newton per meter of length |  |
| has definition Unit of electric current. "The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 × 10-7 newton per meter of length" (CIPM | ![has source: [1946], Resolution 2, approved by the 9th CGPM 1948). A current of 1 A is equivalent to the passage along the filament of a light bulb of about 6 × 10<sup>18</sup> electronic charges per second., 2001-09-19 14:39:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol A |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit |  |
| is an instance of current unit |  |
| Andromeda | has acronym And |  |
has boundary 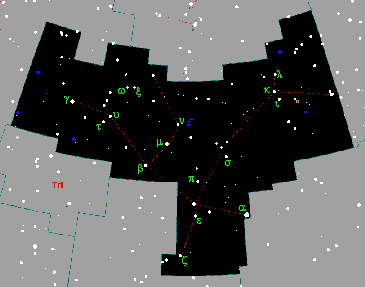  |  |
| has genitive Andromedae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Chained Lady |  |
| has synonym Princess of Ethiopia |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Andromeda galaxy | has definition A spiral galaxy (kS5 in Morgan's classification) in the Local Group, about 650-700 kpc distant (MV = -21), visible to the naked eye as a fuzzy patch in the constellation of Andromeda. Total mass about 3.1 × 1011 Msun ; i = 77°, heliocentric velocity - 180 km s-1. Its nucleus exhibits noncircular gas motions. It is similar to but slightly larger than our Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Major spiral galaxy, 2.2 million light-years from Earth. Gravitationally bound to the Milky Way with which it shares membership in the Local Group, it is currently approaching us, rather than receding as is the case for most galaxies. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The largest galaxy in the Local Group. Also known as the Great Spiral and M31. It is about one and a half times the size of our own galaxy, and contains at least 300 globular clusters. Two smaller, elliptical galaxies (M32 and NGC 205) lie close to it. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The largest member of the local group. It is a giant spiral galaxy that lies 2.4 million light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
has image   |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has synonym M 31 |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids |  |
| is an instance of hypergalaxy | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| is an instance of Sb spiral | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| Andromeda I | has definition Dwarf spheroidal galaxy in the Andromeda subgroup of the Local Group. It is among the intrinsically faintest members of the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer van den Bergh | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1972 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy |  |
| orbits Andromeda galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| Andromeda II | has definition Dwarf spheroidal galaxy in the Andromeda subgroup of the Local Group. It is among the intrinsically faintest members of the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer van den Bergh | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1972 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Andromeda galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| Andromeda III | has definition Dwarf spheroidal galaxy in the Andromeda subgroup of the Local Group. It is among the intrinsically faintest members of the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer van den Bergh | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1972 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Andromeda galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| angle | has unit angle unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| angle unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of angle |  |
| Anglo-Australian Telescope | has acronym AAT |  |
| has altitude 1149 m |  |
| has aperture 3.893 m |  |
| has creation date 1975 |  |
| has focal ratio t/3.3. 8, 15. 36 |  |
| has latitude 31° 17' S |  |
| has location Siding Spring Mtn., Australia |  |
| has longitude 149° 04' E |  |
| has mirror maker Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Mitsubishi |  |
has owner Anglo-Australian Observatory  |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| angstrom | has definition A unit of length used when expressing wavelengths. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-10 meters | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Å | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| is named after Anders Jonas Angstrom (1814-1874) | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| angular momentum | has definition The angular momentum of a system about a specified origin is the sum over all the particles in the system (or an integral over the different elements of the system if it is continuous) of the vector products of the radius vector joining each particle to the origin and the momentum of the particle. For a closed system it is conserved by virtue of the isotropy of space. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The product of mass and angular velocity for an object in rotation; similar to linear momentum. In quantum mechanics, angular momentum is quantized, i.e., is measured in indivisible units equivalent to Planck's constant divided by 2 pi. This corresponds classically to only certain frequencies of rotation being allowed. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol L |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| angular size | has definition The angle subtended by an object on the sky. For example, the angular size of the moon is 30 arcminutes. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| ANIK 1 | is an instance of ANIK satellite |  |
| ANIK 2 | is an instance of ANIK satellite |  |
| ANIK 3 | is an instance of ANIK satellite |  |
| ANIK satellite | is a kind of geosynchronous satellite |  |
| anisotropy | breaks isotropy |  |
| has definition The characteristic of being dependent upon direction. (Light coming with equal intensity from all directions is isotropic; a spotlight's beam is anisotropic.) The cosmic background radiation is generally isotropic - i.e., its intensity is the same in all parts of the sky - but small anisotropies have been detected which are thought to reflect the earth's proper motion relative to the framework of the universe as a whole. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The condition in which the universe appears different in different directions. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry breaking |  |
| Annie Jump Cannon | has career Havard College Observatory  |  |
has greatest achievement the Henry Draper Catalog of spectral types  |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| annular eclipse | has definition A solar eclipse in which the solar disk is never completely covered but is seen as an annulus or ring at maximum eclipse. An annular eclipse occurs when the apparent disk of the Moon is smaller than that of the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An eclipse of the Sun in which the Moon is too far from Earth to block out the Sun completely, so that a ring of sunlight appears around the Moon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of solar eclipse |  |
| anomalistic month | has definition The interval between two successive perigee passages of the Moon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 27.555 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of month |  |
| anomalistic year | has definition A period of time based on the revolution of the Earth around the Sun, where a year is defined as the mean interval between successive passages of the Earth through perihelion. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The interval between two successive perihelion passages of Earth. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 365.2596 ephemeris days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| anomalous Zeeman effect | has cause the influence of magnetic fields on both the orbital angular momentum and the spin angular momentum of electrons in atoms or ions | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Zeeman effet in which spectral lines are split into several components, in contrast to the normal Zeeman effect which results in only two distinct components. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect splitting of spectral lines into more than two components | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Zeeman effect |  |
| antapex | has definition The direction in the sky away from which the Sun seems to be moving (at a speed of 19.4 km s-1) relative to general field stars in the Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Columba | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate |  |
| is opposite of solar apex |  |
| Antares | has B-V magnitude 1.83 |  |
| has declination -26 25 55 |  |
| has definition A red M1 Ib supergiant. It has a B3 V companion, which is a radio source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 125 parsecs | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has location inner edge of the Orion spiral arm | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 16 29 24.4 |  |
| has spectral type M1.5Iab-Ib+B4V |  |
| has synonym alpha Sco |  |
| has synonym HR 6134 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.96 |  |
is a part of Scorpius  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of red supergiant |  |
| anthropic principle | has definition The doctrine that the value of certain fundamental constants of nature can be explained by demonstrating that, were they otherwise, the universe could not support life and therefore would contain nobody capable of worrying about why they are as they are. Were the strong nuclear force slightly different in strength, for instance, the stars could not shine and life as we know it would be impossible. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The weak form of the anthropic principle states that life can exist only during a brief period of the history of our universe. The strong form of the principle states that out of all possible values for the fundamental constants of nature and the initial conditions of the universe, only a small fraction could allow life to form at all, at anytime. (See boundary conditions; fundamental constants of nature.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| anthropocentrism | has definition The belief that humans are central to the universe. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| anthropomorphism | has definition The projection of human attributes onto nonhuman entities such as animals, the planets, or the universe as a whole. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| anti-reflection coating | has definition Also AR coating. A layer of material of lower refractive index of just the right thickness (1/4 wave) is deposited on the optical surface to be coated. More complex coatings are possible which cover a large wavelength range. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coating |  |
| anticenter | has definition The direction of the sky opposite to that of the galactic center. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The point in the galactic plane that lies directly opposite the galactic center. Here we gaze toward the edge of the Galactic disk. The nearest bright star to the anticenter is El Nath, in the constellation Taurus. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic latitude 0 |  |
| has galactic longitude 180 degrees |  |
| is a part of Auriga | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of galactic coordinate |  |
| is opposite of galactic center |  |
| antimony | has abundance 0.2 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 10 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 3 × 10-4 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 206.833 nm for Sb I |  |
| has atomic emission line 217.581 nm for Sb I |  |
| has atomic emission line 252.852 nm for Sb I |  |
| has atomic emission line 259.805 nm for Sb I |  |
| has atomic emission line 231.147 nm for Sb I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 51 |  |
| has atomic radii 182 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 1908 K |  |
| has chief source stibnite, tetrahedrite although mainly a copper ore yields antimony as a by-product |  |
| has covalent radii 141 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 298.6 pm for grey cubic form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 336.9 pm for metal form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 430.84 pm for grey rhombohedral form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension c = 1124.7 pm for grey rhombohedral form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension c = 533 pm for metal form |  |
| has crystal type cubic for grey cubic form |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for metal form |  |
| has crystal type rhombohedral for grey rhombohedral form |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.002 to 1.3 mg |  |
| has definition metalloid element with three forms. The metallic form is the more stable and is bright, silvery, hard and brittle |  |
| has density 6483 kg m-3 for liquid at 903.89 K melting point |  |
| has density 6691 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discovery date 1600 BC probably known to the ancients and certainly to the alchemists |  |
| has electrical resistivity 39.0 × 10-8 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 101 kJ mol-1 from Sb to Sb- |  |
| has electron configuration [Kr]4d105s25p3 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.05 Pauling |  |
| has hazard small doses stimulate metabolism, large doses cause liver damage |  |
| has heat capacity 20.79 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 25.23 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 20.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 67.91 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 245 pm for Sb2- |  |
| has ionic radii 62 pm for Sb5+ |  |
| has ionic radii 89 pm for Sb3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 108 to 136 |  |
| has lethal intake 140 mg for antimony potassium tartrate (oral) for LD50 |  |
| has level in humans 0.0033 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.01 to 0.6 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 0.011 to 0.42 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.042 to 0.191 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 8.5 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has main mining area China, Italy, Peru, Mexico, Bolivia, France |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 270 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 33.1 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -1.0 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 2 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 903.89 K |  |
| has mineral sibiconite, stibnite, tetrahedrite, ullmannite |  |
| has molar volume 18.20 cm3 |  |
| has name origin anti + monos = not alone from greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.557 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 40 |  |
| has number of protons 51 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 3.5 × 105 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.25 to 0.33 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation anti-moni |  |
has registry number 7440-36-0 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 112.760 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 2.5 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 20.7 GPa |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for metal form |  |
| has space group Pm3m for grey cubic form |  |
| has space group R3m for grey rhombohedral form |  |
| has specimen available as pieces, powder or shot. Care ! |  |
| has stable isotope antimony 121 |  |
| has stable isotope antimony 123 |  |
| has symbol Sb |  |
| has symbol origin stibium from latin |  |
| has term symbol 4S3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 24.3 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 4.91 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 100 mg |  |
| has uses hardenning other metals, stotage batteries, bearings |  |
| has van der Waals radii 220 pm |  |
| has world production 53000 tonnes per year |  |
| has young's modulus 54.7 GPa |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of group V element |  |
| is a kind of metallic metalloid |  |
| reacts with stable in dry air, not attacked by dilute acids or alkalis |  |
| antimony 119 | has atomic mass 118.903948 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.59 Mev) |  |
| has half life 38.1 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.45 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 68 |  |
| has number of nucleons 119 |  |
| has symbol 119Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 120 | has atomic mass 119.903821 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.68 Mev) 41% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 59% |  |
| has half life 15.89 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.3 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 69 |  |
| has number of nucleons 120 |  |
| has symbol 120Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 120m | has atomic mass 119.903821 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 5.76 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.34 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 8- |  |
| has number of neutrons 69 |  |
| has number of nucleons 120 |  |
| has symbol 120mSb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 121 | has atomic mass 120.9038212 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 6.4016 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 57.3 % |  |
| has NMR frequency 23.930 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 520 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.3634 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.360 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 70 |  |
| has number of nucleons 121 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.16 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 121Sb |  |
| has uses experimental, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 122 | has atomic mass 121.905179 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (0.619 Mev) 2% |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.9820 Mev) 98% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.73 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.90 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 71 |  |
| has number of nucleons 122 |  |
| has symbol 122Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 123 | has atomic mass 122.9042160 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 3.4668 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 42.7 % |  |
| has NMR frequency 12.959 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 111 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.5498 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.490 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 72 |  |
| has number of nucleons 123 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 4.57 × 10-2 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 123Sb |  |
| has uses experimental, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 124 | has atomic mass 123.905038 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.905 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 60.30 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3- |  |
| has number of neutrons 73 |  |
| has number of nucleons 124 |  |
| has symbol 124Sb |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 125 | has atomic mass 124.905252 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.767 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.758 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.63 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 74 |  |
| has number of nucleons 125 |  |
| has symbol 125Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 126 | has atomic mass 125.907250 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.67 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 12.4 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.3 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 8- |  |
| has number of neutrons 75 |  |
| has number of nucleons 126 |  |
| has symbol 126Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antimony 127 | has atomic mass 126.906919 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.58 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 3.84 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.6 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 76 |  |
| has number of nucleons 127 |  |
| has symbol 127Sb |  |
is an instance of antimony  |  |
| antineutrino | has antiparticle neutrino |  |
| has definition The antiparticle of a neutrino. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of antiparticle |  |
| is a kind of lepton |  |
| is a kind of neutral particle |  |
| antineutron | has antiparticle neutron |  |
| has definition The antiparticle of a neutron. A neutron and antineutron both have the same mass and zero electric charge, but can be differentiated by their interactions: a neutron and an antineutron can annihilate into gamma rays, while two neutrons cannot. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of antiparticle |  |
| is an instance of baryon |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| antiparticle | has definition An elementary particle of opposite charge but otherwise identical to its partner. Most of the observable universe consists of particles and matter, as opposed to antiparticles and antimatter. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Atomic particles that have the same mass as, but opposite charge and orbital direction to, an ordinary particle. Thus, instead of negatively charged electrons, atoms of antimatter have positrons. A quantity of antimatter coming into contact with matter would "cancel out" - annihilate, with total conversion of mass to energy - an exact proportion of matter corresponding to the original quantity of antimatter, provided that the elements in the matter also corresponded with the "elements" in the antimatter, i.e., that the atoms were equivalent but opposite. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition For every known type of particle, there exists an antiparticle with exactly the same mass, but with the opposite electric charge. When a particle and its antiparticle come together, they can always annihilate to form gamma rays. The antiparticle of an electrically neutral particle is sometimes the same as the original particle (e.g., photons) and sometimes it is distinct (e.g., neutrons). | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particles predicted by combining the theories of special relativity and quantum mechanics. For each particle, there must exist an antiparticle with the opposite charge, magnetic moment and other internal quantum numbers (e.g., lepton number, baryon number, strangeness, charm, etc.), but with the same mass, spin and lifetime. Note that certain neutral particles (such as the photon and π0) are their own antiparticles. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particles with identical mass and spin as those of ordinary matter, but with opposite charge. Antimatter has been produced experimentally, but little of it is found in nature. Why this should be so is one of the questions that must be answered by any adequate theory of the early universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| antiproton | has antiparticle proton |  |
| has charge -1 |  |
| has definition The antiparticle of a proton, identical in mass and spin but of opposite (negative) charge. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of antiparticle |  |
| is an instance of baryon |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| antiquark | has antiparticle quark |  |
| has definition The antiparticle of the quark. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of antiparticle |  |
| is a kind of charged particle |  |
| is a kind of parton | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| Antlia | has acronym Ant |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Antliae |  |
| has synonym Air Pump |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Antonia Maury | has career Havard College Observatory  |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| Ap star | has definition Peculiar A-type stars ("magnetic" A stars) that show abnormally strong lines, sometimes of varying intensity, of certain ionized metals. Recent evidence indicates that all Ap stars are slow rotators compared with normal A stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star with spectral type A in which the lines of one or several elements are abnormally enhanced. Traditionally the most important subgroups are Si λ4200, Hg-Mn and Cr-Eu-Sr stars. The latest objects of the latter group correspond to early F-type. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Stars can be classified according to their surface temperatures, which determine, in large part, the spectrum of radiation they emit. A stars have surface temperatures between about 7,500 and 11,000 degrees centigrade. Peculiar A stars are A stars whose emitted radiation spectra have many of the characteristics of A stars but are peculiar in certain ways. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| is a kind of peculiar star |  |
| apastron | has antonym periastron |  |
| has definition The point in the orbit of one component of a binary system where it is farthest from the other. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has participants binary star |  |
| is an instance of binary star orbital event |  |
| aphelion | has antonym perihelion |  |
| has definition The point in a planetary orbit that is at the greatest distance from the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Sun orbital event |  |
| aplanatic system | has definition A system of three lenses which, taken together, correct for spherical aberration, chromatic aberration, and coma. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of lens |  |
| apocenter | has antonym pericenter |  |
| has definition The point in the orbit of one component of a binary system which is farthest from the center of mass of the system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has participants binary star |  |
| is an instance of binary star orbital event |  |
| apogalacticon | has antonym perigalacticon |  |
| has definition The point in a star's orbit farthest from the Galactic center. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of galaxy orbital event |  |
| apogee | has antonym perigee |  |
| has definition The point at which a body in orbit around the Earth reaches its farthest distance from the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Earth orbital event |  |
| Apollo | has definition Prototype of a small group of asteroids whose orbits intersect that of Earth. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.57 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 6°.4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 622d | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 1.486 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Apollo asteroid |  |
| is an instance of Apollo asteroid |  |
| Apollo asteroid | has definition One of a small group of asteroids whose orbits intersect that of Earth. They are named for the prototype, Apollo. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Earth-crossing asteroid |  |
| is a part of Earth-crossing asteroid |  |
| Apollo space program | has definition Successful US lunar exploration program in which the Apollo spacecraft 1 to 6 were unmanned; 7 to 10 were manned but did not land; and 11, 12 and 14 to 17 landed and returned safely. (Apollo 13 was an aborted mission.) The first men to land on the Moon were Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, from Apollo 11, on 20 July 1969. The final Apollo flight (17) lasted from 7 to 19 December 1972, and left a considerable quantity of exploratory devices on the lunar surface. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| apparent magnitude | has definition A measure of how bright a star looks in the sky. The brighter the star, the smaller the apparent magnitude. A star that is one magnitude brighter than another (e.g., +1 versus +2) looks 2.5 times brighter. The brightest star of all, of course, is the Sun, whose apparent magnitude is -26.74, followed by Sirius, whose apparent magnitude is -1.46, Canopus (-0.72), Alpha Centauri (-0.27), Arcturus (-0.04), and Vega (+0.03). Stars of the Big Dipper are fainter, most of them around magnitude +2. On a clear, dark night, the unaided eye can see stars as faint as apparent magnitude +6, and the largest telescopes penetrate to apparent magnitude +30. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Measure of the observed brightness of a celestial object as seen from the Earth. It is a function of the star's intrinsic brightness, its distance from the observer, and the amount of absorption by interstellar matter between the star and the observer. The mv, of Sun, -26.5 mag. A sixth-magnitude star is just barely visible to the naked eye. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of magnitude |  |
| apsidal motion | has definition Rotation of the line of apsides in the plane of the orbit; (in a binary) precession of the line of apsides due to mutual tidal distortion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| Apus | has acronym Aps |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Apodis |  |
| has synonym Bird of Paradise |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| Aquarius | has acronym Aqr |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Aquarii |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Water Bearer |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Aquila | has acronym Aql |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Aquilae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the eagle that belonged to Zeus. Aquila's most famous task was carrying the mortal Ganymede to the heavens to serve as Zeus' cup bearer |  |
| has synonym Eagle |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Ara | has acronym Ara |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Arae |  |
| has historical origin the altar of the centaur Chiron or the altar that Noah built after the great flood |  |
| has synonym Altar |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| arcminute | has definition A unit of angle equal to 1/60 of a degree. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1/60 degree | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle unit |  |
| arcsecond | has definition One sixtieth of an arcminute, or 1/3600 of a degree. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1/3600 degree | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1/60 arcminute | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle unit |  |
| Arcturus | has B-V magnitude 1.23 |  |
| has declination +19 10 57 |  |
| has definition A beautiful orange star that is the brightest in the constellation Bootes and the fourth brightest in the night sky. It lies 34 light-years away and is a member of the thick-disk population. Historically, Arcturus is famous because it was one of the first stars to have its proper motion measured. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An old subgiant disk star (K2 IIIp, mv = 0.06) about 11 pc distant. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 14 15 39.6 |  |
| has spectral type K1IIIbCN-1 |  |
| has synonym Alpha Boötis | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 5340 |  |
| has V magnitude -0.04 |  |
is a part of Boötes  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| area | is a kind of quantity |  |
| area unit | has definition square meter |  |
| has symbol m2 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| Arecibo | has angular resolving power 5 arcminute |  |
| has effective diameter 300 meters |  |
| has position Puerto Rico |  |
has reference NAIC Arecibo Observatory  |  |
| is an instance of radio telescope |  |
| argon | has abundance 1 × 106 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 1.2 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 9300 p.p.m. in atmopshere |  |
| has atomic emission line 695.5431 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 706.7218 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 750.3869 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 801.4786 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 912.2967 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 965.7786 nm for Ar I |  |
| has atomic emission line 811.5311 nm for Ar I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 18 |  |
| has atomic radii 174 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 87.29 K |  |
| has chief source lquid air |  |
| has critical pressure 4862 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 150.87 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 531.088 pm |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c |  |
| has daily dietary intake very low |  |
| has definition colourless, odourless gas comprising 1% of the atmosphere |  |
| has density 1.784 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 1380 kg m-3 for liquid at 87.29 K boiling point |  |
| has density 1656 kg m-3 for solid at 40 K |  |
| has discoverer Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay |  |
| has discovery date 1894 |  |
| has discovery location London and Bristol, England |  |
| has electron affinity -35 kJ mol-1 from Ar to Ar- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p6 in ground state |  |
| has hazard can asphyxiate if it excludes oxygen from the lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 2.21 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 6.53 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has isotope mass range 32 to 46 |  |
| has lethal intake non-toxic |  |
| has level in humans trace amounts in blood |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 123 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 13.5 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -6.16 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person very small for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 83.78 K |  |
| has mineral none |  |
| has molar volume 24.12 cm3 at 40 K |  |
| has name origin argos = inactive from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.1909 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 15 |  |
| has number of protons 18 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| has ocean residence time 28000 years |  |
| has pronunciation ar-gon |  |
has registry number 7440-37-1 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 39.948 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 6.6 × 1013 tonnes in atmosphere |  |
| has space group Fm3m |  |
| has specimen available in small pressurized canisters. Safe. |  |
| has stable isotope argon 36 |  |
| has stable isotope argon 38 |  |
| has stable isotope argon 40 |  |
| has symbol Ar |  |
| has synthesis mechanism extracted from the atmosphere by liquefaction |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.0177 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K for gas |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.675 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has uses inert atmosphere in lamps and high temperature metallurgy |  |
| has van der Waals radii 191 pm |  |
| has world production 700000 tonnes per year |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with nothing |  |
| argon 36 | has atomic mass 35.96754552 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.337 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 18 |  |
| has number of nucleons 36 |  |
| has symbol 36Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 37 | has atomic mass 36.966776 |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.814 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 35.0 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.15 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 19 |  |
| has number of nucleons 37 |  |
| has symbol 37Ar |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 38 | has atomic mass 37.9627325 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.063 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 20 |  |
| has number of nucleons 38 |  |
| has symbol 38Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 39 | has atomic mass 38.962 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.565 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 268 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.3 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 21 |  |
| has number of nucleons 39 |  |
| has symbol 39Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 40 | has atomic mass 39.9623837 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.600 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 40 |  |
| has symbol 40Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 41 | has atomic mass 40.964501 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.492 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 1.82 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 41 |  |
| has symbol 41Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 42 | has atomic mass 41.963050 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.60 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 33 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 24 |  |
| has number of nucleons 42 |  |
| has symbol 42Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argon 44 | has atomic mass 43.963650 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.54 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 11.87 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 44 |  |
| has symbol 44Ar |  |
is an instance of argon  |  |
| argument of the perihelion | has definition An orbital element representing the longitude of the ascending node plus the angle along the orbit from the ascending node to the perihelion point. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Angular distance (measured in the plane of the object's orbit and in the direction of its motion) from the ascending node to the perihelion point. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol ω | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym longitude of the perihelion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of orbital element |  |
| Ariel | has definition Second satellite of Uranus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1600 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Lassell | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1851 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 2.52 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Uranus |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Aries | has acronym Ari |  |
| has genitive Arietis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the ram sent by Hermes to carry the abused children of the King of Thessaly to safety |  |
| has synonym Ram |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Arietids | is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| Aristotelian physics | has definition Physics as promulgated by Aristotle; includes the hypothesis that our world is comprised of four elements, and that the universe beyond the moon is made of a fifth element and so is fundamentally different from the mundane realm. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| array telescope | has definition a telescope composed of an array of separete individual elements acting in concert |  |
| has element aperture |  |
| has element separation |  |
| has number of elements |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| arsenic | has abundance 1.45 × 10-3 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.45 × 10-3 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.5 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 1.53 × 10-3 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.75 × 10-3 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance see list in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has appearance metallic for α form |  |
| has atomic emission line 419.008 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 445.847 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 446.635 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 449.423 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 450.766 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 454.348 nm for As II |  |
| has atomic emission line 193.759 nm for As I (Strong, used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic number 33 |  |
| has atomic radii 125 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to some species including humans |  |
| has boiling point 889 K sublimes |  |
| has chief source arsenopyrite, realgar and orpiment |  |
| has covalent radii 121 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 376.0 pm for β form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 413.18 pm for α form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension alpha angle = 54 deg 10' for α form |  |
| has crystal cell dimension c = 10.548 pm for β form |  |
| has crystal type hexagonal for β form |  |
| has crystal type rhombohedral for α form |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.04 to 1.4 mg |  |
| has definition a metalloid element with two main forms, grey α arsenic and β arsenic |  |
| has density 4700 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K (β form) |  |
| has density 5780 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K (α form) |  |
| has discoverer Albertus Magnus |  |
| has discovery date 1250 |  |
| has discovery location Germany |  |
| has electrical resistivity 26 × 10-8 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 78 kJ mol-1 from As to As- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d104s24p3 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.18 Pauling |  |
| has hardness brittle for α form |  |
| has hazard salts and arsine gases are very poisonous. Stimulates metabolism in small doses, but it is carcinogenic and possibly teratogenic |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure of 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 24.64 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure of 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 27.7 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 31.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 46 pm for As5+ |  |
| has ionic radii 69 pm for As3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 67 to 87 |  |
| has lethal intake 50 to 300 mg |  |
| has level in humans 0.0017 to 0.09 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.009 to 0.65 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.023 to 1.61 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.08 to 1.6 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 4.6 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has main mining area not much mined as such because more than required is produced as a by-product of refining certain sulfide ores |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 69.7 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 83.4 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -3.97 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for β form |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -9.17 × 10-10 kg-1 m3 for α form |  |
| has mass of element in person 0.5 to 15 mg for a 70 kg average person depending on diet |  |
| has melting point 1090 K for α form under pressure |  |
| has mineral arsenopyrite, conichalcite, enargite, lollingite, olivenite, orpiment and realgar |  |
| has molar volume 12.95 cm3 for α form |  |
| has molar volume 15.9 cm3 for β form |  |
| has name origin arsenikon = yellow orpiment from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.658 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 22 |  |
| has number of protons 33 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| has ocean residence time 90000 years |  |
| has pronunciation ahrs-nik |  |
has registry number 7440-38-2 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 74.92159 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has space group R3m for α form |  |
| has specimen available as powder. Danger ! |  |
| has symbol As |  |
| has term symbol 4S3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 50.0 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K for α form |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 4.30 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 5 to 50 mg |  |
| has uses alloys, semiconductors, pesticides, wood preservatives and glass |  |
| has van der Waals radii 200 pm |  |
| has world production 47000 tonnes per year for As2O3 |  |
| is a kind of group V element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic metalloid |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| reacts with hot acids and molten NaOH, tarnishes burns in oxygen |  |
| arsenic 71 | has atomic mass 70.927114 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.013 Mev) 32% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 68% |  |
| has half life 2.72 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.6735 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 38 |  |
| has number of nucleons 71 |  |
| has symbol 71As |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 72 | has atomic mass 71.926755 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.355 Mev) 77% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 26.0 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -2.1566 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 39 |  |
| has number of nucleons 72 |  |
| has symbol 72As |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 73 | has atomic mass 72.923827 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.346 Mev) |  |
| has half life 80.3 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 40 |  |
| has number of nucleons 73 |  |
| has symbol 73As |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 74 | has atomic mass 73.923827 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.354 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.562 Mev) 31% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 37% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.597 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 41 |  |
| has number of nucleons 74 |  |
| has symbol 74As |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 75 | has atomic mass 74.9215942 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 4.5804 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 17.126 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 143 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.43947 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.314 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 42 |  |
| has number of nucleons 75 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0251 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 75As |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 76 | has atomic mass 75.922393 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.97 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 26.3 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.906 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 43 |  |
| has number of nucleons 76 |  |
| has symbol 76As |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| arsenic 77 | has atomic mass 76.920646 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.6904 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 38.8h |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 44 |  |
| has number of nucleons 77 |  |
| has symbol 77As |  |
is an instance of arsenic  |  |
| artifact | has creation date |  |
| has creator |  |
| has definition an object made by humans |  |
| has owner |  |
| has purpose |  |
| is a kind of physical object |  |
| artificial satellite | has attitude control |  |
| has definition a satellite made by humans which is gravitationaly bound and in orbit of a larger physical object |  |
| has ground communication station |  |
| has launch date |  |
| has launch location |  |
| has launch vehicle |  |
| is a kind of instrument |  |
| is a kind of satellite |  |
| can have orbit decay date |  |
| AS Eri | has definition An eclipsing binary whose secondary is close to its Roche limit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| ascending node | has definition In the orbit of a solar-system body, the point where the body crosses the ecliptic from south to north: for a star, out of the plane of the sky toward the observer. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Sun orbital event |  |
| aspheric | has definition An optical surface with departures in shape from a perfect sphere in order to cancel optical imperfections or aberrations. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| association | has definition A sparsely populated grouping (mass range 102-103 Msun) of very young, massive stars lying along a spiral arm of the Milky Way, whose spectral types or motions in the sky indicate a common origin. The star density is insufficient for gravitation to hold the group together against shear by differential galactic rotation, but the stars have not yet had time to disperse completely. OB associations are composed of stars of spectral types O-B2; T associations have many young T Tauri stars. The internationally approved designation for associations is the name of the constellation followed by an arabic numeral - e.g., Perseus OB2. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has most luminous member |  |
| is a kind of collection of stars |  |
| astatine | has image  |  |
| is a kind of halogen |  |
| asterism | has definition a group of bright stars which form a conspicuous pattern on the celestial sphere |  |
| has purpose to easily recognize a part of the sky |  |
| is a part of constellation |  |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
| asteroid | has asteroid number |  |
| has definition A small planet-like body of the solar system, <e> ≃ 0.15, <i> ≃ 9°.7 . More than 1800 have been catalogued, and probably millions of smaller ones exist, but their total mass would probably be less than 3 percent that of the Moon. Their densities are poorly known (about 2.6 g cm-3), but they suggest a composition similar to carbonaceous chondrite. The bright asteroids are presumably original condensations and those fainter than about 14-15 mag are collision fragments. Asteroids and short-period comets have some orbital similarities. Also called minor planet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A small rocky body that orbits a star. In the solar system, most asteroids lie between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The largest asteroid is Ceres, about 900 kilometers in diameter. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Also called planetoids or minor planets, the asteroids are tiny planets most of which orbit the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. The largest - and the first discovered - is Ceres, with a diameter of 1,003 km. It is estimated that there may altogether be no fewer than 40000. A few have very elliptical orbits and cross the orbits of several other (major) planets. One or two even have their own satellites (moons). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym minor planet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym planetoid | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| asteroid belt | has definition A region of space lying between Mars (1.5 AU) and Jupiter (5.2 AU), where the great majority of the asteroids are found. None of the belt asteroids have retrograde motion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 1.5 to 5.2 AU |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| asteroid impact | is a kind of impact event |  |
| astrology | has definition Divination using the positions of the planets, the Sun and the Moon as seen against the stars in the constellations of the zodiac - a "science" almost as old as homo sapiens. Although at one stage in history astrology and astronomy were almost synonymous- the latter has advanced so far during the last three centuries that the two now bear little relation to each other. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The belief that human affairs and people's personalities and characters are influenced by (or encoded in) the positions of the planets. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| astrometric binary | is a kind of binary star |  |
| astrometry | has definition The branch of astronomy that deals with measuring the positions of celestial objects, especially stars. Astrometrists measure parallaxes and proper motions, which allow astronomers to determine the distances and velocities of the stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galactic astronomy |  |
| astronomer | has definition a scientist specializing in astronomy |  |
| has domain astronomy |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| astronomical catalog | is a kind of data collection |  |
| astronomical constant | is a kind of constant |  |
| astronomical horizon event | has definition The time and azimuth at which a celestial body crosses the astronomical horizon of an oberver. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of location dependent periodic celestial event |  |
| Astronomical Image Processing System | has acronym AIPS | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
has definition Developed by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.  | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| astronomical institution | is a kind of institution |  |
| astronomical refraction | has definition The change in direction of travel (bending) of a light ray as it passes obliquely through the atmosphere. As a result of refraction, the observed altitude of a celestial object is greater than its geometric altitude. The amount of refraction depends on the altitude of the object and on atmospheric conditions. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of refraction |  |
| astronomical software | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| astronomical unit | has definition Mean distance between the Earth and the Sun: 1.495985 × 1011 m. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The AU is the preferred unit for distances within the solar system. Mercury, the innermost planet, lies on average 0.39 AU from the Sun; Pluto, normally the farthest planet, lies on average 39.5 AU from the Sun. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mean distance between the Earth and the Sun. The astronomical unit is defined as the length of the radius of the unperturbed circular orbit of a body of negligible mass moving around the Sun with a sidereal angular velocity of 0.017202098950 radian per day of 86400 ephemeris seconds. AU = 1.496 × 1013 cm ≈ 500 lt-sec. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mean distance from the earth to the sun, equal to 92.81 million miles or 499.012 light-seconds. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The radius of a circular orbit in which a body of negligible mass, and free of perturbations, would revolve around the Sun in 2π / k days, where k is the Gaussian gravitational constant. This is slightly less than the semi-major axis of the Earth's orbit. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has value in SI unit 1 au = 1.49598 × 1011 m, approximately |  |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| astronomy | has definition The science that studies the natural world beyond the earth. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| astronomy theory | has domain astronomy |  |
| is a kind of theory |  |
| Astrophysical Data Facility | has acronym ADF |  |
has definition Is responsible for designing, developing, and operating data systems that support the processing, management, archiving and distribution of NASA mission data. The ADF serves three broadly-defined astrophysics disciplines: high-energy astrophysics, UV/optical astrophysics, and infrared/submillimeter/radio astrophysics. The ADF collaborates with the GSFC Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics (LHEA) and the Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics (LASP) in managing data for specific missions. The ADF staff also support the astrophysics community's access to multi-mission and multi-spectral data archives in the National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC).  |  |
| has location Goddard Space Flight Center |  |
| is an instance of database |  |
| Astrophysical Research Consortium Telescope | has altitude 2800 m |  |
| has aperture 3.5 m |  |
| has creation date 1994 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.75 |  |
| has latitude 32° 47' N |  |
| has location New Mexico, US |  |
| has longitude 105° 49' W |  |
| has mirror maker R. Angel, B. Martin |  |
| has mirror type spin-cast borosilicate honey-comb |  |
| has owner Apache Point |  |
| has synonym ARC 3.5 m |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| astrophysics | has definition The science that studies the physics and chemistry of extraterrestrial objects. The alliance of physics and astronomy, which began with the advent of spectroscopy, made it possible to investigate what celestial objects are and not just where they are. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| Astroweb | is an instance of database  |  |
| asymptotic branch star | has definition Globular cluster stars, which are found in that part of the HR diagram that connects the top pf the giant tip with the horizontal branch stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| atmophile element | has definition volatile element that tends to be found in the atmosphere of a planet or asteroid |  |
| has occurrence atmosphere of a planet or asteroid |  |
| is a kind of planetary element |  |
| atmosphere | has composition 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen (with 1% of other gases) by volume | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A unit of pressure. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Mantle of gases round a star planet or moon, sometimes even forming the apparent surface of the body. For a body to retain an atmosphere depends on the body's gravity, and the temperature and composition of the gases. Mean atmospheric pressure at the surface is 10330 kg/m2, and is also referred to as atmosphere. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1.013 bars | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 101325 pascals | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 14.07 lb in-2 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 760 torr | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Earth |  |
| is an instance of pressure unit |  |
| atmospheric dispersion corrector | has definition An optical device usually comprising two thin prisms which can rotate to compensate for the elongation of a star image caused by the wavelength dependence of the refractive index of air. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification wavelength |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| atmospheric extinction | has definition Decrease in the intensity of light from a celestial body due to absorption and scattering by the Earth's atmosphere. The extinction increases from the zenith to the horizon and affects short wavelengths more than long wavelengths, so that objects near the horizon appear redder than they are at the zenith. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of selective absorption |  |
| atomic constant | is a kind of fundamental physical constant |  |
| atomic mass constant | has approval date 1961 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One-twelfth the mean mass of an atom of carbon 12 (including the orbital electrons). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol mu |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000013 × 10-27 kg |  |
| has unit kg |  |
has value 1.66053873 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| atomic mass number | has definition The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. For example, oxygen-16 has a mass number of sixteen, because it has eight protons and eight neutrons. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of integer |  |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| atomic mass unit | has approval agency International Union of Pure and Applied Physics |  |
| has approval date 1960 |  |
| has definition The masses of atoms and molecules are generally given in atomic mass units. These units are based on a scale in which the mass of carbon 12 is taken to be 12. Atomic masses were originally given as atomic weights on a scale where the mass of the hydrogen atom was unity, later they were based on oxygen or oxygen 16; these scales have all been replaced by the carbon 12 scale. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1.6605402 × 10-27 kg | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1959 |  |
| has symbol u | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym dalton |  |
| is a unit of mass |  |
| is an instance of mass unit |  |
| atomic number | has definition The number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This determines the type of element. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1865 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has range 1 to 103 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym charge number | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of integer |  |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| was proposed by J. A. R. Newlands | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| atomic process | has domain atomic physics |  |
| is a kind of event |  |
| is a kind of physical process |  |
| attenuation | has definition The falling off of the energy density of radiation with distance from the source, or with passage through an absorbing or scattering medium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of absorption |  |
| atto | has symbol a |  |
| has value 10-18 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| Auger transition | has definition A radiationless quantum jump that occurs in the X-ray region. When a K-electron is removed from an atom and an L-electron drops into the vacancy in the K-shell, the energy released in the latter transition goes not into radiation, but into the liberation of one of the remaining L-electrons. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ionization |  |
| Auriga | has acronym Aur |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Aurigae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin Erechtheus, the charioteer (son of Hephaestus) is carying two to three children on his arm |  |
| has synonym Charioteer |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| aurora | has definition Light radiated by ions in the Earth's atmosphere, mainly near the geomagnetic poles, stimulated by bombardment by energetic particles ejected from the Sun (see solar wind). Aurorae appear about 2 days after a solar flare and reach their peak about 2 years after sunspot maximum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Spectacular array of light in the night sky, caused by charged particles from the Sun hitting the Earth's upper atmosphere. The aurora borealis is seen in the north of the Northern hemisphere; the aurora australis in the south of the Southern. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition the light produced by excited atoms and ions in the upper atmosphere of a planet |  |
| has location the ionosphere in the polar regions of a planet |  |
| is a kind of celestial event |  |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| aurora australis | has definition an aurora ocurring in the southern hemisphere of the Earth |  |
| has location southern hemisphere |  |
| is a kind of aurora |  |
| aurora borealis | has definition an aurora ocurring in the northern hemisphere of the Earth |  |
| has location northern hemisphere |  |
| is a kind of aurora |  |
| autoionization | has definition A phenomenon occurring when a discrete double-excitation state of an atom lies in the ground-state continuum. In the autoionization process one of the excited electrons is ejected, leaving the ion in an excited state (see dielectronic recombination; see also Auger effect). (also called pre-ionization) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has inverse process dielectronic recombination |  |
| is a kind of ionization |  |
| autumnal equinox | has definition See equinox | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equinox |  |
| Avogadro number | has definition The number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon 12. The number of atoms in a gram-atom (mass in grams numerically equal to the atomic weight) or the number of molecules in a gram-molecule (mass in grams numerically equal to the molecular weight). | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol NA | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has uncertainty 0.00000047 × 1023 mol-1 |  |
has value 6.02214199 × 1023 mol-1  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| is named after Amadeo Avogadro | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
| axion | has definition A hypothetical spin-0 particle with a very small mass of 10-5-10-3 eV. It was postulated in order to provide a natural solution to the "strong CP problem". |  |
| has mass 10-5 to 10-3 eV |  |
| has spin 0 |  |
| is a kind of boson |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| axis | has definition Theoretical straight line through a celestial body, around which it rotates. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line |  |
| axis motion | has definition the motion of the axis of a system | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| axisymmetric collapse | has definition Collapse of mass in such a way that the mass maintains the symmetry of a cylinder. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has symmetry cylindrical |  |
| is a kind of collapse |  |
| azimuth | has definition Angular distance from the north point eastward to the intersection of the celestial horizon with the vertical circle passing through the object and the zenith. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Directional bearing around the horizon, measured in degrees from north (0°). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate component |  |
| azimuthal quantum number | has definition A measure of the minor axis of an elliptic orbital of an electron according to the Bohr-Sommerfeld theory. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol k |  |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| B band | has definition Telluric lines due to O2 absorption in Earth's atmosphere, but originally thought to originate in the Sun by Fraunhofer. |  |
| has species O2 |  |
| has wavelength 7100 Å |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| occurs in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| B ring | is a kind of ring |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| B star | has absorption line He I |  |
| has color blue-white |  |
| has definition Blue-white star of spectral type B whose spectra are characterized by absorption lines of neutral helium which reach their maximum intensity at B2. The Balmer lines of hydrogen are strong, and lines of singly ionized oxygen and other gases are also present. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 11000 to 28000 K |  |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| b-lines | has definition A triplet of spectral lines of Mg I. |  |
| has wavelength λλ 5167-5184 Å |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| B[e] star | has definition Be stars exhibiting forbidden lines in emission. [JJ95] |  |
| has emission line forbidden lines |  |
| is a kind of Be star |  |
| Baade's Window | has definition A clearing in the dust clouds of the constellation Sagittarius where astronomers can view stars in the Galactic bulge. Baade's window lies four degrees south of the Galactic center, so an observer's line of sight passes within 1800 light-years of the Milky Way's center. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
| backscatter | has definition Scattering of radiation (or particles) through angles greater than 90° with respect to the original direction of motion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| Bahcall-Soneira Model | has definition A model for the Galaxy first published by John Bahcall and Raymond Soneira in 1980. In its original form, it sought to reproduce star counts in different parts of the sky by employing only a (thin) disk and a halo; it had no thick disk. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| Bailey type | has definition A classification of RR Lyrae stars according to the shape and amplitude of their light variation | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of RR Lyrae star |  |
| Baily's beads | has definition Small "beads" of sunlight which shine through the valleys on the limb of the Moon in the instant before (or after) totality in a total solar eclipse. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Francis Baily | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1836 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym diamond ring effect | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of solar eclipse |  |
| Baldet-Johnson band | has species CO+ radical | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| Ballik-Ramsay band | has wavelength 1.7625 μ (transition 0-0) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C2 band |  |
| Balmer jump | has definition The sudden decrease in the intensity of the continuous spectrum at the limit of the Balmer series of hydrogen at 3646 Å, representing the energy absorbed when electrons originally in the second energy level are ionized. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has species hydrogen (H I) |  |
| has synonym Balmer discontinuity |  |
| has wavelength 3646 Å |  |
| is a kind of absorption edge |  |
| Balmer line | has definition The series lies in the visible portion of the spectrum. (Deuterium Hα is 1.785 Å short-ward of hydrogen Hα) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has lower energy level 2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has series limit 3647 Å |  |
| is a kind of hydrogen line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| Bamberga | has absolute magnitude +8.14 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has albedo < 0.05 |  |
| has asteroid number 324 |  |
| has definition Asteroid with the darkest known surfaces in the solar system, the only minor planet known to have such a low albedo. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.36, |  |
| has inclination i = 11°.2 |  |
| has mean opposition magnitude +11.41 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has meteorite class carbonaceous chondrite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius larger than Pallas |  |
| has rotation period 8h< sup> -has source: [H76] |  |
| has semi-major axis a = 2.80 AU, |  |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| band head | has definition The conspicuous sharp boundary which usually occurs at the head of a molecular band and which fades gradually toward either longer or shorter wavelengths, depending on the quadratic relation between frequency and rotational quantum number. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of molecular lines |  |
| bar | has definition An absolute unit of pressure equal to 106 dyn cm-2. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit |  |
| is an instance of pressure unit |  |
| barium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 10000 years |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| barium star | has definition Late type giants (G2 to K4) with a very strong BaII 4554 line. Main sequence stars with strong BaII lines have also been discovered recently. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Peculiar low-velocity, strong lined red-giant stars of spectral types G, K, and M, with abnormally large abundances of heavy s-process (but not r-process) elements. They are usually regarded as old disk stars of ~ 1-2 Msun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Ba II star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Ba star |  |
| is a kind of heavy-metal star |  |
| Barnard's star | has definition A faint binary star with the second largest proper motion known. Long-term observations of its light curve suggest a possible third component with a mass about 1.2 that of Jupiter, although this observation has been challenged. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Edward Emerson Barnard | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1916 | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 1.83 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 25 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has proper motion 10.25 arcseconds per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has radial velocity 100 km/sec | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type M5 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Ophiuchus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of M star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of red dwarf |  |
| barotropic gas | has definition A gas in which the pressure is a function of the density only. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gas |  |
| barred spiral | has abundance 20% of spiral galaxies are barred spiral | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition (in Hubble's (1936) classification, SB: in Morgan's classification, B) A spiral galaxy whose nucleus is in the shape of a bar, at the ends of which the spiral arms start. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spiral galaxy |  |
| baryon | has definition Heavy subatomic particle composed of 3 quarks. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of quarks 3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 1/2 or 3/2 |  |
| is a kind of fermion |  |
| is a kind of fermion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hadron | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| base SI unit | has definition a unit assumed to be mutually independent from which all other units are derived |  |
is a kind of SI unit  |  |
| Be star | has definition Irregular variables of spectral type B (or occasionally O or A) with hydrogen emission lines in their spectra. The Be phenomenon involves rapid stellar rotation, circumstellar shells, and mass loss. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Non-supergiant B-type stars, which have shown emission in at least one of the Balmer lines at some time. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line at least one of the Balmer lines at some time |  |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| Beacon explorer A | is an instance of inflatable spacecraft |  |
| Beacon satellite | is a kind of inflatable spacecraft |  |
| beat Cepheid | has definition Dwarf Cepheid in which two or more almost identical periods exist which cause periodic amplitude fluctuations in their light curves. The "beat" period averages about 2 to 21/2 hours. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf Cepheid |  |
| becquerel | has approval agency 15th CGPM | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date May 1975 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has base unit s-1 |  |
| has definition Unit of radioactivity; 1 becquerel represents one disintegration, or other nuclear transformation, per second. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 2.703 × 10-11 curies | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Bq | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| is named after A. H. Becquerel | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| bel | has symbol B |  |
| has value in SI unit (1/2) ln 10 Np |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| belief | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| Bellatrix | has definition A B2 III star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 80 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type B2 III | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym gamma Orionis |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| Bent-yoke equatorial telescope | has mounting bent-yoke equatorial | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| berkelium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| beryllium | has abundance 14 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 17.5 × 10-8 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 2.6 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 22 × 10-8 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.5 × 10-8 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 8.8 × 10-8 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 234.861 nm for Be I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 381.345 nm for Be I |  |
| has atomic emission line 436.099 nm for Be II |  |
| has atomic emission line 467.333 nm for Be II |  |
| has atomic emission line 527.081 nm for Be II |  |
| has atomic emission line 467.342 nm for Be II (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 4 |  |
| has atomic radii 113 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 3243 K under pressure |  |
| has bulk modulus 110 GPa |  |
| has chief source beryl, bertrandite |  |
| has covalent radii 89 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 228.55, c = 358.32 pm for α-Be |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 255.15 pm for β-Be |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for β-Be |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for α-Be |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.01 mg |  |
| has definition Silvery-white, lustrous, relatively soft metal which is unaffected by air or water, even at red heat. Rare and fragile element. Nuclear reactions in stars destroy it. Most and possibly all beryllium originated when cosmic rays smashed into heavier atoms in space and split them into lighter ones, such as beryllium. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 1847.7 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Nicholas Louis Vauquelin |  |
| has discovery date 1797 |  |
| has discovery location Paris, France |  |
| has electrical resistivity 4.0 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity -18 kJ mol-1 from Be to Be- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.57 Pauling |  |
| has hazard deadly poison, carcinogenic for lab animals and maybe for humans |  |
| has hazard inhalation of dust causes severe and irreparable lung damage |  |
| has heat capacity 16.44 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 9.80 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 308.8 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 34 pm for Be+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 6 to 11 |  |
| has lethal intake 317 mg kg-1 acetate in rat |  |
| has level in humans < 1 × 10-5 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.00075 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.0016 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.003 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 11.5 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope beryllium 9 |  |
| has main mining area Brazil, USA, Madagascar, Germany, Czech Republic, Russia, India |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 0.298 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 1.50 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -1.3 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 0.036 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1551 ± 5 K |  |
| has mineral beryl, bertrandite, chrysoberyl, gadolinite, herderite |  |
| has molar volume 4.88 cm3 |  |
| has name origin beryllos = beryl from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.779 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 6 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 4 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 4000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.02 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation be-ril-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7440-41-7 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 9.012182 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 400000 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 156 GPa |  |
| has space group Im3m for β-Be |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for α-Be |  |
| has specimen lumps, powder. Danger ! |  |
| has symbol Be |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of fused BeCl2 |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 200 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.0092 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 13 mg kg-1 in rat |  |
| has uses alloys with copper and nickel increases electrical and thermal conductivities |  |
| has uses copper alloys used to make spark proof tools |  |
| has world production 364 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 318 GPa |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of light element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| beryllium 10 | has atomic mass 10.013534 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.5561 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 1.52 × 106 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 10 |  |
| has symbol 10Be |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 11 | has atomic mass 11.021658 |  |
| has decay mode α (11.48 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode β- |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 13.8 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 7 |  |
| has number of nucleons 11 |  |
| has symbol 11Be |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 12 | has atomic mass 12.02692 |  |
| has decay mode β- (11.71 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode n |  |
| has half life 2.4 × 10-2 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 12 |  |
| has symbol 12Be |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 14 | has atomic mass 13.0375 |  |
| has decay mode β- (16.4 Mev) |  |
| has half life 4 × 10-3 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 10 |  |
| has number of nucleons 14 |  |
| has symbol 14Be |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 6 | has atomic mass 6.019725 |  |
| has decay mode 2p.α |  |
| has half life 5.9 × 10-21 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 2 |  |
| has number of nucleons 6 |  |
| has symbol 6Be |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 7 | has atomic mass 7.016928 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.862 Mev) |  |
| has half life 53.82 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 3 |  |
| has number of nucleons 7 |  |
| has symbol 7Be |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 8 | has atomic mass 8.005305 |  |
| has decay mode 2α (0.046 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 7 × 10-17 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 4 |  |
| has number of nucleons 8 |  |
| has symbol 8Be |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| beryllium 9 | has atomic mass 9.0121822 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 3.7589 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 14.053 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 78.8 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.1779 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.05288 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 5 |  |
| has number of nucleons 9 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 1.39 × 10-2 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 9Be |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of beryllium  |  |
| Besselian element | has definition One of several quantities tabulated for the calculation of accurate predictions of an eclipse or occultation for any point on or above the surface of the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of orbital quantity |  |
| Besselian year | has definition The period of one complete revolution in right ascension of the fictitious mean sun, as defined by Newcomb. The beginning of a Besselian year, traditionally used as as standard epoch, is denoted by the suffix ".0". Since 1984 standard epochs have been defined by the Julian year rather that the Besselian year. For distinction, the beginning of the Besselian year is now identified by the prefix B (e.g., B1950.0). | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| Beta Aquarii | has B-V magnitude 0.83 |  |
| has declination -05 34 16 |  |
| has right ascension 21 31 33.4 |  |
| has spectral type G0Ib |  |
| has synonym HR 8232 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.91 |  |
is a part of Aquarius  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of yellow supergiant |  |
| Beta Arae | has B-V magnitude 1.46 |  |
| has declination -55 31 47 |  |
| has right ascension 17 25 17.9 |  |
| has spectral type K3Ib-IIa |  |
| has synonym HR 6461 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.85 |  |
is a part of Ara  |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of supergiant |  |
| Beta Camelopardalis | has B-V magnitude 0.92 |  |
| has declination +60 26 32 |  |
| has right ascension 05 03 25.1 |  |
| has spectral type G0Ib |  |
| has synonym HR 1603 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.03 |  |
is a part of Camelopardalis  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of yellow supergiant |  |
| Beta Cancri | has B-V magnitude 1.48 |  |
| has declination + 9 11 8 |  |
| has right ascension 8 16 30.9 |  |
| has spectral type K4IIIBa0.5 |  |
| has synonym HR 3249 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.52 |  |
is a part of Cancer  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Beta Cephei | is a part of Cepheus |  |
| is an instance of beta Cephei star |  |
| beta Cephei star | has definition A small group of short-period pulsating variables lying slightly above the upper main sequence. They have a doubly periodic light curve, and are confined within a narrow band of the H-R diagram which lies near the end of core hydrogen-burning stars of roughly 10-20 Msun. beta Cephei itself has at least three components. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has period P = 3.5 to 6 hr |  |
| has prototype beta Cephei |  |
| has spectral type O9-B3 |  |
| has synonym beta Canis Majoris star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| Beta Ceti | has B-V magnitude 1.02 |  |
| has declination -17 59 12 |  |
| has right ascension 0 43 35.3 |  |
| has spectral type K0IIICH-1H,K-0 |  |
| has synonym HR 188 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.04 |  |
is a part of Cetus  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Beta Crucis | has B-V magnitude -0.23 |  |
| has declination -59 41 19 |  |
| has right ascension 12 47 43.3 |  |
| has spectral type B0.5III |  |
| has synonym HR 4853 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.25 |  |
is a part of Crux  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Beta Delphini | has B-V magnitude 0.44 |  |
| has declination +14 35 43 |  |
| has right ascension 20 37 32.9 |  |
| has spectral type F5IV |  |
| has synonym HR 7882 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.63 |  |
is a part of Delphinus  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Beta Herculis | has B-V magnitude 0.94 |  |
| has declination +21 29 22 |  |
| has right ascension 16 30 13.1 |  |
| has spectral type G7IIIa |  |
| has synonym HR 6148 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.77 |  |
is a part of Hercules  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Beta Hydri | has B-V magnitude 0.62 |  |
| has declination -77 15 16 |  |
| has right ascension 0 25 45.3 |  |
| has spectral type G2IV |  |
| has synonym HR 98 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.80 |  |
is a part of Hydrus  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| Beta Librae | has B-V magnitude -0.11 |  |
| has declination -9 22 59 |  |
| has right ascension 15 17 0.3 |  |
| has spectral type B8V |  |
| has synonym HR 5685 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.61 |  |
is a part of Libra  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| beta Lyrae star | has definition A class of eclipsing binary whose secondary minima are intermediate between those of Algol and those of W UMa. The prototype beta Lyr (B8.5 II, F V) is a complex eclipsing system and is presently in a state of rapid mass transfer. The spectrum of one companion is invisible; it may be a black hole. Beta Lyrae is also a weak radio source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of eclipsing binary |  |
| beta Persei star | has definition A class of eclipsing binary (see Algol) with periods of from 2 to 5 days, the depth of whose secondary minimum is almost negligible. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype Algol |  |
| is a kind of eclipsing binary |  |
| Beta Pictoris | has distance 50 light years |  |
has image    |  |
| is a part of Pictor |  |
| is an instance of star |  |
| Beta Trianguli | has B-V magnitude 0.14 |  |
| has declination +34 59 14 |  |
| has right ascension 2 9 32.5 |  |
| has spectral type A5II |  |
| has synonym HR 622 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.00 |  |
is a part of Triangulum  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Beta Volantis | has B-V magnitude 1.13 |  |
| has declination -66 8 13 |  |
| has right ascension 8 25 44.3 |  |
| has spectral type K1III |  |
| has synonym HR 3347 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.77 |  |
is a part of Volans  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| beta-decay | has definition Emission of an electron and an antineutrino (or a positron and a neutrino) by a radioactive nucleus by any one of several processes. e.g., the spontaneous β-decay of a free neutron (n → p + e- + ν bar). The A-number is unchanged, but the Z-number is increased (or decreased) by 1. Beta-decay is a so-called weak interaction. Since electrons of all energies (up to a certain maximum) are emitted in β-decay, this process exhibits a continuous spectrum (unlike α-particle emission, which exhibits a line spectrum). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Spontaneous emission by a heavier element (such as uranium) of negatively charged electrons - beta particles. The result of this radioactive decay is that the original element is very gradually converted into another element. Beta particle emission may be simultaneous with alpha particle decay. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The disintegration of an atomic nucleus, in which an electron (which was historically called a beta particle) and an antineutrino are emitted. Since the electron carries away one unit of negative charge, the final nucleus has a charge one greater than the initial nucleus. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The process in which a neutron disintegrates into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The escaping electron is sometimes called a beta ray. (See neutrino; neutron; proton.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nuclear decay |  |
| beta-particle | has definition An electron or a positron emitted from an excited nucleus when it returns to its ground state via β-decay. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particles first discovered in radioactive β decay - later identified as electrons. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of electron |  |
| Betelgeuse | has definition A red semiregular variable supergiant. Betelgeuse is also a strong infrared emitter - at 2 µ the brightest in the sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A red supergiant star in the constellation Orion and the brightest red supergiant in Earth's sky. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 500 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
has image   |  |
| has spectral type M2 Iab | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha Ori | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of red supergiant |  |
| is an instance of semiregular variable |  |
| biased galaxy formation | has definition The theory that bright galaxies form preferentially from anomalously overdense perturbations in the early universe. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| big bang | has antonym big crunch |  |
| has definition A general class of cosmological models that assume the universe is homogeneous and isotropic on large scales and that allow the universe to evolve in time. Most calculation in the standard big bang model assume a Friedmann cosmology. (See Friedmann equation; homogeneity; isotropy.) A cosmological model that has the same properties as a Friedmann model under some conditions is said to have a Friedmann limit. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A homogeneous, isotropic model of the Universe involving nonstatic (i.e., expanding or contracting) solutions to Einstein's field equations (with zero cosmological constant) calculated by the Russian mathematician A. Friedmann in 1922. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A model of the Universe which started with an initial singularity. The Friedmann model of a homogeneous, isotropic universe (composed of adiabatically expanding matter and radiation, as a result of a primeval explosion) is the standard example. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition According to standard cosmology, the explosion that started the universe expanding 10 to 15 billion years ago. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An evolutionary model of cosmology in which the universe began about 10 billion years ago, in a state of extremely high density and temperature. According to this model, the universe has been expanding, thinning out, and cooling since its beginning. It is an observational fact that distant galaxies are all moving away from our own galaxy, as predicted by the big bang model. (See closed universe; flat universe; Friedmann models; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Model of cosmic history in which the universe begins in a state of high density and temperature, both of which decrease as the universe expands. Less a theory than a school of theories that attempt to trace how the universe evolved. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of three standard Big Bang models that were formulated by Friedmann and Lemaitre of an isotropic and homogeneous universe composed of expanding matter and radiation. In these models space is unbounded. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The initial point of creation. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The most widely accepted theory of the origin of the Universe. It asserts that the Universe began some 1010 years ago from a space-time point of infinite energy density (a singularity). The expansion of the Universe since that time is akin to the expansion of the surface of an inflating balloon: every point on the balloon's surface is moving away from every other point. So, microbes living on the surface see their two-dimensional world expanding, yet there is no center to the expansion which is everywhere uniform. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The state of extremely high (classically, infinite) density and temperature from which the universe began expanding. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory originally proposed by Georges Lemaitre but elaborated by George Gamow and the α-β-hypothesis-γ that the Universe began with the Big Bang, the superexplosion of all the matter now dispersing in the Universe. Since the nuclear physics involved has been explained, and various supporting evidence - notably helium abundance and the sources of radio emission - has been discovered, the theory is almost universally accepted (although at one time the steady state theory rivaled it in popularity). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Friedmann-Lemaitre universe |  |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| Big bang crossover effect | has definition The epoch during the radiation era when the universe switched from being radiation-dominated to being matter-dominated. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has start time 1012 s |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| Big Bang era | has definition A theoretical era postulated to have occurred after the Big Bang. They are in order : - Planck era
- hadron era
- inflation era
- lepton era
- nucleosynthetic era
- radiation era
- matter era
| ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has start time relative to the Big Bang |  |
| has temperature |  |
| is a kind of era |  |
| is followed by |  |
| is preceded by |  |
| big crunch | has antonym big bang |  |
| has definition If the universe has a mass density exceeding the critical mass density, then gravity will eventually reverse the expansion, causing the universe to recollapse into what is often called the big crunch. See also closed universe. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One hypothesized future for the universe in which the current expansion stops, reverses, and results in all space and all matter collapsing together; a reversal of the big bang. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The state of extremely high density and temperature into which a closed universe will recollapse in the distant future. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| binary galaxy | has definition Two galaxies orbiting each other owing to their mutual gravitational attraction. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 2 |  |
| has synonym double galaxy | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of galaxies |  |
| binary pulsar | is a kind of pulsar |  |
| binary star | has definition A system of two stars orbiting around a common center of gravity. Visual binaries are those whose components can be resolved telescopically (i.e., angular separation > 0'.5) and which have detectable orbital motion. Astrometric binaries are those whose dual nature can be deduced from their variable proper motion; spectroscopic binaries, those whose dual nature can be deduced from their variable radial velocity. At least half of the stars in the solar neighborhood are members of binary (or multiple) systems. (See photometric binaries; optical pairs.) |  |
| has number of stars 2 |  |
| has orbital period |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| is a kind of star system |  |
| binary star orbital event | is a kind of orbital event |  |
| binding energy | has definition The energy required to break up a system. In particular, the binding energy of an atomic nucleus is the energy released in the formation of the nucleus. The most strongly bound nuclei are those with atomic weights between about 50 and 65 (the iron group). Lighter nuclei are less strongly bound because of their larger surface-to-volume ratios; heavier nuclei, because the effects of Coulomb repulsion increase with the nuclear charge. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| biochemical process | is a kind of biological process |  |
| is a kind of chemical process |  |
| biological process | has domain biology |  |
| is a kind of process |  |
| biology | has definition The scientific study of life and living matter. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| bismuth | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of group V element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| BL Lacertae | has definition A highly variable object (the most rapid radio variable known, also an optically violent variable - mv = 12 to 15 mag - and an infrared source). Probably an exceedingly compact nonthermal object, and undoubtedly extragalactic. Its optical spectrum is characterized by an absence of lines, so its redshift cannot be measured. (In 1974 Oke and Gunn infer z = 0.07 from an Hβ absorption line in the surrounding halo and conclude that it lies at the center of a bright (Mv = - 23) elliptical. If true, this would make BL Lac the nearest known quasar.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A member of a class of astronomical objects with the following characteristics: (1) rapid variations in intensity at radio, infrared, and optical wavelengths; (2) energy distributions such that most of the energy is emitted at infrared wavelengths; (3) absence of discrete features in low-dispersion spectra; and (4) strong and rapidly varying polarization at visual and radio wavelengths. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym BL Lac |  |
| is a kind of blazar |  |
| black dwarf | has definition The final stage in the evolution of a star of roughly 1 Msun. It is a mass of cold, electron-degenerate gas, and can no longer radiate energy, because the whole star is in its lowest energy state. No black dwarfs have ever been observed. Also, an object (M < 0.085 Msun) that is not massive enough to achieve nuclear chain reactions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf |  |
| is a kind of massive compact halo object |  |
| black hole | has antonym white hole |  |
| has definition A gravitationally collapsed mass inside the Schwarzschild radius (q.v.), from which no light, matter, or signal of any kind can escape. A black hole occurs when the escape velocity of a body becomes the velocity of light (2GM / R = c2). If an object with the mass of the Sun had a radius of 2.5 km, it would be a black hole. Black holes represent one of the possible endpoints of stellar evolution for stars very much more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A mass that is sufficiently compact that not even light can escape its intense gravity. Thus it appears black from the outside. If the sun were compressed to a sphere about four miles in diameter, it would become a black hole. It is believed that some massive stars, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, collapse under their own weight to form black holes. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A singularity in space, surrounded by an event horizon, caused by the collapse of a small but massively dense star through the effects of its own increasing gravity. By the time the state of singularity is reached, the remnants of the star may be minimal, but the gravitational force is so strong it prevents even light from escaping. Black holes may form the "power centers" of galaxies, thus explaining infrared radiation detected in several galactic centres. The properties of matter entering a black hole are the theme of John Wheeler's no hair theorem. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An object that is maximally gravitationally collapsed, and from which not even light can escape. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An object with such a strong gravitational field that even light cannot escape. Matter can fall into a black hole, but according to classical physics no matter or energy can leave it. (Hawking has used quantum theory to show that black holes emit blackbody radiation, but the effect is significant only for black holes much smaller than those that are expected to form by the collapse of stars, which have masses of several solar masses or more.) | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of massive compact halo object |  |
| is a kind of singularity |  |
| blazar | has definition A highly variable active galaxy which, in general, displays no emission lines in its spectrum. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A term collectively used to refer to Optically Violent Variables (OVVs) and BL Lac objects. | ![has source: [adapted from B.M. Peterson <i>An Introduction to Active Galactic Nuclei</i>, Cambridge University Press, (1997)], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of active galaxy |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| blaze angle | has definition The tilt of the facets or grooves of a diffraction grating. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| blazed grating | has definition Diffraction grating so ruled that the reflected light is concentrated into only a few orders, or even a single order, of the spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating |  |
| BLS1 | has definition Broad Line Seyfert 1 |  |
| is a kind of Seyfert galaxy |  |
| blue | is a kind of optical |  |
| blue compact dwarf galaxy | has acronym BCD |  |
| is a kind of dwarf galaxy |  |
| blue compact galaxy | has acronym BCG |  |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| blue dwarf | has definition High-temperature star (as opposed to red stars). Blue dwarfs represent the very dense, but very small, near-final form of what was once a red giant. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf |  |
| blue giant | has definition A giant star with spectral type O or B. [C95] |  |
| has definition High-temperature star (as opposed to red stars). Blue giants are generally on or near the main sequence of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| blue halo star | has definition Hot star in the horizontal-branch, post-horizontal-branch, and post-asymptotic branch phases of evolution. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Population II star |  |
| blue haze | has definition A condition in the Martian atmosphere which sometimes makes it opaque to radiation in the blue-violet end of the visible spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Mars |  |
| blue horizontal-branch star | has definition Blue horizontal-branch star, the first catalog of which was compiled by Humason and Zwicky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Population II star (B3-A0) in the galactic halo, characterized by strong, sharp hydrogen lines and large Balmer jump, and very weak lines of all other elements. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HZ star |  |
| is a kind of Population II star |  |
| blue supergiant | has definition A supergiant star with spectral type O or B. All blue supergiants are hot and young. Rigel, in the constellation Orion, is the best example. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supergiant |  |
| blueshift | has definition The shift of spectral lines toward shorter wavelengths in the spectrum of an approaching source of radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Doppler shift |  |
| BM Orionis | has definition A peculiar eclipsing binary (B2-B3) in the Trapezium, with a flat-bottomed light curve suggesting a total eclipse. The spectrum of the secondary has never been seen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| Bohr atom | has definition The model of an atom whose electrons are pictured as describing "Keplerian" orbits about the central nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| Bohr magneton | has definition Magnetic moment of an electron in the first Bohr orbit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol μB |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000037 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value 927.400899 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| Bohr radius | has definition A unit of length based on the radius of the first Bohr orbit of hydrogen 1. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has proposal date 1928 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposer Hartree | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol a0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol a0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has uncertainty 0.0000000019 × 10-10 m |  |
has value 0.5291772083 × 10-10 m  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| is named after Niels Bohr | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif) |
| bohrium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| Bok globule | has definition A compact, spherical dark nebula that absorbs radiation. Estimates of their mass suggest that their density is too low for gravitational collapse. They tend to lie in regions of much dust but less gas than would be expected for star-forming regions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 103 to 105 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dark nebula |  |
| is a part of dust |  |
| Bol'shoi Teleskop Azimutal'nyi | has altitude 2100 m |  |
| has aperture 6.00 m |  |
| has comment Primary mirror replaced in about 1984, and a third made of Sitall glass was figured in 1992 |  |
| has creation date 1975 |  |
| has focal ratio f/4, 30 |  |
| has latitude 43° 39' N |  |
| has location Mount Pastukhov, Russia |  |
| has longitude 41° 26'E |  |
| has mirror maker LOMO |  |
| has mirror type Sitall glass |  |
| has mounting manufacturer LOMO |  |
| has owner Special Astrophysical Obs. |  |
| has synonym 6 m |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| bolometer | has definition A device for measuring the total amount of radiant energy received from a celestial object. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| bolometric absolute magnitude | has definition A measure of the total amount of energy radiated by a star at all wavelengths. Mbol of Sun = 4.72 mag. The fraction of total energy emitted by a very blue or very red star that lies in the visible range may differ from the total energy by 4 or 5 mag - i.e., only a few percent of the energy lies in the visible. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Mbol |  |
| is a kind of absolute magnitude |  |
| Boltzmann constant | has definition The constant of proportionality relating the mean kinetic energy of an atom to its absolute temperature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has equivalent to molar gas constant divided by the Avogadro number | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol k |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000024 × 10-23 J K-1 |  |
has value 1.3806503 × 10-23 J K-1  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| boron | has abundance 2.63 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 4.41 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 950 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 1166.004 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 1166.247 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 208.891 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 208.957 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 249.667 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 345.129 nm for B I |  |
| has atomic emission line 249.773 nm for B I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 5 |  |
| has atomic radii 83 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to plants; toxic in excess |  |
| has boiling point 3931 K |  |
| has chief source kernite, borax, ulexite, colemanite |  |
| has covalent radii 88 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 506.7, α = 58deg4' pm for α-B |  |
| has crystal type rhombohedral for α-B |  |
| has daily dietary intake 1 - 3 mg |  |
| has definition Non-metal with several forms - the most common form is a dark amorphous powder, unreactive to water, acids and alkalis. Rare and fragile element. Nuclear reactions in stars destroy it. Most boron is created in space, by cosmic rays that smash into heavier atoms and split them. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 2340 kg m-3 for β-rhombohedral solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer L.J. Lussac and L.J. Thenard |  |
| has discovery date 1808 |  |
| has discovery location Paris, France and London, England |  |
| has electrical resistivity 18000 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 26.7 kJ mol-1 from B to B- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.04 Pauling |  |
| has hazard boric acid and borates are poisonous, although once used in medicines |  |
| has heat capacity 11.09 J K-1 mol-1 for α solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 20.799 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 22.2 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 538.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 23 pm for B3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 8 to 13 |  |
| has lethal intake 10 - 20 g as boric acid |  |
| has level in humans 0.13 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.33 - 1 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.4 - 3.3 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 1.1 - 3.3 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 5 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope boron 11 |  |
| has main mining area ulexite in USA, Tibet, Chile; colemanite in USA, Turkey |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.392 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 2.39 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -7.8 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 18 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 2573 K |  |
| has mineral borax, colemanite, datolite, kernite, ulexite |  |
| has molar volume 4.62 cm3 |  |
| has name origin buraq from Arabic |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.535 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 6 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 5 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 1 × 107 years |  |
| has pronunciation bohr-on |  |
has registry number 7440-42-8 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 10.811 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 270 × 106 tonnes as B2O3 |  |
| has space group R3m for α-B |  |
| has specimen crystals, pieces or powder. Safe. |  |
| has symbol B |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| has term symbol 2P1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 27.0 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 767 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 5 g as boric acid |  |
| has uses borosilicate glass, detergents and fire-retardants |  |
| has van der Waals radii 208 pm |  |
| has world production 1 × 106 tonnes year-1 as B2O3 |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of group III element |  |
| is a kind of light element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic metalloid |  |
| reacts with metals to form borides |  |
| boron 10 | has atomic mass 10.0129369 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 2.8740 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 19.9% |  |
| has NMR frequency 10.746 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 22.1 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.80065 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.08459 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 5 |  |
| has number of nucleons 10 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0199 where 1H = 1.00 using (C2H5)2O/BF3 reference |  |
| has symbol 10B |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| boron 11 | has atomic mass 11.0093054 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 8.5794 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 80.1% |  |
| has NMR frequency 32.084 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 754 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.688637 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.04059 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 11 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.17 where 1H = 1.00 using (C2H5)2O/BF3 reference |  |
| has symbol 11B |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| boron 12 | has atomic mass 12.014352 |  |
| has decay mode β- (13.369 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode β-α 1.6% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 0.0202 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.0031 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 7 |  |
| has number of nucleons 12 |  |
| has symbol 12B |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| boron 13 | has atomic mass 13.01778 |  |
| has decay mode β- (13.436 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode β-n 0.25% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 0.0174 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.17778 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 13 |  |
| has symbol 13B |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| boron 8 | has atomic mass 8.024605 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (17.979 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode 2 α |  |
| has half life 0.770 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 1.0355 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 3 |  |
| has number of nucleons 8 |  |
| has symbol 8B |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| boron 9 | has atomic mass 9.013328 |  |
| has decay mode p2α |  |
| has half life 8 × 10-19 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.8007 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 4 |  |
| has number of nucleons 9 |  |
| has symbol 9B |  |
is an instance of boron  |  |
| Borosilicate | is a kind of mirror |  |
| Bose-Einstein nucleus | has definition Nucleus of even A-number (i.e., those with integral spin) (cf. Fermi-Dirac nuclei). Bose-Einstein nuclei do not obey the exclusion principle, and their ground state has zero angular momentum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 0 |  |
| is a kind of boson |  |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| boson | has definition A class of elementary particles whose spin is an integer multiple of a fundamental quantized value. The major function of bosons is to mediate the fundamental forces. The best-known boson is the photon. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A particle which does not obey Pauli's exclusion principle. It is denoted by an integer (or zero) spin. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A particle, or pattern of string vibration, with a whole number amount of spin; typically a messenger particle. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A subatomic particle whose spin is an integral multiple of h bar (cf. fermion). Bosons include the photons, the pions, the gravitons, and all Bose-Einstein nuclei. Boson number is not conserved. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any particle with integer spin: 0, h bar, 2h bar etc. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particles that have integral spins. Force particles such as the photon, gluon, and vector bosons are all bosons. But note that there can also exist composite particles formed out of collections of fermions such as a helium atom-which act collectively as bosons. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particles with integer spin that do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle. They include the photons and the W and Z particles, carriers of the electromagnetic and the electroweak forces respectively. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has quantum behavior Bose-Einstein statistics |  |
| has spin integral |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| bosonic string theory | has definition First known string theory; contains vibrational patterns that are all bosons. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of string theory |  |
| bottom | has charge -1/3 |  |
| has definition A flavor of quark. See flavor. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of heavy quark |  |
| bottom-up scenario | has definition A galaxy-formation scenario in which small galaxies form first. Larger and larger structures are then formed in due course. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The idea that small structures, perhaps galaxies or even smaller substructures, form first in the universe, followed later by larger structures. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| bound electron | has definition Zone in which the electron in atoms reside. Its radius is determined by the quantum principle, its population by the exclusion principle. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of electron |  |
| bound-bound transition | has definition Transition between energy levels of an electron bound to a nucleus (the electron is bound both before and after the transition). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of atomic process |  |
| bound-free transition | has definition Transition in which a bound electron in any energy level is liberated or its reverse process. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of atomic process |  |
| Bowen fluorescence mechanism | has definition A mechanism first discovered by Bowen which explains the anomalously strong lines of O III in the spectra of some planetary nebulae as fluorescence involving the radiative excitation of the 2p3d 3Po2 level of O2+ (54.71 eV) from the 2p2 3P2 state in the ground term by He II Lyman-α photons (54.17 eV). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fluorescence |  |
| Boyle's law | has definition The pressure of an ideal gas kept at constant temperature varies inversely as the volume, i.e., directly as the density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gas law |  |
| Boötes | has acronym Boo |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Boötis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the bear hunter which circles the bears, Ursa Major and Ursa Minor, around the North Pole |  |
| has synonym Bear Driver |  |
| has synonym Bear Hunter |  |
| has synonym Herdsman |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Bp star | has definition Peculiar B stars whose spectra show a deficiency in helium and in which the lines of one or several elements are abnormally enhanced. Traditionally the most important subgroups are Si λ4200, Hg-Mn and Cr-Eu-Sr stars. The latest objects of the latter group correspond to early F-type. | ![has source: [JJ95]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| is a kind of peculiar star |  |
| Br alpha | has wavelength 40512 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Brackett line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| Brackett line | has lower energy level 4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| Bragg angle | has definition Glancing angle between an incident X-ray beam and a given set of crystal planes for which the secondary X-radiation from the planes combines to give a single reflected beam. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| brane | has definition Any of the extended objects that arise in string theory. A one-brane is a string, a two-brane is a membrane, a three-brane has three extended dimensions, etc. More generally, a p-brane has p spatial dimensions. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of string theory |  |
| bremsstrahlung | has antonym inverse bremsstrahlung |  |
| has definition Electromagnetic radiation given out by electrons interacting with the ions in an ionized gas. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Radiation emitted or absorbed when a free electron is accelerated in the field of an atomic nucleus but remains in a hyperbolic orbit without being captured. Since bremsstrahlung is not quantized, photons of any wavelength can be emitted or absorbed. (Also called a free-free transition because the electron is free both before and after the transition.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym deceleration radiation |  |
| has synonym free-free transition |  |
| is a kind of emission |  |
| is a kind of free-free transition |  |
| bright blue variable | has definition Early-type high-luminosity star with peculiar spectra and large-amplitude light variations over a long time scale. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| bright giant | has luminosity class II |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| bright point | has definition Bright region (in X-ray and XUV) observed on the Sun during Skylab missions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 20000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Skylab | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has distribution uniform | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has electron temperature 1 to 2 × 106 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean lifetime 8 hours | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| bright ring | is a kind of ring | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| Brillouin scattering | has definition Slight changes in the frequency of radiation, caused by reflection or scattering from the high-frequency sound waves that arise from thermal vibrations of atoms in the medium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| Broad-line radio galaxy | has acronym BLRG |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| bromine | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state -I |  |
| has ocean residence time 1 × 108 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of halogen |  |
| is a kind of liquid element |  |
| brown dwarf | has definition A self-gravitating, self-luminous gaseous object which is not sufficiently massive to result in thermonuclear hydrogen fusion reactions in its core and cannot therefore be considered a star. Such objects are expected to have a mass less than 7% of the Sun's mass and represent a "missing link" between low-mass stars and gas giant planets like Jupiter (at 0.1% of the Sun's mass). | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A substellar object that is below the minimum mass required for nuclear fusion reactions to occur in its core. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star with too little mass to ignite its hydrogen 1 fuel. If brown dwarfs exist, they shine faint red for a time, as they convert gravitational energy into heat, and then fade and cool. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1 to 8 percent of the Sun | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf |  |
| is a kind of massive compact halo object |  |
| Bruce medalist | has definition a scientist who was awarded the Bruce Medal  |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| bulge | has definition The stellar population that lies within several thousand light-years of the Galactic center. The bulge is old, dense, and metal-rich. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of galactic nucleus |  |
| Bureau des Longitudes | has acronym BDL | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| Bureau International de l'Heure | has acronym BIH | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| Bureau International des Poids et Mesures | has acronym BIPM | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| Bw star | has definition B star with weak helium lines - i.e., B stars which, if classified according to their colors, would have helium lines too weak for the classification, and which, if classified according to their helium lines, would have colors too blue for their spectral type. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| Byurakan 2.6-meter Reflector | has altitude 1500 m |  |
| has aperture 2.64 m |  |
| has creation date 1976 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.6, 16, 40 |  |
| has latitude 40° 20' N |  |
| has location Mount Aragatz, Armenia |  |
| has longitude 44° 18' E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer LOMO |  |
| has owner Byurakan Observatory |  |
| has synonym Byurakan 102 inch |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| C star | has definition A class of carbon star, defined by Morgan and Keenan to replace the Harvard R and N spectral classes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Late type giant with strong bands of carbonated molecules (C2, CN, CH) and no metallic oxide bands. Formerly they were called R or N types, the R types being the hotter and the N types the cooler C stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of carbon star |  |
| C. Donald Shane Telescope | has altitude 1290 m |  |
| has aperture 3.05 m |  |
| has creation date 1959 |  |
| has focal ratio f/5, 17, 36 |  |
| has latitude 37° 21' N |  |
| has location Mount Hamilton, Calif., US |  |
| has longitude 121° 38' W |  |
| has mirror maker Don O. Hendrix |  |
| has mirror type Pyrex |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Judson Pacific-Murphy Corp. |  |
| has owner Lick Observatory |  |
| has synonym 120 inch |  |
| is an instance of Cassegrain |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| C2 band | has species C2 radical | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| Ca H line | has definition A spectral line of singly ionized calcium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 3968 Å |  |
| is a kind of HK lines |  |
| Ca K line | has definition A spectral line of singly ionized calcium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 3933 Å |  |
| is a kind of HK lines |  |
| cadmium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 30 years |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| Caelum | has acronym Cae |  |
| has genitive Caeli |  |
has synonym Chisel  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Calar-Alto-Schmidtspiegel | has altitude 2168 m |  |
| has aperture 0.80 m |  |
| has comment Tube and optics moved from Hamburg, Germany, where the instrument had been in use since 1955 |  |
| has creation date 1980 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.0 |  |
| has latitude 37° 13' N |  |
| has location Calar Alto, Spain |  |
| has longitude 2° 32' W |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.2 m |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has owner Calar Alto Observatory |  |
| has synonym Calar Alto Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| calcium | has abundance 2.24 × 106 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 390 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 390 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 41000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 430 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 440 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 239.856 nm for Ca I |  |
| has atomic emission line 317.933 nm for Ca II |  |
| has atomic emission line 373.690 nm for Ca II |  |
| has atomic emission line 393.366 nm for Ca II (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 393.847 nm for Ca II |  |
| has atomic emission line 422.673 nm for Ca I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic number 20 |  |
| has atomic radii 197 pm for α-form |  |
| has biological role essential to all species |  |
| has boiling point 1757 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 17.2 GPa |  |
| has chief source calcite, dolomite, gypsum (used in cement and plaster) anhydrite (used to make H2SO4) |  |
| has covalent radii 174 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = pm |  |
| has crystal type |  |
| has daily dietary intake 600 - 1400 mg |  |
| has definition silvery-white, relatively soft metal |  |
| has density 1365 kg m-3 for liquid at 1112 K melting point |  |
| has density 1550 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Sir Humphry Davy |  |
| has discovery date 1808 (isolated) |  |
| has discovery location London, England |  |
| has electrical resistivity 3.43 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity -186 kJ mol-1 from Ca to Ca- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]4s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.00 Pauling |  |
| has hazard calcium compounds are only toxic via the other elements they contain |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 25.31 J K-1 mol-1 for solid α form at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 9.33 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 149.95 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 106 pm for Ca2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 36 to 51 |  |
| has lethal intake 6.45 grams kg-1 in carbonate form for rat |  |
| has level in humans 100 - 360 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 140 - 700 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 170000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 60.5 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 22 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope |  |
| has main mining area common everywhere |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 162 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 18.3 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +1.4 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 1.00 kg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1112 K |  |
| has mineral anhydrite, aragonite, calcite, dolomite, gypsum, shortite, vaterite |  |
| has molar volume 25.86 cm3 |  |
| has name origin calx = lime from Latin |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.476 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 16 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 20 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 1 × 106 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.31 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation kal-sium |  |
has registry number 7440-70-2 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 40.078 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves almost unlimited |  |
| has rigidity modulus 7.9 GPa |  |
| has space group |  |
| has specimen granules, pieces or turings. Care ! |  |
| has symbol Ca |  |
| has synthesis mechanism heat calcium oxide (CaO) with aluminium metal in vacuum |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 200 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.43 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has uses alloys and in the manufacture of zirconium, thorium, and uranium and the rare earth metals |  |
| has uses CaO used in metallurgy, water treatment, chemicals industry, cement, etc |  |
| has world production 112 × 106tonnes year-1 for lime, CaO |  |
| has world production 2000 tonnes year-1 for calcium metal |  |
| has young's modulus 19.6 GPa |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| reacts with oxygen and water but soon forms a thin protective oxide-nitride film preventing further corrosion |  |
| calcium 40 | has atomic mass 39.9625906 |  |
| has natural ab39undance 96.941% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 20 |  |
| has number of nucleons 40 |  |
| has symbol 40Ca |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 41 | has atomic mass 40.962278 |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.421 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 1.03 × 105 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.595 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 21 |  |
| has number of nucleons 41 |  |
| has symbol 41Ca |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 42 | has atomic mass 41.9586176 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.647% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 42 |  |
| has symbol 42Ca |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 43 | has atomic mass 42.9587662 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -1.8001 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.135% |  |
| has NMR frequency 6.728 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.0527 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.31727 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.0408 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 43 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 6.40 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 43Ca |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, E |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 44 | has atomic mass 43.9554806 |  |
| has natural abundance 2.086% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 24 |  |
| has number of nucleons 44 |  |
| has symbol 44Ca |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 45 | has atomic mass 44.956185 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.257 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 162.7 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.327 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 25 |  |
| has number of nucleons 45 |  |
| has symbol 45Ca |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 46 | has atomic mass 45.953689 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.004% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 46 |  |
| has symbol 46Ca |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 47 | has atomic mass 46.954543 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.988 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 4.536 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.38 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 27 |  |
| has number of nucleons 47 |  |
| has symbol 47Ca |  |
| has uses research, medical diagnosis |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 48 | has atomic mass 47.952533 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.187% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 48 |  |
| has symbol 48Ca |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calcium 49 | has atomic mass 48.955672 |  |
| has decay mode β- (5.263 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 8.72 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 49 |  |
| has symbol 49Ca |  |
is an instance of calcium  |  |
| calendar year | has definition is an approximation to the tropical year. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| see also Gregorian calendar | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| California Institute of Technology | has acronym Caltech | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Pasadena, USA | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| californium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| Callisto | has albedo 0.15 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A Galilean satellite of Jupiter. It has the lowest density, lowest albedo, and highest temperature of any of the four main satellites of Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fifth (known) moon out from jupiter, and its second largest. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 1.7 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 5050 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital parameters e = 0.0075; i = 0°.3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital rotation period 16.7 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym J IV | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter IV |  |
| has temperature 156 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter |  |
| is an instance of Galilean satellite |  |
| CalTech Submillimeter Observatory | has acronym CSO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| cambrian period | has duration 100 million years |  |
| has start time 600 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| Cambridge catalog | has definition The results of five intensive radio-astronomical surveys (1C, 2C, 3C, 4C and 5C) under the direction of Sir Martin Ryle and Anthony Hewish, during the l950s, 1960s and 1970s, at Cambridge. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radio source catalog |  |
| Camelopardalis | has acronym Cam |  |
| has genitive Camelopardalis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Giraffe |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope | has acronym CFHT |  |
| has altitude 4200 m |  |
| has aperture 3.58 m |  |
| has creation date 1979 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.8, 8, 20, 35 |  |
| has latitude 19° 49' N |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
| has mirror maker Dominion Astrophys. Obs. |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer SNACRP |  |
| has owner Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Corp. |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| Cancer | has acronym Cnc |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Cancri |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the crab sent by Hera to distract Hercules from his battle with the Hydra |  |
| has synonym Crab |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| candela | has approval agency 13th CGPM | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1967 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition the luminous intensity in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian |  |
| has definition The SI unit of luminous intensity, defined as "the luminous intensity, in the perpendicular direction, of a surface of 1/600000 square meter of a blackbody at the temperature of freezing platinum under a pressure of 101325 newtons per square meter." | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has historical origin in 1933 it was based on the luminous emission of a blackbody at the freezing temperature of platinum (2045 K) |  |
| has symbol cd |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit |  |
| is an instance of luminous intensity unit |  |
| Canes Venatici | has acronym CVn |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Canum Venaticorum |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the hunting dogs held on a leash by Boötes as he hunts for the bears Ursa Major and Ursa Minor |  |
| has synonym Hunting Dogs |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| named by Johannes Hevelius in 1687 |  |
| Canis Major | has acronym CMa |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Canis Majoris |  |
| has historical origin one of Orion's hunting dogs |  |
| has synonym Big Dog |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Canis Minor | has acronym CMi |  |
| has genitive Canis Minoris |  |
| has historical origin one of Orion's hunting dogs |  |
| has synonym Little Dog |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Canopus | has B-V magnitude 0.15 |  |
| has declination -52 41 44 |  |
| has definition A supergiant, the second brightest star in the southern sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 55 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 06 23 57.2 |  |
| has spectral type F0 Ib | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type F0II |  |
| has synonym alpha Car | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 2326 |  |
| has V magnitude -0.72 |  |
is a part of Carina  |  |
| is an instance of F star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of supergiant | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| Canum Venaticorum | has B-V magnitude -0.12 |  |
| has declination +38 19 6 |  |
| has right ascension 12 56 1.6 |  |
| has spectral type A0pSiEuHg |  |
| has synonym HR 4915 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.90 |  |
is a part of Canes Venatici  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| capacitance | has unit capacitance unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| capacitance unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of capacitance |  |
| Capella | has B-V magnitude 0.80 |  |
| has declination +45 59 53 |  |
| has definition The sixth brightest star in the night sky, consists of two yellow giants. A spectroscopic triple (F8-G0 III, G5 III, M5 V) (1974 parallax 0'.079). It has a high lithium content and a nearly circular orbit. It may be an X-ray source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 13 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 104.023 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 05 16 41.3 |  |
| has spectral type G5IIIe+G0III |  |
| has synonym Alpha Aurigae |  |
| has synonym HR 1708 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.08 |  |
is a part of Auriga  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Capricornus | has acronym Cap |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Capricorni |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin a goat with a fish tail |  |
| has synonym Goat |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| carbon | has abundance 23 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 26 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 26 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 28 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 350 p.p.m. by volume in Earth's atmosphere as CO2 |  |
| has abundance 4.17 × 108 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 480 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 247.856 nm for C I |  |
| has atomic emission line 283.671 nm for C II (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 426.726 nm for C II (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 723.642 nm for C II (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 6 |  |
| has atomic radii 77 pm |  |
| has biological role DNA constituent, organic molecules required for life |  |
| has boiling point 5100 K (sublimes) |  |
| has chief source graphite |  |
| has covalent radii 60 pm for triple bonds |  |
| has covalent radii 67 pm for double bonds |  |
| has covalent radii 77 pm for single bond |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 1414 pm for buckminsterfullerene |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 246, c = 670.78 pm for hexagonal graphite |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 252, c = 412 pm for hexagonal diamond |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 356.703 pm for cubic diamond |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 364.2 pm, α = 39°30' for rhombohedral graphite |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 894.8, c = 1408 pm for hexagonal carbon (chaoite) |  |
| has crystal type cubic for cubic diamond |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. for buckminsterfullerene |  |
| has crystal type hexagonal for hexagonal carbon (chaoite) |  |
| has crystal type hexagonal for hexagonal diamond |  |
| has crystal type hexagonal for hexagonal graphite |  |
| has crystal type rhombohedral for rhombohedral graphite |  |
| has daily dietary intake 300 g |  |
| has definition pure forms occur as graphite, diamond and buckminsterfullerene C60 |  |
| has density 1650 kg m-3 for buckminsterfullerene at 293 K |  |
| has density 2260 kg m-3 for graphite at 293 K |  |
| has density 3513 kg m-3 for diamond at 293 K |  |
| has discovery date pre-historic |  |
| has electrical resistivity 1 × 1011 Ω m for diamond at 293 K |  |
| has electrical resistivity 1 × 1014 Ω m for buckminsterfullerene at 293 K |  |
| has electrical resistivity 1.375 × 10-5 Ω m for graphite at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 121.9 kJ mol-1 from C to C- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.55 Pauling |  |
| has hazard carbon black is a nuissance but not dangerous, although soot may harbour carcinogenic materials |  |
| has heat capacity 20.838 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 6.113 J K-1 mol-1 for solid diamond at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 8.527 J K-1 mol-1 for solid graphite at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 105.1 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 710.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 260 pm for C4- |  |
| has isotope mass range 9 to 16 |  |
| has level in humans 0.0016 - 0.075 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 300000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 670000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 670000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 1.19 × 10-6 K-1 for diamond |  |
| has longest lived isotope carbon 12 |  |
| has main mining area diamond deposits in South Africa, USA, Russia, Brazil, Zaire, Sierra Leone, Ghana, Canada |  |
| has main mining area graphite deposits in Sri Lanka, Madagascar, Russia, South Korea, Mexico, Czech Republic, Italy |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.625 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 4.60 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -6.2 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for diamond |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -6.3 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for graphite |  |
| has mass of element in person 16 kg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 3800 K for graphite |  |
| has melting point 3820 K for diamond |  |
| has melting point 800 K for buckminsterfullerene (sublimes) |  |
| has mineral diamond, graphite, calcium magnesium carbonates, fossil fuel |  |
| has molar volume 3.42 cm3 for diamond |  |
| has name origin carbo = charcoal from Latin |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.66460 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 8 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 6 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 800000 years |  |
| has pronunciation kar-bon |  |
has registry number 7440-44-0 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 12.011 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 1000 × 109 tonnes for coal |  |
| has reserves 127 × 109 tonnes for natural gas |  |
| has reserves 140 × 109 tonnes for oil |  |
| has reserves large for tar sands |  |
| has space group Fd3m for cubic diamond |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for hexagonal diamond |  |
| has space group P63mc for hexagonal graphite |  |
| has space group R3m for rhombohedral graphite |  |
| has specimen amorphous, fullerenes, bucky tubes, diamond, graphite and soot. Safe. |  |
| has symbol C |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| has term symbol 3P0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 1960 W m-1 K-1 for graphite at 298 K along sheets |  |
| has thermal conductivity 5.7 W m-1 K-1 for graphite at 298 K perpendicular to sheets |  |
| has thermal conductivity 990 - 2320 W m-1 K-1 for diamond at 298 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.0035 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic, but some compounds can be very toxic such as CO or CN- |  |
| has uses coke in steel, carbon black in printing, as a filler, activated charcoal for water treatement and respirators |  |
| has van der Waals radii 185 pm |  |
| has world production 8.6 × |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of group IV element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| reacts with almost everything |  |
| carbon 10 | has atomic mass 10.01686 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (3.650 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 19.3 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 4 |  |
| has number of nucleons 10 |  |
| has symbol 10C |  |
is an instance of carbon  |  |
| carbon 11 | has atomic mass 11.01143 |  |
| has decay mode β+ EC (1.982 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 20.3 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.964 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 5 |  |
| has number of nucleons 11 |  |
| has symbol 11C |  |
| has uses |  |
is an instance of carbon  |  |
| carbon 12 | has atomic mass 12.000000000 by definition |  |
| has natural abundance 98.90 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 12 |  |
| has symbol 12C |  |
is an instance of carbon  |  |
| carbon 13 | has atomic mass 13.003354826 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio × 10 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 1.10 % |  |
| has NMR frequency MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.702411 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment × 10- m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 7 |  |
| has number of nucleons 13 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 13C |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of carbon  |  |
| carbon 14 | has atomic mass 14.003241 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.15648 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 5715 years |  |
| has natural abundance traces |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 14 |  |
| has symbol 14C |  |
| has uses research, carbon dating |  |
is an instance of carbon  |  |
| carbon burning | has definition The stage when a star fuses carbon into heavier elements, making neon and magnesium. Carbon burning eventually occurs in all stars born with more than eight solar masses. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 600 years |  |
| has location center of star heavier than 4 solar masses |  |
| has optimum density 2 × 105 g cm-13 |  |
| has optimum temperature 6 × 108 K |  |
| has part product neon, magnesium |  |
| has reactant carbon |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| requires minimum mass at star birth 8 solar masses |  |
| carbon cycle | has catalyst carbon, nitrogen and oxygen |  |
| has definition A series of nuclear reactions in which carbon is used as a catalyst to transform hydrogen into helium. The carbon cycle can take place only if the necessary C and N nuclei are present, and it requires higher temperatures and is far more temperature-dependent than the proton-proton chain. The cycle yields 26.7 MeV of energy. (On the average, 1.7 MeV of this energy is carried away because of neutrino losses.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An important nuclear fusion process that occurs in stars. Carbon 12 both initiates it and, following interactions with nuclei of nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and other elements, reappears at its conclusion. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One way that a star converts hydrogen into helium. During the CNO cycle, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen catalyze the nuclear reaction, so the total number of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen nuclei remains the same. However, carbon and oxygen gradually get converted into nitrogen. The CNO cycle powers the hydrogen burning that occurs in main-sequence stars with more than 1.5 solar masses and in giants and supergiants of all masses. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Use of carbon and nitrogen as intermediates in the nuclear fusion process of the Sun. Cooler stars undergo the proton-proton cycle. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovered date 1938 |  |
| has minimum mass 1.5 solar masses | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has minimum temperature 15 to 20 million Kelvin |  |
| has part catalyst carbon |  |
| has part catalyst nitrogen |  |
| has part catalyst oxygen |  |
| has part product helium |  |
| has part reactant proton |  |
| has reaction 12C(p, γ) 13N(p, γ) 14O(β+ν) 14N(p, γ) 15O(β+ν) 15N(p, α) 12C | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Bethe-Weizsäcker cycle |  |
| has synonym CNO cycle |  |
| has temperature dependence E ∝ T15 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen burning |  |
| produces energy 26.7 MeV |  |
| carbon detonation supernova model | has definition A supernova model involving the explosive ignition of carbon in the high-density (108 - 1010 g cm-3), electron-degenerate carbon-oxygen core of a 6±2 - 7±2 Msun star by the formation and propagation of a detonation wave. A carbon-detonation supernova seems to leave no dense remnant and converts its C-O core entirely to iron. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of stellar theory |  |
| carbon monosulfide | has symbol CS |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| carbon monoxide | has definition A molecule consisting of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is the most abundant interstellar molecule after molecular hydrogen and is especially useful because it radiates at radio wavelengths, so astronomers can use it to map the distribution of molecular hydrogen. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol CO |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| carbon star | has definition In the HD system, a rather loose category of peculiar red-giant star, usually of spectral types R and N, whose spectra show strong bands of C2, CN, or other carbon compounds and unusually high abundances of lithium. Carbon stars resemble S stars in the relative proportion of heavy and light metals, but they contain so much carbon that these bands dominate their spectra. (C2,0. The number following the comma is an abundance parameter.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| carbonyl sulfide | has symbol OCS |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Carina | has acronym Car |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Carinae |  |
| has synonym Keel |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation formerly part of Argo Navis  |  |
| was named by the IAU along with Vela, Puppis and Pyxis |  |
| Carina galaxy | has definition A dwarf galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1977 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 350000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Carina |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| Carina Nebula | has image   |  |
| has synonym NGC 3372 |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| Carina OB 2 | has definition A rich association of OB stars near η Carinae. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Carina | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of OB association |  |
| carrier boson | carries the force |  |
| has definition A particle that carries one of the fundamental forces between other interacting particles. For example, the carrier boson for the electromagnetic force is the photon. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle that acts as the transmitters of forces. The best known example is the photon, which transmits electromagnetic forces. The gluons are the transmitters of the strong interactions, and the W+, W-, and Z0 particles are the transmitters of the weak interactions. See Table 7.1 on page 120. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym force carrier | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of boson |  |
| is a kind of elementary particle |  |
| Cassegrain | has definition An optical arrangement in which light rays striking the parabolic concave primary mirror of a reflecting telescope are reflected to the hyperbolic convex secondary mirror, and re-reflected through a hole bored in the primary to a focus behind it. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Refers to a design of reflecting telescopes in which the light collected and focussed by the large concave primary mirror is refocussed by a smaller convex secondary mirror on the same axis as the primary. The refocussed beam passes through a central hole cut into the primary mirror and emerges behind the primary. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Telescope devised by Cassegrain in which an auxiliary convex mirror reflects the magnified image, upside down, through a hole in the center of the main objective mirror - i.e., through the end of the telescope itself. It was, however, no improvement on the gregorian telescope invented probably slightly earlier. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has optical design Cassegrain |  |
| has primary mirror shape concave paraboloid |  |
| has secondary mirror shape convex hyperboloid |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| Cassini's division | has definition A gap between the outermost rings of Saturn. The period of a particle in Cassini's division is about two-thirds that of Janus, one-half that of Mimas, one-third that of Enceladus, and one-quarter that of Tethys. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Cassini | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1675 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has width 1800 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ring gap |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| Cassiopeia | has acronym Cas |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Cassiopeiae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin Cassiopeia is chained to her throne as punishment for her boastfulness |  |
| has synonym Andromeda's Mother |  |
| has synonym Queen of Ethiopia |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Cassiopeia A | has definition A radio source in Cassiopeia, the strongest extrasolar source in the sky, believed to be the remnant of a Type II supernova whose light reached Earth about 1667. Optically it is a faint nebula. It has a mass of a few solar masses. It is also an extended source of soft X-rays. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has expansion velocity 800 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3C 461 |  |
| has synonym 3U 2321+58 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cassiopeia |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cat's Eye | has distance 3000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym NGC 6543 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Draco |  |
| cataclysmic variable | has acronym CV |  |
| has definition A collective name for stars in which the brightness increases suddenly because of an explosive event. The class comprises supernovae, novae, recurrent novae, dwarf novae and flare stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A type of variable including flare stars and novae (common, recurrent, and dwarf), all of which are believed to be very close binary systems in which hydrogen-rich matter flows from a late-type star onto a hot white-dwarf primary. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has outburst start time |  |
| has peak brightness |  |
| has recovery time |  |
| has synonym eruptive variable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym explosive variable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of irregular variable |  |
| catalog about star systems | has object type collection of stars |  |
| is a kind of astronomical catalog |  |
| catastrophism | has antonym uniformitarianism |  |
| has definition Nineteenth-century hypothesis that depicted the many changes evinced by the geological record as having resulted from cataclysms occurring during a relatively brief period of history. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| causality | has definition The doctrine that every new situation must have resulted from a previous state. Causation underlay the original atomic hypothesis of the Greeks, and was popular in classical physics. It is eroded in quantum mechanics and has, in any case, never been proved essential to the scientific world view. See chance, determinism. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym causation |  |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| CDA | has definition Centre de Donnees Astronomiques (Strasbourg, France). | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of database |  |
| Cecilia Payne Gaposhkin | has career Havard College Observatory  |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| celestial body | has definition natural object visible in the sky |  |
| has spectra |  |
| is a kind of natural object |  |
| celestial ephemeris pole | has definition The reference pole for nutation and polar motion; the axis of figure for the mean surface of a model Earth in which the free motion has zero amplitude. This pole has no nearly diurnal nutation with respect to a space-fixed or Earth-fixed coordinate system. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate |  |
| celestial equator | has definition Projection of the Earth's equator as a line across the sky (so that to an observer actually on the equator, such a line would pass through the zenith). The directional bearing of a star is given in terms of its right ascension round the celestial equator. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equator |  |
| celestial event | has definition Event involving one or more celestial objects | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of event |  |
| celestial latitude | has definition Angular distance on the celestial sphere measured north or south of the ecliptic along the great circle passing through the poles of the ecliptic and the celestial object. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of ecliptic coordinate component |  |
| celestial longitude | has definition Angular distance along the ecliptic from the vernal equinox eastward. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Angular distance on the celestial sphere measured eastward along the ecliptic from the dynamical equinox to the great circle passing through the poles of the ecliptic and the celestial object. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of ecliptic coordinate component |  |
| celestial mechanics | has definition Study of the movements and physical interactions of objects in space; astrophysical mathematics. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astrophysics |  |
| celestial pole | has definition One of two points at which the Earth's axis of rotation, if extended, would intersect the celestial sphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 0 |  |
| is a kind of equatorial coordinate |  |
| celestial sphere | has definition An imaginary sphere of arbitrary radius upon which celestial bodies may be considered to be located. As circumstances require, the celestial sphere may be centered at the observer, at the Earth's center or at any other location. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
| is an instance of sphere |  |
| Celsius | has absolute zero -273.15 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has base unit K |  |
| has boiling point of water 100 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A mercury-in-glass temperature scale. The zero of the scale represents the melting point of ice and the boiling point of water is taken to be 100 degrees. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposition date 1710 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol °C |  |
| has synonym Centigrade | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water 0.01 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is named after Anders Celsius (1701-1744) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| to convert to Kelvin add 273.15 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| Cen X-1 | is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of transient X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| Cen X-2 | has definition sporadic X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of transient X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| Cen X-4 | has definition sporadic X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| cenozoic era | has duration 63 million years |  |
| has start time 63 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of geological era |  |
| Centaurus | has acronym Cen |  |
| has genitive Centauri |  |
| has historical origin the centaur Chiron which tutored Hercules and Jason |  |
| has synonym Centaur |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Centaurus A | has definition A strong radio source. Optically, it is an elliptical galaxy with a dark obscuring lane. It is the nearest known violent galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4 Mpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1322-42 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 5128 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Centaurus cluster | has definition A cluster of galaxies. Its radio counterpart is compact and located inside NGC 4696. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 200 Mpc |  |
| has synonym 3U 1247-41 |  |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is an instance of galaxy cluster |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| Centaurus X-3 | has definition A pulsating binary X-ray source in the galactic plane. Optical component is Krzeminski's star, a B0 giant or supergiant. The X-ray component is probably a rotating neutron star of about 0.65-0.83 Msun. Cen X-3 is speeding up at a rate of about 1 part in 103-105 per year and will at this rate fall into its companion in about 1000 years. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 5-10 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has eclipse duration 0.488 days in X-ray |  |
| has orbital eccentricity e < 0.002 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 2.087 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 4.8 s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1118-60 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Krzeminski's star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of X-ray pulsar |  |
| centi | has symbol c |  |
| has value 10-2 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| central star of planetary nebula | has acronym CPN |  |
| has synonym planerary nuclei | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales | has acronym CNES | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Paris, France | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| Cep X-4 | is a part of Cepheus |  |
| is an instance of transient X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| Cepheid | has definition A class of stars named after Delta Cephei which vary in brightness over a regular period of time (typically a few days). The period of change is directly related to the true, average brightness or luminosity of the star. Once the period is known the true brightness can be calculated and the distance estimated by observing the "apparent" brightness of the object as seen from Earth. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A type of variable star whose period of variation is tightly related to its intrinsic luminosity. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A yellow supergiant that pulsates, alternately brightening and dimming. Cepheids allow astronomers to measure distances, because the longer a Cepheid's period of variation, the greater the Cepheid's mean intrinsic brightness. To determine a Cepheid's distance, all an astronomer has to do is measure the Cepheid's period; comparing the star's mean intrinsic brightness with the star's mean apparent brightness then yields the distance. Cepheids are so bright that we can see them in other galaxies, allowing us to establish distances to entire galaxies beyond the Milky Way. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of a group of very luminous supergiant pulsating stars. The luminosities of a Cepheid is proportional to its period, but a different P-L relation applies to each type. No Cepheid is near enough for an accurate trigonometric parallax (Polaris is the nearest). Cepheids are useful distance indicators to about 3 Mpc. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Strictly periodic variables with periods 1-50 days, of spectral types F, G and K. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 to 50 days | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype delta Cephei |  |
| has spectral type F star, G star and K star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| Cepheus | has acronym Cep |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Cephei |  |
| has synonym Andromeda's Father |  |
| has synonym King of Ethiopia |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Cer-Vit | is a kind of mirror |  |
| Ceres | has definition Largest asteroid, and the first to be discovered. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Piazzi |  |
| has discovery date 1801 |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.079 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 10°.6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1.17 × 1024 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 2.7673 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean orbital speed 17.9 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has photographic albedo 0.06 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R ≈ 510 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 0.38 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has sidereal period 1682 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface spectra carbonaceous chondrite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 466.6 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| cerium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 100 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| CERN | has definition The European Laboratory for Particle Physics (formerly the Conseil Europeen pour la Recherche Nucleaire). Here, the resources of the European member nations are pooled to construct the large particle accelerators needed for high-energy experiments. The major facilities at CERN include the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) and the Large Electron-Positron (LEP) collider. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has location near Geneva, Switzerland | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high energy physics institution |  |
| cesium | has image 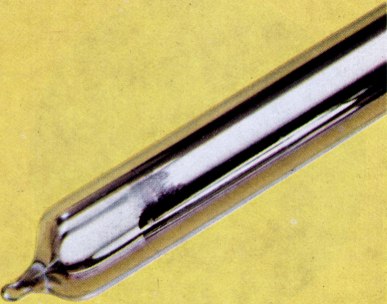 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 600000 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| Cetus | has acronym Cet |  |
| has genitive Ceti |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the sea monster slain by Perseus to save Andromeda. Also known as the biblically famous whale who swallowed Jonah. |  |
| has synonym Jonah's Whale |  |
| has synonym Sea Monster |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| CGS unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| CH star | has definition G-type giant (G5 to K5) in which the molecular bands of CH are very strong. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of G star |  |
| chalcophile element | has definition element that tends to concentrate in sulfides |  |
| has occurrence in sulfide minerals |  |
| is a kind of planetary element |  |
| Chamaeleon | has acronym Cha |  |
| has genitive Chamaeleontis |  |
| has synonym Chameleon |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| Chandra | has acronym AXAF |  |
has definition NASA's premier x-ray observatory  |  |
is an instance of grazing-incidence telescope  |  |
is named after Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar  |  |
| Chandrasekhar limit | has definition A limiting mass for white dwarfs. If the mass exceeds this critical mass (1.44 solar masses, for the expected mean molecular weight of 2), the load of the overlying layers will be so great that degeneracy pressure will be unable to support it, and no configuration will be stable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The maximum mass, approximately 1.4 Msun, above which an object cannot support itself by electron degeneracy pressure; hence, the maximum mass of a white dwarf. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| Chandrasekhar-Schonberg limit | has definition Mass above which the helium core of a star begins to contract (eventually to collapse altogether). The limit is now reckoned as 10 to 15 per cent of the star's total mass. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mass limit for an isothermal core. In order to maintain its luminosity by hydrogen burning just outside the isothermal core, the star must keep a high temperature and a high pressure at the surface of the core. When the helium core exceeds about 12% of the star's total mass, the star can no longer adjust by small changes, but must drastically increase in radius and move rapidly from the main sequence. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| characteristic impedance of vacuum | has symbol Z0 |  |
| has uncertainty 0 |  |
| has unit Ω |  |
has value 376.730313461 Ω  |  |
| is an instance of resistance |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| charge | has definition The fundamental property of a particle that causes it to be affected by the electromagnetic force. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit charge unit |  |
| has unit charge unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| charge multiplet | has definition A group of particles which differ in electrical charge but which are nearly identical in mass and other respects (such as lifetime and angular momentum) and which seem to experience identical nuclear forces. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime -has source: [H76] |  |
| has mass -has source: [H76] |  |
| has spin -has source: [H76] |  |
| is a kind of hadron |  |
| charge unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of charge |  |
| charge-coupled device | has acronym CCD |  |
| has definition A small photoelectronic imaging device (typically 1.5 cm square) made from a crystal of semiconductor silicon in which numerous (at least 250000) individual light-sensitive picture elements (pixels) have been constructed. Each tiny pixel (less than 0.03 mm in size) is capable of storing electronic charges created by the absorption of light. The name derives from the method of extracting the locally stored charges from each pixel which is done by transferring or "coupling" charges from one pixel to the next by the controlled collapse and growth of adjacent storage sites or "potential wells". Each "well" is formed inside the silicon crystal by the electric field generated by voltages applied to tiny, semi-transparent metallic electrodes on the CCD surface. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Highly sensitive photoelectric devices that can electronically record the intensity and point of arrival of tiny amounts of light. CCDs are placed at the receiving end of telescopes, to "take pictures" of very faint astronomical objects; they have almost completely replaced photographic plates. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| charged particle | has charge non-zero |  |
| has definition A particle with non-zero charge | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| is accelerated by electric or magnetic fields |  |
| Charles's law | has definition The pressure of an ideal gas at constant volume varies directly as the absolute temperature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gas law |  |
| charm | has charge 2/3 |  |
| has definition The fourth flavor (i.e. type) of quark, the discovery of which in 1974 contributed both to the acceptance of the reality of quarks and to our understanding of their dynamics. The charmed quark exhibits a property called "charm" which is conserved in strong interactions. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The fourth flavor of quarks. Predicted by theory, charmed quarks were discovered in 1974. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The property that distinguishes one of the types of quarks. At present, there are six types of quarks known, one of which is the "charmed" quark. (See quark.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of heavy quark |  |
| chemical process | has domain chemistry |  |
| is a kind of process |  |
| chemistry | has definition The scientific study of chemicals and chemical reactions. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| Cherenkov detector | has definition Apparatus through which it is possible to observe the existence and velocity of high-speed particles important in experimental nuclear physics and in the study of cosmic radiation. It was originally built to investigate the Cherenkov radiation effect, in which charged particles travel through a medium at a speed greater than that of light in that medium. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy detector |  |
| Chi squared test | has definition A least-squares statistical test that measures the probability of randomness in a distribution. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol χ2 |  |
| is an instance of statistical test |  |
| chirality | has definition An expression of the basic handedness of nature. Fundamental theories of the elementary particles and of superstrings must possess chirality. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Feature of fundamental particle physics that distinguishes left- from right-handed, showing that the universe is not fully left-right symmetric. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym chiral |  |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| chlorine | has abundance 130 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 18000 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.2 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 479.455 nm for Cl II |  |
| has atomic emission line 489.677 nm for Cl II |  |
| has atomic emission line 542.323 nm for Cl II |  |
| has atomic emission line 858.597 nm for Cl I |  |
| has atomic emission line 837.574 nm for Cl I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 17 |  |
| has biological role chloride, Cl-, is essential to many species, including humans |  |
| has boiling point 239.18 K |  |
| has chief source halite (rock salt) |  |
| has covalent radii 99 pm |  |
| has critical pressure 7700 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 417 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 856, c = 612 pm |  |
| has crystal type tetragonal |  |
| has daily dietary intake 3.00 - 6.50 g |  |
| has definition yellow-green, dense, sharp-smelling gas (Cl2) which is a key industrial chemical |  |
| has density 1507 kg m-3 for liquid at 239.18 K boiling point |  |
| has density 2030 kg m-3 for solid at 113 K |  |
| has density 3.214 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has discoverer C.W. Scheele |  |
| has discovery date 1774 |  |
| has discovery location Uppsala, Sweden |  |
| has electron affinity 349.0 kJ mol-1 from Cl to Cl- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p5 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 3.16 Pauling |  |
| has hazard Cl2 0.5 p.p.m. time-weighted average above which there is a threat to health |  |
| has hazard Cl2 15 p.p.m. produces throat irritation |  |
| has hazard Cl2 50 p.p.m. is dangerous even in short doses |  |
| has hazard corrosive, vapours attack eyes and lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 21.840 J K-1 mol-1 for atomic gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 33.907 J K-1 mol-1 for molecular gas (Cl2) at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 6.41 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 20.4033 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 181 pm for Cl- |  |
| has isotope mass range 31 to 41 |  |
| has lethal intake Cl2 inhalation 500 p.p.m. for 5 minutes for humans |  |
| has level in humans 2000 - 5200 p.p.m. chloride in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 2890 mg dm-3 chloride in blood |  |
| has level in humans 3000 - 7200 p.p.m. chloride in liver |  |
| has level in humans 900 p.p.m. chloride in bone |  |
| has longest lived isotope chlorine 35 |  |
| has main mining area vast deposits in USA, Poland, Russia, Germany, China, India, Australia |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 106 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 11.4 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -7.2 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person 95 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 172.17 K |  |
| has mineral halite, carnallite, sylvite |  |
| has molar volume 17.46 cm3 for solid at 113 K |  |
| has name origin chloros = pale green from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.95770 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 13 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 17 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state -I |  |
| has ocean residence time 4 × 108 years |  |
| has pronunciation klor-een |  |
has registry number 7782-50-5 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 35.4527 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves > 1 × 1013 tonnes |  |
| has space group P4/ncm |  |
| has specimen Cl2 in small pressurized canisters. Danger! |  |
| has symbol Cl |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of sodium chloride solution |  |
| has term symbol 2P3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.0089 W m-1 K-1 for gas at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 35.5 barns |  |
| has toxic intake Cl2 is very toxic affecting the eyes and lungs at 3 p.p.m. in air; chloride is non-toxic |  |
| has uses bleaching agent |  |
| has uses manufacture of organochlorine solvents |  |
| has uses PVC |  |
| has uses sterilising agent for water supplies |  |
| has van der Waals radii 181 pm |  |
| has world production 168 × 106 |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of halogen |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| chlorine 34m | has atomic mass 33.973763 |  |
| has decay mode β+ |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode IT |  |
| has half life 32.2 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 17 |  |
| has number of nucleons 34 |  |
| has symbol 34Cl |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 35 | has atomic mass 34.968852721 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 2.6210 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 75.77% |  |
| has NMR frequency 9.798 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 20.2 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.8218736 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.08165 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 18 |  |
| has number of nucleons 35 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 4.70 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 35Cl |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 36 | has atomic mass 35.968306 |  |
| has decay mode β+ |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.709 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.142 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 3.01 × 107 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.28547 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 19 |  |
| has number of nucleons 36 |  |
| has symbol 36Cl |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 37 | has atomic mass 36.96590262 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 2.1718 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 24.23% |  |
| has NMR frequency 8.156 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 3.8 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.6841230 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.06435 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 37 |  |
| has number of nucleons 20 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 2.71 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 37Cl |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 38 | has atomic mass 37.968010 |  |
| has decay mode β- (4.917 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 37.2 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.05 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 21 |  |
| has number of nucleons 38 |  |
| has symbol 38Cl |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 39 | has atomic mass 38.968005 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.44 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 55.6 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 39 |  |
| has symbol 39Cl |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chlorine 40 | has atomic mass 39.970440 |  |
| has decay mode β- (7.5 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 1.38 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 40 |  |
| has symbol 40Cl |  |
is an instance of chlorine  |  |
| chromium | has abundance 1.5 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.8 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 100 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 2.3 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 2.5 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 5.13 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 357.869 nm for Cr I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 359.349 nm for Cr I |  |
| has atomic emission line 360.533 nm for Cr I |  |
| has atomic emission line 427.480 nm for Cr I |  |
| has atomic emission line 428.972 nm for Cr I |  |
| has atomic emission line 520.844 nm for Cr I |  |
| has atomic emission line 425.435 nm for Cr I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 24 |  |
| has atomic radii 125 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to some species, including humans, stimulates metabolism |  |
| has boiling point 2945 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 160.2 GPa |  |
| has chief source chromite |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 288.46 pm |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.01 - 1.2 mg |  |
| has definition hard, blue-white metal which resists oxidation in air, can be polished to a high shine |  |
| has density 6460 kg m-3 for liquid at 2130 K melting point |  |
| has density 7190 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Nicholas Louis Vauquelin |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
| has discovery location Paris, France |  |
| has electrical resistivity 12.7 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 64.3 kJ mol-1 from Cr to Cr- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d54s1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.66 Pauling |  |
| has hazard poison by ingestion, suspected carcinogen, chromates are corrosive to tissue |  |
| has heat capacity 20.79 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 23.35 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 15.3 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 348.78 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 56 pm for Cr4+ |  |
| has ionic radii 64 pm for Cr3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 84 pm for Cr2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 45 to 57 |  |
| has lethal intake 70 mg kg-1 metal taken oraly in humans |  |
| has level in humans 0.006 - 0.11 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.02 - 3.3 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.024 - 0.84 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.1 - 0.33 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 6.2 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope chromium 52 |  |
| has main mining area Turkey, South Africa, Zimbabwe, Russia, Philipipines |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 260 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 31.1 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +4.45 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 14 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 2130 ± 20 K |  |
| has mineral chromite, crocoite |  |
| has molar volume 7.23 cm3 |  |
| has name origin chroma = colour from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.3635 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 13 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 24 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI |  |
| has ocean residence time 10000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.21 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation kroh-mi-uhm |  |
has registry number 7440-47-3 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 51.9961 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 1 × 109 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 115.3 GPa |  |
| has space group Im3m |  |
| has specimen chips, chunks, crystallites or powder. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Cr |  |
| has term symbol 7S3 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 93.7 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 3.1 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 200 mg |  |
| has uses alloys, plating and metal ceramics |  |
| has world production 20000 tonnes year-1 for chromium metal |  |
| has world production 9.6 × 106 tonnes year-1 for chromite ore |  |
| has young's modulus 279 GPa |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with HCL and H2SO4 by disolving |  |
| chromium 48 | has atomic mass 47.954033 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.65 Mev) |  |
| has half life 21.6 hours |  |
| has number of neutrons 24 |  |
| has number of nucleons 48 |  |
| has symbol 48Cr |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 49 | has atomic mass 48.951338 |  |
| has decay mode β+ |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (2.627 Mev) |  |
| has half life 42.3 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.476 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 25 |  |
| has number of nucleons 49 |  |
| has symbol 49Cr |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 50 | has atomic mass 49.9460464 |  |
| has natural abundance 4.345% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 50 |  |
| has symbol 50Cr |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 51 | has atomic mass 50.944768 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.751 Mev) |  |
| has half life 27.70 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.934 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 27 |  |
| has number of nucleons 51 |  |
| has symbol 51Cr |  |
| has uses medical diagnostic |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 52 | has atomic mass 51.9405098 |  |
| has natural abundance 83.789% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 52 |  |
| has symbol 52Cr |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 53 | has atomic mass 52.9406513 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -1.5120 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 9.501% |  |
| has NMR frequency 5.652 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.49 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.47454 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.150 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 53 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 9.03 × 10-4 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 53Cr |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 54 | has atomic mass 53.9388825 |  |
| has natural abundance 2.365% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 30 |  |
| has number of nucleons 54 |  |
| has symbol 54Cr |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 55 | has atomic mass 54.940842 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.603 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 3.497 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 31 |  |
| has number of nucleons 55 |  |
| has symbol 55Cr |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromium 56 | has atomic mass 55.940643 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.62 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 5.9 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 32 |  |
| has number of nucleons 56 |  |
| has symbol 56Cr |  |
is an instance of chromium  |  |
| chromosphere | has definition The part of the solar atmosphere between the photosphere and the corona. It consists of two rather well defined zones: the lower chromosphere and the upper chromosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The part of the Sun's atmosphere immediately above the surface (the photosphere) and beneath the corona. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has has density ρ ≈ 10-16 to 10-8 g cm-3 |  |
| is a part of solar atmosphere |  |
| chromospheric network | has definition A large-scale cellular pattern along the boundaries of which lie bright and dark mottles seen in Hα and other regions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of chromosphere |  |
| Circinus | has acronym Cir |  |
| has genitive Circini |  |
| has synonym Compass |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Circinus X-1 | has definition A highly variable X-ray source. Many of its properties are similar to those of Cygnus X-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1516-56 |  |
| is a part of Circinus |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| circle | has definition An ellipse possessing but one focus. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ellipse |  |
| circumpolar region | has coordinates whose equatorial latitude is greater than the Earth latitude of the observer minus 90 degrees |  |
| has definition a region defined by an equatorial latitude above which stars are visible all year (depends on observers location on Earth) |  |
| has purpose to define a part of the sky which can be observed all year at the observers location |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
| circumpolar star | has definition Star which never sets, from the viewpoint of an observer on Earth. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| class I globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class II globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class III globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class IV globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class IX globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class V globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class VI globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class VII globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class VIII globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class X globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| class XI globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| classical electron radius | has equation  |  |
| has symbol re |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000031 × 10-15 m |  |
has value 2.817940285 × 10-15 m  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| classical nova | has initial rise of light curve typically 12 magnitudes |  |
| has rate of decline of light curve which is nearly exponential |  |
| has rate of decline of light curve which is proportional to the absolute magnitude at maximum (can be used as a distance measureing technique) |  |
| has ultraviolet flux light curve which increases after optical maximum |  |
| is a kind of nova |  |
| classical physics | has definition Physics prior to the introduction of the quantum principle. Classical physics incorporates Newtonian mechanics, views energy as a continuum, and is strictly causal. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| close binary | is a kind of binary star |  |
| closed string | has definition A type of string that is in the shape of a loop. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of string theory |  |
| closed universe | has definition A homogeneous, isotropic universe is said to be temporally closed if gravity is strong enough to eventually reverse the expansion, causing the universe to recollapse. It is said to be spatially closed if gravity is strong enough to curve the space back on itself, forming a finite volume with no boundary. Triangles would contain more than 180°, the circumference of a circle would be less than π times the diameter, and a traveler intending to travel in a straight line would eventually find herself back at her starting point. If Einstein's cosmological constant is zero, as is frequently assumed, then a universe which is temporally closed is also spatially closed, and vice versa. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A standard universe with a spherical three-dimensional spatial geometry. Such a universe is finite in both space and time, and recollapses. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A universe that has a finite size. Closed universes expand for a finite time, reach a maximum size, and then collapse. In closed universes, the inward pull of gravity dominates and eventually reverses the outward flying apart of matter; that is, gravitational energy dominates the kinetic energy of expansion. The value of omega is greater than 1 for a closed universe. If a universe begins closed, it remains closed; if it begins open, it remains open; if it begins flat, it remains flat. In the big bang model of the universe, the question of whether the universe is closed, open, or flat is determined by the initial conditions, just as the fate of a rocket launched from earth is determined by its initial upward velocity relative to the strength of earth's gravitational pull. If the initial rate of expansion of the universe was lower than a critical value, determined by the mass density, the universe will expand only for a certain period of time and then collapse, just as a rocket launched with a velocity below a critical value, dependent on the strength of earth's gravity, will reach a maximum height and then fall back to earth. This is the behavior of a closed universe. If the initial rate of expansion of the universe was larger than a critical value, the universe is open and will keep expanding forever. If the initial rate of expansion was precisely the critical value, the universe is flat and will expand forever, but with a rate of expansion that approaches zero. (See flat universe; omega; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any model of the Universe in which the gravity of the matter content can reverse the expansion and cause a collapse. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang model that was formulated by Friedmann and Lemaitre which has a positive curvature, like the surface of a sphere, in which case the universe is finite, closed, and will eventually recollapse. This space is unbounded. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Cosmological model in which the universe eventually stops expanding and begins to collapse, presumably to end in a fireball like that of the big bang. Compare open universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has geometry of space positive curvature |  |
| is a kind of big bang |  |
| CN-strong star | has definition Late type giant with strong CN bands. Metallic lines are also stronger than in normal giants. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of giant | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of late star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| CN-weak star | has definition High-velocity star with both weak metallic lines and weak CN bands. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of weak line star |  |
| CNO bi-cycle | has definition Similar to the CNO cycle, except that it also includes a cycle in which the next-to-last step becomes 15N(p, γ) 16O(p, γ) 17F(β+ν) 17O(p, α) 14N. This reaction occurs once in about 2000 CN cycles. For main-sequence stars greater than a few solar masses, hydrogen burning by the CNO bi-cycle is the main source of energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has probability 2% of the energy of our Sun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of carbon cycle |  |
| CNO tri-cycle | has definition Similar to the CNO bi-cycle, with the addition of the cycle 17O(p, γ) 18F(β+ν) 18O(p, α) 15N. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of carbon cycle |  |
| co-moving coordinate | has definition A set of coordinates which do not change in an expanding (or otherwise moving) medium. i.e. the coordinates of a distant galaxy do not change just because of the expansion of space. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Coordinates fixed with respect to the overall Hubble flow of the universe, so that they do not change as the universe expands. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| Coalsack | has definition A prominent dark nebula readily visible to the naked eye, located on the galactic plane. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 170 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Crux | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of dust |  |
| is an instance of dark nebula |  |
| coating | is a kind of optical device |  |
| cobalt | has abundance 1.1 × 10-6 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 20 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 6.9 × 10-6 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 7.94 × 104 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 240.725 nm for Co I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 242.493 nm for Co I |  |
| has atomic emission line 340.512 nm for Co I |  |
| has atomic emission line 344.364 nm for Co I |  |
| has atomic emission line 350.228 nm for Co I |  |
| has atomic emission line 356.938 nm for Co I |  |
| has atomic emission line 345.350 nm for Co I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 27 |  |
| has atomic radii 125 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to most species, including humans |  |
| has boiling point 3143 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 181.5 GPa |  |
| has chief source cobaltite, skutterudite |  |
| has covalent radii 116 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 250.7, c = 406.9 pm for ε-Co |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 354.41 pm for α-Co |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. for α-Co |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for ε-Co |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.005 - 1.8 mg |  |
| has definition lustrous, silvery-blue, hard metal which is also ferromagnetic. Cobalt 60 is an important radioisotope |  |
| has density 7670 kg m-3 for liquid at 293 K at melting point |  |
| has density 8900 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Georg Brandt |  |
| has discovery date 1735 |  |
| has discovery location Stockholm, Sweden |  |
| has electrical resistivity 6.24 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 63.8 kJ mol-1 from Co to Co- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d74s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.88 Pauling |  |
| has hazard compounds have low toxicity when ingested, but produce vomiting. Suspected carcinogen. |  |
| has heat capacity 23.020 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 24.81 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 15.2 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 382.4 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 64 pm for Co3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 82 pm for Co2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 35m to 64 |  |
| has lethal intake 80 mg kg-1 chloride ingested by rat |  |
| has level in humans 0.0002 - 0.04 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.01 - 0.04 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 0.028 - 0.65 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.06 - 1.1 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 13.36 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope cobalt 59 |  |
| has main mining area Zaire, Morocco, Sweden, Canada |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 313 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 42.5 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility ferromagnetic |  |
| has mass of element in person 3 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1768 K |  |
| has mineral cobaltite, erythrite, glaucodot, linnaerite, skutterudite (smaltite) |  |
| has molar volume 6.62 cm3 |  |
| has name origin kobald = goblin from German |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.278 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 17 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 27 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 40 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.32 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation koh-bolt |  |
has registry number 7440-48-4 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 58.93320 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has rigidity modulus 82 GPa |  |
| has space group Fm3m for α-Co |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for ε-Co |  |
| has specimen foil, pieces, powder, rod and wire. Care ! |  |
| has symbol Co |  |
| has term symbol 4F9/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 100 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 37.2 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 500 mg |  |
| has uses magnet alloys, ceramics, catalysts and paints |  |
| has world production 17000 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 211 GPa |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with dilute acids |  |
| cobalt 55 | has atomic mass 54.942001 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (3.452 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 17.53 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +4.822 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 55 |  |
| has symbol 55Co |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 56 | has atomic mass 55.939841 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.566 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 77.3 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.85 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 4+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 56 |  |
| has symbol 56Co |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 57 | has atomic mass 56.936294 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.836 MeV) |  |
| has half life 271.8 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +7.72 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 30 |  |
| has number of nucleons 57 |  |
| has symbol 57Co |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 58 | has atomic mass 57.935755 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.30 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 70.88 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +4.04 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 31 |  |
| has number of nucleons 58 |  |
| has symbol 58Co |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 59 | has atomic mass 58.9331976 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 6.3472 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 23.614 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 1570 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +4.627 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +0.420 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 32 |  |
| has number of nucleons 59 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.28 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 59Co |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 60 | has atomic mass 59.933819 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.824 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 5.27 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.799 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 33 |  |
| has number of nucleons 60 |  |
| has symbol 60Co |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
| has uses medical therapy |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| cobalt 61 | has atomic mass 60.932478 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.322 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 1.650 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 34 |  |
| has number of nucleons 61 |  |
| has symbol 61Co |  |
is an instance of cobalt  |  |
| coherent scattering | has definition A scattering process that leaves atoms in the same energy state after the scattered photon departs in a direction different from that of the incident photon. The energy of the scattered photon is the same (in the rest frame of the atom) as that of the incident photon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| cold dark matter | has acronym CDM | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A model of structure formation in which an exotic particle whose energy is low at the time it decouples from other matter is responsible for structure formation. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any dark matter candidate which was non-relativistic at the point of decoupling. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Hypothetical subatomic particles that move slowly compared with the speed of light. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dark matter |  |
| collapse | has definition Sudden contraction of a celestial body | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of contraction |  |
| collection of galaxies | has number of galaxies |  |
| is a kind of collection of stars |  |
| collection of particles | is a kind of natural object |  |
| collection of stars | has catalog catalog about star systems |  |
| has definition Two or more stars forming a gravitationally bound system |  |
| has number of stars |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| collider | has definition A particle accelerator in which beams of particles with equal but opposite momentum are made to collide head on. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle accelerator |  |
| collision | is a kind of atomic process |  |
| color | is a kind of radiation measurement |  |
| color temperature | has definition A stellar temperature determined by comparison of the spectral distribution of the star's radiation with that of a blackbody. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| Columba | has acronym Col |  |
| has genitive Columbae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Dove |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation formerly part of Argo Navis  |  |
| column grouped element | has group a column number in the table of the elements |  |
| is a kind of element |  |
| coma | has definition The spherical region of diffuse gas, about 150000 km in diameter, which surrounds the nucleus (q.v.) of a comet. Together, the coma and the nucleus form the comet's head. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym comet head | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of comet |  |
| Coma Berenices | has acronym Com |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Comae Berenices |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Berenice's Hair |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Coma cluster | has definition The nearest massive cluster of galaxies. A symmetric cluster with primarily E and S0 galaxies. Luminous mass 4 × 1014 Msun = 8 × 1047 g; virial theorem mass about 5 × 1048 g; mass needed to bind the cluster about 4 × 1049 g. R ≈ 9 × 1024 cm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 10 million light years | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 300 million light years | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 4 × 1014 Msun (luminous matter) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 1000 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has redshift z = 0.023 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Abell 1656 |  |
| has synonym Coma X-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is an instance of rich cluster |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| Coma open cluster | has definition Open cluster similar to the Hyades in overall binary frequency. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 80 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars 100 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is a part of disk | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of open cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| Coma X-1 | has definition An extended X-ray source in the Coma cluster of galaxies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1257+28 |  |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is a part of Coma cluster |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| comet | has definition A diffuse body of gas and solid particles (such as CN, C2, NH3, and OH), which orbits the Sun. The orbit is usually highly elliptical or even parabolic (average perihelion distance less than 1 AU; average aphelion distance, roughly 104 AU). Comets are unstable bodies with masses on the order of 1018 g whose average lifetime is about 100 perihelion passages. Periodic comets comprise only about 4% of all known comets. Comets are obviously related in some manner to meteors, but no meteorites from a comet have ever been recovered. Observations of comets Bennett and Kohoutek have established that a comet is surrounded by a vast hydrogen halo. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| comet impact | is a kind of impact event |  |
| comet nucleus | has definition The stellar-appearing frozen core, containing almost the entire cometary mass, in the head of a comet. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of comet |  |
| comet tail | has definition The long streamer behind the comet head which does not usually appear until the comet is inside the orbit of Mars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 10-18 atm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has length 107 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun inside the orbit of Mars | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of comet |  |
| cometary nebula | has definition A reflection nebula with a fan shape that bears a superficial resemblance to a comet. Classical examples of the heads of cometary nebulae are R Mon, R CrA, and RY Tau. All have A0-G0 type spectra that resemble the spectrum of a T Tauri star, and their brightness varies from year to year. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of reflection nebula |  |
| commensurate orbit | has definition A term applied to two bodies orbiting around a common barycenter when the period of one is an integral multiple of that of the other. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has period an integral multiple of that of the other body | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elliptical orbit |  |
| communication satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| compact galaxy | has definition A galaxy similar to an N galaxy but with no disk or nebulous background. It is an object of high surface brightness which appears slightly nonstellar on photographs and which has a larger redshift than normal stars in our Galaxy. Nearest "compact" galaxy is M32. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| compact group | has definition Galaxy group with a few galaxies separated by a few galaxy diameters. | ![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies < 10 |  |
| is a kind of galaxy group |  |
| compact H II region | has definition A dense (ne ≥ 103 cm-3) H II region of small linear dimensions (≤ 1 pc). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of H II region |  |
| composite spectrum star | has definition Object with a spectrum due to superposition of the spectra of two different stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Compton | is an instance of X-ray space telescope |  |
| Compton scattering | has antonym inverse Compton effect |  |
| has definition Decrease in the frequency of high-energy radiation (such as X-rays) caused when a photon loses some of its energy to a free electron by collision. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Scattering of a photon due to the Compton effect (see also noncoherent scattering). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The scattering of photons by free electrons in an ionized medium. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| condensation | has definition from gas to liquid or from gas to solid |  |
| has final phase liquid |  |
| has initial phase gas |  |
| has inverse process evaporation |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| conductance | has unit conductance unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| conductance quantum | has equation  |  |
| has symbol G0 |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000028 × 10-5 S |  |
has value 7.748091696 × 10-5 S  |  |
| is an instance of conductance |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| conductance unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of conductance |  |
| conic section | has dimensions 2 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| conjunction | has definition The phenomenon in which two bodies have the same apparent celestial longitude (see longitude, celestial) or right ascension as viewed from a third body. Conjunctions are usually tabulated as geocentric phenomena. For Mercury and Venus, geocentric inferior conjunction occurs when the planet is between the Earth and Sun, and superior conjunction occurs when the Sun is between the planet and Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has elongation 0° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planetary elongation event |  |
| conservation law | has definition A quantity that remains unchanged in the course of the evolution of a dynamical system. There are seven known quantities that are conserved: energy (including mass), momentum, angular momentum (including spin), charge, electron-family number, muon-family number, and baryon-family number. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Law that identifies a quantity, such as energy, that remains unchanged throughout a transformation. All conservation laws are thought to involve symmetries. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of law |  |
| conservation of angular momentum | has conserved quantity angular momentum | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that the angular momentum of a system (the momentum of rotation about a point) remains the same as long as no external torque acts. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The total angular momentum of an isolated dynamical system does not change during the course of its evolution. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservation of charge | has conserved quantity charge | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservation of energy | has conserved quantity energy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that the total energy of a closed system never changes, that energy is only converted from one form to another. This principle must be enlarged under special relativity to include mass-energy. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The total energy of a system (including kinetic energy and gravitational energy) is conserved and does not vary. Thus, kinetic energy can only increase at the expense of gravitational potential energy. Modern physics has modified the law of conservation of energy, since matter can be created or annihilated; a more general law is the conservation of mass and energy. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservation of mass and energy | has conserved quantity mass and energy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Important physical principle and one of the basic laws of physics stating that matter is neither created nor destroyed (although mass may become energy, the energy quantitatively represents the mass). One exception to this principle is a singularity; another follows from the theory of virtual particles. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservation of matter | has conserved quantity matter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that matter is neither created nor destroyed. This principle is only approximately true, since special relativity shows that matter and energy are equivalent and interconvertible. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservation of momentum | has conserved quantity momentum | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that the linear momentum of a system (in Newtonian mechanics, mass times velocity) remains the same as long as no external force acts. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conservation law |  |
| conservative scattering | has definition Scattering that occurs in the absence of absorption. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| consistent | has definition The property possessed by a scientific theory when it contains and extends an earlier well-supported theory; for example, general relativity is consistent with Newtonian gravity. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| constant | is a kind of number |  |
| constellation | has boundary defined in equatorial coordinates |  |
| has component asterism |  |
| has definition Precisely defined area of the celestial sphere, associated with a grouping of stars, that the International Astronomical Union has designated as a constellation. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has genitive which is used when referring to a star in the constellation |  |
| has historical origin asterism with pictorial or mythical significance |  |
| has purpose to divide the celestial sphere into small visually recognizable star classification regions |  |
is a kind of equatorial sky area  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| constellation formerly part of Argo Navis | has definition a constellation created by the international astronomical union by breaking up the constellation Argo Navis  |  |
has historical origin part of the large constellation Argo Navis
  |  |
| is a kind of constellation |  |
| constellation named by Bayer | has definition a constellation named by Johann Bayer the author of the Uranometria star atlas 1607 |  |
| is a kind of constellation |  |
| is named by Johann Bayer |  |
| constellation named by de Lacaille | has definition a constellation named by Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille |  |
| is a kind of constellation |  |
| is named by Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille |  |
| contraction | has definition A mass motion towards the center of gravity of a celestial body | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| convection | has definition A mass motion in a circulatory pattern. Process in the Sun (and possibly other stars) perhaps caused by solar rotation, which produces the immensely powerful electrical and magnetic fields associated with sunspots. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| convective zone | has definition Region in a stellar interior where convection dominates the heat flow | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of solar interior |  |
| coordinate | has component coordinate component |  |
| has definition Quantities that provide references for locations in space and time. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of point |  |
| coordinate component | has definition A component of a coordinate system, components are usually an angle or a length | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a component of coordinate |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| coordinate transformation | has definition Method of relating observations from one frame of reference to another. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of transformation |  |
| Copenhagen interpretation | has competing theory Copenhagen interpretation |  |
| has definition The view of quantum mechanics holding that prior to the measurement, a system has no physical existence and is describable only in terms of the probability of each possible result of a measurement. After a measurement the physical system exists in one and only one of its possible states. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum mechanics interpretation |  |
| Copernicus | has contribution the Copernican model of the solar system with the sun at its center |  |
| is an instance of scientist |  |
| copper | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 3000 years |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| core-halo galaxy | has abundance 20% of the known extended radio sources | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A class of radio source characterized by an emission "halo" surrounding a more intense "core". About 20% of the known extended radio sources are of the core-halo type. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| corona | has definition Outermost atmosphere of the Sun immediately above the chromosphere, consisting of hot (1-2 × 106 K), low-density (about 10-16 g cm-3) gas that extends for millions of miles from the Suns's surface. Ordinarily it can be seen only during a total solar eclipse. Its shape varies from almost spherical at sunspot maximum to unsymmetrical at minimum. Its high temperature is probably caused by MHD shock waves generated below the photosphere. The corona, together with solar flares, is the source of solar X-rays. It is the corona, not the photosphere, that is studied by radio astronomers, except at very short wavelengths. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of solar atmosphere |  |
| Corona Australis | has acronym CrA |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Coronae Austrinae |  |
| has synonym Southern Crown |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Corona Borealis | has acronym CrB |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Coronae Borealis |  |
| has synonym Northern Crown |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| coronal green line | has definition An emission line of Fe XIV, the strongest line in the solar corona. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Fe XIV |  |
| has transition 2P3/2 - 2P1/2 |  |
| has wavelength 5303 Å |  |
is a kind of emission line  |  |
| coronal hole | has definition An area where the extreme-ultraviolet and X-ray coronal emission is abnormally low or absent; a coronal region apparently associated with diverging magnetic fields. A great part, if not all, of the solar wind starts from coronal holes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| coronene | has definition The first ultraviolet phosphor to be tried on the surface of a CCD. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coating |  |
| corrector plate | has definition Thin lens-like optical piece which removes certain optical aberrations. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of aspheric |  |
| Corvus | has acronym Crv |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Corvi |  |
| has synonym Crow |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Cosmic Background Explore | has acronym COBE |  |
| has definition satellite that studies the microwave background. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif) |
is an instance of NASA satellite  |  |
| cosmic matter density | has definition The average number of fermions per unit volume of space throughout the universe. Since matter is depicted in general relativity as bending space, the value of the cosmic matter density, if known, could reveal the overall curvature of cosmic space. See critical density, omega. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of density |  |
| cosmic rays | has composition 85% protons, 14% alpha-particles, 1% electrons, << 1% heavy nuclei | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition High-energy charged particles which stream at relativistic velocities down to Earth from space. The Sun ejects low-energy (107 - 1010 eV) cosmic rays during solar flares (those of lower energy than this are unobservable from Earth because of solar system magnetic fields). Those of intermediate energy (1010 - 1016 eV) have an isotropic distribution, and are apparently produced in the Galaxy. Possible sources of acceleration are shock waves accompanying supernovae (although cosmic rays have a higher hydrogen content than would be expected from a star that has processed material to iron), and the rotating magnetic fields of pulsars. The light elements Li, Be, and B have a higher abundance ratio in cosmic rays than in the solar system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy 2 GeV (average) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym corpuscular radiation |  |
| is a kind of charged particle |  |
| is a kind of radioactive particle |  |
| cosmic string | has definition Long, stringlike concentrations of matter-energy that may have formed during symmetry breaking in the first moments of the big bang. If they exist, they would be candidates for the seed perturbations of structure formation. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Microscopically thin, spaghetti-like objects which, according to some theories of elementary particles, could form randomly during a phase transition in the early universe. Cosmic strings could provide the seeds for structure formation in the universe, as an alternative to the possibility that the seeds originated as quantum fluctuations during inflation. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Some contemporary cosmological theories suggest that boundaries were formed between different regions of the universe at the moment of creation. These boundaries survive today as "cosmic strings", incredibly thin but very massive strings many light years in length. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| is a kind of theoretical celestial body |  |
| cosmic year | has definition Time the Sun takes to "orbit" in galactic rotation: about 225 million years. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 225 million years | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time unit |  |
| cosmogony | has definition The study of the origin of celestial systems, especially the solar system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology |  |
| cosmological constant | has definition A constant introduced into Einstein's field equations of general relativity in order to provide a supplement to gravity. If positive (repulsive), it counteracts gravity, while if negative (attractive), it augments gravity. It can be interpreted physically as an energy density associated with space itself. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A contribution to gravity that results from the effective mass density, or energy density, in the vacuum. A positive cosmological constant acts as if it were negative gravity - it makes two masses repel each other instead of attract each other. Einstein's first cosmological model contained a cosmological constant, which appeared as an additional term in the equations of general relativity. (See false vacuum; vacuum.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A parameter that determines the strength of the cosmological term in the equations of general relativity. This term was added by Einstein because he thought the universe was static, and the term provided a repulsive gravitational force that was needed to prevent the universe from collapsing under the force of ordinary gravity. The false vacuum of inflationary models creates a similar repulsive gravitational force, except that it prevails for only a brief period in the early universe. The cosmological constant is often assumed to be zero, but it might make a significant contribution to the evolution equations of our universe. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A possible third parameter in cosmology, in addition to the Hubble constant and omega (Ω). Most cosmologists believe the cosmological constant is zero, but if it is not, it would make the universe older than astronomers calculate from the Hubble constant and Ω. The size of the cosmological constant is designated by the Greek letter lambda (λ). | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A term added by Einstein to the gravitational field equations of his theory of general relativity. Such a term would produce a repulsive antigravity force at very large distances and would correspond to energy locked up in the curvature of space-time itself. There is, at present, no evidence for the existence of a cosmological constant (although one may have existed in the past). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A term introduced by Einstein into his field equations of gravitation to permit a static model of the universe. It corresponded, as introduced originally, to a cosmic repulsion force that could withstand the attractive tendency of gravity. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A term sometimes employed in cosmology to express a force of "cosmic repulsion", such as the energy released by the false vacuum thought to power exponential expansion of the universe in the inflationary universe models. Whether any such thing as cosmic repulsion exists or ever played a role in cosmic history remains an open question. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Einstein's general theory of relativity allows for space-time curvature even in an empty universe. The amount of this curvature is given by the cosmological constant. Current indications are that this constant must be zero, but the reason for its vanishing remains a mystery. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| cosmological constant problem | has definition The puzzle of why the cosmological constant has a value which is either zero, or in any case roughly 120 orders of magnitude or more smaller than the value that particle theorists would expect. Particle theorists interpret the cosmological constant as a measure of the energy density of the vacuum, which they expect to be large because of the complexity of the vacuum. See vacuum. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of problem |  |
| cosmological redshift | has anomaly A few galaxies show blueshifts, the most famous being Andromeda galaxy, but most show redshifts, due to the expansion of the universe. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The redshift due to the expansion of the Universe. Contrary to popular belief, this is not a Doppler shift. Most galaxies move away from us, but this is not the cause of their redshifts. Instead, as a light wave travels through the fabric of space, the universe expands and the light wave gets stretched and therefore redshifted. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Slipher | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1926 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has property wavelength shift is directly proportional to distance | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol z |  |
| has value the cosmological redshift as observed is the ratio of the radius of the Universe at the present epoch to the radius of the Universe at the time the radiation left the distant object. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wavelength shift |  |
| cosmology | has definition The study of the origin, structure, and evolution of the Universe on the largest possible scale. In present usage, it frequently includes cosmogony. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of extragalactic astronomy |  |
| cosmology theory | has domain cosmology |  |
| is a kind of astronomy theory |  |
| Coster-Kronig transition | has definition An Auger transition in which the vacancy is filled by an electron from a higher subshell of the same shell. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Auger transition |  |
| Cotton Candy nebula | has image   |  |
| has synonym IRAS 17150-3224 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| coudé focus | has definition A focus used primarily for spectroscopy. In this arrangement light from the primary mirror is reflected along the polar axis to focus at a fixed place separate from the moving parts of the telescope, where large pieces of equipment can be fitted without interfering with the telescope's balance. (The word comes from a French word meaning "bent like an elbow", not from a man's name) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A stationary focal point in an equatorial mounted telescope obtained by an arrangement of small auxiliary mirrors in the converging beam which eventually directs the light down the hollow polar axle of the telescope. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of focus |  |
| coulomb | has base unit s·A |  |
| has definition The practical and the SI unit of charge. It is the quantity of electricity transported in one second by a current of one ampere. From 1908 to 1948 the international coulomb, derived from the international ampere, was in use. Like the other international units it was replaced by the absolute unit on 1 January 1948. The name coulomb was given to the unit at the first meeting of the IEC in Paris in 1881. At this meeting two of the five units which were given definitions were named after French scientists. These were the ampere (A. M. Ampère 1775-1836) and the coulomb (C. A. Coulomb 1736-1806). (1 international coulomb = 0.99985 absolute coulomb.) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of charge. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 2.998 × 109 esu | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol C | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of charge unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| represents electric charge, quantity of electricity |  |
| Coulomb collision | has definition The collision between two charged particles. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collision |  |
| Coulomb's law | has definition The force between two charged particles varies directly as the size of the charges and inversely as the square of the distance between them. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of electromagnetic law |  |
| CP violation | breaks CPT invariance |  |
| has definition A reaction between subatomic particles is said to be a "CP violating" reaction if the reaction produces a different result when the electrical charges of the particles are changed to their opposites and the mirror image of the particle trajectories is used. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry breaking |  |
| CPT invariance | has definition A symmetry which is believed to hold true for all particles throughout the course of universal history. It states that matter and antimatter would only react in the same way if the spins of the antimatter particles were reversed and the reaction was caused to run backwards in time. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A theory has "CPT invariance" if for every possible reaction between subatomic particles, a reaction can also occur in which the electrical charges of the particles changed to their opposites, the mirror image of the particle trajectories is used, and the directions of motion are reversed. Assuming general notions of modern physics, all conceivable theories of nature are CPT invariant. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| Crab Nebula | has age 947 years |  |
| has definition A chaotic, expanding mass of gas in Taurus, the remnant of a Type I supernova whose light reached Earth in 1054. It is an intense radio source, and its visible light is strongly polarized. It is also a source of X-rays and gamma-rays. Its total mass is about 1 Msun, but the total energy radiated by the Crab is 1037-1038 ergs s-1. It is periodically occulted by the Moon, and every June its radio spectrum is occulted by the solar corona. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A supernova remnant. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has explosion date 1054 A.D. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
has image     |  |
| has Messier number 1 |  |
| has synonym 2U 0531+22 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym M 1 |  |
| has synonym Taurus A | ![has catalog: Radio source, has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Taurus |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| Crab pulsar | has definition A pulsar associated with the Crab Nebula. It has the shortest period of any known pulsar. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 0.0331 seconds | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NP 0532 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Crab Nebula |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| is a part of Taurus |  |
| is an instance of pulsar |  |
| Crater | has acronym Crt |  |
has boundary  |  |
| has genitive Crateris |  |
| has synonym Cup |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of constellation |  |
| creationism | has definition Belief that the universe was created by God in the relatively recent past, as implied by literal interpretations of biblical chronology, and that the species of terrestrial life did not arise through Darwinian evolution but, rather, all came into existence at once. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of religious belief |  |
| Crepe Ring | has definition Rather transparent inner ring of the saturn ring system. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The second innermost ring of Saturn, it has fewer particles and is less dense than the outer rings; therefore, it is harder to observe. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 149300 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Bond | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1850 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym C ring |  |
| has width 18000 to 20000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ring |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| cretacious period | has duration 72 million years |  |
| has start time 135 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of mesozoic era |  |
| critical density | has definition If the cosmological constant is assumed to vanish, then the critical mass density is that density which puts the universe just on the border between eternal expansion (open universe) and eventual collapse (closed universe). | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The cosmic density of matter required to "close" the universe and so, eventually to halt cosmic expansion. Its value amounts to about ten hydrogen atoms per cubic meter of space. The observed density is so close to the critical value that the question of whether the universe is open or closed has not yet been resolved by observation. See open universe, closed universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The density that just stops the expansion of space, after infinite cosmic time has elapsed. In the standard models, the critical density requires that the spatial geometry be flat. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The value of average cosmic mass density above which the universe is closed. The average mass density of the universe is obtained by measuring the mass in a very large volume of space, including many galaxies, and dividing by the size of the volume. The critical mass density is determined by the current rate of expansion of the universe. According to estimates of the current rate of expansion, the current critical mass density is about 10-29 grams per cubic centimeter. According to the best measurements, the average mass density of our universe appears to be about one tenth the critical mass density. (See closed universe; omega; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of density |  |
| critical equatorial velocity | has definition In rotating early-type stars, that velocity at which the ratio of centrifugal force to gravity at the equator is unity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial velocity |  |
| Cross-axis equatorial telescope | has mounting equatorial with cross-axis | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| crossing time | has definition The time it takes a particle to travel from one point in its orbit to another point 180° away. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| crucial experiment | has definition An experiment that has the power to decide between two competing theories. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of experiment |  |
| Crux | has acronym Cru |  |
| has genitive Crucis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Southern Cross |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| CS star | has definition Group characteristics are: strong bands of CN, outstandingly strong absorption near the Na D lines, usually sufficient structure in the 6400-6500 Å region to suggest ZrO. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star exhibiting combined characteristics of C- and S-type stars - i.e. the presence of both C2 and ZrO bands. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of carbon star |  |
| culmination | has definition Passage of a celestial object across the observer's meridian. More precisely, culmination is the passage through the point of greatest altitude in the diurnal path. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The instant at which a celestial object crosses the meridian. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 day |  |
| has synonym meridian passage | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of location dependent periodic celestial event |  |
| curie | has definition A unit of radioactivity which is now defined as the quantity of any radioactive nuclide undergoing 37.00 × 109 disintegrations per second. The unit was adopted at a Radiography Conference in Brussels in 1910 when it was defined as the radioactivity associated with the quantity of radon in equilibrium with one gram of radium. The present definition, which refers to a unit of the same size but described in terms independent of the disintegration of radon, was agreed at the Copenhagen meeting of the International Commission on Radiological Units in July 1953. The unit is named after Pierre Curie (1859-1906), one of the discoverers of radium. The curie is too large for normal laboratory work where the radioactivity is of the order of millicuries. The number of disintegrations occurring per second is called the activity of a sample and a unit for this was originally the reciprocal second but this has been superseded by the curie. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of radioactivity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 3.7 × 1010 becquerel | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| Curie temperature scale | has definition This is sometimes used for indicating temperature in the vicinity of absolute zero. It is based on Curie's law, which states that the susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is approximately proportional to its absolute temperature. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym magnetic temperature | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| curium | has image 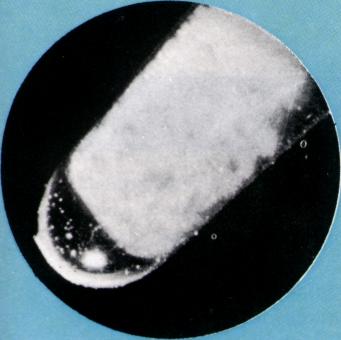 |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| current | has unit current unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| current density | has definition Amount of charge passing through a unit area per unit time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| current density unit | has definition ampere per square meter |  |
| has symbol A·m-2 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| current unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of current |  |
| Curtis | has birth date 1872 |  |
has career - 1893-1900 : Taught Latin & Greek, later math
- 1902-1920 : Lick
- 1920-1930 : Director, Allegheny
- 1931-1942 : Director, U. Michigan Observatories
|  |
| has death date January 9, 1942 |  |
has degree - 1893 : classics, U. Michigan
- 1902 : PhD. U. Virginia
|  |
| has name Heber Doust Curtis |  |
| has orbituary 1942, PASP 54, 54. |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| CV Serpentis | has definition A sometimes-eclipsing binary composed of a Wolf-Rayet star and a B0 star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 29.6 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Serpens |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of Wolf-Rayet |  |
| cyan | is a kind of optical |  |
| cyanoacetylene | has symbol HC3N |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| cyanogen band | has definition Molecular absorption band found in the spectra of stars of type G0 and later. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has species CN |  |
| has use luminosity criterion; it is more pronounced in giants than in dwarfs of the same spectral type | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of interstellar band |  |
| occurs in G0 star or later |  |
| cyanogen radical | has symbol CN |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Cygnus | has acronym Cyg |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Cygni |  |
| has synonym Northern Cross |  |
| has synonym Swan |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Cygnus A | has definition A double radio source, the third strongest radio source in the sky (after the Sun and Cas A), at one time believed to be caused by the collision of two galaxies. It has now been identified with a distant peculiar cD galaxy (z ≈ 0.056). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 2U 1957+40 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3C 405 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of double radio source |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cygnus Loop | has age 20000 years |  |
| has definition A supernova remnant, consisting of a large loop of gas ejected from a star. It is 100 pc above the galactic plane. (X-ray observations give a distance of 2-3 kpc.) It is a thermal bremsstrahlung source of soft X-rays with a spectral temperature of 2 × 106 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 770 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
has image   |  |
| has synonym Cygnus X-5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NG6 6992 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Veil Nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cygnus X-1 | has definition A black hole candidate in the constellation Cygnus and a source of X-rays. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An X-ray source. The visible component is the ninth-magnitude supergiant HDE 226868 (O9.7 Iab). It has rapid night-to-night variations in spectral features. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2.5 kpc |  |
| has eccentricity e ≈ 0.06 |  |
| has inclination i ≈ 27° |  |
| has period 5.5998 days |  |
| has primary mass 20 Msun |  |
| has secondary mass > 6 Msun |  |
| has synonym 3U 1956+35 |  |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cygnus X-2 | has definition An X-ray source optically identified with an irregular variable star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 2142+38 |  |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cygnus X-3 | has definition An X-ray binary. It is also an infrared source, a cosmic ray source, and a strongly variable radio source (interstellar extinction is too high for visible light observations). It is best fitted by a model of an expanding cloud of relativistic electrons emitting synchrotron radiation around a neutron star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1966 |  |
| has distance 10 kpc |  |
| has orbital period 4.8 hour |  |
| has synonym 2U 2030+40 |  |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Cyrillids | is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| D galaxy | has definition A supergiant radio galaxy (the most common type of radio galaxy) which has an elliptical nucleus surrounded by an extended envelope. Or, an optical galaxy with a very bright nucleus. In the Morgan classification, a galaxy with rotational symmetry but without pronounced spiral or elliptical structure (a dustless galaxy). In the Yerkes 1974 system a galaxy with an elliptical-like nucleus surrounded by an extensive envelope (see also R galaxy). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| D layer | has altitude > 100 km or higher |  |
| has definition The lowest part of Earth's ionosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has radio reflectivity "broadcast" radio waves |  |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| D line | has definition Spectral line of neutral sodium, also the strongest interstellar line. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Na I |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is a kind of interstellar line |  |
| is a kind of interstellar line |  |
| D ring | has definition The innermost ring of Saturn. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1969 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ring |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| d-electron | has definition An orbital electron whose l quantum number is 2. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital quantum number 2 |  |
| is a kind of bound electron |  |
| D1 line | has definition Spectral line of neutral sodium. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 5896 Å |  |
| is a kind of D line |  |
| D2 line | has definition Spectral line of neutral sodium. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 5890 Å |  |
| is a kind of D line |  |
| DA white dwarf | has definition only strong hydrogen lines present |  |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| dark cloud gravitational contraction | is a kind of gravitational contraction |  |
| dark flight | has definition phase in the flight of a meteor after the ratardation point when the meteoroid is no longer incandescent |  |
| has duration from the point of intial contact with atmosphere until the retardation point |  |
| has start time the point of intial contact with the atmosphere |  |
| is a kind of meteor event |  |
| dark halo | has definition Massive, nonluminous matter of unknown kind that surrounds and envelope of a galaxy | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The massive outer region of the Milky Way that surrounds the disk and stellar halo. The dark halo consists mostly of dark matter, whose form is unknown. Though it emits almost no light, the dark halo outweighs the rest of the Galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The unseen mass that is believed to surround each galaxy and whose gravitational effects are believed to hold the galaxy together. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| dark matter | has definition Any form of matter which exists in the Universe in a non-luminous form. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Material astronomers cannot see but whose presence they believe in either because they detect its gravitational influence or because certain theories predict its existence. For example, astronomers believe that the outer part of the Galaxy harbors dark matter, because they notice its gravitational influence on the stars they can see; and inflationary cosmologists believe that the universe is full of dark matter, because inflation predicts that the universe has a large density. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Matter in the universe that we detect by its gravitational influences, yet do not see. Dark matter that has small random speed and is easily concentrated by gravity is called cold dark matter. Dark matter that has large random speed and is thus able to resist gravitational clumping is called hot dark matter. Recent models to explain the observed pattern of galaxy clustering can be characterized, in part, as to whether they invoke hot dark matter or cold dark matter. However, since we do not know what the dark matter is, we do not have any direct evidence of whether it is cold or hot. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Matter that is detected only by its gravitational pull on visible matter. At least 90%, and possibly 99% of the matter in the universe is dark. The composition is unknown; it might consist of very low mass stars or supermassive black holes, but big-bang nucleosynthesis calculations limit the amount of such baryonic matter to a small fraction of the critical mass density. If the mass density is critical, as predicted by the simplest versions of inflation, then the bulk of the dark matter must be a gas of weakly interacting non-baryonic particles, sometimes called WIMPS (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles). Various extensions of the standard model of particle physics suggest specific candidates for the WIMPs. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Matter that is invisible to us because it emits little or no light. As much as 90%-99% of the mass of the universe may be dark. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Matter whose existence is inferred on the basis of dynamical studies - e.g., the orbits of stars, in galaxies - but which does not show up as bright objects such as stars and nebulae. Its composition is unknown: It might consist of subatomic particles, or of dim dwarf stars or black holes, or a combination of various sorts of objects. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Matter whose presence is inferred from dynamical measurements but which has no optical counterpart. The luminous regions of galaxies have mass-luminosity ratios of about 10. However, the mass-luminosity ratio in the outer halos of many spiral galaxies is 100 or more; one sees the brightness fall off with distance from the center of the galaxy but considerable mass is present. A similar situation prevails in galaxy clusters, where nonluminous matter must provide most of the self-gravitational attraction that holds the clusters together. The missing mass is not really missing; it is present but invisible (at least to current detectors). It is generally believed to consist either of the remnants of massive stars or of planetary-sized objects comparable in mass to Jupiter. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym hidden mass |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| is a part of dark halo |  |
| dark nebula | has definition A relatively dense cloud of interstellar matter whose dust particles obscure the light from stars beyond it and give the cloud the appearance of a region devoid of stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has density up to 104 particles per cm3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nebula |  |
| is a part of dust |  |
| data collection | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| data standard | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| database | is a kind of data collection |  |
| day | has definition An interval of 86400.51 seconds, unless otherwise indicated. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol d |  |
| has value 86400.51 seconds | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value in SI unit 24 h = 86400 s |  |
| is a kind of non SI unit |  |
| is a kind of time unit |  |
| db galaxy | has definition One of a small number of dumbbell-shaped radio galaxies. They might be called D systems with double nuclei, in which two elliptical nuclei share a common extended envelope. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of D galaxy |  |
| DB white dwarf | has definition only strong helium lines present |  |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| DC white dwarf | has definition continuous spectrum, no lines clearly visible |  |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| de Sitter model | has definition A geometrical model (1917) of an empty universe, based on Einstein's field equations. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A model of the universe that contains no matter but only a positive cosmological constant. It expands exponentially forever. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A particular solution to Einstein's cosmological equations, found by Wilhelm de Sitter in 1917, in which space expands at a rapid, exponential rate. This solution was very different from the solutions of Friedmann and of Lemaitre, in which the universe expands at a much slower rate (a rate with the distance between any two points increasing as something between the square root of time and linearly with time). The Friedmann and Lemaitre type solutions became incorporated in the standard big bang model. Recent modifications of the big bang model, such as the inflationary universe model, propose that the universe went through a period of exponential growth, or a de Sitter phase, early in its evolution. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| dead person | has death date |  |
| has definition a person that has died |  |
| has orbituary |  |
| is a kind of person |  |
| decay process | is a kind of physical process |  |
| deceleration parameter | has definition A dimensionless quantity describing the rate at which the expansion of the Universe is slowing down because of self-gravitation: it gives a measure of the matter density. In Friedmann's equation (which describes many cosmological models) q0 = - 1 indicates a steady-state universe, q0 < +1/2 indicates an open universe, q0 = +1/2 indicates a flat Euclidean universe, and q0 > 1/2 indicates a universe that is decelerating and will eventually contract. Sandage and Tammann (1975) obtain q0 = 0.10 for H0 = 55 km s-1 Mpc-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A parameter (that denotes the rate of change with time of the Hubble constant. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A parameter that measures the rate of slowing down of the expansion of the universe. Gravity causes the slowing down. The deceleration parameter equals omega (another cosmological parameter) when the universe is dominated by radiation, approximately the first 100000 years after the big bang, and 1/2 omega when the universe is dominated by matter. Since the deceleration parameter is equivalent to omega (assuming a cosmological constant of zero, as often done), it determines the ultimate fate and spatial geometry of the universe. The deceleration parameter is often denoted by the symbol q0. (See omega.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Quantity designating the rate at which the expansion of the universe is slowing down, owing to the braking effect of the galaxies' gravitational tug on one another. It is a function of the cosmic matter density. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol q0 | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| deci | has symbol d |  |
| has value 10-1 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| declination | has definition Angular distance above (positive) or below (negative) the celestial equator. One of the co-ordinates, with right ascension, that defines the position of a heavenly body. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Angular distance north (+) or south (-) of the celestial equator to some object, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds of arc along an hour circle passing through the object. Declination is analogous to latitude on the Earth's surface. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Angular distance on the celestial sphere north or south of the celestial equator. It is measured along the hour circle passing through the celestial object. Declination is usually given in combination with right ascension or hour angle. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Astronomical coordinate. Equivalent to latitude. The angle in degrees above or below the Celestial Equator, i.e. the projection onto the sky of the Earth's equator. Range of declination is from from zero to ± 90°. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Location on the sky in a north-south direction. Lines of declination are the celestial equivalent of latitude on Earth. Compare right ascension. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol δ |  |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate component |  |
| deduction | has definition Process of reasoning in which a conclusion is derived from a given premise or premises, without a need for additional information. Compare induction. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of reasoning process |  |
| DEep Near Infrared Survey | has acronym DENIS | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of sky survey | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| deformable mirror | has definition A very thin mirror whose shape can be changed by the force applied by many small pistons behind the mirror. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| degeneracy pressure | has definition Pressure in a degenerate electron or neutron gas. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Pressure in a degenerate electron or neutron gas. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pressure |  |
| degenerate gas | has definition A gas of electrons (or, more generally, fermions) in which all the lowest quantum states are occupied. For such a gas, the pressure in the nonrelativistic limit is proportional to the 5/3 power of the density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A state of matter found in white dwarfs and other extremely dense objects, in which strong deviations from classical laws of physics occur. As the density increases at a given temperature, the pressure rises more and more rapidly, until it becomes independent of temperature and dependent on density alone. At this point, the gas is said to be degenerate. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A state of matter found in white dwarfs and other ultrahigh-density objects, in which the electrons follow Fermi-Dirac statistics. According to the classical laws of physics, the pressure of a gas is proportional to the temperature and the density. However, in 1926 Fermi and Dirac showed that if the density were high enough, departures from classical laws would occur, in that if at a given temperature the density is increased, the pressure increases more and more rapidly until it becomes independent of the temperature and is a function of the density only. When this point is reached, the gas is said to be degenerate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Fermi gas |  |
| is a kind of plasma |  |
| degree | has definition An angle subtended in the sky: From the zenith to the horizon is 90 degrees. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle unit |  |
| degree (angle) | has symbol ° |  |
| has value in SI unit (π/180) rad |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| Deimos | has albedo 0.06 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The outer satellite of Mars. Mariner 9 has shown that both Phobos and Deimos are locked in synchronous rotation with Mars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer A. Hall | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1897 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.003 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination 1°.6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 1.26 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 12 × 13 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Mars |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| deka | has symbol da |  |
| has value 101 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| delay time | has definition Time lapse between the time a signal (e.g., a radar beam) is propagated out to a distant object and the time it is received after the object bounces it back. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| Delphinus | has acronym Del |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Delphini |  |
| has synonym Dolphin |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| delta | has definition Short-lived baryon. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of hyperon | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| Delta Aquarid | has duration 8 days |  |
| has radiant Delta Aquarii |  |
| has rate 30 per hour |  |
| has start time 29 July |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| Delta Capricorni | has B-V magnitude 0.29 |  |
| has declination -16 07 38 |  |
| has right ascension 21 47 02.3 |  |
| has spectral type Amv |  |
| has synonym HR 8322 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.87 |  |
is a part of Capricornus  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Delta Cephei | has definition A pulsating star in the constellation Cepheus. It was the second Cepheid discovered and lent its name to the entire class of stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cepheus |  |
| is an instance of Population I Cepheid |  |
| Delta Crateris | has B-V magnitude 1.12 |  |
| has declination -14 46 43 |  |
| has right ascension 11 19 20.4 |  |
| has spectral type G8III-IV |  |
| has synonym HR 4382 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.56 |  |
is a part of Crater  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Delta Del star | has definition A type of late A-type and early F-type star with very weak Ca II HK lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Delta Scuti | has B-V magnitude 0.35 |  |
| has declination -09 03 09 |  |
| has right ascension 18 42 16.3 |  |
| has spectral type F2IIIp<04>Del |  |
| has synonym HR 7020 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.72 |  |
is a part of Scutum  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| delta-ray | has definition A recoil electron ejected from an atom by an energetic charged particle. Delta-rays appear as branches in the main track of a cloud chamber. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of free electron |  |
| Demeter | has definition Unofficial name for Jupiter X. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Nicholson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1938 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.12 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 29° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 259.2 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| Deneb | has B-V magnitude 0.09 |  |
| has declination +45 16 49 |  |
| has definition An A2 Ia supergiant at the head of the Northern Cross. Most distant first-magnitude star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 430 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 20 41 25.8 |  |
| has spectral type A2Iae |  |
| has synonym alpha Cyg | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 7924 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.25 |  |
is a part of Cygnus  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of white supergiant |  |
| density | has definition An object's mass divided by its volume. Cotton has a low density; lead has a high density. Red giants have a low density; white dwarfs have a high density. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The amount per unit volume |  |
| has definition The mean density of a celestial body is generally reckoned as its mass divided by its volume, expressed either in comparison with the density of water, in kilograms per cubic meter, or in relation to some other known density. The mean density of the Earth is thus 5.5 times that of water, i.e. 5.5 × 103 kg m-3 and is just less than four times that of the Sun. Yet the mean density of rocks at the surface is about half the overall mean value, and that of the Earth's central core is perhaps 2 1/2 times the overall value. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| density wave theory | has author Lindblad (1925) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Spiral structure is modelled as a small-amplitude wave propagating with fixed angular velocity, as the compression wave goes through, it triggers star formation on the leading edge of the spiral arms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has implication the density waves rotate more slowly than the galaxy's stars and gas | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| derived SI unit | has base unit defined in terms of the seven SI base units via a system of quantity equations |  |
| has unit defined in terms of derived SI unit via a system of quantity equations |  |
| is a kind of SI unit |  |
| descending node | has definition The point in the orbit of a solar-system body where the body crosses the ecliptic from north to south. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Sun orbital event |  |
| DESI | has definition The German national laboratory for high-energy physics, located near Hamburg. It is the home of the e+e- storage rings DORIS and PETRA, and the electron-proton machine, HERA. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Hamburg, Germany | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high energy physics institution |  |
| detached binary | has definition Binary star which is not in contact and in which no significant mass exchange is occurring. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of binary star |  |
| detector | is a kind of optical device |  |
| determinism | has definition The doctrine that all events are the predictable effects of prior causes. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| deuterium | has atomic mass 2 |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 338, c = 560 pm for tetragonal |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 360.0, c = 585.8 pm for h.c.p. |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 509.2 pm for cubic |  |
| has crystal type cubic for cubic |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for h.c.p. |  |
| has crystal type tetragonal for tetragonal |  |
| has definition A rare heavy isotope of hydrogen. Believed to be the first compound nucleus formed in the infant universe. It was discovered in interstellar space in 1965. Because deuterium is quickly destroyed in nuclear reactions, one view is that most of the deuterium in the universe is primordial. | ![has source: [LB90][H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has interstellar space D H ratio 1.4 × 10-5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetogyric ratio 4.1064 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.015 % |  |
| has NMR frequency 15.351 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 8.2 × 10-313C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.8574376 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 2.860 × 10-31 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1 |  |
| has number of neutrons 1 |  |
| has number of nucleons 2 |  |
| has oceanic D H ratio 1.6 × 10-4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 9.65 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has solar D H ratio < 10-6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has space group Fm3m for cubic |  |
| has space group I4 for tetragonal |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for h.c.p. |  |
| has symbol 2H |  |
| has symbol D |  |
| has synonym hydrogen 2 |  |
| has synonym hydrogen 2 |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, water containing deuterium instead of ordinary hydrogen is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors |  |
is an instance of hydrogen  |  |
| deuteron | has charge 1 |  |
| has definition The nucleus of a deuterium atom. md = 2.01355 amu. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The nucleus of deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen. It consists of one proton and one neutron bound together. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol d |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of nucleus |  |
| deuteron magnetic moment | applies to particle deuteron |  |
| has symbol μd |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000018 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value 0.433073457 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment |  |
| deuteron mass | applies to particle deuteron |  |
| has symbol md |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000026 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 3.34358309 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| device | has definition an instrumentality invented for a particular purpose |  |
| is a kind of artifact |  |
| devonian period | has duration 60 million years |  |
| has start time 405 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| diatomic molecule | has decompostion temperature < 10000 K |  |
| has definition a molecule containing only two atoms which can be of different elements | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecule |  |
| dielectronic recombination | has inverse process autoionization |  |
| is a kind of recombination |  |
| differential rotation | has definition As an object rotates, different parts of it may move at different rates. The Galaxy rotates differentially. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Of a stellar cluster or galaxy, the "orbiting" of stars nearer the center faster than those at the edge. Of a single body (such as the Sun or a gaseous planet), the axial rotation of equatorial latitudes faster than polar latitudes. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of rotation |  |
| diffraction | has definition A property which distinguishes wave-like motions. When a wave is incident upon a barrier which is broken by a narrow slit (of comparable size to the wavelength), then the slit will act as a new isotopic source of secondary waves. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A wave-like property of light which allows it to curl around obstacles whose size is about that of the wavelength of the light. The disturbed waves then interfere to produce ripple-patterns. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The bending of light in passing a sharp edge or tiny aperture. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation direction modification |  |
| diffraction grating | has definition A system of parallel slits, where the slit width is of the same order as the wavelength of the incident radiation, which is capable of dispersing light into its spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An optical device containing thousands of very fine parallel grooves which produce interference patterns in a way which separates out all the components of the light into a spectrum. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Polished metallic surface (usually a metallic mirror on a block of glass or quartz) on which has been ruled a great number (in thousands) of parallel lines, used to split light to produce a spectrum. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph dispersing element |  |
| diffraction grating spectrograph | is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| dimethyl ether | has symbol (CH3)2O |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Dione | has definition Fifth satellite of Saturn | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Cassini | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1684 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 4.5 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 440 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| direct motion | has definition For orbital motion in the solar system, motion that is counterclockwise in the orbit as seen from the north pole of the ecliptic; for an object observed on the celestial sphere, motion that is from west to east, resulting from the relative motion of the object and the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Motion of a solar-system body from west to east across the sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| disk | has definition The central plane of a spiral galaxy, as distinguished from the halo or the nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The plate-shaped component of a spiral galaxy, in which the spiral arms are found. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| dispersion | has definition Resolution of white light into its component wavelengths, either by refraction or by diffraction. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The separation of a beam of light into the individual wavelengths of which it is composed by means of refraction or diffraction. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation direction modification |  |
| dissociative recombination | has definition Capture of an electron by a positive molecular ion, wherein part of the recombination energy dissociates the molecule into two neutral atoms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of recombination |  |
| distance | has definition The distance to a celestial object measured from the center of the Earth or Sun, in units of parsec or lightyear | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate component |  |
| is an instance of length |  |
| diurnal motion | has definition The apparent daily motion of celestial bodies across the sky from east to west, caused by the Earth's rotation. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The apparent westward motion of celestial bodies, as seen from Earth, due to the Earth's axial rotation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| dKe star | has definition K dwarf with hydrogen emission lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of K star |  |
| is a kind of UV Ceti star |  |
| dMe star | has definition M dwarf with hydrogen emission lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of M star |  |
| is a kind of UV Ceti star |  |
| DMSP satellite | is a kind of military spacecraft |  |
| DNA replication | is a kind of biochemical process |  |
| DO white dwarf | has definition both He and H lines present |  |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| doctrine | is a kind of belief |  |
| Doppler broadening | has cause thermal, turbulent, or mass motions of atoms along the line of sight | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Line broadening caused by the thermal, turbulent, or mass motions of atoms along the line of sight. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect small displacements of radiation absorbed or emitted by atoms toward longer and shorter wavelengths result in broadening of the lines | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| Doppler shift | has definition Change in the apparent wavelength of radiation (e.g., light or sound) emitted by a moving body. A star moving away from the observer will appear to be radiating light at a lower frequency than if at rest; consequently, lines in the star's spectrum will be shifted toward the red (lower frequency) end of the spectrum. The existence of a direct relationship between the redshift of light from galaxies and their distances is the fundamental evidence for the expansion of the universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Displacement of spectral lines in the radiation received from a source due to its relative motion along the line of sight. A motion of approach results in a blueshift; a motion of recession results in a redshift. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Displacement of spectral lines in the radiation received from a source due to its relative motion in the line of sight. Sources approaching (-) the observer are shifted toward the blue; those receding (+), toward the red. The Doppler shift makes it possible to determine the radial velocity and the rotation of stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Effect on the wavelengths of light (or sound) emitted by a source at a distance that is increasing or decreasing in relation to the observer. If the distance is increasing, the wavelengths are "stretched" (the light received shifts towards the red end of the spectrum; sound received goes down in pitch). If the distance is increasing, the wavelengths are "squeezed" (the light received shifts towards the blue end of the spectrum; sound received goes up in pitch). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The alteration in frequency of electromagnetic radiation due to relative motion between the source and observer. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The alteration in frequency of electromagnetic radiation due to relative motion between the source and observer. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The apparent change of frequency or wavelength of radiation from an object due to its motion toward or away from us. If the object is receding the frequency is decreased and the wavelength is increased, i.e. becomes red-shifted. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The blueshift or redshift produced by an object's motion toward or away from us. If a star moves toward us, its light waves get compressed and its spectrum is blueshifted; if a star moves away from us, its light waves get stretched and its spectrum is redshifted. The Doppler shift allows astronomers to measure the radial velocities of stars. The Doppler shift is not responsible for the redshifts that most galaxies exhibit; that is a cosmological redshift. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The change in frequency of a wave (light, sound, etc.) due to the relative motion of source and receiver. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The shift in the received frequency and wavelength of a sound wave or electromagnetic wave that occurs when either the source or the observer are in motion. Approach causes a shift toward shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies, called a blueshift. Recession has the opposite effect, called a redshift. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value the amount of shift is directly proportional to relative velocity |  |
| is a kind of wavelength shift |  |
| Dorado | has acronym Dor |  |
| has genitive Doradus |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Goldfish |  |
| has synonym mahi-mahi (a Hawaiian fish) |  |
| has synonym Swordfish |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| double line spectroscopic binary | has definition a spectroscopic binary in which periodic Doppler shift is detected in both components of the binary star each out of phase by 180 degrees |  |
| is a kind of spectroscopic binary |  |
| can be used as a distance measuring technique |  |
| double radio source | has definition A radio galaxy, the bulk of whose radio emission comes from two sources on opposite sides of the visual galaxy. The radiation is presumably the result of an explosion in the nucleus of the parent galaxy, which caused the ejection at high speed of energetic particles in two opposite directions. About one-third of all known radio galaxies are double sources. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| double star | has definition A "system" of two stars that appear - because of coincidental alignment when viewed from Earth - to be close together; it is, however, an optical effect only, and therefore not the same as a binary star system (although until the twentieth century there were few means of distinguishing double and binary stars). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| doublet | has definition In a spectrum, a pair of associated lines arising from transitions having a common lower energy level. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of multiplet |  |
| down | has charge -1/3 |  |
| has definition A flavor of quark. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of light quark |  |
| DQ Herculis | has definition A slow nova which also happens to be an eclipsing binary. It also has a regular flickering period of 71 seconds, the shortest period of regular variations known, except for pulsars and compact X-ray objects. It is probably composed of an M dwarf and a white dwarf with an accretion disk. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has erruption date 1934 |  |
| has orbital period 4h39m |  |
| has primary star white dwarf |  |
| has secondary star M dwarf |  |
| has synonym Nova Herculis 1934 |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of slow nova |  |
| DQ white dwarf | has definition carbon lines (atomic or molecular) present. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| Draco | has acronym Dra |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Draconis |  |
| has synonym Dragon |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Draco galaxy | has definition A dwarf elliptical galaxy, the intrinsically faintest (Mv = - 8.5) member of the Local Group (next to And I-III). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 80 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 250000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Draco |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| Draconids | is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| dubnium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| DUMAND | is an acronym for Deep Underwater Muon and Neutrino Detector. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of neutrino telescope |  |
| Dumbbell Nebula | has definition A planetary nebula of large apparent diameter and low surface brightness. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 220 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 27 |  |
| has synonym M 27 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 6853 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Vulpecula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| dust | has definition The dust component of a galaxy, includes dark cloud | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| dust tail | has charge little or none | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Curved part of comet tail composed of dust driven by radiation pressure | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym type II comet tail | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of comet tail | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| dwarf | has definition Star that is on the main sequence - that is, a star fusing hydrogen into helium at its core. |  |
| has definition Star with mass equal to or less than that of the sun. More generally, any star on or below the main sequence in the Hertzprung-Russell diagram. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star, like the Sun, that fuses hydrogen into helium at its core. Ninety percent of all stars are main-sequence stars; examples are Sirius, Vega, Altair, and Alpha Centauri A, B, and C. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class V |  |
| has symbol d |  |
| has synonym main sequence star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| dwarf Cepheid | has definition A group of pulsating variable stars with small variations in amplitude. They lie in the lower part of the Cepheid instability strip. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Type I Cepheids ( <Mv> +4 to +2). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 to 3 hours | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type A star to F star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym delta Scuti star |  |
| has synonym ultrashort-period Cepheid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Cepheid |  |
| is a kind of Delta Del star |  |
| dwarf elliptical galaxy | has mass > 107 Msun (among the least massive galaxies) | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elliptical galaxy |  |
| dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | is a kind of satellite galaxy |  |
| dwarf galaxy | has definition A galaxy with low luminosity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A small, faint galaxy, exemplified by those that orbit the Milky Way: Ursa Minor, Draco, Sculptor, Sextans, Carina, Fornax, Leo II, and Leo I. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| dwarf nova | has definition A short-period binary system consisting of a hot white dwarf (or a hot blue sdBe subdwarf) and a much cooler and slightly more massive late-type main-sequence companion which fills its Roche lobe and is ejecting mass onto the white dwarf through its inner Lagrangian point. (The light from dwarf novae comes from four sources: a white dwarf, a cool main-sequence star, a hot spot, and a disk.) The outbursts are usually assumed to be caused by the explosive nuclear burning of hydrogen-rich material accreted onto the surface of a degenerate star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Cataclysmic variable in which the brightness increases suddenly at intervals ranging from several days to years. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nova |  |
| dynamical equinox | has definition The ascending node of the Earth's mean orbit on the Earth's equator; i.e., the intersection of the ecliptic with the celestial equator at which the Sun's declination is changing from south to north. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of ascending node |  |
| see also catalog equinox | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| see also equinox | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| dynamical parallax | has definition The "parallax" (i.e., distance) for a binary star whose orbit is well known, derived by using the mass-luminosity relation and Newton's generalization of Kepler's third law. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of parallax |  |
| dynamics | has definition Study, in physics, of the motion and equilibrium of systems under the influence of force. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The physics that explains how particles and systems move under the influence of forces. The dynamical laws of a theory give a quantitative statement of the response of a particle to an applied force. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| dyne | has definition A unit of force equal to the force necessary to give an acceleration of 1 cm sec-2 to a mass of 1 gram. 1 dyne of force is roughly equivalent to 1 mg of weight. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The force necessary to cause a mass of one gram to accelerate at one centimeter per second per second. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of force unit |  |
| dysprosium | has image 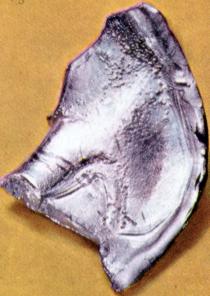 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 300 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| DZ white dwarf | has definition no He nor H lines, but metallic lines present |  |
| is a kind of white dwarf |  |
| E layer | has altitude 150 km |  |
| has definition Former name for the D and E layers (q.v.). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The part of Earth's ionosphere where the temperature gradient reverses and starts to rise. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has radio reflectivity "short-wave" radio waves |  |
| has synonym Kennelly-Heaviside layer | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| E line | has definition Spectral line consisting of a blend of Fe I and Ca I. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Fe I and Ca I |  |
| has wavelength 5270 Å |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| E ring | is a kind of ring |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| e-process | has definition A hypothetical group of nuclear reactions by which the iron group is assumed to be synthesized. At temperatures > 5 × 109 K and densities > 3 × 106 g cm-3 there are great numbers of collisions between high-energy photons and nuclei. These collisions break up the nuclei, the fragments of which promptly combine with other particles. Thus, there is in effect an equilibrium between formation and breakup. Since the iron group has the largest binding energies, the particles over the long run will tend to be trapped in these nuclei. The e-process (the e stands for equilibrium) is presumed to occur in a supernova explosion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| Eagle Nebula | has distance 7000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
has synonym IC 4703  |  |
| is a part of Serpens |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| early star | has definition Hot star of spectral types O, B, A, and early F. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O, B, A, and early F | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Earth | has age 4.6 ± 0.1 × 109 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has albedo 0.39 (water and land about 0.2; snow and clouds about 0.8) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has aphelion distance 152100000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition 78% N2; 20.9% O2; 0.9% Ar, 0.03% C02 (by volume) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere density 1.3 × 10-3 g cm-3 (at sea level) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmospheric pressure 1.013 × 106 dyn cm-2 (at sea level) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has core density 10 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has core temperature 6400 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Third planet from the Sun. First forms of life appeared about 3.2 to 3.5 × 109 years ago (Homo sapiens appeared as a species about 105 years ago). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0167 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has ecliptic inclination i = 0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has effective temperature 287 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has equatorial radius 6378.17 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 11.19 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field at surface 0.5 gauss | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field in core 100 gauss | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 5.977 × 1027 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 5.517 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 149598500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 23°26'34" (in 1973) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 365.2564 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity vorb = 29.78 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has perihelion distance 147100000 km in early January | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has polar radius 6356.9 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has precession 50'.256 per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has relativistic advance of perihelion 4'.6 per century | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 23 hours 56 minutes 4.1 seconds | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 980 cm s-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of naked eye planet |  |
| is an instance of terrestrial planet |  |
| Earth based telescope | has altitude height above sea level in meters | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A telescope located on the surface of the Earth. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has latitude in degrees, minutes, seconds (N or S) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has longitude in degrees, minutes, seconds (E or W) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has mounting designed to operate within a 1 g gravitational field | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has mounting manufacturer the person, company or institution that constructed the mounting | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature ambient |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| Earth orbital event | has participants satellite, Earth |  |
| is a kind of orbital event |  |
| Earth's lithosphere | is a part of Earth |  |
| Earth-crossing asteroid | is a kind of asteroid |  |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| east point | has azimuth 90 |  |
| has definition The point on the celestial horizon 90° clockwise from the north point. At the equinoxes the Sun rises in the east point. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has elevation 0 |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate |  |
| EBS | has definition Electron Bombarded Silicon. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| eccentricity | has definition A measure of how round or elliptical an orbit is. A perfect circle has an eccentricity of 0 percent, and an extremely elliptical orbit has an eccentricity of just under 100 percent. The Sun has an orbital eccentricity of 6 percent, which means that at perigalacticon the Sun is 6 percent closer to the Galactic center than its mean distance and at apogalacticon the Sun is 6 percent farther from the Galactic center than its mean distance. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A parameter that specifies the shape of a conic section; one of the standard elements used to describe an elliptic orbit. (See elements, orbital.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An orbital element representing the eccentricity of the elliptical orbit |  |
| has definition In astronomy, the extent to which an elliptical orbit departs from a circular one. It is usually expressed as a decimal fraction, regarding a circle as having an eccentricity of 0. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The amount by which the elliptical orbit deviates from circularity: e = c/a, where c is the distance from the center to a focus and a is the semimajor axis. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol e | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of orbital element | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| eccentrics | has definition In Ptolemaic cosmology, displacement of the center of a rotating celestial sphere from the center of the universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| echelle | has definition A type of diffraction grating with groove angles of 90°. With the grating at an angle of 45° the grooves resemble a staircase. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating |  |
| eclipse | has definition Obscuration of one astronomical object (such as the sun) by another such object (such as the moon). | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Occultation of one celestial body by another which passes between it and the observer. The solar eclipse is caused by the passing of the Moon between the Sun and the Earth in this way; such an eclipse may be complete (total) or incomplete (partial). Eclipsing binary stars also accord with this pattern. Alternatively - and exceptionally - a lunar eclipse is caused by the passage of the Earth between the Sun and the Moon, so that the Earth's shadow falls across the Moon, again either totally or partially, depending upon the position of the observer. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The obscuration of a celestial body caused by its passage through the shadow cast by another body. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The total or partial obscuration of the light from a celestial body caused by its passage into the shadow of another body (cf. occultation). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of occultation |  |
| eclipse year | has definition The interval of time between two successive passages of the Sun through the same node of the Moon's orbit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 346.62 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| eclipsing binary | has definition A binary star of which, from the viewpoint of Earth, one of the two bodies regularly passes in front of the other. The resulting variation is perceived luminosity of some eclipsing binaries has led to their classification as variable stars. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A double star in which at least one of the two stars passes in front of and/or behind the other so that the system's total light periodically fades. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Eclipsing variables whose orbital plane lies so nearly in the line of sight that eclipses, as seen from the Earth, can occur and can be detected from their light curves. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has eclipse duration |  |
| is a kind of close binary |  |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| ecliptic | has definition Apparent linear path through the 12 constellations of the zodiac that the Sun seems to take during one Earth year, also representing therefore the "edge" of the plane of Earth's orbit. Because the equator of the Earth is at an angle of more than 22° to the plane of its orbit, the ecliptic is at the identical angle to the celestial equator, intersecting it at two points: the vernal and autumnal equinoxes. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Plane of the Earth's orbit. (Strictly speaking, the ecliptic is a mathematical fiction corresponding not to the actual plane of the Earth's orbit, but to one with all minor irregularities smoothed out.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mean plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| ecliptic coordinate | has celestial latitude |  |
| has celestial longitude |  |
| has component ecliptic coordinate component |  |
| has definition A system of coordinates based on the plane defined by Earth's orbit around the Sun, which is inclined to the celestial equator. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| ecliptic coordinate component | is a component of ecliptic coordinate |  |
| is a kind of coordinate component |  |
| Eddington approximation | has definition An approximation used in the study of radiative transfer. It is the assumption that the ratio of the second moment of the radiation field to the mean intensity is everywhere equal to 1/3, the value of this ratio for an isotropic field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of stellar theory |  |
| Eddington limit | has definition In essence, radiation pressure must not exceed gravity. It is the limit beyond which the radiation force on matter in the emitting region is greater than the gravitational forces that hold the star together. LE = 4πcGM/Ks, where Ks = Thomson and/or Compton scattering opacity. Eddington limit for a 1 Msun star, 1038 ergs s-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| Eddington's standard model | has definition A stellar model in which energy is transported by radiation throughout the whole star and the ratio of the radiation pressure to the gas pressure is assumed to be constant. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of stellar theory |  |
| Eddington-Lemaitre universe | has definition A cosmological model in which the cosmological constant plays a crucial role by allowing an initial phase that is identical to the Einstein static universe. After an arbitrarily long time, the universe begins to expand. The difficulty with this model is that the initiation of galaxy formation may actually cause a collapse rather than initiate an expansion of the universe. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| effective temperature | has definition The temperature that a blackbody would have which emitted the same amount of energy per unit area as the star does: it is a temperature characteristic of the surface region. Teff of Sun, 5800 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Teff |  |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| Egg Nebula | has distance 3000 light years |  |
| has expansion rate 20 km/s |  |
has image     |  |
| has synonym CRL 2688 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| EHF band | has frequency 30 to 300 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 1 mm to 1 cm |  |
| is a kind of microwave |  |
| Einstein | is an instance of grazing-incidence telescope |  |
| einsteinium | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| elastic collision | has definition A collision between two particles which conserves the total kinetic energy and momentum of the system. For atomic collisions it is one involving energy less than the excitation potential of the atom. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle reactions in which the same particles emerge from the reaction as entered it (e.g. π- p → π- p). In inelastic scattering, where different and/or new particles emerge, energy is used to create new particles. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collision |  |
| electric constant | has symbol ε0 |  |
| has uncertainty 0 |  |
has value 8.854187817 × 10-12 F m-1  |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| electric potential | has unit electric potential unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| electric potential unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| electrodynamics | has definition Study of the behavior of electromagnetic force in motion. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dynamics |  |
| electromagnetic constant | is a kind of fundamental physical constant |  |
| electromagnetic gauge symmetry | has definition Gauge symmetry underlying quantum electrodynamics. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gauge symmetry |  |
| electromagnetic law | has domain electromagnetism |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| electromagnetic quantity | is a kind of quantity |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| electromagnetic telescope | has definition telescope designed to collect and record electromagnetic radiation |  |
| is a kind of telescope |  |
| electromagnetic unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| electromagnetism | has carrier boson photon |  |
| has definition Force field of the electromagnetic force, consisting of electric and magnetic lines of force at each point in space. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fundamental force of nature that acts on all electrically charged particles. Classical electromagnetics is based on Maxwell's and Faraday's equations, quantum electromagnetics on the theory of quantum electrodynamics (QED). | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the four fundamental forces of nature, governing the electric and magnetic interaction between particles. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the four fundamental forces of nature. Electricity and magnetism arise from the electromagnetic force. The other three fundamental forces are the gravitational force, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The force between charged particles, which accounts for electricity and magnetism. One of the four fundamental forces of nature, it is carried by photons and is responsible for all observed macroscopic forces, except for gravity. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The phenomena associated with electrical and magnetic forces. Electrical and magnetic forces are intimately related, since a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and vice versa. Electromagnetic waves are an example of electromagnetism. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has range infinite |  |
| has strength 1 (relative to electromagnetism) |  |
| is a kind of fundamental force |  |
| electron | has antiparticle positron |  |
| has charge -1 |  |
| has definition A lepton with an electric charge of -1. An electron is also a fermion because it has a spin of one half. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A negatively charged spin-1/2 particle, which interacts via the electromagnetic, weak and gravitational forces. It has a mass of 0.511 MeV / c2, some 1800 times lighter than the proton. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A small, negatively charged particle that appears in every neutral atom, surrounding the positively charged nucleus like bees around honey. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A stable, negatively charged elementary particle - the lightest massive particle known. The classical electron radius is 2.82 × 10-13 cm; me = 9.1 × 10-28 g = 5.48597 × 10-4 amu. The electron family (see lepton) includes the electron e-, the positron e+, the electron neutrino νe, and the electron antineutrino νebar. Rest-mass energy of electron 8.186 × 10-7 ergs. Electron charge = 1.60219 × 10-19 coulombs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Light elementary particle with a negative electrical charge. Electrons are found in shells surrounding the nuclei of atoms; their interactions with the electrons of neighboring atoms create the chemical bonds that link atoms together as molecules. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Negatively charged fundamental particle (also called a beta particle) found in the atoms of all elements, where it "orbits" (at different energy levels and with different directions of spin) round the central nucleus. The combined charge of the orbiting electrons is balanced (in a neutral atom) by the charge of an equal number of positively charged protons in the atomic nucleus. An electron is also the fundamental unit of electricity. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charged particle |  |
| is a kind of lepton |  |
| is a part of element |  |
| electron bombarded charge-coupled device | has acronym EBCCD |  |
| has definition An imaging device containing a thin target material which emits electrons by the photoelectric effect when illuminated and then magnetically focuses these electrons to impact onto a silicon CCD where they generate a large charge. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| electron Compton wavelength | applies to particle electron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol λC |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000018 × 10-12 m |  |
has value 2.426310215 × 10-12 m  |  |
| is an instance of particle Compton wavelength |  |
| electron g factor | applies to particle electron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol ge |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000000000082 |  |
has value -2.0023193043737  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| electron gyromagnetic ratio | applies to particle electron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol γe |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000071 × 1011 s-1 T-1 |  |
has value 1.760859794 × 1011 s-1 T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| electron magnetic moment | applies to particle electron |  |
| has symbol μe |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000037 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value -928.476362 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment |  |
| electron magnetic moment anomaly | applies to particle electron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol ae |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000000041 × 10-3 |  |
has value 1.1596521869 × 10-3  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment anomaly |  |
| electron mass | applies to particle electron |  |
| has symbol me |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000072 × 10-31 kg |  |
has value 9.10938188 × 10-31 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| electron temperature | has definition The temperature that appears in the Maxwell distribution of velocities for electrons. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| electron volt | has definition Unit employed to indicate the energy of a charged particle in terms of the energy received by the charge on an electron due to a potential difference of one volt. An approximate value (1 in 104) for the energy of electromagnetic radiation expressed in electron volts is given by 1234 / λ, where λ is the wavelength in nanometres. In recent years it has become customary to write MeV and GeV for mega (106) and giga (109) electron volts. In the USA 109 electron volts are often written as BeV, the letter B being used in this case as an abbreviation for the American billion (109), but in 1948 the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics disapproved of the use of BeV and expressed a preference for GeV or 109 eV. The electron volt was called the equivalent volt when it was originally introduced in 1912. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of energy used in atomic and nuclear physics; the kinetic energy acquired by one electron in passing through a potential difference of 1 volt in vacuum. Sometimes used as a unit of mass (see rest-mass energy) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 160.219 × 10-21 joule | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol eV |  |
| has symbol eV | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of energy unit |  |
| is an instance of energy unit |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| is equivalent to 1.6 × 10-12erg | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is equivalent to 1.6 × 10-19 joules | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| electrostatic unit | has definition Unit of charge defined as the charge which exerts a force of 1 dyne on a charge of equal magnitude at a distance of 1 cm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol esu |  |
| is an instance of charge unit |  |
| electroweak | has carrier boson vector boson |  |
| has definition A unification of electromagnetism and the weak nuclear force. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Responsible for certain kinds of radioactivity; for example, the disintegration of a neutron into a proton, electron, and antineutrino. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The combination of the electromagnetic force and the weak nuclear force which takes place at high energy. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The theory that unifies the electromagnetic force and the weak nuclear force into a single force. This theory was developed in the 1960s by Sheldon Glashow, Steven Weinberg, and Abdus Salam and has been subsequently confirmed in the laboratory. One of the mathematical properties of this theory is called the electroweak symmetry. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The unified description of the weak interactions and electromagnetism, developed between 1967 and 1970 by Sheldon Glashow, Steven Weinberg, and Abdus Salam. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory demonstrating links between the electromagnetic and the weak nuclear forces. Indicates that in the high energies that characterized the very early universe, electromagnetism and the weak force functioned as a single, electroweak force. Also known as the Weinberg-Salam theory. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has range |  |
| has strength (relative to electromagnetism) |  |
| has synonym weak force |  |
| is a kind of fundamental force |  |
| element | has definition Different elements are distinguished by the number of protons in their nuclei. All hydrogen atoms have one proton; all helium atoms have two protons; all oxygen atoms have eight protons. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The building block of matter. The nucleus of an atom consists of one or more protons and may contain neutrons as well; any electrons surround the nucleus. The number of protons in the atom - the atomic number - determines the element. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The fundamental unit of a chemical element. An atom consists of a nucleus, which may contain protons and neutrons, and electrons, which occupy shells that surround the nucleus and are centered on it. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The smallest component of matter that retains its chemical properties. An atom consists of a nucleus and at least one electron. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym atom |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| is a part of Universe |  |
| element 110 | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| element 111 | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| element 112 | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| elementary charge | has symbol e |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000063 × 10-19 C |  |
has value 1.602176462 × 10-19 C  |  |
| is an instance of charge |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| elementary particle | has definition A particle considered to be fundamental, i.e. not composite, a particle which cannot be separated into components | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| elementary particle symmetry | has definition Abstract mathematical relationships that relate elementary particles together and allow them to be grouped into families. A particular symmetry transformation has the effect of, in a theoretical way, transforming one elementary particle into another. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| is a kind of unitary transformation |  |
| elevation | has definition Angular distance above the horizon. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The angle in degrees above the horizon toward the zenith or overhead point. Sometimes loosely called the "altitude" of a star, but not to be confused with height above sea level. Elevation angle is 90° minus the zenith distance (or zenith angle). | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The angular distance of a celestial body above or below the horizon, measured along the great circle passing through the body and the zenith. Elevation is 90 deg. minus zenith distance. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym altitude |  |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate component |  |
| eleven-dimensional supergravity | has definition Promising higher-dimensional supergravity theory developed in the 1970s, subsequently ignored, and more recently shown to be an important part of string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supergravity |  |
| ELF band | has frequency 300 Hz to 3 kHz |  |
| has wavelength 100 km to 1000 km |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| ellipse | has definition A plane curve in which the sum of the distances of each point along its periphery from two points - its "foci" - are equal. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conic section |  |
| elliptical galaxy | has classification criteria E0 (spherical) to E7 (greatest eccentricity) |  |
| has definition A galaxy with an ellipsoidal shape, without spiral arms. Ellipticals have little interstellar matter and no blue giants - the only giants are red, and they give ellipticals a slightly redder color than spirals. Ellipticals apparently produce only Type I supernovae. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| elliptical orbit | has amplitude equal to the semimajor axis |  |
| has parameters orbital element |  |
| has period proportional to the orbital period |  |
| is a kind of ellipse |  |
| is a kind of harmonic motion |  |
| is a kind of orbit |  |
| elongation | has elongation |  |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| emersion | has definition The reappearance of a celestial body after eclipse or occultation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of occultation phase |  |
| is preceeded by transit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| emission | has definition The process of transition of an electron from an outer orbit to an inner orbit around the nucleus results in a characteristic amount of energy being radiated (as line emission) that corresponds to the lost energy of the electron. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has inverse process absorption |  |
| is a kind of radiation intensity modification |  |
| emission line | has antonym absorption line |  |
| has definition Bright line superposed on a continuous spectrum. Can be produced in the laboratory by a glowing gas under low pressure. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Bright lines produced in a spectrum by a luminous source, such as a star or a bright nebula. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| emission line galaxy | has emission lines |  |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| emission line star | has emission line |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| empiricism | has definition An emphasis on sense data as a source of knowledge, in opposition to the rationalist belief that reasoning is superior to experience. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| Enceladus | has definition Third satellite of Saturn | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Herschel | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1789 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 1.37 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Encke's comet | has definition The comet with the shortest known period (3.30 years) (a = 2.21 AU, e = 0.847, i = 12°.4). It has been observed at every apparition since its discovery in 1819. Its period is gradually decreasing. Named after J. F. Encke, who computed its orbit. (It was discovered by Pons.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of comet |  |
| Encke's division | has definition A region of decreased brightness in the outermost ring of Saturn. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gap within Saturn's A ring. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ring gap |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| endothermic fusion process | has definition a fusion process which requires energy |  |
| is a kind of energy sink |  |
| is a kind of fusion |  |
| energy | has unit energy unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| energy level | has definition Allowed energy state for electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any of the several discrete states of energy in which an atom or ion can exist. For example, an orbital electron can exist only in those energy levels that correspond to an integral number of deBroglie wavelengths in a Bohr atom. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| energy sink | is a kind of physical phenomena |  |
| energy source | is a kind of physical phenomena |  |
| energy unit | has definition (1) The capacity to do work. (2) Manifestation of a particular variety of force. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of energy |  |
| English equatorial telescope | has mounting English equatorial | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| enthalphy | has definition The heat content of a body. H = U + pV, where U is the internal energy, p is the pressure, and V is the volume. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol H |  |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| eocene epoch | has duration 22 million years |  |
| has start time 58 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of tertiary period |  |
| ephemeris second | has definition The length of a tropical second (1/31556925.97474 of the tropical year) on 1900 January 0.5 ephemeris time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 1/31556925.97474 tropical year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of second unit |  |
| epicycle | has definition A means of accounting for the apparent motions of the planets in terms of circular motions in a geocentric cosmology. Each planet moves in a circle, the center of which moves in a circle of larger radius, and so on, the largest circles being centered on the earth. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Circular orbit of a body round a point that is itself in a circular orbit round a parent body. Such a system was formulated to explain some planetary orbits in the Solar System before they were known to be elliptical. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In Ptolemaic cosmology a circular orbit around a point that itself orbits another point. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| epoch | has definition A date and time that specifies the reference system to which celestial coordinates are referred. Prior to 1984 coordinates of star catalogs were commonly referred to the mean equator and equinox of the beginning of a Besselian year. Beginning with 1984 the Julian year has been used, as denoted by the prefix J, e.g., J2000.0. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A point of time selected as a fixed reference. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An arbitrary fixed instant of time or date used as a chronological reference datum for calendars (see calendar), celestial reference systems, star catalogs, or orbital motions (see orbit). | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An orbital element representing the time of perihelion passage. |  |
| has symbol T | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of orbital element | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| epsilon Aurigae | has definition An eclipsing binary with an invisible supergiant companion. The primary is an extremely luminous A8 Ia supergiant of 30 Msun in a post-main-sequence stage of evolution; the secondary may be a collapsed star or black hole. It has at least six components. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 1 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 27 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has primary A8 Ia |  |
| is a part of Auriga |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of white supergiant |  |
| Epsilon Eri | has apparent magnitude 4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In 1973 van de Kamp announced that this star has a planet-like object in orbit around it at a distance of about 8 AU and with a period of about 25 years. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3.30 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type K2 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Eridanus |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| Epsilon Eridani | has definition A young orange dwarf star that is visible to the naked eye. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 10.7 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Eridanus |  |
| is an instance of dwarf | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| Epsilon Indi | has definition An old orange dwarf star in the southern constellation Indus. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 11.2 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of dwarf | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| Epsilon Pegasi | has B-V magnitude 1.53 |  |
| has declination +9 52 30 |  |
| has right ascension 21 44 11.1 |  |
| has spectral type K2Ib |  |
| has synonym HR 8308 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.39 |  |
is a part of Pegasus  |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of supergiant |  |
| Epsilon Sagittarii | has B-V magnitude -0.03 |  |
| has declination -34 23 5 |  |
| has right ascension 18 24 10.3 |  |
| has spectral type B9.5III |  |
| has synonym HR 6879 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.85 |  |
is a part of Sagittarius  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Epsilon Ursae Majoris | has B-V magnitude -0.02 |  |
| has declination +55 57 35 |  |
| has right ascension 12 54 1.7 |  |
| has spectral type A0pCr |  |
| has synonym HR 4905 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.77 |  |
is a part of Ursa Major  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| equator | has definition The great circle on the surface of a body formed by the intersection of the surface with the plane passing through the center of the body perpendicular to the axis of rotation. (See celestial equator.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| equatorial coordinate | has component equatorial coordinate component |  |
| has declination |  |
| has right ascension |  |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| equatorial coordinate component | is a component of equatorial coordinate |  |
| is a kind of coordinate component |  |
| equatorial sky area | has definition A fixed region on the sky defined using equatorial coordinates | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| is defined using equatorial coordinates | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| equatorial telescope | has definition The classic type of telescope mount with one axis parallel to the Earth's polar axis (i.e. pointing at the celestial pole) and the other at right angles. Once the object is located, only the polar axis need be driven by a motor to counteract the Earth's rotation. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has mounting equatorial | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Earth based telescope |  |
| equatorial velocity | has definition The velocity at the surface of a rotating body, on its equator |  |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| equinox | has definition Either of the two points on the celestial sphere at which the ecliptic intersects the celestial equator; also the time at which the Sun passes through either of these intersection points; i.e., when the apparent longitude (see apparent place; celestial longitude) of the Sun is 0° or 180°. (See catalog equinox; dynamical equinox for precise usage.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Either of the two points on the celestial sphere where the celestial equator intersects the ecliptic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of two points in the sky that represent where the Sun appears to cross the plane of the Earth's equator. From the Earth's viewpoint therefore, the Sun reaches one point at a quarter, the other at three quarters of the way through the sidereal year: the vernal (spring) equinox is thus on or around 21 March, the autumnal on or around 22 September. The actual points in the sky change slightly every year through a process called precession. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 year |  |
| is a kind of periodic celestial event |  |
| equivalence principle | has definition Core principle of general relativity declaring the indistinguishability of accelerated motion and immersion in a gravitational field (over small enough regions of observation). Generalizes the principle of relativity by showing that all observers, regardless of their state of motion, can claim to be at rest, so long as they acknowledge the presence of a suitable gravitational field. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In a freely falling and nonrotating laboratory the laws of physics, including their numerical content, are the same everywhere including gravity-free space. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition States that inertial mass is indistinguishable from gravitational mass. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that it is impossible to distinguish between gravitational and inertial forces; gravitational mass is precisely equal to inertial mass. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The statement that a gravitational force is completely equivalent in all of its physical effects to an overall acceleration in the opposite direction. For example, a person in an elevator in space accelerating upward at 32 feet per second per second would feel the floor pushing upward against her feet in exactly the same way as if the elevator were at rest on earth, where gravity pulls downward with an acceleration of 32 feet per second per second. The "weak equivalence principle," which is not as strong as the equivalence principle, states that all objects, independent of their mass or composition, fall with the same acceleration in the presence of gravity. The Eötvös experiment, and later refinements of this experiment, have proven the weak equivalence principle. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gravity law |  |
| Equuleus | has acronym Equ |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Equulei |  |
| has synonym Little Horse |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| era | has definition A system of chronological notation reckoned from a given date. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration |  |
| has start time |  |
| is a kind of event |  |
| erbium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 400 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| erg | has definition Unit of energy; the work done by a force of 1 dyne acting over a distance of 1 cm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 g cm2 s-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-7joules | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has name origin Greek verb 'to work' | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1873 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposer British Association | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym dyne cm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of energy unit |  |
| ergodic motion | has definition Motion by one or more particles which fills phase space with uniform density after a sufficiently long time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| Eridanus | has acronym Eri |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Eridani |  |
has synonym River Eridanus  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Eros | has asteroid number 433 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has closest approach to Earth < 0.15 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A small Asteroid. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 35 × 16 × 17 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer G. Witt | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1898 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.223 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 10°.8 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 642 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has perihelion distance 1.084 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 5h16m12s.913 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 1.48 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has shape elongated | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| erruptive prominence | has definition A violent prominence which may reach heights of 2 million km | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has height < 2 million km | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of prominence | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| ESA satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| escape velocity | has definition Speed a satellite must attain in order to free itself from returning to the parent body under the effects of gravity. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The speed at which an object can leave another object behind, without being recalled by its gravitational force. The escape velocity of Earth - which must, for instance, be attained by a spacecraft if it is to reach another planet - is 25,000 miles per hour. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The velocity that a body requires to achieve a parabolic orbit around its primary (Ve = sqrt(2GM/R)). Escape velocity at Earth's surface is 11.2 km s-1; of Moon, 2.4 km s-1; of Sun, 617.7 km s-1 (cf. orbital velocity). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| ESO 1-meter Schmidt Telescope | has altitude 2318 m |  |
| has aperture 1.00 m |  |
| has creation date 1972 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.06 |  |
| has latitude 29° 15' S |  |
| has location La Silla, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 44' W |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.6 m |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss (Ober.) |  |
| has mirror type Schott Duran 50 |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Heidenreich & Harbeck |  |
| has owner European Southern Observatory |  |
| has synonym ESO Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| ESO 3.6-meter Telescope | has altitude 2387 m |  |
| has aperture 3.57 m |  |
| has creation date 1977 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.0, 8.1, 32 |  |
| has latitude 29° 16' S |  |
| has location La Silla, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 44' W |  |
| has mirror maker REOSC |  |
| has mirror type Fused-silica |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Creusot-Loire |  |
| has owner European Southern Observatory |  |
| has synonym ESO 3.6 m |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| Eta Aquarid | has duration 6 days |  |
| has parent object Comet Halley |  |
| has radiant Eta Aquarii |  |
| has rate 60 per hour |  |
| has start time 4 May |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| Eta Aquilae | has definition A pulsating star in the constellation Aquila. It was the first Cepheid discovered, in 1784. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1784 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Aquila |  |
| is an instance of Population I Cepheid | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| eta Carinae | is an instance of bright blue variable |  |
| Eta Piscium | has B-V magnitude 0.97 |  |
| has declination +15 20 45 |  |
| has right ascension 1 31 28.9 |  |
| has spectral type G7IIIa |  |
| has synonym HR 437 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.62 |  |
is a part of Pisces  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| etalon | has definition Essentially an optical filter that operates by multiple-beam interference of light reflected and transmitted by a pair of parallel flat reflecting plates. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Fabry-Perot interferometer |  |
| ethyl alcohol | has symbol C2H5OH | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| ethynyl | is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| EUMETSAT satellite | has definition meteorological satellite launched and maintained by Europe's Meteorological Satellite Organization  |  |
| is a kind of meteorological satellite |  |
| Europa | has definition One of the Galilean satellites of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 3600 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.00 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 0°.01 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 3.07 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 3.55 days -has source: [H76] |  |
| has synonym Jupiter II | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter |  |
| is an instance of Galilean satellite |  |
| European Southern Observatory | has acronym ESO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| European Space Agency | has acronym ESA | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| European Synchrotron Research Facility | has acronym ESRF | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high energy physics institution |  |
| europium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 500 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| evaporation | has final phase gas |  |
| has initial phase liquid |  |
| has inverse process condensation |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| even-odd nucleus | has definition Nucleus that contain even numbers of protons but odd numbers of neutrons. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fermion |  |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| event | has definition A point in four-dimensional spacetime referenced by three spatial coordinates and a complementary temporal ordinate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration |  |
| has synonym world point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has time of occurrence |  |
| is a kind of physical phenomena |  |
| Evershed effect | has definition The radial motion outward (from the central umbra) of the gases in the penumbral regions of sunspots. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solar motion |  |
| exa | has symbol E |  |
| has value 1018 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| excitation potential | has definition Amount of energy required to bring an electron from its ground state to a given excited state (measured in electron volts). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| exclusion principle | applies to fermion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Two identical fermions cannot occupy the same quantum state (i.e. cannot have the same charge, spin, momentum, quantum numbers etc. within the same region of space). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has example No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of values for the four quantum numbers n, l, mb, ms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has implication solid objects cannot exist in the same physical space. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Pauli exclusion principle |  |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| exothermic fusion process | has definition A fusion reaction which linerates energy. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy source |  |
| is a kind of fusion |  |
| liberates energy |  |
| expanding arm | has definition A spiral arm of neutral hydrogen receding from the galactic nucleus at about 135 km s-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center between 2.5 and 4 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| expanding emission nebula | has composition enhanced with heavy elements relative to the interstellar medium |  |
| has expansion velocity |  |
| has explosion date |  |
| has progenitor star |  |
| is a kind of gaseous nebula |  |
| expansion | is a kind of mass motion |  |
| experiment | is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| Explorer 22 | is an instance of inflatable spacecraft |  |
| explosive galaxy formation | has definition A theory of galaxy formation wherein the explosion of a large number of stars creates a giant shock wave that travels outward and compresses the surrounding gas. Galaxies form in the regions of high-density gas. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| explosive nucleosynthesis | has definition The nucleosynthesis processes that are believed to occur in supernovae. Explosive carbon burning occurs at a temperature of about 2 × 109 K and produces the nuclei from neon to silicon. Explosive oxygen burning occurs near 4 × 109 K and produces nuclei between silicon and calcium in atomic weight. At higher temperatures, still heavier nuclei, up to and beyond iron, are produced. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The nucleosynthetic processes which are thought to occur in supernovae. These explosive processes are thought to produce the nuclei from neon up to and including the e-process nuclei and possibly the r-process nuclei. Explosive carbon burning occurs for a temperature of about 2 × 109 K and a density of 104-107 g cm-3 and produces nuclei from neon to silicon. Explosive oxygen burning occurs for a temperature of about 4 × 109 K and produces nuclei from silicon to calcium, and the e-process occurs at a temperature greater than 5 × 109 K and produces the iron peak nuclei. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of stellar nucleosynthesis |  |
| exponential expansion | has definition An expansion described by a fixed doubling time. The size doubles after one doubling time, quadruples after two doubling times, octuples after three doubling times, etc. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Extremely rapid expansion. "Exponential" is a mathematical term that precisely defines the rate of expansion. For example, a balloon that doubles its size every second is expanding exponentially. By contrast, a balloon whose radius is one inch after one second, two inches after two seconds, three inches after three seconds, and so on, is expanding linearly with time, rather than exponentially. According to the inflationary universe model, the early universe went through a brief period of exponential expansion, during which its size increased enormously. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of expansion |  |
| extinction level event | has average interval time 100 million years |  |
| has definition impact event which can cause the extinction of many species on a planet |  |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| extragalactic astronomy | has definition The field that deals with objects beyond the Milky Way, especially galaxies and quasars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomy |  |
| extragalactic globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| extremal black hole | has definition Black hole endowed with the maximal amount of force charge possible for a given total mass. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| extreme ultraviolet | has acronym EUV | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ultraviolet |  |
| extremely red galaxy | has acronym ERG |  |
| is a kind of infrared galaxy |  |
| F corona | has definition The outer part of the solar corona which emits a continuous spectrum in which absorption lines can be seen. The F corona is caused by radiation from the photosphere scattered by interplanetary dust, and it decreases slowly with distance from the Sun. (the F stands for Fraunhofer) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym F component | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| F layer | has definition One of two layers in the Earth's ionosphere immediately above the E layer. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Appleton layer | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| F region | has definition Region of the ionosphere above the F layers. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| F star | has color yellow-white |  |
| has definition Star of spectral type F in which lines of hydrogen and Ca II are of about equal strength. Metal lines also become noticeable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 6000 to 7500 K |  |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| f-electron | has definition An orbital electron whose l quantum number is 3. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital quantum number 3 |  |
| is a kind of bound electron |  |
| f-spot | is a kind of sunspot |  |
| F1 layer | has altitude 200 km |  |
| is a part of F layer |  |
| F2 layer | has altitude 300 km |  |
| is a part of F layer |  |
| Fabry-Perot interferometer | has acronym FP | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A device that measures distances and changes of distance very accurately, using the pattern of overlap of waves of light. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A type of interferometer wherein the beam of light is passed through a series of pairs of partly reflecting surfaces set at various angles to it and spaced at certain prechosen numbers of the wavelength to be examined. It differs from the Michelson interferometer in that it has only one arm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph dispersing element |  |
| faculae | has definition Bright areas on the face of the Sun, commonly in the vicinity of sunspots. Named by Johannes Hevelius, they are thought to be caused by luminous hydrogen clouds close to the photosphere. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Bright regions of the photosphere seen in white light, visible only near the limb of the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime 15 days |  |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| Fahrenheit | has absolute zero -459.67 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A temperature scale based on three fixed temperature points - the temperature of an ice and salt mixture, the freezing point of water and normal human temperature - which were taken to be 0, 32 and 96 respectively. It is mere coincidence that the temperature interval between the freezing (32 °F) and boiling (212 °F) points of water is 180° when expressed in the Fahrenheit scale. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1710 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water 32.018 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is named after G. D. Fahrenheit (1686-1736) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| faint blue galaxy | has definition A distant, irregularly shaped galaxy in which a large amount of star formation is taking place. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of irregular galaxy | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| far infrared | has acronym FIR |  |
| has source atomic transitions, rotational transitions in molecules | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of infrared |  |
| farad | has base unit m-2·kg-1·s4·A2 |  |
| has symbol F |  |
| has unit C·V-1 |  |
| is an instance of capacitance unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| Faraday constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol F |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0039 C mol-1 |  |
has value 96485.3415 C mol-1  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| Fechner's law | has definition The intensity of a sensation increases as the logarithm of the stimulus. (See Pogson's ratio.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of law |  |
| femto | has symbol f |  |
| has value 10-15 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| fermi | has approval date 1956 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A unit of distance used for describing nuclear distances just as the ångström is used for atomic distances. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A unit of length. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-13 cm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-15 m | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| is named after Enrico Fermi | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| Fermi coupling constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol Gf/(hc)3 |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00001 × 10-5 GeV-2 |  |
has value 1.16639 × 10-5 GeV-2  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| Fermi level | has definition The maximum energy of any particle in a group of low-temperature subatomic particles called fermions. Fermions, such as electrons, cannot occupy the same space at the same energy. Thus, if many fermions are placed close together, their energies must all be different. The energy of that particle with the largest energy is the Fermi energy of the system. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory | has acronym Fermilab | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Home of the Tevatron, the world's most powerful accelerator, a p p bar collider with a maximum collision energy of 1.8 Te V (= 1800 Ge V = 1.8 × 1012 eV). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Batavia, Illinois, USA | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high energy physics institution |  |
| Fermi-Dirac nuclei | has definition Nuclei of odd A-number (i.e., nuclei that do not have integral spin) (cf. Bose-Einstein nuclei). Fermi-Dirac nuclei therefore obey the exclusion principle (q.v.). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| Fermi-Dirac-Sommerfeld law | has acronym FDS | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A law which gives the algebraic number of a quantized system of particles which have velocities within a small range. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| fermion | has definition A particle, or pattern of string vibration, with half a whole odd number amount of spin; typically a matter particle. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An elementary particle whose spin is a half-integral multiple of h/2π. Fermions include the baryons, the leptons and their antiparticles, and obey the Pauli exclusion principle (cf. boson). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any particle with half-integer spin: 1/2 h bar, 3/2 h bar, 5/2 h bar, etc. All fermions obey Pauli's exclusion principle. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particle with fractional spin. The proton, electron, neutron, and other elementary particles are all fermions. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle with half-integral spin. Fermions obey the exclusion principle, which says that no two fermions can exist in an atom in the same quantum state; in practice this restricts the number of electrons, which are fermions, permitted in each electron shell. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has quantum behavior Fermi-Dirac statistics |  |
| has spin half-integral |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| obeys exclusion principle |  |
| fermium | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| fibrille | has definition Striation or streak which is observed to form whirls in the solar chromosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of chromosphere |  |
| field galaxy | has definition An isolated galaxy which does not belong to any cluster of galaxies. The ratio of galaxies in clusters to field galaxies is about 23:1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| field horizontal branch star | has definition High-velocity metal-weak star of either B or A spectral type. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type B star or A star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Population II star |  |
| field lens | has definition A lens placed in or near the focal plane of a telescope to create an image of the primary mirror inside the instrument. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of lens |  |
| field star | has definition A star that is not part of any star cluster. Most stars, including the Sun, are field stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star distributed at random in space and not belonging to any particular star cluster. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| filament | has definition A prominence seen in projection on the solar disk. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of prominence |  |
| fine structure | has definition Splitting of spectral lines by the spin-orbit energy - i.e., the potential energy of the inherent electron magnetic moment in the atom's own magnetic field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of lines |  |
| fine-structure constant | has definition A "coupling constant," e2 / h bar c, approximately 1/137, that measures the strength of an interaction between a charged particle and the electromagnetic field. It gives a rough measure of the relative importance of relativistic and spin effects in the spectra of atoms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A coupling constant e2 / h bar c, approximately equal to 1/137 (where e is the electron charge, h bar is Plancks constant, and c is the speed of light), that measures the strength of the interaction between a charged particle and the electromagnetic field. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A parameter that measures the strength of the electromagnetic force. The fine-structure constant is a combination of other fundamental constants of nature - the electrical charge of the electron, the speed of light, and Planck's constant of quantum mechanics. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol α |  |
| has symbol α |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000027 × 10-3 |  |
has value 7.297352533 × 10-3  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| fine-tuning | has definition A phrase meaning a highly constrained and implausible adjustment of the parameters of a theory. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| fireball | is a kind of meteor event |  |
| FIRST | has definition Far-InfraRed Space Telescope. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared space telescope |  |
| first law of thermodynamics | has definition The law of conservation of energy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of thermodynamics law |  |
| first order phase transition | has definition A phase transition which occurs in a manner similar to the way water boils. Bubbles of the new phase (steam) form in the midst of the old phase (water), so that temporarily the two distinct phases (steam and water) coexist. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has final phase |  |
| has initial phase |  |
| is a kind of phase transition |  |
| first point of Aries | is an instance of ecliptic coordinate |  |
| first radiation constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol c1 |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000029 × 10-16 W m2 |  |
has value 3.74177107 × 10-16 W m2  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| fission | has antonym fusion |  |
| has definition In nuclear physics, the splitting of the atomic nucleus of a heavy element, resulting in the emission of nuclear energy and possibly causing a chain reaction (with similar results) within a mass of the element. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Interaction in which nucleons previously united in an atomic nuclei are disjoined, releasing energy. Fission powers atomic bombs. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| fission of stable elements lighter than iron | is a kind of energy sink |  |
| five-minute oscillations | has definition Vertical oscillations of the solar atmosphere with a well-defined period of 5 minutes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of harmonic motion |  |
| is a kind of solar motion |  |
| fixed mount telescope | has mounting fixed direction | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Earth based telescope |  |
| fixed vertical mount telescope | has mounting fixed vertical |  |
| is a kind of fixed mount telescope |  |
| flare star | has definition A member of a class of dwarf stars (usually dM3e-dM6e) that show sudden, intense outbursts of energy. The flares are usually rare and very short with mean amplitudes of about 0.5-0.6 mag. All known flare stars are intrinsically faint and have emission lines of H I and Ca II. It is generally believed that flares in flare stars have certain properties in common: rapid rise to peak light followed initially by a rapid decline and later by a slower phase that occasionally does not return to a preflare level within practical monitoring times (several hours). An increase in radio emission is often detected simultaneously with the optical outburst. About 30 flare stars are known, all within 20 pc. (In at least one theory, the flare star stage directly follows the T Tauri stage.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A star that emits flares, which can outshine the entire star. Many red dwarfs are flare stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Dim red dwarf star that suddenly lights up with great - but brief - luminosity, corresponding to an equally powerful but short-lived burst of radio emission. The cause is thought to be a sudden and intense outburst of radiation on or above the star's surface. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Stars undergoing erratic jumps in brightness (up to a few magnitudes) on time scales of the order of minutes. During the quiescent phase the spectrum is that of an M dwarf with emissions in the CaII and Balmer lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym UV Ceti star |  |
| is a kind of cataclysmic variable |  |
| is a kind of radio star |  |
| is a kind of red dwarf | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| flat universe | has definition A cosmological model in which a static (neither expanding nor collapsing) universe is maintained by introducing a cosmological repulsion force (in the form of the cosmological constant) to counterbalance the gravitational force. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A Friedmann model of the Universe in which the spacetime continuum is not curved. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A homogeneous world model (the simplest relativistic model) of finite density, zero curvature, and nonzero cosmological constant, subject to the field equations of general relativity in an expanding Euclidean space. The radius increases rapidly from zero, and, although it always increases, the rate of increase becomes less as time goes on. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A homogeneous, isotropic universe is called flat if it is just on the borderline between being spatially closed and spatially open, so the geometry is precisely Euclidean. If Einstein's cosmological constant is zero, then a flat universe will go on expanding forever, but the velocity of recession between any two objects would approach zero at large times. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A particular solution to Einstein's cosmological equations in which the universe is flat. (See flat universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A Universe in which there is no curvature to the spacetime continuum. This means that the kinetic energy of the expansion is exactly balanced by the potential gravitational energy of the matter. Thus, after an infinite amount of time the Universe will stop expanding. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A universe that is at the boundary between an open and closed universe. In a flat universe, the average mass density always has precisely the critical value. A flat universe has zero total energy and an infinite size. Flat universes have the geometry of an infinite, flat surface, that is, Euclidean geometry. The value of omega is 1 for a flat universe. (See closed universe; critical mass density; Euclidean geometry; omega; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A world model of a static universe with a positive cosmological constant, whose radius of curvature is constant and independent of time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang model that was formulated by Friedmann and Lemaitre which has a zero curvature, or flat (Euclidian). This space is unbounded. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The flat (k = 0), pressureless standard model of the universe. | ![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The Friedmann-Lemaitre model in which space is Euclidean was advocated by Einstein and de Sitter in 1932. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has geometry of space flat or Euclidian |  |
| has synonym Einstein-de Sitter universe |  |
| is a kind of big bang |  |
| flatness problem | has definition A problem of the traditional big bang theory (without inflation) related to the precision required for the initial value of omega, the ratio of the actual mass density to the critical mass density. If the description is started at one second after the big bang, for example, omega must have been equal to one to an accuracy of fifteen decimal places, or else the resulting universe would not resemble our own. Yet the traditional big bang theory offers no explanation for this special value, which must be incorporated as an arbitrary postulate about the initial conditions. See also horizon problem. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Poses the question: why, out of an infinite number of possibilities, is our Universe so close to the one special case: the "flat" Universe? | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The puzzle of why the universe today is so close to the boundary between open and closed, that is, why it is almost flat. Equivalently, why should the average mass density today be so close to the critical mass density, but not exactly equal to it? If omega begins bigger than 1, it should get bigger and bigger as time goes on; if it begins smaller than 1, it should get smaller and smaller. For omega to be near 0.1 today, about 10 billion years after the big bang, it had to be extraordinarily close to 1 when the universe was a second old. Some people consider such a fine balance to have been highly unlikely according to the standard big bang model, and thus are puzzled as to why the universe today is almost flat. (See closed universe; critical mass density; flat universe; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The riddle of why the universe is neither dramatically open nor closed, but appears to be almost perfectly balanced between these states. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of problem |  |
| flavor | has definition Designation of quark types - up down, strange, charmed, top, and bottom. Flavor determines how the weak nuclear force influences quarks. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In particle physics, another word for "type". For example, there are 6 flavors of quarks, meaning that there are 6 different types of quarks. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The known quarks exist in six different types, or flavors: up, down, charmed, strange, top, and bottom. The up and down quarks belong to the first generation, the charmed and strange quarks belong to the second, and the top and bottom quarks belong to the third. The up, charmed, and top quarks each have an electrical charge 2/3 that of a proton, while the down, strange, and bottom quarks have a charge -1/3 that of a proton. See Table 7.1 on page 120. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The term used to describe different quark types. There are six quark flavors: up, down, strange, charm, bottom and top. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| Flexible image transport system | has acronym FITS |  |
| has definition A method for saving image data which has become standard in astronomy. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of data standard |  |
| fluorescence | has definition The absorption of a photon of one wavelength and reemission of one or more photons at longer wavelengths, especially the transformation of ultraviolet radiation into visible light. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The emission of light at one wavelength, the green say, following absorption of light with a much shorter wavelength such as the ultraviolet. The UV photon parts with its energy by ejecting the electron into a high-energy level from which it cascades back down, releasing photons of lower energy and therefore longer wavelengths. A material which has this property is called a phosphor. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of bound-bound transition |  |
| is a kind of emission |  |
| fluorine | has abundance 0.4 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.96 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.0 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.0 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.63 × 104 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 950 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 690.248 nm for F I |  |
| has atomic emission line 703.747 nm for F I |  |
| has atomic emission line 712.789 nm for F I |  |
| has atomic emission line 685.603 nm for F I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 9 |  |
| has atomic radii 70.9 pm |  |
| has biological role essential in trace quantities for mammals, including humans, in the form of fluoride (F-) |  |
| has boiling point 85.01 K |  |
| has chief source fluorite |  |
| has covalent radii 58 pm |  |
| has critical pressure 5573 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 144.3 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 550, b = 328, c = 728 pm, β = 102.17 deg for α-F2 |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 667 pm for β-F2 |  |
| has crystal type cubic for β-F2 |  |
| has crystal type monoclinic for α-F2 |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.3 - 0.5 mg |  |
| has definition pale yellow gas (F2) which is the most reactive of all the elements, and is the strongest oxidizing agent |  |
| has density 1.696 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 1516 kg m-3 for liquid at 85.01 K boiling point |  |
| has discoverer H. Moissan |  |
| has discovery date 1886 (isolated) |  |
| has discovery location Paris, France |  |
| has electron affinity 328 kJ mol-1 from F to F- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p5 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 3.98 Pauling |  |
| has hazard gas is highly corrosive and toxic, low concentration exposure can cause eye and lung irritation |  |
| has hazard metal florides are very toxic |  |
| has hazard organic fluorides are often quite harmless |  |
| has heat capacity 22.744 J K-1 mol-1 for atomic gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 31.30 J K-1 mol-1 for molecular gas (F2) at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 5.10 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 6.548 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 133 pm for F- |  |
| has isotope mass range 17 to 23 |  |
| has lethal intake 185 p.p.m. for 1 hour F2 inhalation for rat |  |
| has lethal intake 5 - 25 g NaF |  |
| has lethal intake 5 - 25 g NaF |  |
| has lethal intake 52 mg kg-1 NaF ingestion for rat |  |
| has level in humans 0.05 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.22 - 7 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.5 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 2000 - 12000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has longest lived isotope fluorine 19 |  |
| has main mining area Canada, USA, UK, Russia, Mexico, Italy |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 1.80 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 16.4 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass of element in person 2.6 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 53.53 K |  |
| has mineral apatite, cryolite, fluorite |  |
| has molar volume 18.05 cm3 |  |
| has name origin fluere = to flow from Latin |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.5654 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 7 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 9 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state -I |  |
| has ocean residence time 400000 years |  |
| has pronunciation floor-een |  |
has registry number 7782-41-4 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 18.9984032 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 123 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has space group C2/m for α-F2 |  |
| has space group Pm3n for β-F2 |  |
| has specimen not available for sale as pure gas because it is too reactive and dangerous |  |
| has symbol F |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of molten KF·2HF |  |
| has term symbol 2P3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.0248 W m-1 K-1 at 273 K |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.0279 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.0096 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 250 mg NaF |  |
| has uses AlF3 in aluminium production |  |
| has uses CaF2 as a flux in metallurgy |  |
| has uses fabrication of UF6, SF6 and fluorinating agents such as ClF3 |  |
| has uses polymers, pesticides and antibiotics |  |
| has van der Waals radii 135 pm |  |
| has world production 2400 tonnes year-1 for gas (F2) |  |
| has world production 4.7 × 106 tonnes year-1 for fluorite (CaF2) |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of halogen |  |
| reacts with almost everything violently |  |
| fluorine 17 | has atomic mass 17.002095 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.761 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 64.5 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +4.722 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 17 |  |
| has symbol 17F |  |
is an instance of fluorine  |  |
| fluorine 18 | has atomic mass 18.000937 |  |
| has decay mode β+ EC (1.655 Mev) 97% |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 1.83 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 9 |  |
| has number of nucleons 18 |  |
| has symbol 18F |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of fluorine  |  |
| fluorine 19 | has atomic mass 18.99840322 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 25.1665 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 94.077 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 4730 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.628867 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 10 |  |
| has number of nucleons 19 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.83 with CFCl3 reference where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 19F |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of fluorine  |  |
| fluorine 20 | has atomic mass 19.999981 |  |
| has decay mode β- (7.029 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 11.0 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.094 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 11 |  |
| has number of nucleons 20 |  |
| has symbol 20F |  |
is an instance of fluorine  |  |
| FOC | has definition Faint Object Camera (Hubble). | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| focal reducer | has definition An optical component or system for changing the image scale of a telescope to achieve a better match between the seeing disk and the pixel size. See optical matching. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| focus | is a kind of optical device |  |
| Fomalhaut | has B-V magnitude 0.09 |  |
| has declination -29 37 20 |  |
| has definition An A star. The brightest star in the constellation Piscis Austrinus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 7 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 22 57 39.0 |  |
| has spectral type A3 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha PsA |  |
| has synonym HR 8728 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.16 |  |
is a part of Pisces Australis  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| forbidden line | has definition Spectral line emitted from a metastable state (q.v.), or those which have a very low probability (10-9-10-10) of occurrence. They appear at particle densities ≤ 108 cm-3. All forbidden lines have low excitation potentials. Forbidden lines are designated by enclosing them in brackets, e.g., [O II]. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym nebular line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| Forbush decrease | has definition A decrease in cosmic-ray intensity during active Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Forbush | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1954 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 11 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of periodic celestial event |  |
| is an instance of solar event |  |
| force | has carrier boson |  |
| has range |  |
| has strength (relative to electromagnetism) |  |
| is a kind of physical phenomena |  |
| force quantity | has definition Agency responsible for a change in a system. In Newtonian mechanics, gravitational force bends the moon away from the straight trajectory it would otherwise pursue. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit force unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| force unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of force quantity |  |
| Fork equatorial telescope | has mounting equatorial fork | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| formaldehyde | has definition An organic molecule, the first polyatomic molecule to be discovered in interstellar space. In 1973 It was discovered in two external galaxies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery in space date 1969 |  |
| has symbol H2CO |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| formamide | has definition An interstellar molecule discovered in space at a wavelength of 6.5 cm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery in space date 1971 |  |
| has symbol HCONH2 |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| formic acid | has definition The first organic acid to be detected in interstellar space at 18.3 cm. Formic acid is the "sting" of an insect. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery in space date 1970 |  |
| has symbol H2CO2 |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Fornax | has acronym For |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Fornacis |  |
| has historical origin the laboratory Furnace or chemical furnace in honor of Antoine Lavoisier |  |
has synonym Furnace  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Fornax A | has apparent magnitude 10 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 1316 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Fornax |  |
| is an instance of radio galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of S0 galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| Fornax galaxy | has definition A dwarf spheroidal galaxy, in the Local Group, that orbits the Milky Way. (Mv ≈ -12). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1938 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 190 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 440000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 2 × 107 Msun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Fornax |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| Four-shooter | has definition An astronomical instrument comprised of four highly sensitive photoelectric cells (CCDs). The four-shooter is placed at the end of a telescope and used to electronically record incoming light. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| Fourier Transform Spectrometer | has acronym FTS | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| Fourier transformation | has acronym FT | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of transformation |  |
| fractal | has definition A geometric figure in which a pattern is repeated ad infinitum on smaller and smaller scales. A classic example is Von Koch's snowflake, for which the construction begins with an equilateral triangle. Trisect each side, and replace the middle section by two sides of a smaller equilateral triangle, bulging outward. The snowflake is obtained by repeating this process for each side of the resulting figure, then for each side of the subsequent figure, and continuing forever. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A pattern that repeats itself or nearly repeats itself on many different scales of magnification. For example, suppose that some ink on a piece of paper appears to form a star. If you look at the piece of paper with a magnifying glass, you see that the dark areas are not solid black, but are formed of tiny stars themselves. If you look at one of these small stars with a microscope, you see that the dark areas of each of the tiny stars is formed from an arrangement of even tinier stars. Such a repeating pattern of stars would be called a fractal. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has dimensions fractional |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| frame of reference | has acceleration |  |
| has definition A set of axes to which positions and motions in a system can be referred. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation rate |  |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| frame transfer | has definition A CCD construction in which one half of the imaging area of the device is purposely covered with a mask opaque to light to provide a temporary charge storage section. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| francium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| Fraunhofer line | has definition Absorption line in the spectrum of the Sun, studied by Fraunhofer in 1814. The nine most prominent he labeled with capital letters (from the red end) A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. and K. The A band and B band are now known to be groups of telluric lines due to O2 absorption in Earth's atmosphere, and C and F are respectively known as Hα and Hβ. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has dicovery date 1814 |  |
| has discoverer Joseph Fraunhofer |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| occurs in Sun |  |
| free electron | has definition Electron not bound to a nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of electron |  |
| free parameter | has definition A number which is needed to define a theory well enough so that predictions can be made, but which must be determined by experiment or observation. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| free-fall | has definition A collapse in which gas clouds do not hit or impede one another. According to ELS, the Galactic halo formed in a free-fall collapse. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collapse |  |
| free-free transition | has definition The acceleration of an unbound (or free) electron by a proton or atomic nucleus results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of atomic process |  |
| frequency | has definition Number of oscillations per second of an electromagnetic wave. The amplitude of a wave depends on the intensity; the wavelength, on the frequency. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The number of complete wave cycles a wave completes each second. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The number of cycles or complete alternations per unit time of a carrier wave, band, or oscillation. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The number of oscillations or wave cycles per second passing a given point. For electromagnetic radiation, the product of the frequency and the wavelength is the speed of light. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The number of peaks (often called crests) of a propagating wave that cross a given point in a unit of time. For example, if 1000 peaks cross a given point in one second, one says that the frequency is 1000 cycles per second or 1000 hertz. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol ν |  |
| has unit frequency unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| frequency distribution | has definition A statistical arrangement of numerical data according to size or magnitude (see also distribution function). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical distribution |  |
| frequency unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of frequency |  |
| FU Ori star | has definition A kind of T Tau stars with considerable changes in brightness. The post-eruption spectrum is that of a late supergiant. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym fuors |  |
| is a kind of T Tauri star |  |
| Fundamental Catalog | has acronym FK | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star catalog |  |
| fundamental force | has definition One of four fundamental forces which mediate particle interaction. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of force |  |
| fundamental frequency | has definition The lowest characteristic frequency of oscillation of a dynamical system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frequency |  |
| fundamental physical constant | has accuracy |  |
| has unit |  |
| has value changes in value are due solely to an increase in measurement accuracy or convention |  |
is a kind of constant  |  |
| fundamental star | has definition Star for which coordinates have been determined to a very high degree of accuracy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Fused-quartz | is a kind of mirror |  |
| fusion | has antonym fission |  |
| has catalyst |  |
| has definition In nuclear physics, the combining of the atomic nuclei of lighter elements to form nuclei of a heavier element. Such a process involving the atomic nuclei of elements lighter than iron is accompanied by the emission of energy; for fusion of heavier elements, energy must be supplied. The process is thought to contribute to the condensation of stars from interstellar gas and dust. See also nuclear fusion. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Interaction in which nucleons are forged together, creating new atomic nuclei and releasing energy. Fusion powers hydrogen bombs. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Process by which the Sun (and other stars) radiates energy. The nucleus of an atom fuses with the nuclei of other atoms to form new, heavier atoms at the same time releasing large amounts of energy. In the Sun, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium by this process, with carbon and nitrogen as intermediates. Cooler stars undergo the proton-proton cycle with a similar result. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has minimum temperature |  |
| has product |  |
| has reactant |  |
| has reaction probability |  |
| is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| produces energy |  |
| fusion device | is a kind of instrument |  |
| G band | has definition A band of CH. It is conspicuous in the spectra of G-K stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has species CH |  |
| has wavelength 4303 Å |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| occurs in G star, K star |  |
| G star | has color yellowish |  |
| has definition Spectral type for yellow stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Yellowish star in which the H and K lines of Ca II have become dominant and in which a tremendous profusion of spectral lines of both neutral and ionized metals, particularly iron, begins to show. The Balmer lines of hydrogen are still recognizable. Examples are the Sun and Capella. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 5000 to 6000 K |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| G1 | has image   |  |
| has synonym Mayall II |  |
| is a part of Andromeda galaxy |  |
is an instance of extragalactic globular cluster  |  |
| gadolinium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 300 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| galactic astronomy | has definition The study of the Milky Way. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomy |  |
| galactic center | has definition Now thought to comprise black holes - which would explain why the centre of our Galaxy appears strangely obscure, and emits only infrared radiation. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The direction of the sky toward the center of the Milky Way. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic latitude 0 |  |
| has galactic longitude 0 |  |
| is a part of galactic nucleus |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of galactic coordinate |  |
| is opposite of anticenter |  |
| galactic coordinate | has component galactic coordinate component |  |
| has definition A system of coordinates based on the mean plane of the Galaxy, which is inclined about 63° to the celestial equator. Galactic latitude (b) is measured from the galactic equator north (+) or south (-); galactic longitude (l) is measured eastward along the galactic plane from the galactic center. In 1958, because of increased precision in determining the location of the galactic center, a new system of galactic coordinates was adopted, with the origin at the galactic center in Sagittarius at α(1950) = 17h42m.4, δ(1950) = - 28°55'. The new system is designated by a superior roman numeral II (i.e., bII, lII) and the old system by a superior roman numeral I: lII ≈ lI + 32°.31. Galactic coordinates are independent of precession. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic latitude |  |
| has galactic longitude |  |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| galactic coordinate component | is a component of astronomical coordinate |  |
| is a kind of coordinate component |  |
| galactic equator | has definition The primary circle defined by the central plane of the Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equator |  |
| galactic latitude | has definition The angle between the line of sight to a star and the Galactic plane. Galactic latitude ranges from +90 degrees to -90 degrees; the Galactic plane has a Galactic latitude of 0 degrees. Regions north of the Galactic plane have positive Galactic latitude; regions south have negative Galactic latitude. The point with a Galactic latitude of +90 degrees is called the north Galactic pole, and the point with a Galactic latitude of -90 degrees is called the south Galactic pole. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of galactic coordinate component |  |
| galactic longitude | has definition A measure of a star's position with respect to the Sun and Galactic center. Galactic longitude ranges from 0 degrees to 360 degrees. Imagine the Sun at the center of a giant clock, with the Galactic center located in the direction of six o'clock. A Galactic longitude of 0 degrees would correspond to the direction of six o'clock, a Galactic longitude of 90 degrees to the direction of three o'clock, a Galactic longitude of 180 degrees to the direction of twelve o'clock, and a Galactic longitude of 270 degrees to the direction of nine o'clock. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of galactic coordinate component |  |
| galactic nucleus | has definition In the innermost region of a galaxy, there is often a concentration of stars and gas, sometimes extending over thousands of light-years from the center of the galaxy. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The central region of a galaxy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| galactic plane | has definition The plane that contains the disk of the Milky Way. By definition, one direction perpendicular to this plane is called "above" or "north", and the opposite direction, also perpendicular to the Galactic plane, is called "below" or "south". From Earth, due Galactic north is marked by the north Galactic pole, which lies near the bright star Arcturus, and due Galactic south is marked by the south Galactic pole, which lies in the faint constellation Sculptor. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| galactic pole | has definition Either of the two points in the sky where we look perpendicular to the disk of the Milky Way. The north Galactic pole is the Galactic pole located above the disk; the south Galactic pole is the Galactic pole located below the disk. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The poles of the galactic plane. The new system puts the galactic north pole in Coma at α(1950) = 12h49m, δ(1950) = 27°.4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic longitude 0 degrees |  |
| is a kind of galactic coordinate |  |
| galactic rotation | has definition The revolving of a galaxy round its central nucleus even as it continues its proper motion. Such rotation, however, is not uniform but differential. One revolution of the Sun within our own Galaxy takes about 225 million years, or 1 cosmic year. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of differential rotation |  |
| is a kind of galaxy motion |  |
| galactic velocity component | has definition One of three components of a star's motion with respect to the center of a galaxy. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| galactic wind | has definition A hypothetical outflow of tenuous material from a galaxy, analogous to the solar wind. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| Galactocentric distance | has definition A star's distance from the Galactic center. The Sun's Galactocentric distance is about 27000 light-years. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of galactic coordinate component |  |
| is an instance of length |  |
| galaxy | has catalog galaxy catalog |  |
| has definition A collection of matter which usually manifests itself by the production of stars. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A huge collection of millions, billions, or trillions of stars. When referring to the Milky Way, "galaxy" is capitalized, otherwise not; thus: "Andromeda is the nearest giant galaxy to the Galaxy". | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A large (108-1013 Msun), gravitationally bound aggregate of stars and interstellar matter. Galaxy formation is currently believed to have occurred around z ≈ 3-4. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A large aggregation of stars, bound together gravitationally. There are three major classifications of galaxies - spiral, elliptical, and irregular - and several subclassifications. The sun belongs to a spiral galaxy, the Milky Way galaxy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An isolated aggregation of stars and gas, held together by their mutual gravity. A typical galaxy has about 100 billion stars, has a total mass equal to about a trillion times the mass of the sun, is about 100,000 light years in diameter, and is separated from the nearest galaxy by a distance of about 100 times its own diameter. Thus, galaxies are islands of stars in space. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. Galaxies come in two major shapes: flattened disks with a central bulge, called spirals, and amorphous, semispherical blobs, called ellipticals. If galaxies are found bunched up next to each other, they are said to lie in groups or clusters. Clusters with a particularly large number of galaxies in them are called rich clusters. Galaxies that do not lie in such groups but rather seem to be scattered uniformly and randomly through space are called field galaxies. Some galaxies are characterized by the dominant type of radiation they emit. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Vast system of celestial objects, typically consisting of between 106 and 1012 stars, plus interstellar gas and dust. There are three basic types: spiral (further subdivided into normal spirals and spirals with a "bar" at the centre, and yet further subdivided according to the "openness" of the spiral arms), elliptical (subdivided according to ellipticity) and irregular (subdivided according to whether they are made up of Population I or Population II stars). Another not uncommon type of galaxy is a lenticular form mid-way between the spiral and the elliptical. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars 106 to 1012 | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of stars |  |
| galaxy catalog | has object type galaxy or nebula (some nebulae are misidentified as galaxies) |  |
| is a kind of catalog about star systems |  |
| galaxy cluster | has definition A conglomeration of hundreds or thousands of galaxies. The nearest large galaxy cluster is the Virgo cluster. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An aggregate of galaxies. Bautz and Morgan divide them into three morphological types: type I contains a supergiant cD galaxy; Coma is type II, type III contains no members significantly brighter than the general bright population. Virgo is type III. 21 known X-ray sources are associated with clusters of galaxies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 102 to 103 (order of magnitude) | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of galaxies |  |
| galaxy containing Cepheids | has distance determined from Cepheid period-luminosity relation |  |
| has number of Cepheids |  |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| galaxy group | has definition A small gathering of galaxies, smaller than a cluster. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which contains about thirty galaxies. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies < 100 |  |
| is a kind of galaxy cluster |  |
| galaxy merger | has definition The formation of a galaxy from the collision of two or more separate galaxies. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of merger |  |
| galaxy motion | is a kind of mass motion |  |
| galaxy orbital event | has participants star, galaxy |  |
| is a kind of orbital event |  |
| galaxy peculiar velocity | has definition A deviation in the velocity of a galaxy from that expected on the basis of a uniform expansion of the universe. (See Hubble law.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| galaxy theory | has domain extragalactic astronomy |  |
| is a kind of astronomy theory |  |
| Galilean satellite | has definition The largest satellites of Jupiter - Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. All are locked in synchronous rotation with Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Galileo |  |
| has discovery date 1610 |  |
| is a kind of natural satellite |  |
| is a part of Jupiter |  |
| Galilean transformation | has definition The non-relativistic method of relating observations from one frame of reference to another. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate transformation |  |
| Galileo Galilei | is an instance of astronomer |  |
| gallium | has image 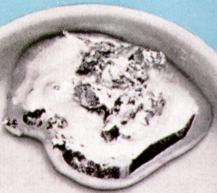 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 10000 years |  |
| is a kind of group III element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Gamma Corvi | has B-V magnitude -0.11 |  |
| has declination -17 32 31 |  |
| has right ascension 12 15 48.3 |  |
| has spectral type B8IIIpHgMn |  |
| has synonym HR 4662 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.59 |  |
is a part of Corvus  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Gamma Draconis | has B-V magnitude 1.52 |  |
| has declination +51 29 20 |  |
| has right ascension 17 56 36.3 |  |
| has spectral type K5III |  |
| has synonym HR 6705 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.23 |  |
is a part of Draco  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Gamma Microscopii | has B-V magnitude 0.89 |  |
| has declination -32 15 28 |  |
| has right ascension 21 1 17.4 |  |
| has spectral type G6III |  |
| has synonym HR 8039 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.67 |  |
is a part of Microscopium  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Gamma Normae | has B-V magnitude 1.08 |  |
| has declination -50 09 20 |  |
| has right ascension 16 19 50.3 |  |
| has spectral type G8III |  |
| has synonym HR 6072 |  |
| has V magnitude 4.02 |  |
is a part of Norma  |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| gamma ray | has definition An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength in the range of 10-13 to 10-10 meter, corresponding to photons with energy in the range of 104 to 107 electron volts. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Electromagnetic radiation similar to X-radiation, although of shorter wavelength, emitted spontaneously by some radioactive substances from atomic nuclei during radioactive decay. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength less than about 1 Å (10-10 m); blends from the "hard" X-ray region. Photons of energy greater than about 10 keV. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Extremely short-wavelength electromagnetic energy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Photon of very high frequency (wavelength shorter than a few tenths of an angstrom); the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, although there is no sharp boundary between γ-ray photon and an X-ray photon. Usually γ-ray photons come from the nucleus and X-ray photons come from the inner orbital electrons. Galactic γ-ray photons seem to originate primarily in the spiral arms. | ![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Photons of very high frequency and very short wavelength; the most energetic and penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Rays first discovered in radioactive material, and later identified as very high energy photons. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 3 EHz or more |  |
| has wavelength 100 pm or less |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| gamma ray source | has wavelength gamma ray |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| Gamma Sagittae | has B-V magnitude 1.57 |  |
| has declination +19 29 32 |  |
| has right ascension 19 58 45.3 |  |
| has spectral type M0III |  |
| has synonym HR 7635 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.47 |  |
is a part of Sagitta  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of M star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Gamma Velorum | has absolute magnitude Mv = - 5.6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has B-V magnitude -0.22 |  |
| has declination -47 20 12 |  |
| has definition A triple system (WC8, B1 IV, O9 I) embedded in the Gum Nebula. It is the brightest Wolf-Rayet star in the sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 400 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 78.5 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 8 9 31.9 |  |
| has spectral type WC8+O7.5e |  |
| has synonym HR 3207 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.78 |  |
| is a part of Vela |  |
is a part of Vela  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of triple star |  |
| is an instance of WC star |  |
| gamma-ray burst | has definition Short, intense, low-energy bursts, first recorded by the Vela satellite system on 1967 July 2. Their isotropic distribution suggests an extragalactic origin, but a galactic disk origin cannot be ruled out: there is a large increase in γ-ray flux in the direction of the galactic center. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date July 2, 1967 |  |
| has distribution isotropic with an increase towards the galactic center |  |
| has duration 0.1 - 4 s |  |
| has energy spectrum 0.1-1.2 MeV |  |
| has frequency of occurrence 5 per year |  |
| is a kind of gamma ray source |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| Ganymede | has definition The largest satellite of Jupiter. |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0015 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1.65 × 1026 g |  |
| has orbital period 7.155 days |  |
| has radius 2635 km |  |
| has synonym Jupiter III |  |
| is a part of Jupiter |  |
| is an instance of Galilean satellite |  |
| gas | has definition The gaseous component of a galaxy, includes nebula | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A phase of matter consisting of a low density collection of particles which have no short range order | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of phase of matter |  |
| is a part of disk |  |
| gas giant | has composition Mostly made of various light elements such as gases and simple compounds |  |
| has definition Giant planet that has a gaseous surface. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jovian planet |  |
| is a kind of planet |  |
| gas law | is a kind of thermodynamics law |  |
| gaseous element | has state gas at standard temperature and pressure |  |
| is a kind of element |  |
| gaseous fragmentation | has definition The systematic breakup of a gas cloud into smaller and smaller subunits as the gas cools and continues to collapse. The gravitational forces continually overtake the opposing pressure gradients as long as the cloud is able to radiate freely; consequently, the Jeans mass decreases, and fragments divide into smaller subfragments. The process stops only when opacity intervenes to inhibit the cooling and radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of contraction |  |
| gaseous nebula | has catalog gaseous nebula catalog |  |
| has definition An H II region, a supernova remnant, or a planetary nebula. H II regions have an emission-line optical spectrum, and a thermal continuous spectrum declining in intensity as the wavelength increases (from maximum in the ultraviolet) through infrared and radio. Supernova remnants have an emission-line optical spectrum and a nonthermal radio spectrum. Temperatures of planetary nebulae are much higher than those of H II regions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym emission nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of H II region |  |
| gaseous nebula catalog | has object type gaseous nebula |  |
| is a kind of nebula catalog |  |
| gauge symmetry | has definition A property of modern theories of physics, formulated in the 1960s and confirmed by experiment. A symmetry, in general, is a property that allows a system to behave in the same way even though it has undergone some change. For instance, a snowflake has a 6-sided "rotational symmetry" - a snowflake appears identical after every 60 degree rotation. A gauge symmetry is something like a rotation, in which the amount of rotation can vary randomly from one point of space to the next. (See field theory.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Symmetry principle underlying the quantum-mechanical description of the three nongravitational forces; the symmetry involves the invariance of a physical system under various shifts in the values of force charges, shifts that can change from place to place and from moment to moment. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| Gauge theory | has author Chen Ning Yang and Robert Mills (1954) | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A theory that treats force in a geometrical way in terms of global and local symmetries. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A theory whose dynamics originate from a symmetry. That is, the formulae describing the theory (in particular, the Lagrangian) are unchanged under certain symmetry transformations, called "gauge" transformations. For example, the equations of classical electrodynamics are invariant under local redefinitions of the electrostatic potential. This symmetry is ultimately responsible for the conservation of electric charge. However, in quantum electrodynamics this gauge symmetry is reinterpreted as invariance under local redefinitions of the phase of the electron wave function. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Account of forces that views them as arising from broken symmetries. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In 1973 David Gross, Frank Wilczek, and David Politzer showed that these theories possess a property called asymptotic freedom, just what was needed for a theory of how quarks bind to form protons and neutrons. The new theory, dubbed quantum chromodynamics or QCD, proposed that the color of the quarks acts as the charge of the Yang-Mills interactions. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| gauge theory | has gauge symmetry |  |
| Gauge theory | has name origin the term "gauge theory" is an archaic one, coming from earlier theories which were based on invariance under transformation of scale (i.e. gauge) | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Yang-Mills theories | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| gauge theory | is a kind of quantum field theory |  |
| Gauge theory | is a kind of unified theory |  |
| gauss | has definition Unit of magnetic flux density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-4 tesla | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux density unit |  |
| Gaussian distribution | has definition A random distribution of initial conditions is often referred to as a Gaussian distribution. Also, a certain kind of bell-shaped curve is called a Gaussian. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A statistical distribution defined by the equation p = c exp(-k2x2), in which x is the statistical variable. It yields the familiar bell-shaped curve. Accidental errors of measurement and similar phenomena follow this law. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of statistical distribution |  |
| Gaussian gravitational constant | has definition The constant defining the astronomical system of units of length (astronomical unit), mass (solar mass) and time (day), by means of Kepler's third law. The dimensions of k2 are those of Newton's constant of gravitation: L3M-1T-2. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol k | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 0.01720209895 | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| Gaussian year | has definition The period associated with Kepler's third law with a = 1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| gegenschein | has definition A very faint glow (about 10° across) which can occasionally be seen in a part of the sky opposite the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Faint nebulous light about 20° across near the ecliptic and opposite the Sun, best seen in September and October. Also called counterglow. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Faint oval patch of light visible from Earth only at certain times of the year, opposite the Sun. Its nature and cause are still not known. It is sometimes known as "counterglow". | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym counterglow |  |
| is a kind of backscatter |  |
| Gemini | has acronym Gem |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Geminorum |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the twins Castor and Pollux, Greek heroes Jason led on his voyages on the Argo |  |
| has synonym Twins |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Gemini Telescope North | has altitude 4100: m |  |
| has aperture 8.1 m |  |
has comment Coming ULE meniscus primary mirror; this northem instrument is to be optimized for IR work  |  |
| has creation date (1999) |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.8, 16IR, 19.6 |  |
| has latitude 19° 49' N |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
| has owner Joint Astronomy Center |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| Gemini Telescope South | has altitude 2725 m |  |
| has aperture 8.1 m |  |
has comment Partners in the Gemini project are the US, UK, Canada, Chile, Brazil, and Argentina  |  |
| has creation date (2000) |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.8, 6 |  |
| has latitude 30° 21' S |  |
| has location Cerro Pachon, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 49' W |  |
| has owner Cerro Tololo Inter-American Obs. |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| Geminid | has duration 3 days |  |
| has parent object Asteroid Phaethon |  |
| has radiant Gemini |  |
| has rate 90 per hour |  |
| has start time 13 December |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| general precession | has definition The sum of the lunisolar and the planetary precession. It causes the ecliptic longitude to increase at a constant rate but has no effect on ecliptic latitude. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has rate 50".27 per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| general relativity | has author Einstein (1915) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has competing theory twistor theory | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gravitation is a curvature in four-dimensional space-time rather than as a force existing between two masses. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has implication four-dimensional structure of space-time | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has phenomena gravity |  |
| has subset special relativity |  |
| has synonym Einstein's theory of gravity | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of relativity theory |  |
| geocentric coordinate | has component geocentric coordinate component |  |
| has coordinate origin Earth |  |
| has definition The latitude and longitude of a point on the Earth's surface relative to the center of the Earth; also celestial coordinates given with respect to the center of the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The longitude and latitude of a point on the Earth relative to the geoid. These coordinates are influenced by local gravity anomalies. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has height |  |
| has terrestrial latitude |  |
| has terrestrial longitude |  |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| geocentric coordinate component | is a component of geocentric coordinate |  |
| is a kind of coordinate component |  |
| geocentric cosmology | has definition A model of the universe in which the earth is centrally located, and the Sun, planets, and stars revolve around the Earth. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition School of ancient theories that depicted the earth as standing, immobile, at the center of the universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| geocorona | has definition The outermost part of Earth's atmosphere, a hydrogen halo extending out to perhaps 15 Earth radii, which emits Lyman-α radiation when it is bombarded by sunlight. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| geodesy | has definition Measurement and study of the Earth's size and shape. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of geology |  |
| geodetic coordinate | has definition The latitude and longitude of a point on the Earth's surface determined from the geodetic vertical (normal to the specified spheroid). (See zenith; latitude, terrestrial; longitude, terrestrial.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| geodetic precession | has definition A small, relativistic, direct motion of the equinox along the ecliptic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has rate 1".915 per century | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| geological era | is a kind of era |  |
| geology | has definition Scientific study of the dynamics and history of the earth, as evidenced in its rocks, chemicals, and fossils. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| geometrical object | has dimensions |  |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| geophysical satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| George Ellery Hale Telescope | has altitude 1706 m |  |
| has aperture 5.08 m |  |
| has creation date 1948 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.3. 16, 30 |  |
| has latitude 33° 21' N |  |
| has location Palomar Mountain, Calif., US |  |
| has longitude 116° 52' W |  |
| has mirror maker J.A. Anderson |  |
| has mirror type ribbed Corning Pyrex |  |
| has mounting Horseshoe yoke mount |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Westinghouse |  |
| has operator California Institute of Technology |  |
| has owner Palomar Observatory |  |
| has synonym 200 inch |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| GEOS 10 | is an instance of GEOS satellite |  |
| GEOS 11 | is an instance of GEOS satellite |  |
| GEOS 8 | is an instance of GEOS satellite |  |
| GEOS satellite | is a kind of geosynchronous satellite  |  |
| is a kind of NOAA satellite |  |
| is an acronym for Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite |  |
| geosynchronous satellite | has constant longitude |  |
| has definition an artificial satellite which orbits Earth every 24 hours |  |
| has location above the same position on the Earth |  |
| has orbital inclination approximately zero degrees |  |
| has orbital period 24 hours (one day) |  |
| is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| is a part of Earth |  |
| orbits Earth |  |
| German equatorial telescope | has mounting German equatorial | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| germanium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 20000 years |  |
| is a kind of group IV element |  |
| is a kind of metallic metalloid |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| giant | has definition 1. A star that has evolved off the main sequence and is roughly a hundred times as luminous as the Sun. Giants can be of any color, but yellow, orange, and red giants are the most common. 2. A planet much more massive than Earth. The solar system has four giant planets, all far from the Sun: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition High-luminosity star that lies above the main sequence on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class III |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| giant elliptical galaxy | has definition Massive elliptial galaxy which is too far for individual stars to be resolved. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1013 Msun (most massive galaxies known) | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elliptical galaxy |  |
| giga | has symbol G |  |
| has value 109 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| GIS | has definition Gas Imaging Spectrometer (ASCA X-ray satellite). |  |
| is a kind of high energy detector |  |
| global inertial frame | has definition A coordinate system or frame of reference anchored with respect to the overall distribution of matter in the universe. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nonaccelerating reference frame |  |
| is a kind of nonrotating reference frame |  |
| globular cluster | has age oldest stellar formation in the Galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has catalog globular cluster catalog |  |
has definition A tightly packed, symmetrical group of thousands of very old (pure Population II) stars. The stellar density is so great in the center that the nucleus is usually unresolved. The stars within a globular cluster orbit each other because of their mutual gravity.  | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter about 100 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has location most are in the halo some are members of the thick disk | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 104 to 106 Msun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars 105 to 106 | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbit elongated, around the galactic center | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectra low abundances of heavy elements | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has velocity very high | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star cluster | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of halo |  |
| globular cluster catalog | has object type globular cluster |  |
| is a kind of catalog about star systems |  |
| glueball | has definition Theoretical particles made exclusively of gluons. Tentative evidence of the existence of glueballs had been found in accelerator experiments by the mid-1980s. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| gluon | carries the force strong force |  |
| has color charge |  |
| has definition Gluons are the massless gauge bosons of QCD which mediate the strong color force between quarks. Because of the non-Abelian structure of the theory, gluons can interact with themselves, and may form particles consisting of gluons bound together. The existence of these "glueballs" has yet to be confirmed. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Quanta that carry the strong nuclear force. Like photons, vector bosons, and gravitons - the carriers respectively of electromagnetism, the weak force, and gravitation - gluons are massless bosons. Consequently, for simplicity's sake, some physicists lump together all the force-carrying quanta under the term "gluons". | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Smallest bundle of the strong force field; messenger particle of the strong force. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The force-carrying particles associated with the strong interactions, the forces which bind quarks inside of protons and neutrons. For more details, see Yang-Mills theories. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothetical particle that carries the force between quarks. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of carrier boson |  |
| is a kind of massless particle | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of parton | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| GMS | has launch date 14 Jul 1977 |  |
| has launch location Kenedy Space Center |  |
| has launch vehicle Delta rocket |  |
| has mass 315 kg |  |
| is an instance of GMS satellite |  |
| GMS satellite | has definition Geostationary Meteorological Satellite |  |
has specification  |  |
| is a kind of geosynchronous satellite |  |
| is a kind of NASDA satellite |  |
| GMS-2 | has launch date 11 Aug 1981 |  |
| has launch location Tanegashima Space Center, Kagoshima, Japan |  |
has launch vehicle N-II rocket  |  |
| has mass 296 kg |  |
| is an instance of GMS satellite |  |
| GMS-3 | has launch date 3 Aug 1984 |  |
| has launch location Tanegashima Space Center, Kagoshima, Japan |  |
has launch vehicle N-II rocket  |  |
| has mass 303 kg |  |
| is an instance of GMS satellite |  |
| GMS-4 | has attitude control spin stabilized |  |
| has constant longitude 140 deg east |  |
| has dimension 2.146 m diameter cylinder, height 0.3451 m |  |
| has launch date 6 Sept 1989 |  |
| has launch location Tanegashima Space Center, Kagoshima, Japan |  |
has launch vehicle H-I rocket  |  |
| has mass 325 kg |  |
| is an instance of GMS satellite |  |
| GMS-5 | has attitude control spin stabilized |  |
| has constant longitude 140 deg east |  |
| has dimension 2.146 m diameter cylinder, height 0.3451 m |  |
has image   |  |
| has launch date early 1995 |  |
| has launch location Tanegashima Space Center, Kagoshima, Japan |  |
has launch vehicle H-II rocket  |  |
| has mass 344 kg |  |
| is an instance of GMS satellite |  |
| Goddard Space Flight Center | has acronym GSFC |  |
is an instance of space science institution  |  |
| GOES-L | has creator NASA |  |
has image   |  |
| has launch date 3 May 2000 |  |
has launch vehicle Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA rocket  |  |
is an instance of GEOS satellite  |  |
| Golay cell | has definition A gas bulb used to detect infrared radiation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| gold | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of supernova produced element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Goldstone boson | has definition A massless spin-0 particle which arises whenever a (continuous) global symmetry is spontaneously broken. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 0 | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of boson |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| Gould Belt | has definition The local system of stars and gas within about 300 pc of the Sun in which the greatest concentration of naked-eye O and B stars occurs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from Sun 300 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination 10° to 20° to the galactic plane | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion arm |  |
| GPS satellite | is a kind of navigation satellite |  |
| Gran Telescopio Canarias | has acronym GTC |  |
| has altitude 2400 m |  |
| has aperture 10 m |  |
| has comment Design similar to that of the Keck instruments; funded by Spain with international partners |  |
| has creation date 2003 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.75. 15, 25 |  |
| has latitude 28° 45' N |  |
| has location La Palma, Canary Islands |  |
| has longitude 17°54' W |  |
| has owner Obs. del Roque de los Muchachos |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| is an instance of segmented mirror telescope |  |
| grand unified theory | has acronym GUT | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A speculative class of theories of particle interactions, first developed in 1974, which attempt to describe electromagnetism, the weak interactions, and the strong interactions in a fully unified theory. Of the known forces, only gravitation is omitted. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An attempt to produce a unification of all the forces of nature. While some success was made in unifying the gluon force between quarks with the electroweak force, problems always arose when gravity was included. Grand unification eventually gave way to superstring theory. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Class of theories that merge all three nongravitational forces into a single theoretical framework. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Class of theories that purport to reveal identities linking the strong and electroweak forces. The differences between these forces in nature today is attributed to the breaking of symmetrical relationships among force-carrying particles as the very early universe expanded and cooled. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory in physics that attempt to explain the forces of nature as manifestations of a single underlying force. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym grand unification | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| granule | has definition Convective cell in the solar photosphere. A granule represents a temperature roughly 300° higher than the surrounding dark areas. At any one time, granules cover about one-third of the solar photosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mottled appearance of the solar photosphere, caused by gases rising from the interior of the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1000 km in diameter |  |
| has lifetime 5 minutes |  |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| gravitational collapse | has definition The sudden collapse of a massive star when the radiation pressure outward is no longer sufficient to balance the gravitational pressure inward. In gravitational collapse there is a sudden, catastrophic release of great quantities of gravitational potential energy, and this release has been postulated as the cause of supernovae, neutron stars, and black holes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collapse |  |
| gravitational contraction | is a kind of energy source |  |
| gravitational lens | has definition A galaxy that intervenes between us and a distant astronomical object and that gravitationally deflects the light from that distant object. (Light, like matter, is attracted by gravity.) Gravitational lenses can focus, distort, and split light beams in the same way that ordinary glass lenses do. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| gravitational lensing | has definition Deflection of electromagnetic radiation from a distant background source by a strong gravitational field associated with a foreground source resulting in more than one image of the original source. Many double-quasars are produced by this phenomenon. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gravitational effect that bends a ray of light. Such an effect was predicted within the general theory of relativity, although previously considered impossible. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The apparent path of a photon is altered from a straight line by the gravitational field of the Sun. The path is deflected radially away from the Sun by up to 1".75 at the Sun's limb. Correction for this effect, which is independent of wavelength, is included in the reduction from mean place to apparent place. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The bending of light caused by the gravity of an object lying between us and the light source. This may cause the light source to look brighter than it normally does. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The bending of the beam of light due to gravity. It is observable when the light from a star or planet passes a massive object such as the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The effect of matter in curved spacetime, which tends to focus any beam of radiation from a distant source. In effect, the spacetime curvature is a lens of great focal length. At z ≈ 1, the angular size of an object starts increasing with distance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym deflection of light | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation direction modification |  |
| gravitational mass | has definition That property of matter which makes it create a gravitational field and attract other particles (cf. inertial mass; equivalence principle). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| gravitational potential energy | has definition Energy that a body can acquire by falling through a gravitational field and that decreases as the kinetic energy increases. There is no general reference level (analogous to the state of rest of a body in defining kinetic energy), and so we customarily define the change in gravitational potential energy as the negative of the work done by the gravitational forces during the bodys change of position. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition When we lift a weight from the floor to a tabletop, we clearly put energy into it. The energy is not lost, however, because we can retrieve it by allowing the weight to fall back to the floor. While the weight is on the table, we say that the energy is stored as gravitational potential energy. The energy is stored in the gravitational field. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of potential energy |  |
| gravitational radius | has definition The radius which an object should have in order that light emitted from its surface just ceases to escape from its surface. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| gravitational redshift | has definition Displacement of spectral lines toward longer wavelengths due to the effects of gravity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Light is emitted at a lower frequency and longer (or redder) wavelength in a gravitational field than in the absence of a gravitational field. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The rate at which a clock keeps time when it is in a gravitational field is slower than the rate at which it will keep time in the absence of a gravitational field. (The gravitational redshift was experimentally verified by Pound and Rebka in 1960.) The amount of redshift is directly proportional to the mass of the emitting body and inversely proportional to its radius. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has example | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Einstein effect |  |
| is a kind of wavelength shift |  |
| gravitino | has definition Hypothetical force-carrying particles predicted by supersymmetry theories. The gravitino's spin would be 1/2. Its mass is unknown. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| graviton | carries the force gravity |  |
| has definition A hypothetical elementary particle associated with the gravitational interaction. It is a stable particle with zero rest mass, zero charge, and a spin of ± 2, and travels with the speed of light. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A massless spin-2 particle which is the hypothetical quantum of the gravitational field. It mediates the force of gravity in a similar way to that in which the spin-1 gauge bosons (i.e. the photon, W±, Z0, and gluons) mediate the other forces. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A quantum of gravitational radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Smallest bundle of the gravitational force field; messenger particle for the gravitational force. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothetical quantum particle of the gravitational field. It could also be thought of as a quantized element of space-time curvature. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The quanta thought to convey gravitational force; analogous to the photons, gluons, and intermediate vector bosons of electromagnetism and the strong and weak nuclear forces. Predicted by quantum theory of gravity, gravitons have not yet been detected. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of carrier boson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of massless particle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of neutral particle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| gravity | has carrier boson graviton |  |
| has definition As described first by Isaac Newton, gravity is a force that exists between bodies of any mass whatever (from particles to stars) in proportion to the product of their masses, and in inverse proportion to the square of the distance between them. The weakest of the four natural forces (the other three being the electromagnetic and the two nuclear interactive forces), its real nature is still not fully understood. Einstein's General Theory of Relativity presented another viewpoint. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fundamental force of nature, generated by all particles that possess mass. Interpreted by means of Newtonian mechanics or by the general theory of relativity. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In Aristotelian physics, an innate tendency of the elements earth and water to fall. In Newtonian physics, the universal, mutual, attraction of all massive objects for one another; its force is directly proportional to the mass of each object, and decreases by the square of the distance separating the objects involved.In Einstein's general relativity, gravity is viewed as a consequence of the curvature of space induced by the presence of a massive object. In quantum mechanics the gravitational field is said to be conveyed by quanta called gravitons. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the four fundamental forces of nature, and the one most different from the other three. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mutual attraction between any two masses, as was first described accurately by Newton. Gravity appears strong because it has infinite range and it is always attractive (except for a false vacuum), but on a subatomic level gravity is the weakest of the known interactions; the gravitational force between a proton and an electron is 2 × 1039 times weaker than the electrical attraction. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The universal ability of all material objects to attract each other; F = Gm1m2 / r2. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The weakest of the four fundamental forces of nature, the gravitational force between any two masses is proportional to the product of the masses and varies inversely as the square of the distance between them. The other three fundamental forces are the electromagnetic force and two kinds of nuclear forces. (See electromagnetic force; nuclear forces.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The weakest of the four fundamental forces of nature. Described by Newton's universal theory of gravity, and subsequently by Einstein's general relativity. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has range infinite |  |
| has strength (relative to electromagnetism) |  |
| is a kind of fundamental force |  |
| gravity law | has domain gravity |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| gravity wave telescope | is a kind of telescope |  |
| gray | has base unit m2·s-2 |  |
| has symbol Gy |  |
| has unit J·kg-1 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| represents absorbed dose, specific energy (imparted), kerma |  |
| grazing-incidence telescope | has acronym XRT |  |
| has definition A telescope used in X-ray and gamma-ray astronomy. It focuses these rays by making use of the fact that they behave like light rays if they strike surfaces at a shallow enough angle. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of concentric surfaces |  |
| is a kind of X-ray space telescope |  |
| great circle | has definition A circle on the surface sphere whose diameter equal to the diameter of the sphere. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of circle |  |
| Great Rift | has definition A split in the Milky Way between Cygnus and Sagittarius caused by a succession of large, overlapping dark clouds in the equatorial plane of the Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from Sun 100 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion arm |  |
| Great Wall | has definition A sheet of galaxies which stretches more than 500 million light-years across the sky. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of galaxies |  |
| greatest elongation | has definition The instants when the geocentric angular distances of Mercury or Venus are at a maximum from the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has elongation varies | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planetary elongation event |  |
| is an instance of planetary elongation |  |
| green | is a kind of optical |  |
| Gregorian | has definition A class of reflecting telescope which uses a concave secondary mirror placed after the prime focus is reached instead of a convex secondary placed before the prime focus. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Telescope devised - but never constructed - by James Gregory, in which an auxiliary concave mirror reflects the magnified image, the right way up, through a hole in the centre of the main objective mirror, i.e., through the end of the telescope itself. The Cassegrain telescope is similar but produces an inverted image. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has secondary mirror shape concave |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| grism | has definition This is a right-angled glass prism with a transmission diffraction grating deposited on the hypotenuse surface. The spectrum produced by the grating is deflected by the prism to remain on the optical axis and the apex angle of the prism is chosen to get a certain wavelength in the center of the detector. Grisms can be placed in a filter wheel. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating |  |
| Groombridge 1830 | has definition A famous halo star whose proper motion, discovered in 1841, was then the largest known, displacing that of 61 Cygni. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 28 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Ursa Major | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high proper motion star |  |
| Grosser Refraktor | has altitude 241 m |  |
| has aperture 0.67 m |  |
| has creation date 1880 |  |
| has focal ratio f/15.7 |  |
| has latitude 48° 14' N |  |
| has lens maker Grubb |  |
| has location Vienna, Austria |  |
| has longitude 16° 20' E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb |  |
| has owner Astronomisches Inst., Univ. Obs. |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| Grosser Refraktor^2 | has altitude 41 m |  |
| has aperture 0.68 m |  |
| has creation date 1896 |  |
| has focal ratio f/30.9 |  |
| has latitude 52° 29' N |  |
| has lens maker C.A. Steinheil |  |
| has location Alt Treptow, Berlin, Germany |  |
| has longitude 13° 29'E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Hoppe-Berlin |  |
| has owner Arehenhold-Sternwarte |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| ground state | has definition The state in which all electrons are in the lowest possible energy states. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| group III element | has group 13 |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| group IV element | has group 14 |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| group V element | has group 15 |  |
| has synonym pnictogen |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| group VI element | has group 16 |  |
| has synonym chalcogen |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| Grus | has acronym Gru |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Gruis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the crane or Phoenicopterus (Flamingo), in the past used to be part of Piscis Austrinus. |  |
| has synonym Crane |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| gyrofrequency | has definition The frequency with which an electron or other charged particle executes spiral gyrations in moving across a magnetic field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frequency |  |
| H alpha | has upper energy level 3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 6563 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Balmer line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is an instance of spectral line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| h and Chi Persei | has definition A double stellar association. It contains many young O and B stars and also many M supergiants. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym double cluster in Perseus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Perseus OB1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Perseus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Perseus arm | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye object | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of OB association |  |
| H and K emission line star | has definition Late objects (F4 to M), which exhibit emission features in their Ca II HK lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line Ca II HK lines |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| H beta | has upper energy level 4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 4861 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Balmer line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Fraunhofer line |  |
| is an instance of spectral line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| H delta | has upper energy level 6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 4101 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Balmer line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of spectral line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| H gamma | has upper energy level 5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 4342 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Balmer line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of spectral line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| H II condensation | has definition A high-density H II region. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of H II region |  |
| H II region | has composition ionized hydrogen |  |
| has definition An area of ionized hydrogen. Most H II regions are red and arise from hot blue O and B stars, whose ultraviolet light can ionize all the hydrogen for dozens or even hundreds of light-years in every direction. The most famous H II region is the Orion Nebula. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Hydrogen gets ionized by hot O and B stars in H II regions. The most famous H II region is the Orion Nebula. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Region of ionized hydrogen in interstellar space. H II regions occur near stars with high luminosities and high surface temperatures. The kinetic temperature of H II regions is about 10,000-20,000 K, and the density is about 10 atoms per cm3. Ionized hydrogen, of course, having no electron, does not produce spectral lines; however, occasionally a free electron will be captured by a free proton and the resulting radiation can be studied optically (see also radio recombination lines). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nebula |  |
| H magnitude | has band 1.6 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 1.6 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| h-line | has definition Singly ionized magnesium resonance line. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Mg II |  |
| has wavelength 2803 Å |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| Hades | has definition An unofficial name for Jupiter IX, the outermost satellite of Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Nicholson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1914 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.28 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 156° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 758 days retrograde | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter IX | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| hadron | has definition High mass elementary particles that are influenced by the strong nuclear force. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle |  |
| hadron era | has definition The Big Bang era during which quantum and general-relativistic effects are expected to modify each other in an unknown way. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The Big Bang era when the Universe was matter-dominated, containing many hadrons in equilibrium with the radiation field and when kT ≈ mπ. The hadron era ended when the characteristic photon energy fell below the rest mass of a pion or π-meson (270 electron masses), and very few hadrons remained (about one hadron for every 108 photons). | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has density ρ = 1093 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 10-5 s |  |
| has start time 10-43 s after Big Bang |  |
| has synonym hadron barrier |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is followed by lepton era |  |
| is preceded by Planck era |  |
| hafnium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Hale | has associate Shapley |  |
| has birth date 29 June 1868 |  |
| has career |  |
| has death date 21 February 1938 |  |
has degree - 1890 : BSc. MIT
- 12 honorary PhDs
|  |
has image  |  |
| has name George Ellery Hale |  |
| has name George Ellery Hale |  |
| has orbituary |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
is an instance of astronomer   |  |
| half-life | has definition Time it takes for the number of particles to halve. For a radioactive substance, the length of time required for half the atoms to disintegrate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol τ1/2 | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time |  |
| see also mean life |  |
| half-power beamwidth | has acronym HPBW | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The angle across the main lobe of an antenna pattern between the two directions where the sensitivity of the antenna is half the value at the center of the lobe. This is the nominal resolving power of the antenna system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| Halley's comet | has definition Probably the best known of all comets. Its orbit was computed by Edmund Halley in 1704, at which time he predicted that the bright comet of 1682 would return in 1758 (Halley died in 1742, before he could see his prediction verified). Records of Halley's comet (a = 17.8 AU, e = 0.967, i = 162°.3, P = 76.2 yr perihelion distance 0.587 AU) have been traced back to 240 B.C. Last appearance 1910, next appearance 1986. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of comet |  |
| halo | has definition A spherical aggregation of stars, globular star clusters, and thin gas clouds, centered on the nucleus of the galaxy and extending beyond the known extremities of the galactic disk. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition the galactic halo, however, describes the spherical collection of stars forming a surrounding "shell" for our otherwise compact, discoid Galaxy. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The somewhat round population of old, metal-poor stars in the Milky Way. Also, the huge entity that surrounds the disk and contains most of the Galaxy's dark matter. To distinguish between the two, astronomers call the former the stellar halo and the latter the dark halo. Most of the stellar halo lies closer to the Galactic center than the Sun, while most of the dark halo lies farther from the Galactic center than the Sun. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| halogen | has group 17 |  |
| has synonym group VII element |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| hard gamma ray | is a kind of gamma ray |  |
| hard X-ray | is a kind of X-ray |  |
| Harlan J. Smith Telescope | has altitude 2075 m |  |
| has aperture 2.72 m |  |
| has creation date 1969 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.9, 8.8, 18 |  |
| has latitude 30° 4d N |  |
| has location Mount Locke, Texas, US |  |
| has longitude 104° 01' W |  |
| has mirror maker Davidson Optronics |  |
| has mirror type Fused-silica |  |
| has mounting Cross-axis equatorial |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Westinghouse |  |
| has owner McDonald Observatory |  |
| has synonym 107 inch |  |
| is an instance of Cross-axis equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| harmonic motion | has amplitude |  |
| has definition A motion that repeats itself in equal intervals of time. An oscillating particle in harmonic motion is a harmonic oscillator. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has period |  |
| has synonym periodic motion |  |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| harmonic overtone | has definition Any integral multiple of the fundamental frequency | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frequency |  |
| Haro galaxy | has definition Blue object whose spectra show sharp emission lines. |  |
| is a kind of emission line galaxy |  |
| Hartree energy | has equation  |  |
| has symbol Eh |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000034 × 10-18 J |  |
has value 4.35974381 × 10-18 J  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| is an instance of energy |  |
| Harvard College Observatory | has owner Harvard |  |
is an instance of observatory  |  |
| hassium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| HD 141569 | has distance 320 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of Libra |  |
| is an instance of star |  |
| He II Balmer alpha | has wavelength 1640 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of ionized helium Balmer line |  |
| He II Lyman alpha | has wavelength 303.78 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of ionized helium Lyman line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of resonance line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| He II Paschen alpha | has wavelength 4686 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of ionized helium Paschen line |  |
| He2-104 | has image   |  |
| is an instance of symbiotic star |  |
| head-tail galaxy | has definition A class of relatively weak radio sources associated with clusters of galaxies and characterized by a high-brightness "head" close to the optical galaxy and a long low-brightness "tail". | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| HEAO | has definition High-Energy Astronomical Observatory. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of X-ray space telescope |  |
| heavy quark | is a kind of quark  |  |
| heavy-metal star | has definition A class of peculiar giant that includes the Ba II stars and the S stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| hecto | has symbol h |  |
| has value 102 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| height | has definition Elevation above ground or distance upwards from a given level (especially sea level) to a fixed point. (See altitude.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of geocentric coordinate component |  |
| is an instance of length |  |
| Hektor | has albedo 0.28 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has asteroid number 624 |  |
| has definition Largest and brightest Trojan asteroid. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 100 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity large | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 6.9225 hours | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has shape elongated | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has visual magnitude +14.5 (at mean opposition) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Trojan asteroid |  |
| is an instance of Trojan asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| heliocentric cosmology | has definition School of models in which the sun was portrayed as standing at the center of the universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| heliograph | has definition Device for recording the positions of sunspots. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| helion mass | applies to particle helion |  |
| has symbol mh |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000039 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 5.00641174 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| helium | has abundance 0.008 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 4 × 10-6 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 5.2 p.p.m. by volume in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| has abundance 6.31 × 1010 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 1083.025 nm for He I |  |
| has atomic emission line 1868.534 nm for He I |  |
| has atomic emission line 2058.130 nm for He I |  |
| has atomic emission line 388.865 nm for He I |  |
| has atomic emission line 587.562 nm for He I |  |
| has atomic emission line 1083.034 nm for He I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 2 |  |
| has atomic radii 128 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 4.216 K |  |
| has chief source natural gas which may contain up to 7% helium |  |
| has critical pressure 229 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 5.25 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 353.1, c = 569.3 pm for α-He at 1.15 K, 6.69 MPa |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 411 pm for γ-He at 1.73 K, 2.94 MPa |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 424.0 pm for β-He at 16K, 127 MPa |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for γ-He at 1.73 K, 2.94 MPa |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. for β-He at 16K, 127 MPa |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for α-He at 1.15 K, 6.69 MPa |  |
| has daily dietary intake very low |  |
| has definition |  |
| has definition Colourless, odorless gas obtained mainly from gas wells. Element which, after hydrogen, is the second lightest and second most abundant in the Universe. Its atom comprises two protons and two electrons. The nucleus of helium 4 is sometimes called an alpha particle. Helium is the product of the nuclear fusion of hydrogen in most stars, but this does not explain the overall helium abundance. Most of it was produced by the big bang, with main-sequence stars making an additional contribution. | ![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 0.1785 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 124.8 kg m-3 for liquid at 4.216 K boiling point |  |
| has discoverer Norman Lockyer and Edward Frankland |  |
| has discovery date 1868 |  |
| has discovery location England |  |
| has electron affinity 0.0 kJ mol-1 from to - |  |
| has electron configuration 1s2 = [He] in ground state |  |
| has hazard harmless but could asphyxiate if it excludes oxygen from the lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 0.021 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 0.082 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has isotope mass range 3 to 8 except 7 |  |
| has lethal intake non-toxic |  |
| has level in humans traces |  |
| has longest lived isotope helium 4 |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.207 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.383 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -5.9 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person very small for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 0.95 K under pressure |  |
| has mineral present in some minerals |  |
| has molar volume 32.07 cm3 at 4 K |  |
| has name origin helios = sun from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.326 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 5 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 2 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| has pronunciation heel-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7440-59-7 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 4.005602 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 3.7 × 109 tonnes in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| has space group Fm3m for β-He at 16K, 127 MPa |  |
| has space group Im3m for γ-He at 1.73 K, 2.94 MPa |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for α-He at 1.15 K, 6.69 MPa |  |
| has specimen small pressurized canisters. Safe. |  |
| has stable isotope helium 3, helium 4 |  |
| has symbol He |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.152 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.007 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has uses deep-sea diving, weather baloons, low temperature research |  |
| has van der Waals radii 120 pm |  |
| has world production 4500 tonnes year-1 |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of light element |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with nothing |  |
| helium 3 | has atomic mass 3.01602931 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -20.378 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.000137 % stable isotope |  |
| has NMR frequency 76.178 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.00326 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -2.127624 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2 |  |
| has number of neutrons 1 |  |
| has number of nucleons 3 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.44 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 3He |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, tracer |  |
is an instance of helium  |  |
| helium 4 | has atomic mass 4.00260324 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.999863 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 2 |  |
| has number of nucleons 4 |  |
| has symbol 4He |  |
is an instance of helium  |  |
| helium 6 | has atomic mass 6.018886 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.5010 Mev) 100 % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 0.807 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 4 |  |
| has number of nucleons 6 |  |
| has symbol 6He |  |
is an instance of helium  |  |
| helium 8 | has atomic mass 8.03392 |  |
| has decay mode β- (14 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode β- n |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 0.119 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 8 |  |
| has symbol 8He |  |
is an instance of helium  |  |
| helium burning | has definition The stage when a star fuses helium into carbon and oxygen. All stars born with more than half a solar mass eventually burn helium. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 5 × 105 years |  |
| has next higher temperature reaction carbon burning |  |
| has optimum density 700 g/cm3 |  |
| has optimum temperature 2 × 108 K |  |
| has part product carbon |  |
| has product carbon, oxygen |  |
| has reactant helium |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| requires minimum mass at star birth 0.5 solar masses |  |
| Helium discontinuity | has species helium (He I) |  |
| is a kind of absorption edge |  |
| helium flash | has definition The onset of runaway helium burning under degenerate conditions. The helium flash occurs in the hydrogen-exhausted core of a star in the red-giant phase of evolution. When gravitational pressure has brought the degenerate core to a temperature of about 108 K, the helium nuclei can start to undergo thermonuclear reactions. Once the helium burning has started, the temperature builds up rapidly (without a cooling, stabilizing expansion), and the extreme sensitivity of the nuclear reaction rate to temperature causes the helium-burning process to accelerate. This in turn raises the temperature, which further accelerates the helium burning, until a point is reached where the thermal pressure expands the core and thus removes the degeneracy and limits the flash. The helium flash can only occur when the helium core is less than the 1.4 Msun Chandrasekhar mass limit and thus it is restricted to low-mass stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has minimum temperature 108 K |  |
| is a kind of helium burning |  |
| helium problem | has definition Poses the question: what physical process caused the current abundance of helium in the Universe? | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of problem |  |
| helium shell flash | has definition It has been shown that helium shell burning outside a degenerate core is unstable; the helium-burning shell does not generate energy at a constant rate but instead produces energy primarily during short flashes. During a flash, the region just outside the helium-burning shell becomes unstable to convection. The resultant mixing probably leads to the s-process as well as to the upward movement of carbon produced by helium burning. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of helium burning |  |
| helium temperature scale | has approval date 1958 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The vapour pressure of helium 4 is used as an indication of temperature in the region 1 to 5.2 K. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| helium variable star | has definition Bp star in which the strength of the helium lines varies periodically. At the extreme phases the objects appear as helium-rich, whereas at other phases He can be very weak or absent. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Bp star |  |
| helium-strong star | has definition B star in which the helium lines are stronger than in normal stars. One distinguishes usually the extreme helium stars (also called hydrogen-deficient stars), in which no trace of hydrogen is seen, and the intermediate helium-rich stars, in which the hydrogen lines are still visible, but weaker than in normal stars. Related to these objects are the hydrogen deficient C stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| helium-weak star | has definition B-type star in which the helium lines are weaker than in normal stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Bp star |  |
| Helix Nebula | has definition A planetary nebula with the largest known angular diameter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 140 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| Helix nebula | has distance 450 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym NGC 7293 |  |
| Helix Nebula | has synonym NGC 7293 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Aquarius | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| Helix nebula | is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Aquarius |  |
| henry | has base unit m2·kg·s-2·A-2 |  |
| has symbol H |  |
| has unit Wb·A-1 |  |
| is an instance of inductance unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| Henry Draper catalog | has number of objects 225300  |  |
| has object properties position, spectral type and magnitude |  |
| has publication date 1924 |  |
| is a kind of star catalog |  |
| Hera | has definition Unofficial name for Jupiter VII. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Perrine | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1905 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.21 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 28° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 259.65 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter VII | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| Hercules | has acronym Her |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Herculis |  |
| has historical origin Hercules defeated the Nemean Lion (Leo), the many-headed beast (Hydra) and the little crab (Cancer) |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Hercules cluster | has definition An unsymmetrical cluster. Half of the galaxies are spiral or irregular and about half elliptical or S0. It contains a rather large number of disturbed and peculiar galaxies. The "missing mass", if present, must constitute more than 95% of the total. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 75 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has redshift z = 0.036 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1551 + 15 |  |
| is a part of Hercules |  |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is an instance of galaxy cluster |  |
| Hercules X-1 | has definition An X-ray pulsar, a member of an occulting binary system. The visible component has been identified as the blue variable HZ Herculis, whose spectrum varies from late A or early F to B. Her X- l has a pulsation period of 1.2378 seconds, presumably its rotation period, and exhibits a 35-day quasi-periodicity in the X-ray region (but not in the optical). It is probably a rotating neutron star in a circular orbit with a mass of about 0.7 Msun, which is accreting matter from HZ Her. The orbital period is stable, but the pulsation period is speeding up at a rate of about 1 part in 105 per year. The X-ray eclipse lasts 0.24 days. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 5 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e < 0.1 |  |
| has eclipse duration 0.24 days (in X-rays) |  |
| has orbital period 1.7 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 1653+35 |  |
| is a part of Hercules |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of X-ray pulsar |  |
| hertz | has base unit s-1 |  |
| has definition A unit of frequency equal to one cycle (or wave) per second. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Hz |  |
| is a kind of frequency unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| Hertzsprung | is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| Hestia | has definition Unofficial name for Jupiter VI. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Perrine | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1904 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.16 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 29° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 250 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter VI | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| heterotic e-string theory | has definition One of the five superstring theories; involves closed strings whose right-moving vibrations resemble those of the Type II string and whose left-moving vibrations involve those of the bosonic string. Differs in important but subtle ways from the Heterotic-O string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym E8 × E8 | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of heterotic string theory |  |
| heterotic o-string theory | has definition One of the five superstring theories; involves closed strings whose right-moving vibrations resemble those of the Type II string and whose left-moving vibrations involve those of the bosonic string. Differs in important but subtle ways from the Heterotic-E string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym O(32) | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of heterotic string theory |  |
| heterotic string theory | has definition Gross's version of string theory in which space-times of different dimensions are associated with the same closed loop. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of superstring theory |  |
| HF band | has frequency 3 to 30 MHz |  |
| has wavelength 10 to 100 m |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| Hidalgo | has asteroid number 944 |  |
| has definition Asteroid with the largest known orbit with the second highest inclination to the ecliptic and second highest eccentricity of any asteroid. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 20 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Baade | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1920 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.66 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination 42°.5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbirtal period 13.7 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 5.8 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| hierarchy problem | has definition In the context of grand unified theories, the hierarchy problem is our inability to understand theoretically why the energy scale at which the unification becomes apparent, about 1016 GeV (billion electron volts), is so much higher than other energy scales of relevance to particle physics, such as the mass/energy of a proton, which is only 1 GeV. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of problem |  |
| Higgs boson | has definition A hypothetical, spinless particle that plays an important role in the Glashow-Weinberg-Salam electroweak theory (and in other theories involving spontaneous symmetry breaking, e.g. GUTs). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The particle or particles associated with the bundles of energy in the Higgs field. Such particles are analogous to the photons that are associated with the electromagnetic field. The standard model of particle physics predicts one electrically neutral Higgs particle which has not yet been found, but which will be sought in upcoming particle accelerator experiments. The grand unified theories predict many Higgs particles, but they are too massive to be accessible at existing or foreseeable accelerators. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of boson |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center | HEASARC -has URL: http://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov |  |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| high energy detector | has definition Device for recording the presence of subatomic particles. A typical modem detector consists of an array of electronic sensors connected to a computer, capable of recording the paths of the particles as they fly out from the collision site in a particle accelerator. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of instrument |  |
| High energy peaked BL Lac object | has acronym HBL |  |
| is a kind of BL Lacertae |  |
| high energy physics | is a kind of physics |  |
| high energy physics institution | is a kind of institution |  |
| high proper motion star | has proper motion high |  |
| is a kind of high-velocity star |  |
| high-velocity star | has definition A star whose U and/or V and/or W velocities are much greater or much less than zero. Such stars usually have eccentric orbits around the Galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Late type stars whose spatial velocities are greater than 100 km s-1. Other authors prefer the definition, with radial velocities greater than 60 km s-1. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has spatial velocity > 100 km s-1 | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| higher-dimensional supergravity | has definition Class of supergravity theories in more than four spacetime dimensions. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supergravity |  |
| highly polarized quasar | has acronym HPQ |  |
| is a kind of quasar |  |
| Hiltner Telescope | has altitude 1938 m |  |
| has aperture 2.34 m |  |
| has comment Mirrors repolished 1991 |  |
| has creation date 1986 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.07, 13.5 |  |
| has latitude 31° 57' N |  |
| has location Kitt Peak, Arizona, US |  |
| has longitude 111° 37' W |  |
| has mirror maker Contraves (USA) |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting Equatorial fork, friction-disk drives |  |
| has mounting manufacturer DFM Engineering, L & F Industries |  |
| has owner Michigan-Dartmouth-MIT Obs. |  |
| has synonym Hiltner 2.3 m |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| Hind's nebula | has definition A reflection nebula illuminated by the star T Tauri. It is remarkable for its changes in brightness. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Hind | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1852 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 1554, NGC 1555 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of dust |  |
| is a part of Taurus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of reflection nebula |  |
| Hiparcos catalog | is a kind of star catalog |  |
| Hipparcos | is an instance of ESA satellite |  |
| Hirayama family | has definition A group of asteroids with similar orbital elements. The members of a given family are widely believed to have resulted from collisions between larger parent bodies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of asteroid |  |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| HK line | is a kind of interstellar line |  |
| HK lines | has definition Two spectral lines of singly ionized calcium. The second strongest interstellar line. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Ca II |  |
| is a kind of Fraunhofer line |  |
| Hobby-Eberly Telescope | has altitude 2002 m |  |
| has aperture 9.2 m equivalent |  |
| has comment A project of five universities in US and Germany; 91 spherical mirrors with combined focus for spectroscopy |  |
| has creation date 1997 |  |
| has focal ratio (f/1.4) f/4.7 |  |
| has latitude 30° 41' N |  |
| has location Mount Fowlkes, Texas, US |  |
| has longitude 104° 01' W |  |
| has mirror maker Univ. of Texas, Penn. State |  |
| has mounting altazimuth fixed in altitude but rotates in azimuth |  |
| has optical design Spherical figure |  |
| has owner University of Texas |  |
| has purpose spectroscopic survey telescope |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| hold-time | has definition The time taken to use up all the liquid cryogens, like LN2, in a cooled CCD cryostat. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| Holmberg radius | has definition The radius of an external galaxy at which the surface brightness is 26.6 mag arcsec-2. This criterion was developed by Holmberg in 1958 to estimate the actual dimensions of the major and minor axes of a galaxy without regard to its orientation in space. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| holmium | has image 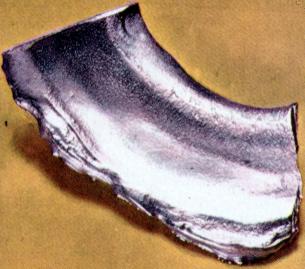 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| hologram | has definition An interferometric method of recording information about the three-dimensional nature of an object which relies on preserving both the amplitudes and phases of the wavefronts which reach the detector, instead of merely the amplitudes. Hologram means "whole record". The basic principle was outlined by D. Gabor in 1948. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| honeycomb mirror | has definition A construction method for a large mirror in which the back is hollowed-out to leave a ribbed structure that resembles a honeycomb. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| Hooker Telescope | has altitude 1742 m |  |
| has aperture 2.5 m |  |
| has comment telescope out of service 1985-92 |  |
| has creation date 1917 |  |
| has focal ratio f/5, 16, 30 |  |
| has latitude 34° 13' N |  |
| has location Mount Wilson, Calif., US |  |
| has longitude 118° 03' W |  |
| has mirror maker G.W. Ritchey from Saint-Gobain (Paris) |  |
| has mirror type plate-glass |  |
| has mounting manufacturer FG. Pease and Fore River Shipyards |  |
has owner Mount Wilson Observatory  |  |
| has synonym 100 inch |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of English equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| horizon | has definition A plane perpendicular to the line from an observer to the zenith. The great circle formed by the intersection of the celestial sphere with a plane perpendicular to the line from an observer to the zenith is called the astronomical horizon. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The maximum distance that an observer can see. In cosmology, our horizon is the distance from us that light has traveled since the beginning of the universe. Objects more distant than our horizon are invisible to us because there hasn't been enough time for light to have traveled from there to here. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| horizon problem | has definition A problem of the traditional big bang theory (without inflation) related to the large scale uniformity of the observed universe. The problem is seen most clearly in the cosmic background radiation, which is believed to have been released at about 300000 years after the big bang, and has been observed to have the same temperature in all directions to an accuracy of one part in 100,000. Calculations in the traditional big bang theory show that the sources of the background radiation arriving today from two opposite directions in the sky were separated from each other, at 300000 years after the big bang, by about 100 horizon distances. Since no energy or information can be transported further than one horizon distance, the observed uniformity can be reconciled only by postulating that the universe began in a state of near-perfect uniformity. See also flatness problem. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A quandary in standard big bang theory, which indicates that few of the particles of the early universe would have had time to be in causal contact with one another at the outset of cosmic expansion. It appears to have been resolved in the inflationary universe theory. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Cosmological puzzle associated with the fact that regions of the universe that are separated by vast distances nevertheless have nearly identical properties such as temperature. Inflationary cosmology offers a solution. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The puzzle that widely separated regions of the universe are observed to share the same physical properties, such as temperature, even though these regions were too far apart when they emitted their radiation to have exchanged heat and homogenized during the time since the beginning of the universe. In particular, we detect the same intensity of cosmic radio waves (cosmic background radiation) from all directions of space, suggesting that the regions that emitted that radiation had the same temperature at the time of emission. However, at the time of emission, when the universe was about 1 million years old, those regions were separated by roughly 100 million light years, much exceeding the distance light or heat could have traveled since the big bang. The horizon problem is also called the causality puzzle. (See horizon.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym homogeneity problem | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of problem |  |
| horizontal branch star | has color blue to yellow |  |
| has definition A metal-poor star after it has undergone the helium flash and begins to quietly burn helium into carbon and oxygen in its core and hydrogen in a surrounding envelope. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has location on H-R diagram extends shortward from the asymptotic branch at an approximately constant absolute bolometric magnitude of about 0.3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of metal-poor star |  |
| horizontal parallax | has definition The difference between the topocentric and geocentric positions of an object, when the object is on the astronomical horizon. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of parallax |  |
| Horologium | has acronym Hor |  |
| has genitive Horologii |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the clock in honor of Christian Huygens, the inventor of the pendulum clock in 1656-57 |  |
| has synonym Clock |  |
| has synonym Horologium Oscillitorium |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Horsehead Nebula | has definition An absorption nebula in the middle of Orion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 2024 |  |
| is a part of dust |  |
| is an instance of dark nebula |  |
| Horseshoe equatorial telescope | has mounting Horseshoe equatorial | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| hot dark matter | has definition Any form of dark matter which was relativistic at its point of decoupling. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dark matter |  |
| hour | has symbol h |  |
| has value in SI unit 60 min = 3600 s |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| hour circle | has definition A great circle passing through the celestial poles - i.e., perpendicular to the celestial equator. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of great circle |  |
| Hourglass Nebula | has definition A compact H II region in the center of Lagoon Nebula. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 8000 light-years away |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym MyCn18 |  |
| is a part of Lagoon Nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of compact H II region |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| Hoyle-Narlikar theory | has definition A reformulation of the general theory of relativity that incorporates and extends Mach's principle (q.v.). In this theory, the inertial mass of a particle is a function of the masses of all other particles, multiplied by a coupling constant which is a function of cosmic epoch. In cosmologies based on this theory, the gravitational constant G decreases strongly with time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| HR 4247 | has B-V magnitude 1.04 |  |
| has declination +34 12 53 |  |
| has right ascension 10 53 18.6 |  |
| has spectral type K0III-IV |  |
| has V magnitude 3.83 |  |
is a part of Leo Minor  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| HR 4796A | has image   |  |
| is an instance of star |  |
| HRS | has definition High-Resolution Spectrograph (Hubble). | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating spectrograph |  |
| Hubble | has birth date November 20, 1889 |  |
| has career |  |
| has death date September 28, 1953 |  |
has degree - 1910 : BSc. U. Chicago
- 1913 : law, Oxford
- 1917 : PhD. Yerkes, ("Photographic Investigations of Faint Nebulae", Frost as supervisor)
|  |
has image  |  |
| has name Edwin Powell Hubble |  |
has orbituary - Adams, W.S. : 1954, Observatory 74, 32.
- Humason, M.L. : 1954, MNRAS 114, 291.
- Robertson, H.P. : 1954, PASP 66, 120.
- Sandage, A. : 1989, JRASC 83, 352.
|  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
is an instance of astronomer   |  |
| Hubble 5 | has distance 2200 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Sagittarius |  |
| Hubble constant | has definition According to Hubble's law, discovered by Edwin Hubble in 1929, distant galaxies are receding from us, on average, with a speed equal to the product of the Hubble constant and the distance to the galaxy. Hubble's "constant" is independent of distance, but actually decreases slowly in time as the expansion is slowed by the gravitational pull of each galaxy on all the others. The present value is somewhere between 15 and 30 kilometers per second per million light-years. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Hubble's constant in units of 100 km s-1 Mpc-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The constant of proportionality in the Hubble law. Its value must vary with time, so it is often referred to as the Hubble parameter. The Hubble constant is generally used to mean the value of the Hubble parameter at the current epoch, and is somewhere between 50 and 100 km/s/Mpc with possibly a value close to 75 km/s/Mpc. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The present expansion rate of the universe, in units of kilometers per second per megaparsec. The larger the Hubble constant, the younger the universe. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The rate at which the universe expands, equal to approximately fifty kilometers of velocity per megaparsec of distance. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The rate of expansion of the universe. The Hubble constant is equal to the recessional speed of a distant galaxy, divided by its distance from us. Assuming a homogeneous and isotropic universe, the recessional speed of a distant galaxy is proportional to its distance; thus the Hubble constant as determined by any receding galaxy should be the same, yielding a universal rate of expansion of the universe. According to estimates, the current value of the Hubble constant is approximately 100 km/s/Mpc, meaning that the distance between any two distant galaxies will double in about 10 billion years at the current rate of expansion. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has rate of change non-zero because gravity is slowing down the rate of expansion of the universe | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol H0 | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit km/s/Mpc | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 75 km/s/Mpc | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| Hubble flow | has definition The movement of the galaxies away from us caused by the expansion of the Universe. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy motion |  |
| Hubble law | has definition A relation which states that recessional speed is proportional to distance for a homogeneous and isotropic universe. Galaxies moving away from us with a speed precisely following this relation are said to follow the Hubble flow. Because the actual universe is not precisely homogeneous, with lumpiness arising from clustering of galaxies and voids of empty space, the motions of actual galaxies deviate somewhat from the Hubble flow. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| Hubble nebula | has definition A cometary nebula whose apex star is R Mon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 2261 |  |
| is a part of dust |  |
| is an instance of cometary nebula |  |
| Hubble radius | has definition The radius of the observable universe (). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol c/H |  |
| has value > 1027 cm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| Hubble Space Telescope | has acronym HST |  |
| has acronym HST |  |
| has angular resolving power 0.05 arcseconds |  |
| has aperture 2.4 m |  |
| has creation date 1981 |  |
| has creation date 1990 |  |
| has definition Hubble Space Telescope. A space-based reflecting telescope with a primary mirror diameter of 2.4 m (94 in) capable of high-resolution imaging from the far ultraviolet to the near infrared. A joint NASA/ESA mission. Launched in 1990 with a planned lifetime of 15 years. Encountered reduced performance when the mirror was found to have spherical aberration. Solved by the installation of corrective optics (COSTAR) in 1994. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has effective diameter 2.1 meters |  |
| has elliptical orbit 500 km altitude, 35 degree inclination |  |
| has focal ratio f/12.9, 30, 48, 96 |  |
| has launch date 1986 |  |
| has location Earth orbit |  |
| has mirror maker Perkin Elmer |  |
| has mirror type Corning ULE glass |  |
| has mounting 3-axis-stabilized spacecraft |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Lockheed |  |
has owner Space Telescope Science Institute  |  |
has reference Hubble Space Telescope from CADC  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| is an instance of optical space telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| orbits Earth |  |
| Hubble time | has definition The Hubble time is one divided by the Hubble constant, which gives a number from 10 to 20 billion years. For a flat universe with no cosmological constant, the age of the universe is two-thirds of the Hubble time. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The inverse of the Hubble constant and a crude measure of the universe's age. For a Hubble constant of 50, one can calculate that the Hubble time is 19.6 billion years; for a Hubble constant of 80, the Hubble time is 12.2 billion years. If there is no cosmological constant, the universe is younger than the Hubble time. In particular, if the mass density of the universe (designated Ω) is 0.1, the universe's age is 90 percent of the Hubble time; if Ω is 1.0, the universe's age is 67 percent of the Hubble time. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol H0-1 |  |
| has value 10 to 20 billion years | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| is an instance of time |  |
| Hulse-Taylor pulsar | has definition A binary pulsar probably consisting of a neutron star and an even more compact object in an eccentric orbit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1974 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 0.3230 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has pulsation period 59 ms | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym PSR 1913+16 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary pulsar |  |
| Humason | has name Milton La Salle Humason |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| is associated with Mayall |  |
| Hyades | has age 5 × 108 yr | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has composition spectral types A1-K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 40 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has note Aldebaran is a foreground star in that region of the sky, it is not a member of the Hyades. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars 200 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has radial velocity + 36 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Taurus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| is an instance of open cluster |  |
| hybrid array | has definition A device in which the roles of radiation (infrared mostly) detector and signal multiplexer are separated. The device is a sandwich of two slabs. Other names include focal plane array (FPA) and sensor chip assembly (SCA). | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| Hydra | has acronym Hya |  |
| has genitive Hydrae |  |
| has synonym Serpent of Lerna |  |
| has synonym Water Monster |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| hydrodynamic soliton | has definition A finite-amplitude disturbance which is propagated through a fluid without any change of shape. MHD solitons are also known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| hydrodynamics | has definition The study of how gases and fluids flow under applied forces. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dynamics |  |
| hydrogen | has abundance 0.5 p.p.m. by volume in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| has abundance 1 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 1520 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance main constituent of water; some dissolved H2 in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 1875.10 nm for H I |  |
| has atomic emission line 434.047 nm for H I |  |
| has atomic emission line 486.133 nm for H I |  |
| has atomic emission line 656.272 nm for H I |  |
| has atomic emission line 656.285 nm for H I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 1 |  |
| has atomic radii 78 pm |  |
| has biological role constituent element of DNA. Component of water, essential to life. |  |
| has boiling point 20.28 K |  |
| has chief source natural methane gas |  |
| has covalent radii 30 pm |  |
| has critical pressure 1297 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 33.35 K |  |
| has daily dietary intake mainly as water |  |
| has definition |  |
| has definition Colourless, odourless gas, insuluable in water. Lightest, most abundant element in the Universe. Its atom comprises one proton and one electron. The element occurs both in stars and as interstellar clouds, in regions where it may be neutral (H I regions) or ionized (H II regions). It was produced by the big bang. Hydrogen 1 is the most common isotope; deuterium, is rarer; and tritium, is radioactive. | ![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 0.08988 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 70.8 kg m-3 for liquid at 20.28 K boiling point |  |
| has density 76.0 kg m-3 for solid at 11 K |  |
| has discoverer H. Cavendish |  |
| has discovery date 1766 |  |
| has discovery location London, England |  |
| has electron affinity 72.8 kJ mol-1 from H to H- |  |
| has electron configuration 1s1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.20 Pauling |  |
| has French translation hydrogene |  |
| has German translation Wasserstoff |  |
| has hazard flammable and explosive when mixed with air; can asphyxiate if it excludes oxygen from lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 20.784 J K-1 mol-1 for atomic gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 28.824 J K-1 mol-1 for molecular gas (H2) at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 0.12 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 0.46 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 0.00066 pm for H+ |  |
| has ionic radii 154 pm for H- |  |
| has isotope mass range 1 to 3 |  |
| has Italian translation idrogeno |  |
| has lethal intake non-toxic |  |
| has level in humans 52000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 93000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 93000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans constituent of water in blood |  |
| has longest lived isotope hydrogen 1 |  |
| has main mining area |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.380 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.435 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -2.50 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person 7 kg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 14.01 K |  |
| has mineral water |  |
| has molar volume 13.26 cm3 |  |
| has name origin hydro genes = water forming from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length -0.37390 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 3 |  |
| has number of protons 1 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has pronunciation hy-dro-jen |  |
has registry number 1333-74-0 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 1.00794 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves almost limitless |  |
| has Spanish translation hidrogeno |  |
| has specimen small pressurized canisters. Warning ! |  |
| has stable isotope hydrogen 1, deuterium |  |
| has symbol H |  |
| has synthesis mechanism CH4 + 2H2O = 3H2 + CO (main production mechanim) |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of brine using a mercury amalgam cell (minor production mechanism) |  |
| has synthesis mechanism steam flowing over red hot coke produces H2 and CO (minor production mechanism) |  |
| has term symbol 2S1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.1815 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K for gas |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.3326 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has triple point temperature 13.96 K at 7.2 kPa |  |
| has uses making ammonia, cyclohexane, methanol, etc. |  |
| has van der Waals radii 120 pm |  |
| has world production 350 × 109 m3 year-1 as H2 gas |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of light element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with air explosively |  |
| hydrogen 1 | has atomic mass 1.0078 |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 377.6, c = 616.2 pm for h.c.p. |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 450, c = 368 pm for tetragonal |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 533.8 pm for cubic |  |
| has crystal type cubic for cubic |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for h.c.p. |  |
| has crystal type tetragonal for tetragonal |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 26.7510 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.985 % |  |
| has NMR frequency 100.000 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 5680 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.7928456 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2 |  |
| has number of neutrons 0 |  |
| has number of nucleons 1 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 1.0 by definition |  |
| has space group Fm3m for cubic |  |
| has space group I4 for tetragonal |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for h.c.p. |  |
| has symbol 1H |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of hydrogen  |  |
| hydrogen burning | has catalyst |  |
| has definition The fusion of hydrogen into helium and the process by which all main-sequence stars generate energy. Every star born with more than 0.08 solar masses burns hydrogen. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has minimum mass 0.08 solar masses |  |
| has next higher temperature reaction helium burning |  |
| has product helium |  |
| has reactant hydrogen |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| hydrogen cyanide | has symbol HCN |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| hydrogen isocyanide | has symbol HNC |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| hydrogen line | has definition Set of spectral features associate with neutral hydrogen (H I) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has species hydrogen (H I) |  |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| hydrogen sulfide | has symbol H2S |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| hydrogen-deficient C star | has definition A subgroup of high-luminosity C stars with weak or absent hydrogen lines, mostly of types F and G. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type F star, G star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C star |  |
| is a kind of hydrogen-deficient star |  |
| hydrogen-deficient early type star | has definition Early type star of type O, B or A in which the hydrogen lines are very weak or absent. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O star, B star or A star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen-deficient star |  |
| hydrogen-deficient star | has hydrogen line strength weak |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| hydroxyl radical | has definition An interstellar molecule first detected in 1963 at a wavelength of 18 cm. The four transitions that occur near 18 cm are caused by the splitting of the ground level. Galactic OH sources have been divided into three classes according to whether the OH emission is strongest in the main lines, particularly at 1665 MHz (Class 1), whether the emission and absorption are highly anomalous only in the satellite lines (Class 2) (Class 2a, 1720-line emitters; Class 2b, 1612-line emitters), or whether there is only absorption in all four lines (Class 3). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol OH |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Hydrus | has acronym Hyi |  |
| has genitive Hydri |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin Julius Schiller combined Hydrus and Tucana to form the Biblical figure Archangel Raphael |  |
| has synonym Sea Serpent |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| hyperbola | is a kind of conic section |  |
| hyperbolic orbit | is a kind of hyperbola |  |
| is a kind of orbit |  |
| hypergalaxy | has definition A system consisting of a dominant spiral galaxy surrounded by a cloud of dwarf satellite galaxies, often ellipticals. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of galaxies |  |
| Hyperion | has definition Eighth satellite of Saturn | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 160 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Bond | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1848. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 21d6h38m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| hyperon | has definition Baryons heavier than the neutron (this term is seldom used today). They have non-zero strangeness. Free hyperons are unstable and decay into end products, one of which is a proton. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime 10-8 to 10-10 seconds | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 1/2 or 3/2 |  |
| is a kind of baryon |  |
| is a kind of radioactive particle |  |
| hypothesis | has definition A scientific proposition that purports to explain a given set of phenomena; less comprehensive and less well established than a theory. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of abstraction |  |
| hypothetical particle | has acceptance status hypothetical |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| Iapetus | has definition The ninth satellite of Saturn. It has the most extreme variation in albedo of any satellite in the solar system (0.04 for the leading side, 0.28 for the trailing side). Discovered by Cassini in 1671. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccetricity e = 0.028 |  |
| has inclination inclination 14°.7 to Saturn's orbital plane |  |
| has period 79d7h55m |  |
| has radius 850±100 km |  |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| IC 1613 | is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of irregular galaxy |  |
| IC 3568 | has distance 9000 light years |  |
| has extent 0.4 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Camelopardalis |  |
| Icarus | has asteroid number 1566 |  |
| has definition Asteroid with the smallest orbit and highest eccentricity of any asteroid. It is the only asteroid known to come closer to the Sun than Mercury. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1.1 km |  |
| has dicovery date 1948 |  |
| has discoverer Baade |  |
| has eccetricity e = 0.827 |  |
| has inclination i = 23° |  |
| has perihelion distance 0.19 AU |  |
| has period P = 408d |  |
| has rotation period 2h16m |  |
| has semi-major axis a = 1.07 AU |  |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid |  |
| ideal gas | has definition A nondegenerate gas in which the individual molecules are assumed to occupy mathematical points and to have zero volume, and in which the mutual attraction of neighboring molecules is zero. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition he pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the product of its temperature and density (p = CρT). The higher the temperature and the more rarefied a gas, the more closely it obeys the ideal gas laws, so the gases in most stars closely approximate ideal gases. For a degenerate gas, the pressure depends only on the density and is independent of the temperature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym perfect gas | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gas |  |
| image dissector scanner | has definition A specialized television camera used as a light detector (instead of a photographic plate) in the 1970's. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| image intensifier | has definition An electronic device for increasing the brightness of a faint optical image. The image is first formed on a thin metallic surface called a photocathode from which electrons are then ejected. The stream of electrons is accelerated and focussed onto a phosphorescent screen which glows brightly as a result of the impact. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of imager |  |
| image photon counting system | has acronym IPCS |  |
| has definition A form of very low light level detector used in astronomy. By means of an image intensifier the IPCS is capable of counting individual photons of light. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of image intensifier |  |
| Image Reduction and Analysis Facility | has acronym IRAF | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An extensive suite of programs developed for astronomy applications and supported by the US National Optical Astronomy Observatories. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| image tube | has definition An electronic camera in which electrons, emitted from a photocathode surface exposed to light, are focused electronically onto a phosphor or photographic plate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym image intensifier |  |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| imager | is a kind of detector |  |
| imaging spectrometer | has definition Class of instruments which preserve the image field while also determining the spectrum. Integral Field Unit (IFU). Usually implies some kind of image slicing either with facets or fiber optics. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| immersion | has definition The disappearance of a celestial body due to eclipse or occultation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of occultation phase |  |
| is followed by transit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| impact event | has definition The collision of two celestial bodies  |  |
| is a kind of celestial event |  |
| can produce a crater |  |
| incandescent flight | has definition phase in the flight of a meteor before the ratardation point when the meteoroid is producing its own incandescent light |  |
| has duration from the point of intial contact with atmosphere until the retardation point |  |
| has start time the point of intial contact with the atmosphere |  |
| is an instance of meteor event |  |
| inclination | has definition An orbital element representing the inclination of the object's orbital plane to the ecliptic |  |
| has definition The angle between one plane and another. The (equatorial) inclination of a planet is the angle between the plane of its equator and that of its orbit. The inclination of the orbit of a planet in the Solar System other than Earth is the angle between the plane of that orbit and the ecliptic. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The angle between two planes or their poles; usually the angle between an orbital plane and a reference plane. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol i | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of orbital element | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| indium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of group III element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| inductance | has unit inductance unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| inductance unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of inductance |  |
| induction | has definition System of reasoning in which the conclusion, though implied by the premises and consistent with them, does not necessarily follow from them. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of reasoning process |  |
| Indus | has acronym Ind |  |
| has genitive Indi |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin Julius Schiller combined Indus and Pavo to form the Biblical figure Job |  |
| has synonym American Indian |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| inelastic collision | has definition A reaction involving a change in the kinetic energy of the system, as in ionization, excitation, or capture; or a process which changes the energy level of the system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collision |  |
| inert gas | has group 18 |  |
| has synonym group VIII element |  |
| has synonym noble gas |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| inflatable spacecraft | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| inflation era | has definition Big Bang era in which the infant universe went through a brief period of extremely rapid (exponential) expansion, after which it settled back into the more leisurely rate of expansion of the standard model. The period of rapid expansion began and ended when the universe was still much less than a second old, yet it provides a physical explanation for the flatness and horizon puzzles. The inflationary universe model also suggests that the universe is vastly larger than the portion of it that is visible to us. (See exponential expansion.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang era in which the spacetime continuum underwent an intense period of exponential expansion, in response to the separation of the strong nuclear force from the electroweak force. This idea solves the flatness and horizon problems. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang era in which the universe is driven into exponential expansion by the repulsive gravitational field created by a false vacuum. The inflation would end with the decay of the false vacuum. Although the inflation would occur in far less than a second, it could account for the "bang" of the big bang theory, it could explain the origin of essentially all the matter in the observed universe, and it can solve the horizon problem and the flatness problem. It could also generate the density perturbations that would later become the seeds for galaxy formation. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang era in which universe undergoes a brief burst of enormous expansion. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The idea that, when it was a fraction of a second old, the universe expanded dramatically. If inflation is correct, then the mass density of the universe (Ω) should be 1.0, if there is no cosmological constant; if there is a cosmological constant and inflation is correct, the sum of Ω and the cosmological constant (λ) should be 1.0. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has start time 10-35 s |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| infrared | has acronym IR | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition That part of the electromagnetic spectrum that lies beyond the red, having wavelengths from about 7500 Å to a few millimeters (about 1011-1014 Hz). Infrared radiation is caused by atomic transitions, or by vibrational (near-IR) and rotational (far-IR) transitions in molecules. (IRe1, IRc1, IRs1: the e sources are extended; the c sources are unresolved; the s indicates an infrared nebula surrounding a visible star.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The region of the electromagnetic spectrum from a wavelength of about 1 μm (10-6 m) to about 200 μm. The region from 1 to 5 µm is the near infrared: 5-30 is the mid infrared and 30-200 µm is the far infrared. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 3 THz to 430 THz |  |
| has wavelength 700 nm to 100 μm |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| infrared galaxy | is a kind of galaxy |  |
| infrared magnitude | has band |  |
| has definition The magnitude derived from the observations at an infrared wavelength |  |
| is a kind of apparent magnitude |  |
| is a kind of apparent magnitude |  |
| Infrared Space Observatory | is an instance of ESA satellite |  |
| infrared space telescope | has wavelength sensitivity 1 to 250 microns |  |
| is a kind of space telescope |  |
| inner bremsstrahlung | has definition The continuous electromagnetic radiation that accompanies the β-decay of nuclei. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of bremsstrahlung |  |
| inner Lagrangian point | has definition An unstable Lagrangian point between the two bodies on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies. Mass transfer occurs through this point in a close binary star system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has location between the two bodies on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym L1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of unstable Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| inner transition metal | is a kind of transition metal |  |
| inner Van Allen belt | has altitude 3000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has composition mostly protons | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has particle energy higher than the outer Van Allen belt | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Van Allen belt |  |
| inspector satellite | is a kind of reconnaissance spacecraft |  |
| Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimetrique | has acronym IRAM | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| Institute of Space and Astronautical Science | has acronym ISAS |  |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| institution | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| instrument | has definition a device that requires skill for proper use |  |
| has operator |  |
| is a kind of device |  |
| integer | has value whole number |  |
| is a kind of number |  |
| integrating detector | has definition Any imaging device, like a photographic emulsion or CCD, which can build up more signal and contrast by a longer exposure to light or other electromagnetic energy. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of imager |  |
| integration time | has definition The interval of time used to collect photons of light on a detector and build-up a strong signal. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| Interactive Data Language | has acronym IDL | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| intercombination line | has definition Spectral line emitted in transitions between two levels with different values of S. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| interference filter | has definition A filter used to shut out all light except the desired wavelengths. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A method of constructing an optical filter to select a particular wavelength band for transmission and reject wavelengths outside this band. Similar to a Fabry-Perot etalon. The construction relies on constructive and destructive interference effects in a multilayer stack of quarter-wave reflective layers and half-wave spacer layers. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph dispersing element |  |
| interline transfer | has definition A CCD construction consisting of vertical strips which are alternately opaque and light sensitive. The opaque strips conceal charge transfer registers. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| Intermediate Frequency | has acronym IF | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The beat frequency between the signal and the local oscillator in a radio detection system. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frequency |  |
| internal symmetry | has definition The properties of different elementary particles can be related to each other by mathematical transformations that look very much like the more familiar symmetry properties of our own physical space. Physicists have therefore hypothesized an abstract internal space in which these internal symmetries are defined. With the help of these internal symmetries, the elementary particles can be gathered into families. The relationship between space-time and these internal symmetries remains to be fully explained. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| International Astronomical Union | has acronym IAU | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| International temperature scale | has acronym ITS90 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
has definition A temperature scale defined between 0.65 K and the highest temperatures practicably measurable in terms of the Planck radiation law using monochromatic radiation. There are 17 fixed temperature points : - Below 5 K are defined in terms of the vapour pressures of helium 3 and helium 4
- Between 5 K and the triple point of water are marked by the triple points of certain elements, e.g. neon (24.5561 K)
- Above 0.01 °C are defined with reference to the freezing points of specified metallic elements
- Upper limit is 1064.43 °C (1337.58 K), the freezing point of gold
[JN92] -has source: J. A. Hall, 1967 |  |
| has proposal date 1927 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| interstellar band | is a kind of molecular band |  |
| interstellar gas | has composition mainly hydrogen |  |
| has definition Sparse, cool gas (mainly hydrogen) in interstellar space. Dust absorbs and scatters radiation; gas does not interact directly with radiation but is coupled to the dust by collisions. Interstellar gas affects only light of certain wavelengths. Temperature 10-100 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has density very low |  |
| is a kind of gas |  |
| interstellar line | has definition Sharp, distinct absorption lines superposed on stellar spectra, produced by the interstellar gas located between the source and the observer. Strongest are the D lines, followed by the H and K lines, and the K I doublet at 7699 and 7644 Å. |  |
| has detection procedure narrow absorption lines which don't participate in the periodic Doppler shift of intrinsic absorption lines in a binary star |  |
| has equivalent width depends on the amount of absorbing matter between the source and the observer |  |
| has width narrow |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| occurs in O stars |  |
| interstellar molecule | has definition Molecule present in interstellar space. As of late 1974, at least 33 molecular species had been identified with reasonable certainty. |  |
| has discovery in space date |  |
| is a kind of molecule |  |
| intrinsic luminosity | has definition The amount of light an object actually emits, as opposed to how bright the object looks from Earth. An apparently bright star can be intrinsically bright and far away or intrinsically faint and nearby. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The energy per second emitted by an astronomical object, analogous to the wattage of a light bulb. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of luminosity |  |
| invariable plane | has definition The plane through the center of mass of the solar system perpendicular to the angular momentum vector of the solar system. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| invariant plane | has definition The plane defined by the total angular momentum of the solar system. It is within about 1°.5 of the ecliptic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| inverse beta-decay | has definition The relatively rare process p + vbar → n + e+. Free-electron capture (e + p → n + v) is sometimes called inverse β-decay in astrophysics. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nuclear decay |  |
| inverse bremsstrahlung | has antonym bremsstrahlung |  |
| has definition Absorption of a photon by an electron in the field of a nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of absorption |  |
| is a kind of free-free transition |  |
| inverse Compton effect | has antonym Compton scattering |  |
| has definition The collision between a photon and an energetic (cosmic-ray) electron, in which some of the energy of the electron is transferred to the photon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| inverse P Cygni line | has definition An emission line in which the emission is on the violet side of the absorption. It is usually interpreted to mean infall of matter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| Io | has albedo 0.91 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The innermost Galilean satellite of Jupiter, similar in size and density to the Moon. Jupiter's decametric radiation has been linked at least partially to Io. It has the highest mean density of any of the Galilean satellites. Pioneer 10 also detected the presence of an ionosphere, and Na D emission. It also has the highest albedo in the solar system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.01 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 0.03 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 3.48 g (data from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has period 1.77 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R &asmyp; 1850 km (data from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has synonym Jupiter I |  |
| has synonym Jupiter I | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter |  |
| is an instance of Galilean satellite |  |
| iodine | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| has ocean residence time 300000 years |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of halogen |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| ionic tail | has charge large |  |
| has definition Straight part of comet tail composed of ions driven by the solar wind |  |
| has synonym type I comet tail | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of comet tail |  |
| ionization | has antonym recombination |  |
| has definition Loss or gain by an atom of one or more electrons, by which process the atom becomes an ion and instead of being neutral, has a charge: positive if it has lost an electron, negative if it has gained one. High temperature is particularly conducive to ionization. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of atomic process |  |
| ionization potential | has definition The minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It always takes a higher energy to remove a second electron from a singly ionized atom, a still higher energy to remove a third, etc. The ionization potential for hydrogen is 13.596 eV, which corresponds to a wavelength of 912 Å. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| ionized helium Balmer line | is a kind of ionized helium line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| ionized helium line | has definition Set of spectral features associate with ionized helium (He II) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has species ionized helium (He II) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| ionized helium Lyman line | has lower energy level 1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has series limit 227 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ionized helium line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| ionized helium Paschen line | has lower energy level 3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has series limit 2040 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ionized helium line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| ionized methylidyne | has charge 1 |  |
| has symbol CH+ |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| ionosphere | has definition The region of Earth's atmosphere (80-500 km), immediately above the stratosphere. The ionosphere consists of the D layer, the E layer, and the F layers (q.v.). It is strongest at the end of the day. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| IRAS | is an instance of infrared space telescope |  |
| orbits Earth |  |
| IRAS galaxy | emits excessive amounts of infrared light | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any galaxy which was discovered by the Infra-Red Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) to possess an excessive amount of infrared emission. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of infrared galaxy |  |
| iridium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| iron | has abundance 1 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 1 × 10-5 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.16 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 4 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 41000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 248.814 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 252.285 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 344.061 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 371.994 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 373.713 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 374.556 nm for Fe I |  |
| has atomic emission line 248.327 nm for Fe I (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 385.991 nm for Fe I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 26 |  |
| has atomic radii 124 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to all species |  |
| has boiling point 3023 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 109.5 GPa for cast iron |  |
| has bulk modulus 160 GPa for steel |  |
| has chief source hematite, magnetite, goethite, lepidocrocite, siderite |  |
| has covalent radii 116 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 286.645 pm for α-Fe |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 293.22 pm for δ-Fe |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 364.68 pm for γ-Fe |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for α-Fe |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for δ-Fe |  |
| has crystal type c.c.p. for γ-Fe |  |
| has daily dietary intake 6 - 40 mg |  |
| has definition lustrous, silvery and soft or workable metal when absolutely pure |  |
| has density 7035 kg m-3 for liquid at 1808 K melting point |  |
| has density 7874 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discovery date 2500 B.C. |  |
| has electrical resistivity 9.71 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 15.7 kJ mol-1 from Fe to Fe- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d64s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.83 Pauling |  |
| has hazard deficiency leads to anemia but excess causes liver and kidney damage |  |
| has hazard fire or explosion of dust chronic exposure can cause pneumoconiosis |  |
| has heat capacity 25.10 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 25.677 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 14.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 351.0 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 67 pm for Fe2+ |  |
| has ionic radii 82 pm for Fe3+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 49 to 63 |  |
| has lethal intake 7 - 35 grams |  |
| has level in humans 180 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 250 - 1400 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 3 - 380 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 447 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 12.3 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope iron 56 |  |
| has main mining area USA, Canada, Sweden, South Africa, Russia, India, Japan |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 308 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 38.5 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility ferromagnetic |  |
| has mass of element in person 4.2 kg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1808 K |  |
| has mineral goethite, hematite, lepidocrocite, magnetite, siderite, ... |  |
| has molar volume 7.09 cm3 |  |
| has name origin iron from Anglo-Saxon |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.954 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 16 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 26 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 98 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.27 GPa for cast iron |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.27 GPa for steel |  |
| has pronunciation iy-on ? |  |
has registry number 7439-89-6 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 55.845 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 1.1 × 1011 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 60.0 GPa for cast iron |  |
| has rigidity modulus 81 GPa for steel |  |
| has space group Fm3m for γ-Fe |  |
| has space group Im3m for α-Fe |  |
| has space group Im3m for δ-Fe |  |
| has specimen chips, filings, foil, granules, powder and wire. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Fe |  |
| has symbol name origin ferrum = iron from Latin |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| has term symbol 5D4 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 80.2 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 2.56 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 200 mg Iron (II) compounds are more toxic than iron (III) |  |
| has uses steel etc... |  |
| has world production 7.16 × 108 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 152.3 GPa for cast iron |  |
| has young's modulus 208 GPa for steel |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with damp air by rusting |  |
| reacts with dilute acids by disolving |  |
| iron 52 | has atomic mass 51.948114 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.37 Mev) 57% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 43% |  |
| has half life 8.28 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 52 |  |
| has symbol 52Fe |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 54 | has atomic mass 53.939612 |  |
| has natural abundance 5.8 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 54 |  |
| has symbol 54Fe |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 55 | has atomic mass 54.938296 |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.2314 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 2.73 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 55 |  |
| has symbol 55Fe |  |
| has uses research, medical diagnosis |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 56 | has atomic mass 55.934939 |  |
| has natural abundance 91.72 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 30 |  |
| has number of nucleons 56 |  |
| has symbol 56Fe |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 57 | has atomic mass 56.935395 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 0.8661 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 2.2 |  |
| has NMR frequency 3.231 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 4.2 × 10-3 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.09062294 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 31 |  |
| has number of nucleons 57 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 3.37 × 10-5 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 57Fe |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 58 | has atomic mass 57.933277 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.28 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 32 |  |
| has number of nucleons 58 |  |
| has symbol 58Fe |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 59 | has atomic mass 58.934877 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.565 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 44.51 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.29 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 33 |  |
| has number of nucleons 59 |  |
| has symbol 59Fe |  |
| has uses research, medical diagnosis |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron 60 | has atomic mass 59.934080 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.243) |  |
| has half life 1.5 × 106 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 34 |  |
| has number of nucleons 60 |  |
| has symbol 60Fe |  |
is an instance of iron  |  |
| iron core of supernova gravitational contraction | is a kind of gravitational contraction |  |
| iron fusion | is a kind of endothermic fusion process |  |
| irregular galaxy | has definition A galaxy with amorphous structure and with relatively low mass (108-1010 Msun). Fewer than 10% of all galaxies are classified as irregular. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| irregular variable | is a kind of variable |  |
| Irénée du Pont Telescope | has altitude 2282 m |  |
| has aperture 2.54 m |  |
| has creation date 1976 |  |
has diameter corrector plate 741 mm  |  |
has diameter hole in primary 826 mm  |  |
has diameter primary 2540 mm  |  |
has diameter secondary 953 mm  |  |
has distance between mirrors 5153 mm  |  |
has focal length Cassegrain 19050 mm  |  |
has focal length primary 7620 mm  |  |
has focal point distance behind surface of primary 1013 mm  |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.0 |  |
has image   |  |
| has latitude 29° 00' S |  |
| has location Las Campanas, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 42' W |  |
| has mirror maker Donald A. Loomis |  |
| has mirror type fused-silica |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Bruce H. Rule |  |
| has operator Carnegie Inst. of Washington |  |
| has owner Las Campanas Observatory |  |
has radius of curvature of focal surface 9.042 mm  |  |
| has scale 0.0924 mm/arcsec |  |
| has synonym du Pont 100 inch |  |
has unvignetted corrected field of view 1.45 degrees  |  |
has vignetting at 63 arcmin field angle 3%  |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| Isaac Newton | is an instance of physicist |  |
| Isaac Newton Telescope | has altitude 2336 m |  |
| has aperture 2.5 m mirror |  |
| has comment originally set up in England in 1967 |  |
| has creation date 1984 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3, 15 |  |
| has latitude 28° 46' N |  |
| has location La Palma, Canary Islands |  |
| has longitude 17° 53' W |  |
| has mirror maker Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has operator Royal Greenwich Observatory |  |
| has owner Obs. del Roque de Ins Muchachos |  |
| has synonym Isaac Newton 98 inch |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Polar-disk equatorial telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| ISO | has image  |  |
| has launch date 1998 |  |
has reference 'Infrared Space Observatory', ESA  |  |
| is an instance of infrared space telescope |  |
| isocyanic acid | has symbol HNCO |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| isomer | has definition Nucleus with the same A and Z numbers but in different energy states. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| isomer shift | has definition Displacement of an absorption line due to the fact that the absorbing nuclei have a different s-electron density from that of the emitting nuclei. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wavelength shift |  |
| isoplanatic patch | has definition The angular region on the sky over which the wavefront correction applied by an adaptive optics system remains valid. It is relatively small and therefore a nearby reference star is also required. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solid angle |  |
| isotone | has definition Nucleus with the same number of neutrons but with different A and Z numbers. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| isotope | has definition An atomic nucleus having the same number of protons as a more commonly found atomic nucleus but a different number of neutrons. For example, the hydrogen nucleus has a single proton; deuterium has one proton and one neutron and would be called an isotope of hydrogen. (see neutron; proton.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Two nuclei with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are said to represent the same element, but different isotopes. For example, helium-3, with two protons and one neutron in each nucleus, and helium-4, with two protons and two neutrons, are two different isotopes of helium. For another example, see deuterium. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| isotropy | has antonym anisotropy |  |
| has definition A universe is said to be isotropic, from the point of view of a given observer, if it looks the same in all directions. The isotropy of the real universe is seen most strikingly in the cosmic background radiation, which has the same temperature in all directions to an accuracy of about one part in 100,000. See also homogeneous. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Having equal and uniform properties at all points and in all directions. In astronomy the term describes microwave background radiation. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In cosmology, the property that the universe appears the same in all directions. The uniformity of the cosmic background radiation, coming from all directions of space, suggests that on the large scale the universe is isotropic about our position. If we then assume that our position is not unique, we conclude that: the universe appears isotropic about all points. This last result requires that the universe be homogeneous. (See cosmic background radiation; homogeneity.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Quality of being the same in all directions. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The property of being unchanged by a rotation. A sphere is rotationally invariant, but a rectangle is not. As far as we know the fundamental laws of physics are rotationally invariant. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The same in all directions. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym rotational invariance | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| J magnitude | has band 1.3 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 1.3 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| Janus | has definition The innermost satellite of Saturn, just outside Saturn's rings. Named Janus for the first and the last. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Dollfus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1966 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e ≈ 0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i ≈ 0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period P = 0.75 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R = 175 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Jeans mass | has definition The critical mass a volume of space must contain before it will collapse under the force of its own gravity. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mass enclosed within a sphere of diameter equal to the Jeans length. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| Jet Propulsion Laboratory | has acronym JPL | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Funded by NASA and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Pasadena, California | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| Jodrell Bank | has definition A telescope in England designed to detect radio waves emitted by astronomical objects. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| Johann Bayer | has career named many of the constellations in the southern hemisphere |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| Josephson constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol KJ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.019 × 109 Hz V-1 |  |
has value 483597.898 × 109 Hz V-1  |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| joule | has approval agency International Conference on Weights and Measures | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1948 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has base unit m2kg·s-2 |  |
| has definition Unit of energy, work, or quantity of heat. 1 J is equal to a force of 1 newton acting over a distance of 1 meter. 1 J = 107 ergs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of work which is equal to a force of one newton acting over a distance of one metre in the direction of the force. It was recognized by the IEC in 1889. The specific heat of water at 15 °C is 4185.5 joule (kg °C)-1, a figure previously always associated with J, the mechanical equivalent of heat. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 watt second (electrical units) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 107 ergs | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 2.78 × 10-7 kW h | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 9.47 × 10-4 Btu | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 9.47 × 10-9 therm | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1888 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposer British Association |  |
| has symbol J | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit N·m |  |
| is an instance of energy unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is named after J. P. Joule | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif) |
| Jovian aurora | has definition an aurora ocurring on the planet Jupiter |  |
| has location Jupiter |  |
| is a kind of aurora |  |
| Julian year | has definition A period served as the basis for the Julian calendar. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 365.25 days | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| Juno | has albedo 0.2 |  |
| has definition An asteroid with a relatively large albedo. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 250 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.256 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 13°.0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 1594 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 7h.21 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 2.67 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| Jupiter | has atmosphere composition primarily H2 (85%) and He (14%), with traces of methane, ammonia |  |
| has central density 35 megabar |  |
| has central temperature 5 × 104 K |  |
| has core composition metallic hydrogen in a pressure-ionized liquid phase |  |
| has definition Fifth planet from the Sun. It is more massive than all other planets and satellites combined; if it were about 80 times more massive, it would become self-luminous due to fusion reactions. The heat flux to from the center to the surface is mainly convective. For both Jupiter and Saturn it is necessary to invoke a substantial source of internal heating (presumably gravitational contraction) to account for the surface temperature (Jupiter radiates about 2 1/2 times as much heat as it receives from the Sun). Jupiter's surface shows pronounced horizontal striations: the light layers (zones) are at a slightly higher altitude and about 15° cooler than the dark layers (belts). It is surrounded by a partial torus of atomic H in the orbit of Io. Thirteen satellites, the four outermost of which have retrograde motion, high eccentricity, and high inclination. (Jupiter XIII, discovered in 1974, has a period of 239 days; i = 26°.7, e = 0.147.) |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.048 |  |
| has equatorial radius 7.135 × 109 cm = 11 REarth |  |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 61 km s-1 |  |
| has has albedo 0.51 |  |
| has has mean orbital velocity 13.06 km s-1 |  |
| has has orbital period 11.86 years |  |
| has has surface temperature 120 K |  |
| has has synodic period 398.9 days |  |
| has inclination i = 1°18'18" |  |
| has magnetic axis inclination 15° to the rotational axis (data from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has magnetic axis offset 0.1 Jupiter radius from the center of the planet (data from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has magnetic field 4 gauss (data from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has mass 1.90 × 1030 g = 318 MEarth |  |
| has mean density 1.33 g cm-3< sup> |  |
| has oblateness 0.065 (from Pioneer 10) |  |
| has obliquity 3°.1 |  |
| has polar radius 6.7 × 109 cm |  |
| has rotational period 9h50m at equator; 9h55m at polar regions (see Systems I and II longitude). |  |
| has semi-major axis 5.203 AU |  |
| has surface gravity 2.7 that of Earth |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of gas giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye planet |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| jurassic period | has duration 181 million years |  |
| has start time 46 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of mesozoic era |  |
| K alpha | has definition A spectral line in the X-ray region (α = 0.334 Å), produced by the transition between the lowest level of the K shell and the lowest level of the L shell. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| K corona | has definition The inner part of the Solar corona (the gaseous phase) which emits a continuous spectrum without absorption lines. Physically, the K component results from Thomson scattering of photospheric radiation by free electrons in the corona. The K component is polarized and decreases rapidly with distance from the Sun. (from the German Kontinuum) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym K component | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| K edge | has definition The absorption edge of the K shell (see absorption edges). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of absorption edge |  |
| K electron | has definition An electron in the K shell, the innermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. All elements heavier than hydrogen have a filled K shell, which consists of two 1s electrons orbiting the nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy quantum number 1 |  |
| is a kind of bound electron |  |
| K I doublet | has species potassium (K I) |  |
| has wavelength 7699 and 7644 Å |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| k line | has definition Singly ionized magnesium resonance line. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has species Mg II |  |
| has wavelength 2795.5 Å |  |
| is a kind of absorption line |  |
| K magnitude | has band 2.2 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 2.2 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| K star | has color orange to red |  |
| has definition Cool star with spectral type K with spectra resembling those of sunspots, in which the hydrogen lines have been greatly weakened. The HK lines (q.v.) reach their greatest intensity. Strongest lines are Ca I (4227 Å) and the G-band (4303 Å). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 3600 to 5000 K |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| Kaluza-Klein theory | has definition An early attempt to unify general relativity and electromagnetism by working in five dimensions. The electromagnetic field was obtained by curling up or compactifying the extra dimension. With the advent of higher dimensional theories such as superstrings, the Kaluza-Klein approach came back into fashion. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Class of theories incorporating extra curled-up dimensions, together with quantum mechanics. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| Kamiokande II | has component water detector |  |
| is an instance of neutrino telescope |  |
| kaon | has definition Meson with non-zero strangeness quantum number. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym K meson |  |
| is a kind of meson |  |
| Kapteyn Universe | has definition An incorrect model for the Galaxy proposed by Jacobus Kapteyn in which the Milky Way was small and the Sun located at or near the Galaxy's center. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| Kapteyn's star | has definition A nearby high-velocity M0 subdwarf that is both the nearest halo star to the Sun and the nearest star that orbits the Galaxy backward. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has discover Jacobus Kapteyn | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1897 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 13 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has radial velocity +242 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type M0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym CD -45 1841 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HD 33793 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of M star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of subdwarf | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| katal | has base unit s-1·mol |  |
| has symbol kat |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| represents catalytic activity |  |
| kbTop | has definition Astronomy |  |
| Keck | has comment Uses 36 hexagonal mirror segments. Plans include using both Keck I and Keck II as an optical interferometer |  |
| has creation date 1991 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.75, 15, 25 IR |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has mirror diameter 9.82 m |  |
| has mirror maker Itek, Tinsley |  |
| has mirror type Zerodur |  |
| has mounting manufacturer TIW Systems |  |
| has number of segments 36 |  |
| has operator Univ. of California and Calif. Institute of Technology |  |
| has owner W.M. Keck Observatory |  |
| is a kind of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is a kind of optical telescope |  |
| is a kind of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
is a kind of segmented mirror telescope  |  |
| Keck I | has altitude 4150 m |  |
| has creation date 1991 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.75, 15, 25 IR |  |
| has latitude 19° 49' N |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
is an instance of Keck  |  |
| Keck II | has altitude 4150 m |  |
| has creation date 1996 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.75 |  |
| has latitude 19° 49' N |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
is an instance of Keck  |  |
| Kelvin | has absolute zero 0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval agency 16th CGPM | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1968 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water (the point at which the solid, liquid and gaseous phase of pure water are in equilibrium). Absolute zero corresponds to zero energy. Represents the same temperature interval as those on the Celsius scale. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water |  |
| has symbol K | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym absolute | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water 273.16 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of base SI unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is named after Lord Kelvin (1824-1907) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| Kelvin contraction | has definition The contraction of a star contemplated by Kelvin and Helmholtz as a consequence of a star's radiating its thermal energy. It is currently believed that the contraction of a star occurs in this manner in its pre-main-sequence evolution. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of contraction |  |
| Kelvin timescale | has definition The time it takes a star to contract gravitationally from infinite radius down to its present radius by radiating its thermal energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has value (gravitational binding energy) / luminosity | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time |  |
| see also nuclear time scale |  |
| Kelvin | to convert to Celsius subtract 273.15 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| Kepler's first Law | has definition Each planetary orbit is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kepler's Law |  |
| Kepler's Law | has definition One of three orbital laws formulated by Kepler | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Johannes Kepler |  |
| is a kind of gravity law |  |
| Kepler's second Law | has definition Equal areas are swept out in equal times. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym law of areas | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kepler's Law |  |
| Kepler's Supernova | has definition A Type I supernova (SN Oph 1604) whose light reached Earth in 1604. If H0 = 50, then Kepler's supernova is out in the galactic halo at a distance of 12.1 kpc and 1.4 kpc above the galactic plane, according to van den Bergh. Kepler's supernova is the prototype of Type I supernovae; at its brightest it reached an apparent magnitude of about -2.2. (3C 358) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of type I supernova |  |
| Kepler's third Law | has definition The square of the period is proportional to the cube of the distance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has equation P2 = 4π2 a3 / [G (m1 + m2)] | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym harmonic law | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kepler's Law |  |
| Keplerian orbit | has definition The orbit of a spherical particle of a finite mass around another spherical particle, also of finite mass, by virtue of the gravitational attraction between them. In the Bohr-Sommerfeld picture of atoms, the electrons are considered as describing Keplerian orbits in the field of the positive nucleus by virtue of the inverse square electric attraction between the electrons and the nuclei. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The path that an orbital body (e.g., a planet) would follow if it were subject only to the inverse-square attraction of the Sun or other central body. In practiced secondary bodies, such as Jupiter, produce perturbations. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has parameters osculating element |  |
| has synonym osculating orbit |  |
| is a kind of conic section |  |
| is a kind of orbit |  |
| Kerr black hole | has definition A rotating, axisymmetric black hole based on Kerr's 1963 solution to Einstein's field equations. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| Keyhole Nebula | is a part of Carina Nebula |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| kilo | has symbol k |  |
| has value 103 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| kilogram | has definition Unit of mass (not of weight or of force). Kilogram is equal to the mass of 1.000028 cubic decimeters of water at the temperature of its maximum density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of mass equal to the international prototype of the kilogram |  |
| has historical origin at the end of the 18th century, a kilogram was the mass of a cubic decimeter of water |  |
| has symbol kg |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit |  |
| is an instance of mass unit |  |
| kinematic relativity | has definition Theory proposed by Edward Milne as a viable alternative to Einstein's general theory of relativity, and based generally on kinematics (the science of pure motion, without reference to matter or force), from which Milne successfully derived new systems of dynamics and electrodynamics. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| kinematics | has definition The branch of mechanics that studies bodies undergoing continuous change of position. Whereas dynamics takes into account mass, force, distance, and time, kinematics is concerned only with distance and time. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mechanics | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| kinetic energy | has definition The energy associated with motion; the work that must be done to change a body from a state of rest to a state of motion, equal to 1/2 mv2 for a body of mass m moving at velocity v. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| kinetic temperature | has definition A measure of the average random motion of the particles in a system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| Kirchhoff's first law | has definition To each chemical species there corresponds a characteristic spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kirchhoff's law |  |
| Kirchhoff's law | has definition (1) To each chemical species there corresponds a characteristic spectrum. (2) Every element is capable of absorbing the radiation which it is able to emit; this is the phenomenon of the reversal of the lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantum law |  |
| Kirchhoff's second law | has definition Every element is capable of absorbing the radiation which it is able to emit; this is the phenomenon of the reversal of the lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kirchhoff's law |  |
| Kirkwood gap | has definition Region in the asteroid belt which has been swept clear of asteroids by the perturbing effects of Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| named after American astronomer Daniel Kirkwood |  |
| Kiso Schmidt Telescope | has altitude 1130 m |  |
| has aperture 1.05 m |  |
| has comment alternate secondary mirror offers an f/22.6 Cass. focus |  |
| has creation date 1975 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.1 |  |
| has latitude 35° 48' N |  |
| has location Kiso, Japan |  |
| has longitude 137° 38' E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.5 m |  |
| has mirror maker Nikon |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Nikon |  |
| has operator Univ. of Tokyo |  |
| has owner Kiso Observatory |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| Klein-Alfvén cosmology | has definition A cosmological model in which the early universe is depicted as a giant collapsing spherical cloud of matter and antimatter. When a critical density is reached, the matter and antimatter begin to annihilate, the resulting release of radiation and energy causing the universe to expand. There are many difficulties with this model of the expanding universe, which is largely discredited on observational grounds. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A cosmology in which the observed expansion of the Universe results from the bounce of an originally collapsing cloud of matter and antimatter. The bounce is caused by radiation pressure generated by annihilations when the cloud reaches high density (10-2 cm-3). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| Kolmogorov-Smirnov test | has definition A nonparametric test used in statistics. The Kolmogorov statistic is simply the magnitude of the maximum deviation between the integral distribution function of a sample and the theoretical distribution one wishes to test. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of statistical test |  |
| KREEP | has definition Lunar basaltic material rich in radioactive elements. (from K for potassium, REE for rare-earth elements, P for phosphorus) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Moon |  |
| Kruger 60 AB | has apparent magnitude 12 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A faint dM binary in the Solar neighborhood. It may be a subluminous star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3.93 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 44.5 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of dwarf | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of M star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| krypton | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Kuiper Airborne Observatory | has acronym KAO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of airborne telescope | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif) |
| Kuiper band | has species methane | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 7500 Å | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| occurs in Uranus and Neptune | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| kurtosis | has definition The peakedness or flatness in the graphical representation of a statistical distribution. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| Kvistaberg Schmidt Telescope | has altitude 33 m |  |
| has aperture 1.00 m |  |
| has creation date 1963 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.00 |  |
| has latitude 59° 30' N |  |
| has location Kvistaberg, Sweden |  |
| has longitude 17° 36' E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.35 m |  |
| has mirror maker Uppsala Univ. Obs. |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Various Swedish factories |  |
| has owner Uppsala University Observatory |  |
| has synonym Uppsala Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| L corona | has definition The part of the solar corona whose spectrum consists of emission lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| L magnitude | has band 3.5 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 3.5 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| L2 | has definition An unstable Lagrangian point beyond the most massive body on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has location beyond the most massive body on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of unstable Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| L3 | has definition An unstable Lagrangian point beyond the less massive body on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has location beyond the less massive body on the line passing through the centers of mass of the two bodies | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of unstable Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| L4 | has definition A stable Lagrangian point in the orbit of the less massive component which is equidistant from the two main components in the orbit direction | ![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has location point in the orbit of the less massive component which is equidistant from the two main components in the orbit direction | ![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of stable Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| L5 | has definition A stable Lagrangian point in in the orbit of the less massive component which is equidistant from the two main components opposite the orbit direction | ![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has location point in the orbit of the less massive component which is equidistant from the two main components opposite the orbit direction | ![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of stable Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics | has acronym LHEA |  |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| Lacaille | has birth date 1713 |  |
has career  |  |
| has contribution named many of the constellations in the southern hemisphere |  |
| has death date 1762 |  |
| has name Abbé Nicholas Louis de la Caille |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| Lacerta | has acronym Lac |  |
| has genitive Lacertae |  |
| has synonym Lizard |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Lagoon Nebula | has definition An emission nebula in Sagittarius 2 kpc distant. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 5000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 8 |  |
| has synonym M 8 |  |
| has synonym NGC 6523 |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| Lagrangian point | has definition One of five points in the orbital plane of two massive particles in circular orbits around a common center of gravity, where a third particle of negligible mass can remain in equilibrium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has equilibrium stable or unstable |  |
| has location a point in the orbital plane of the system |  |
| is a kind of rotating coordinate |  |
| Lallemand camera | has definition A type of image tube (q.v.). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of image tube |  |
| Lamb shift | has definition A tiny change in the energy of an electron orbiting the nucleus of an atom, caused by the interaction of the electron with other particles that appear and quickly disappear in "quantum fluctuations". (See quantum fluctuations.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The difference in energy levels of the H atom between 2S1/2 and 2P4. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wavelength shift |  |
| lambda | has definition Heavy short-lived baryon. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of hyperon | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| lambda Bootis star | has definition A type of young (usually early A), weak-lined, metal-poor stars with low radial velocities. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A-type stars with weak metallic lines, low rotational velocity and low radial velocity. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has radial velocity small |  |
| is a kind of weak line star |  |
| rotational velocity small |  |
| lambda doublet | has definition Two lines in the microwave region of the spectrum of the OH molecule caused by splitting of electronic levels. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has species OH |  |
| is a kind of set of lines |  |
| Landsat 5 | is an instance of Landsat satellite |  |
| Landsat satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| lanthanum | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 200 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| Laplacian determinism | has definition Clockwork conception of the universe in which complete knowledge of the state of the universe at one moment completely determines its state at all future and past moments. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of determinism |  |
| Laplacian plane | has definition For a system of satellites, the fixed plane relative to which the vector sum of the disturbing forces has no orthogonal component. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| Large Binocular Telescope | has acronym LBT |  |
| has altitude 3170 m |  |
| has aperture 11.8 m |  |
| has comment Twin 8.4-m reflectors; a project of Univ. of Arizona, Arcetri Astrophysical Obs., and Research Corp. (Tucson) |  |
| has creation date 2004 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.14, 5.4, 15 (each) |  |
| has latitude 32° 42' N |  |
| has location Mount Graham, Arizona, US |  |
| has longitude 109° 51' W |  |
| has mirror maker R. Angel, B. Martin |  |
| has mounting altazimuth "two-shooter" with telescopes 14.4 m apart (center to center) |  |
| has owner Columbus Project |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| Large Magellanic Cloud | has acronym LMC |  |
| has declination -69d45m22s |  |
| has definition The nearest and largest of the many galaxies that orbit the Milky Way. It is 160000 light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 645 × 550 arcminutes |  |
| has distance from galaxy center 50 kpc |  |
has image   |  |
| has magnitude 0.9 |  |
| has mass 10 billion solar masses |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has right ascension 05h23m34.5s |  |
| is a part of Dorado |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of Magellanic Cloud | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| large-scale motions | has definition Bulk motions of distant galaxies deviating from the Hubble flow. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy motion |  |
| Larmor frequency | has definition The frequency of precession of a charged particle orbiting in a uniform magnetic field. It is equal to eH / 4πme, where e is the electron charge, me is the electron mass, and H is the magnetic field strength. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frequency |  |
| Larmor radius | has definition The radius of the circular orbit that a charged particle describes transverse to a magnetic field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| late star | has definition Star with spectral type later than the sun (G2). | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type cooler than G2 | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| law | has definition A theory of such wide and invariable application that its violation is thought to be impossible. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer |  |
| is a kind of theory |  |
| lawrencium | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| lead | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 50 years |  |
| is a kind of group IV element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| leap second | has definition A second (see second, Système International) added between 60s and 0s at announced times to keep UTC within 0s.90 of UT1. Generally, leap seconds are added at the end of June or December. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of second unit |  |
| Leavitt | had appointment reaserch assistant, Harvard College Observatory, 1908 |  |
| has accomplishment discovered 2400 Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| has greatest achievement the Cepheid period-luminosity relation used in Cepheid distance determination |  |
| has name Henrietta Leavitt |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| is associated with Pickering |  |
| length | has unit length unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| length unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of length |  |
| lens | has focal length |  |
| has focal ratio |  |
| has index of refraction |  |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| Lense-Thirring effect | has definition The precession of the plane of the geodesic orbit of a test particle around a rotating mass in general relativity. It arises from the coupling of the rotation of the central mass with the orbital angular momentum of the test particle. This precession is described as resulting from the dragging of inertial frames. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| Lenz's law | has definition The current induced by an electromotive force will appear in such a direction that it opposes the charge that produced it. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of electromagnetic law |  |
| Leo | has acronym Leo |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Leonis |  |
| has historical origin the Nemean Lion strangled to death by Hercules |  |
| has synonym Lion |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Leo dwarf | has definition Two dwarf elliptical galaxies (about 220-250 kpc distant) belonging to the Local Group. Leo I (dE3), Mv ≈ - 11, diameter 1.8 kpc; Leo II, Mv = -9.5, diameter 1.3 kpc. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf elliptical galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of satellite galaxy |  |
| Leo I | has definition The most distant galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. It is close to the bright star Regulus, whose glare interferes with the study of the galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1950 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 890000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Leo |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of Leo dwarf | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| Leo II | has definition The second most distant galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. Like Leo I, Leo II is a dwarf galaxy that was discovered in 1950. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1950 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 720000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Leo |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of Leo dwarf | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| Leo Minor | has acronym LMi |  |
| has genitive Leonis Minoris |  |
| has synonym Little Lion |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Leonid | has definition Shower of meteors emanating from an apparent point in Leo every 33 years; the next is due in about 1999. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 2 days |  |
| has parent object Comet Tempel-Tuttle 1866 I | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has radiant Leo |  |
| has rate 20 per hour |  |
| has start time 16 November |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| lepton | has definition A class of non-strongly-interacting particles that includes the electron, muon, tau, and their associated neutrinos. See Table 7.1 on page 120. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A fermion which is not made of quarks. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A fundamental particle of nature, which may interact via all of the fundamental forces except the strong nuclear force. The electron is an example of a lepton. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any fermion that does not participate in the strong interactions. Leptons include the electron family and the muon family. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particle like the electron and neutrino that do not experience the strong nuclear force. Unlike the strongly interacting hadrons, the leptons have small masses. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particle that does not participate in the strong interactions, including electrons, muons, and neutrinos. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particle that have no measurable size and are not influenced by the strong nuclear force. Electrons, muons, and neutrinos are leptons. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The generic name for any spin-1/2 particle which does not feel the strong nuclear force. The six known leptons are the electron, the muon, the tau lepton, and their respective neutrinos. The name was originally coined to refer to light particles. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 1/2 | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle |  |
| is a kind of fermion |  |
| lepton era | has definition The Big Bang era when the temperature had dropped to about 1012 K and when the Universe consisted mainly of leptons and photons. It lasted until the temperature fell below 1010 K. At this stage, the characteristic photon energy fell below the rest mass energy of an electron, and the abundance of electron-positron pairs fell by many orders of magnitude. Only one electron survived for every 108 photons. The universe was subsequently radiation-dominated (substantial numbers of neutrinos were also present, but they did not interact directly with the matter or the radiation). | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 1 s |  |
| has start time 10-5 s after Big Bang |  |
| has temperature 1010 K to 1012 K |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is followed by nucleosynthetic era |  |
| is preceded by hadron era |  |
| Lepus | has acronym Lep |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Leporis |  |
| has historical origin one of the many animals hunted by Orion, the Hunter |  |
| has synonym Hare |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| LF band | has frequency 30 to 300 kHz |  |
| has wavelength 1 to 10 km |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| LHe | has definition The symbol for liquid helium. The temperature of liquid helium is normally 4 K, that is, four degrees above absolute zero. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of liquid |  |
| Libra | has acronym Lib |  |
| has genitive Librae |  |
| has synonym Scales |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| libration | has definition Any of several oscillations in the apparent aspect of the Moon as seen from Earth, which, when combined, enable Earth-based observers over a period of time to see altogether about 59 percent of the Moon's surface. Physical librations are angular motions about the center of mass due to gravitational torques on the Moon. Optical librations are the apparent rotations of the Moon, caused by our observing it from somewhat different directions at different times. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The "turning" of the Moon so that although the same face is presented to Earth at all times, the overall surface of the Moon visible is 59% of the total. Libration is described as latitudinal, longitudinal and diurnal. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Variations in the orientation of the Moon's surface with respect to an observer on the Earth. Physical librations are due to variations in the rate at which the Moon rotates on its axis. The much larger optical librations are due to variations in the rate of the Moon's orbital motion, the obliquity of the Moon's equator to its orbital plane, and the diurnal changes of geometric perspective of an observer on the Earth's surface. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of rotation |  |
| libration orbit | has definition An elliptical orbit associated with a stable Lagrangian point. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elliptical orbit |  |
| life zone | has definition The region around a star where a planet can have liquid water and so may support life. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of solar system |  |
| lifetime | has definition The time it takes for a sample of identical particles to decay to 1/e of its initial population. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent half-life / ln 2 | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol τ | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym mean life | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time |  |
| see also half-life |  |
| light element | has definition In astronomy these elements are hydrogen, helium, and lithium; sometimes also beryllium and boron. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of element |  |
| light quark | is a kind of quark  |  |
| light-year | has definition Distance traveled at the speed of light for one Earth-year: 9.46 million million km. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance light travels in a vacuum in 1 year. 1 lt-yr = 9.4605 × 1012 km = 0.307 pc (c = 299792.46 km s-1 = 186274 miles s-1). (1 lt-min ≈ 0.13 AU.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance light travels in one year, equal to 5.8 × 1012 (about six trillion) miles. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance light travels in one year: 5.88 trillion miles, or 9.46 trillion kilometers. The nearest star system to the Sun is 4.3 light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance that light traverses in a vacuum during one year. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance traveled in a vacuum by light in one year, equal to 9.46 × 1017cm. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol lt-yr |  |
| has symbol ly |  |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| LIGO | has definition Large Interferometric Gravitational Wave Observatory. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gravity wave telescope |  |
| line | has definition A geometrical object with one dimension |  |
| has dimensions 1 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| line broadening | changes property spectral line width |  |
| has definition Increase in the range of wavelengths in which some characteristic emission or absorption occurs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation modification |  |
| line of apsides | has definition The major axis of an elliptical orbit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line |  |
| line of nodes | has definition The intersection between the orbital plane of the Moon or a planet and the plane of the ecliptic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line |  |
| liquid | has definition a high density cohesive collection of particle which move relative to one another and which has short range order | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of phase of matter |  |
| liquid element | has definition element which is in liquid form at standard temperature and pressure |  |
| has state liquid at standard temperature and pressure |  |
| is a kind of element |  |
| liter | has symbol L |  |
| has value in SI unit 1 dm3 = 10-3 m3 |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| lithium | has abundance 0.17 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 10 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 20 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 323.266 nm for Li I |  |
| has atomic emission line 548.355 nm for Li II |  |
| has atomic emission line 548.565 nm for Li II |  |
| has atomic emission line 610.362 nm for Li I |  |
| has atomic emission line 670.776 nm for Li I (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 670.791 nm for Li I (strong, used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic number 3 |  |
| has atomic radii 152 pm |  |
| has biological role none; but lithium acts to stimulate metabolism and can control manic-depressive disorders |  |
| has boiling point 1620 K |  |
| has chief source petalite, lepidolite |  |
| has covalent radii 123 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 351.00 pm for α-Li |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 437.9 pm for β-Li |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for α-Li |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. for β-Li |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.1 - 2 mg |  |
| has definition Soft, silvery-white, metal. Lightest of all solid elements, third in the periodic table after hydrogen and helium. Its atom comprises one proton and three electrons. One of the electrons is at a higher energy level than the other two. Some lithium formed in the big bang, along with huge amounts of hydrogen and helium. | ![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 515 kg m-3 for liquid at 453.69 K melting point |  |
| has density 534 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer J.A. Arfvedson |  |
| has discovery date 1817 |  |
| has discovery location Stockholm, Sweden |  |
| has electrical resistivity 8.55 × 10-8 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 59.6 kJ mol-1 from Li to Li- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 0.98 Pauling |  |
| has hazard moderately toxic by ingestion but there are wide variations of tolerances. |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 24.77 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 4.60 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 134.7 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 78 pm for Li+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 5 to 9 |  |
| has lethal intake 525 mg kg-1 carbonate ingested by rat |  |
| has level in humans 0.004 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.023 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 0.025 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 1.3 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 56 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope lithium 7 |  |
| has main mining area USA, brines of Searles Lake, California |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.217 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.716 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +2.56 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 7 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 453.69 K |  |
| has mineral amblygonite, lepidolite, petalite, spodumene |  |
| has molar volume 13.00 cm3 |  |
| has name origin lithos = stone from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length -0.190 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 5 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 3 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 2 × 106 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.36 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation lith-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7439-93-2 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 6.941 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 7.3 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 4.24 GPa |  |
| has space group Fm3m for β-Li |  |
| has space group Im3m for α-Li |  |
| has specimen chunks, ingot, powder, ribbon, rod, shot or wire. Care ! |  |
| has stable isotope lithium 6, lithium 7 |  |
| has symbol Li |  |
| has term symbol 2S1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 84.7 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 70.5 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 20 - 200 g |  |
| has uses light-weight alloys, especially with aluminium and magnesium, greases, batteries, glass, medicine and nuclear bombs |  |
| has world production 39000 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 4.91 GPa |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| is a kind of light element |  |
| reacts with oxygen and water slowly |  |
| lithium 6 | has atomic mass 6.015121 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 3.9366 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 7.5% |  |
| has NMR frequency 14.716 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 3.58 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.8220467 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.00082 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 3 |  |
| has number of nucleons 6 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 8.50 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 6Li |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of lithium  |  |
| lithium 7 | has atomic mass 7.016003 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 10.3964 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 92.5% |  |
| has NMR frequency 38.863 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 1540 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.256424 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.041 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 4 |  |
| has number of nucleons 7 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.29 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 7Li |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of lithium  |  |
| lithium 8 | has atomic mass 8.022485 |  |
| has decay mode β- α (16.005 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 0.84 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.6536 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 5 |  |
| has number of nucleons 8 |  |
| has symbol 8Li |  |
is an instance of lithium  |  |
| lithium 9 | has atomic mass 9.026789 |  |
| has decay mode β- (13.6068 Mev) 65% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode n2α 35% |  |
| has half life 0.177 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.439 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 9 |  |
| has symbol 9Li |  |
is an instance of lithium  |  |
| lithium star | has definition C star with a very strong Li I 6078 line. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Peculiar giant star (spectral types G-M) whose spectra show high abundances of lithium. They are primarily S stars and carbon stars, although Li is also found in T Tauri stars, and is sometimes observed in normal late-type giants. Interstellar Li / H ≈ 2 × 10-10. (Solar system Li / H ≈ 10-9.) Lithium is destroyed rapidly (in about 7500 years) at typical nuclear burning temperatures. Spallation is the only production mechanism known for 6Li, but 7Li can be transported from the core in the form of 7Be and converted in the envelope to 7Li by electron capture. Observed 7Li / 6Li > 10. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type G star, M star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C star |  |
| lithophile element | has definition element that tends to concentrate in silicate materials such as igneous rocks |  |
| has occurrence in silicate materials such as igneous rocks |  |
| is a kind of planetary element |  |
| Littrow | has definition The configuration of a diffraction grating spectrograph in which the diffracted ray returns along the same direction as the incident ray. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating spectrograph |  |
| LN2 | has definition The symbol for liquid nitrogen. The temperature of liquid nitrogen is normally 77 K, that is, 77 degrees above absolute zero. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of liquid |  |
| local bubble | has definition The region of the Galaxy near the Sun which has little neutral hydrogen gas. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 100 light-years (up to 10000 light-years in certain directions) | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion spur |  |
| is produced by supernovae | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| local coordinate | has azimuth |  |
| has component local coordinate component |  |
| has coordinate origin observer location on the surface of the Earth |  |
| has elevation |  |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| local coordinate component | is a component of local coordinate |  |
| is a kind of coordinate component |  |
| Local Group | has definition A conglomeration of about twenty galaxies including our own Milky Way. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The association of galaxies to which the Milky Way galaxy belongs. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The cluster of galaxies of which our own, the Milky Way, is one. Its radius is estimated at 106 parsecs. Largest of the Group is the Andromeda galaxy. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The cluster of galaxies to which our Galaxy belongs. It is a poor, irregular cluster with some 20 certain members: three spirals (the Galaxy, M31, and M33); four irregulars (LMC, SMC, IC 1613, and NGC 6822); and about 13 intermediate or dwarf ellipticals (NGC 147; NGC 185; NGC 205; M32; the Sculptor, Fornax, Leo I and II, UMi, and Draco systems; and three companions to M31 discovered by van den Bergh in 1972). It may also include several other dwarf galaxies as well as the giant elliptical Maffei 1. The total mass of the Local Group is less than 1.5 times the combined masses of the Galaxy and M31. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The gravitationally bound collection of nearby galaxies ruled by the Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way, which are its largest members. The Local Group has about 30 known galaxies. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The system of galaxies to which our Milky Way galaxy belongs is a small group, containing only two large spirals (our galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy, Messier 31) and twenty or more smaller systems. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 2 Mpc |  |
| has members Milky Way, M31, M33, LMC, SMC, IC 1613, NGC 6822, NGC 147, NGC 185, NGC 205, M32, Sculptor galaxy, Fornax galaxy, Leo I, Leo II, UMi galaxy, Draco system and three companions to M31 |  |
| has number of galaxies 30 |  |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is an instance of loose group |  |
| local hypothesis of quasars | has definition The hypothesis that quasars are not at the distances inferred from their redshifts. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| local inertial frame | has definition A coordinate system or frame of reference defined in the vicinity of the earth in which Newtons first law of motion is valid; that is, a nonrotating and nonaccelerating reference frame. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nonaccelerating reference frame | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nonrotating reference frame | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| local standard of rest | has acronym LSR | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A frame of reference in which the mean motion of stars in the immediate neighborhood is zero. In such a reference system, the motions of stars in the solar neighborhood (a volume of space about 100 pc in diameter) average out to zero (cf. solar motion). It is a coordinate system in which the origin is a point in the galactic plane moving in a circular orbit around the galactic center, and in which the three velocity components are Π, in the direction from the galactic center to the origin; θ, in the direction of galactic rotation; and Z, perpendicular to the galactic plane. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An imaginary point, located at the Sun's distance from the Galactic center, that revolves clockwise around the Galaxy on a circular orbit. Astronomers measure a star's U, V, and W velocities with respect to the local standard of rest rather than with respect to the Sun, because the Sun has a slightly noncircular orbit. The orbital velocity of the local standard of rest around the Galaxy is about 220 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation rate equal to one complete orbit of the Sun around the Milky Way | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of rotating reference frame |  |
| Local Supercluster | has definition A loosely knit assemblage of some 100 clusters of galaxies, including the Local Group. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An aggregation of galaxies - roughly ten thousand of them - to which the Virgo Cluster and our own galaxy belong. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The supercluster of galaxies to which the Local Group may belong (see Virgo Supercluster). De Vaucouleurs lists 54 groups of galaxies in the LSC (R ≈ 17 Mpc). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The supercluster to which the Local Group belongs. It is shaped like a cigar, with the Virgo cluster of galaxies at its center and the Local Group near one end. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of clusters 100 |  |
| has synonym Virgo supercluster | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Universe |  |
| is an instance of supercluster |  |
| location dependent periodic celestial event | has definition Periodic celestial event which depends on the observers location on the planet |  |
| has observer location |  |
| is a kind of periodic celestial event |  |
| long-period variable | has amplitude 9 magnitudes in the visible, but only 2 or 3 magnitudes in the integrated spectrum | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Cyclic variable with cycles 100-500 days, and of spectral types K, M, S and C. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Pulsating red giant or supergiant. Population I typically have periods greater than 200 days; Population II, periods less than 200 days. Long-period variables emit most of their radiation in the infrared. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 100 to 1000 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype Mira | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type M star, R star, or N star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Mira variable |  |
| has synonym red variable |  |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| is a part of disk | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| longitude of the ascending node | has definition An orbital element representing the point where the body crosses the ecliptic from south to north | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Ω |  |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of orbital element |  |
| longitudinal wave | has definition A wave vibrating along the direction of propagation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wave |  |
| lookback time | has definition Phenomenon that, owing to the finite velocity of light, the more distant an object being observed, the older is the information received from it. A galaxy one billion light-years away, for instance, is seen as it looked one billion years ago. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The time in the past at which the light we now receive from a distant object was emitted. Galaxies of a certain type (redshift and luminosity) can be seen only at a certain distance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| loose group | has definition Galaxy group with on the order of 10 galaxies separated by 10-100 galaxy diameters. | ![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 10 to 100 |  |
| is a kind of galaxy group |  |
| Lorentz contraction | has definition A moving object appears shortened along its direction of motion. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a consequence of special relativity | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of relativity process |  |
| Lorentz invariance | has definition A law which states that laws of physics are identical for all observers moving at constant velocity relative to each other. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has generalization equivalence principle | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym principle of relativity |  |
| has transformation Lorentz transformation | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a principle of special relativity | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of law |  |
| Lorentz transformation | has definition A transformation which enables one to relate the physical parameters describing an object when viewed in one frame of reference to those which are appropriate to an observer moving with a uniform velocity in that frame. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The transformation which keeps the speed of light invariant between relativistic frames of reference. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate transformation |  |
| Loschmidt constant | has definition Number of molecules of an ideal gas per unit volume (2.687 × 1019 molecules per cm3). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition This is the number of molecules in a cubic metre of an ideal gas at s.t.p. It is equal to the Avogadro constant divided by the molar volume. In Germany it is sometimes called Avogadro's constant. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has pressure 101.325 kPa |  |
| has proposal date 1865 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol n0 |  |
| has temperature 273.15 K |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000047 × 1025 m-3 |  |
has value 2.6867775 × 1025 m-3  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| is named after J. Loschmidt (1821-1895) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
| low surface brightness galaxy | has acronym LSBG |  |
| has definition A galaxy which is very faint because it contains a very limited number of stars. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| Low-excitation radio galaxy | has acronym LERG |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| low-velocity star | has definition A star whose U, V, and W velocities are all near zero. Such stars have nearly circular orbits around the Galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Lowell | 19th century scientist |  |
| has death date 1916 |  |
| has degree 1876 Harvard (distinction in mathematics) |  |
| has greatest achievement Lowell Observatory (financed with his own money) |  |
| has greatest blunder believes he observed a network of linear canals on the planet Mars built by extraterrestrial beings |  |
| has name Percival Lowell |  |
is an instance of astronomer  |  |
| Lowell Observatory | has address 1400 Mars Hill Road, Flagstaff, Arizona 86001 |  |
| has altitude 2100 m |  |
| has creation date 1894 |  |
| has creator Lowell |  |
| has location Flagstaff, Arizona, USA. |  |
| has telescope 0.5 m (1894) |  |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| Lowell's band | has definition A dark border sometimes found on the Martian polar cap. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Mars |  |
| lower chromosphere | has composition neutral hydrogen |  |
| has definition The lower part of the chromosphere and consists of cool neutral hydrogen in which radiation at certain wavelengths is absorbed from the continuous spectrum emitted from the Sun's photosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has density ρ ≈ 10-13 to 10-8 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has location 0 to 4000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym reversing layer |  |
| has temperature 7500 K |  |
| is a part of chromosphere |  |
| lower culmination | has definition Passage of a celestial object across the observer's meridian. The crossing farther from the zenith. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym culmination below pole | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of culmination | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| lower precambrian period | has duration million years |  |
| has start time million years ago |  |
| is a kind of precambrian era |  |
| lumen | has base unit m2·m-2·cd = cd |  |
| has symbol lm |  |
| has unit cd·sr |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| represents luminous flux |  |
| luminance unit | has definition candela per square meter |  |
| has symbol cd·m-2 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| luminosity | has definition Brightness of a celestial body, measured in terms of (apparent) magnitude, absolute magnitude, or using the Sun's brightness as 1.0 on a solar scale. The luminosity of a star corresponds with its internal radiation pressure, which in turn depends on its mass. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The intrinsic brightness of a star. Usually defined in terms of absolute magnitude. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The total amount of energy radiated by a star - that is, its true, or intrinsic, brightness. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Total radiant energy output per second (absolute brightness, usually expressed in ergs s-1 or in magnitudes). L = 4πR2σT4 (see Stefan's law). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation measurement |  |
| luminous blue variable | has definition A variable-star designation for the high-luminosity early type objects. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Hubble-Sandage variable | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym S Dor variable | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| luminous intensity unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of luminous intensity |  |
| luminous mass | has definition The mass contributed by luminous matter in galaxies (see missing mass). Luminous mass density, 5 × 10-32 g cm-3 for H0 = 50 km s-1 Mpc-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| Lumogen | has definition Fluorescent UV coating which improves the blue sensitivity of a CCD by emitting light at approximately 540 to 580 nm when excited with light of wavelengths shorter than 450 nm. |  |
| is a kind of coating |  |
| lunar eclipse | has definition An eclipse in which the Moon passes through the shadow cast by the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of eclipse |  |
| lunar fines | has definition Small particles of rock or powdered rock on the Moon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Moon |  |
| lunar spacecraft | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| Lundmark | has country of origin Sweden |  |
| has name Knut Lundmark |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| Lunette Bischoffscheim | has altitude 372 m |  |
| has aperture 0.74 m |  |
| has creation date 1886 |  |
| has focal ratio f/24.2 |  |
| has latitude 43° 43' N |  |
| has lens maker Henry Brothers |  |
| has location Mont Gros, France |  |
| has longitude 7° 18' E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer P. Gautier |  |
| has owner Observatoire de Nice |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| Lupus | has acronym Lup |  |
| has genitive Lupi |  |
| has synonym Wolf |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Lupus Loop | has definition A radio source, a large broken shell 4°.5 in diameter, identified as a prehistoric supernova remnant. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Lupus |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| lutetium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 4000 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| lux | has base unit m2·m-4·cd = m-2·cd |  |
| has symbol lx |  |
| has unit lm·m-2 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| represents illuminance |  |
| Luyten 726-8 | has definition A binary (M5.5e V, M6e V) (component B is UV Cet) with a very small mass (total mass of system (1974) 0.3 Msun ). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2.7 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| Lyman alpha | has definition The resonance line of hydrogen. It can only be studied from spacecraft or in the spectra of highly redshifted quasars. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has upper energy level 2 | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 1215.67 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Lyman line |  |
| is an instance of resonance line |  |
| Lyman beta | has upper energy level 3 | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 1026 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Lyman line |  |
| lyman break galaxy | has acronym LBG |  |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| Lyman line | has lower energy level 1 |  |
| has series limit 912 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line |  |
| Lynx | has acronym Lyn |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Lyncis |  |
| has synonym Lynx |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Lyon Meudon Extragalactic Database | has acronym LEDA |  |
is an instance of database  |  |
| Lyot division | has definition A gap between the B ring and the C ring. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ring gap |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| Lyra | has acronym Lyr |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Lyrae |  |
| has historical origin invented by Hermes as a gift to his half-brother Apollo, who gave it to Orpheus, the musician of the Argonauts |  |
| has synonym Lyre |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Lyrid | has duration 1 day |  |
| has parent object Comet Thatcher |  |
| has radiant Lyra |  |
| has rate 15 per hour |  |
| has start time 22 April |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| M 10 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 10 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6254 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class VII globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 100 | has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1781 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 100 |  |
| has synonym NGC 4321 |  |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of Sc spiral |  |
| M 107 | has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1782 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 107 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6171 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class X globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 12 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 12 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6218 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class IX globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 13 | has discoverer Edmond Halley |  |
| has discovery date 1714. |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 13 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6205 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Hercules |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 14 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 14 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6402 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class VIII globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 15 | has discoverer Jean-Dominique Maraldi |  |
| has discovery date 1746 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 15 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 7078 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Pegasus |  |
| is an instance of class IV globular cluster |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| M 19 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 19 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6273 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class VIII globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 2 | has discoverer Jean-Dominique Maraldi |  |
| has discovery date 11 September 1746 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 2 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 7089 |  |
| is a part of Aquarius |  |
| is a part of Aquarius |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is an instance of class II globular cluster |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| M 22 | has discoverer Abraham Ihle |  |
| has discovery date 1665 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 22 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6656 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class VII globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 28 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 28 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6626 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class IV globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 3 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 3 May 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 3 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 5272 |  |
| is a part of Canes Venatici |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is an instance of class VI globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 30 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 30 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 7099 |  |
| is a part of Capricornus |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 32 | has definition An elliptical galaxy that orbits the Andromeda galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 32 |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| orbits Andromeda galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| M 4 | has discoverer Philippe Loys de Cheseaux |  |
| has discovery date 1746 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 4 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6121 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Scorpius |  |
| is an instance of class IX globular cluster |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| M 5 | has discoverer Gottfried Kirch |  |
| has discovery date 1702 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 5 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 5904 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Serpens |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 53 | has discoverer Johan Elert Bode |  |
| has discovery date 1775 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 53 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 5024 |  |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 54 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1778 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 54 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6715 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class III globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 55 | has discoverer Abbe Nicholas Louis de la Caille |  |
| has discovery date 1751 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 55 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6809 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class XI globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 56 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1779 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 56 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6779 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Lyra |  |
| is an instance of class X globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 62 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1771 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 62 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6266 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class IV globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 68 | has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 68 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 4590 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Hydra |  |
| is an instance of class X globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 69 | has discoverer Abbe Nicholas Louis de la Caille |  |
| has discovery date 1751 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 69 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6637 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 70 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 70 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6681 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 71 | has discoverer Philippe Loys de Cheseaux |  |
| has discovery date 1745 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 71 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6838 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagitta |  |
| is an instance of class X globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 72 | has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 72 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6981 |  |
| is a part of Aquarius |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is an instance of class IX globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 75 | has apparent magnitude 8.5 (V) |  |
| has diameter 6.0 arc min |  |
| has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
| has distance 57.7 kly |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 75 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6864 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of class I globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 79 | has discoverer Pierre Mechain |  |
| has discovery date 1780 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 79 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 1904 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Lepus |  |
| is an instance of class V globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 80 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1781 |  |
| has distance 28000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 80 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6093 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Scorpius |  |
| is an instance of class II globular cluster |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| M 81 | has definition A giant spiral galaxy 11 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It rules the M81 group, the second nearest galaxy group to the Local Group. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Johan Elert Bode |  |
| has discovery date 1774 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 81 |  |
| has synonym NGC 3031 |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Ursa Major |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of Sb spiral |  |
| M 81 group | is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is an instance of loose group |  |
| M 87 | has definition A strong radio source. Optically, it is an elliptical galaxy with a luminous blue jet about 1500 pc long. It is also one of the most powerful extragalactic sources of radiation at infrared wavelengths. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 87 |  |
| has synonym 2U 1228+12 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3C 274 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Virgo A | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Virgo X-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Virgo |  |
| is a part of Virgo cluster | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of giant elliptical galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of radio galaxy |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| M 9 | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1764 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 9 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6333 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of class VIII globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M 92 | has discoverer Johan Elert Bode |  |
| has discovery date 1777 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 92 |  |
| has reference NED, SIMBAD |  |
| has synonym NGC 6341 |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Hercules |  |
| is an instance of class IV globular cluster |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| M magnitude | has band 5 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 5 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| M star | has definition Having a spectral type of M, that is, red like Betelgeuse and Antares. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Spectral type for red stars, such as Betelgeuse, Antares, and Proxima Centauri. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star of spectral type M are cool red stars with surface temperatures of less than 3600 K whose spectra are dominated by molecular bands, especially those of TiO. M dwarfs are the most numerous type in our galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| M-Theory | has definition Theory emerging from the second superstring revolution that unites the previous five superstring theories within a single overarching framework. M-theory appears to be a theory involving eleven spacetime dimensions, although many of its detailed properties have yet to be understood. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of superstring theory |  |
| M2-9 | has distance 2100 light years |  |
| has expansion velocity 200 miles per second |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Ophiucus |  |
| Mach's Principle | has definition A pre-relativity statement to the effect that the local inertial frame is determined by some average of the motion of all the matter in the universe. In essence, mach's principle says that space, which is the arena in which matter interacts, is itself an aspect of that matter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothesis that the inertia of bodies - that is, their resistance to acceleration by applied forces - is determined not by any absolute properties of space but by the effects of distant matter in the universe. equivalently, Mach's principle proposes that the distinction between accelerated and nonaccelerated frames of reference is determined by the effects of distant matter. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothesis that the local inertial frame and the inertia of any body is determined by the distribution of all the matter in the universe. | ![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The precept that the inertia of objects results not from their relationship to Newtonian absolute space, but to the rest of the mass and energy distributed throughout the universe. Though unproved and perhaps unprovable, Mach's principle inspired einstein, who sought with partial success to incorporate it into the general theory of relativity. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| Magellan Project | has altitude 2300 m |  |
| has aperture 6.5 m |  |
| has comment a twin, Magellan II is to be built in 2001 |  |
| has creation date (1999) |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.25, 11, 15 |  |
| has latitude 29° 00' S |  |
| has location Las Campanas, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 42' W |  |
| has mirror maker R. Angel, B. Martin |  |
| has mounting manufacturer L & F Industries |  |
| has operator Carnegie Institution of Washington |  |
| has optical design Cassegrain and Gregorian |  |
| has owner Las Campanes Observatory |  |
| has synonym Magellan I |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| Magellanic Cloud | has definition The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, the two nearest and largest of the galaxies that orbit the milky way. The Magellanic Clouds lie in the southern sky and cannot be seen from the United States. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Two galaxies that lie close to the milky way galaxy. They are visible in the southern skies of Earth. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Two relatively small, nebulous stellar systems visible only in the southern hemisphere; the larger is, however, the brightest "nebular" object in the sky. both are members of the local group of galaxies, and in fact seem to be associated, though detached, parts of the milky way system. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Two small irregular (or possibly barred spiral) galaxies (satellites of the Milky Way galaxy) about 50-60 kpc (LMC, in Dorado) and 60-70 kpc (SMC, in Toucana) distant, visible to the naked eye from the southern hemisphere. Both clouds contain mainly Population I stars. The LMC contains numerous ob stars and at least 10 stars that are an order of magnitude brighter (mv = - 9) than any supergiants known in our galaxy. It also contains several times our galaxy's concentration of interstellar matter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of irregular galaxy |  |
| is a kind of naked eye object |  |
| is a kind of satellite galaxy |  |
| Magellanic Stream | has definition A name given to the common envelope of neutral hydrogen in which the LMC and SMC are embedded. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A name given to the long H I filament that extends from the region between the Magellanic Clouds down to the south galactic pole and which appears to make a 180° arc of a great circle across the sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A strand of gas that the Milky Way has ripped out of the Magellanic Clouds. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has length 300000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of halo |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is a part of Small Magellanic Cloud |  |
| magnesium | has abundance 1200 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 23000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 4.0 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 279.553 nm for Mg II |  |
| has atomic emission line 280.270 nm for Mg II |  |
| has atomic emission line 383.829 nm for Mg I |  |
| has atomic emission line 518.361 nm for Mg I |  |
| has atomic emission line 285.213 nm for Mg I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 12 |  |
| has atomic radii 160 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to all species |  |
| has boiling point 1363 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 35.6 GPa |  |
| has chief source seawater; and the ores or dolomite, magnesite; carnallite and brucite |  |
| has covalent radii 136 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 320.94; c = 521.03 pm |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. |  |
| has daily dietary intake 250 - 380 mg |  |
| has definition silvery white, lustrous and relatively soft metal |  |
| has density 1585 kg m-3 for liquid at 922.0 K melting point |  |
| has density 1738 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Joseph Black |  |
| has discovery date 1755 |  |
| has discovery location Edinburgh, Scotland |  |
| has electrical resistivity 4.38 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity -21 kJ mol-1 from Mg to Mg- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.31 Pauling |  |
| has hazard compounds vary in toxicity but no evidence that metal produces systemic poisoning |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 24.89 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 9.04 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 128.7 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 79 pm for Mg2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 20 to 31 |  |
| has lethal intake 8100 mg kg-1 for chloride, oral, rat |  |
| has level in humans 37.8 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 590 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 700 - 1800 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 900 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 26.1 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope magnesium 24 |  |
| has main mining area Austria, China, Poland, Russia, USA, India, Greece, Canada |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 38.6 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 4.11 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +6.8 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 19 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 922.0 K |  |
| has mineral brucite, carnalite, cordierite, diopside, dolomite, enstatite, epsomite, kiersite, magnesite, pyrope, spinel |  |
| has molar volume 13.98 cm3 |  |
| has name origin Magnesia = district of Thessaly from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.5375 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 12 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 12 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 1 × 107 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.291 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation mag-neez-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7439-95-4 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 24.3050 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves > 2 × 1010 tonnes as ores; and > 1 × 1024 tonnes in the sea |  |
| has rigidity modulus 17.3 GPa |  |
| has space group P63/mmc |  |
| has specimen chips, granules, powder, ribbon, rod or turnings. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Mg |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of fused MgCl2 |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 156 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.063 barns |  |
| has toxic intake low toxicity |  |
| has uses as a 'sacrificial' electrode to protect other metals exposed to seawater and ground |  |
| has uses bulk metal and lightweight alloys |  |
| has world production 325000 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 44.7 GPa |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| reacts with air when ignited |  |
| reacts with hot water |  |
| magnesium 23 | has atomic mass 22.994124 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.058 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 11.32 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2 h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 11 |  |
| has number of nucleons 23 |  |
| has symbol 23Mg |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnesium 24 | has atomic mass 23.985042 |  |
| has natural abundance 78.99% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 12 |  |
| has number of nucleons 24 |  |
| has symbol 24Mg |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnesium 25 | has atomic mass 24.985837 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.6375 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 10.00% |  |
| has NMR frequency 6.1195 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 1.54 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.85546 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.1994 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 13 |  |
| has number of nucleons 25 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 2.67 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 25Mg |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nulclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnesium 26 | has atomic mass 25.982593 |  |
| has natural abundance 11.01% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 14 |  |
| has number of nucleons 26 |  |
| has symbol 26Mg |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnesium 27 | has atomic mass 26.984341 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.610 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 9.45 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 15 |  |
| has number of nucleons 27 |  |
| has symbol 27Mg |  |
| has uses research (radioactive nuclide) |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnesium 28 | has atomic mass 27.983876 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.832 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 21.0 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 16 |  |
| has number of nucleons 28 |  |
| has symbol 28Mg |  |
| has uses research (radioactive nuclide) |  |
is an instance of magnesium  |  |
| magnetic constant | has symbol μ0 |  |
| has uncertainty 0 |  |
has value 4π × 10-7 = 12.566 370 614 × 10-7 N A-2  |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| magnetic field strength unit | has definition ampere per meter |  |
| has symbol A·m-1 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| magnetic flux | has unit magnetic flux unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| magnetic flux density | has unit magnetic flux density unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| magnetic flux density unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of magnetic flux density |  |
| magnetic flux quantum | has equation  |  |
| has symbol Φ0 |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000081 × 10-15 Wb |  |
has value 2.067833636 × 10-15 Wb  |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux |  |
| magnetic flux unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of magnetic flux |  |
| magnetic monopole | has definition A hypothetical particle that carries an isolated north or south magnetic pole. This is in contrast to magnets which are north-south pole pairs. If magnetic monopoles exist, they must be very massive. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A magnet with an isolated north (or south) pole, rather than a pair of equal-strength north and south poles, as in conventional magnets. Magnetic monopoles have never been observed, but they are predicted to exist by grand unified theories. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition a massive particle with but one magnetic pole, the production of which is indicated in some theories of the early universe. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An hypothesized particle that would have either a magnetic north pole or a magnetic south pole but not both. all magnetic particles and magnets ever observed have both poles. Magnetic monopoles are predicted by grand unified theories of physics. that grand unified theories predict the existence of large numbers of magnetic monopoles, when none have been discovered, is called the monopole problem. (see grand unified theories.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition has definition A hypothetical quantum object being a single, isolated magnetic pole. Normally, magnetic poles, the sources of a magnetic field, occur in pairs as north and south poles. |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| magnetic monopole problem | has definition A problem, discovered by John Preskill in 1979, concerning the compatibility of grand unified theories with standard cosmology. Preskill showed that if standard cosmology were combined with grand unified theories, far too many magnetic monopoles would have been produced in the early universe. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of problem |  |
| magnetic pressure | has definition The pressure exerted by a magnetic field on the material that contains the field. in gaussian units it is given by pm = b2 / 8π, where b is the magnetic field strength. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pressure |  |
| Magnetic star | has definition Star (usually of spectral type A) with strong integrated magnetic fields ranging up to 30000 gauss. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| magnetohydrodynamics | has acronym MHD |  |
| has definition The study of the collective motions of charged particles in a magnetic field. (Sometimes called hydromagnetics) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym hydromagnetics | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrodynamics |  |
| magnetopause | has definition The region in earth's ionosphere where the magnetosphere meets the solar wind. Essentially, it is the place where earth's magnetic field stops; the region above the magnetopause is no longer part of earth's atmosphere, but is part of interplanetary space. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of magnetosphere |  |
| magnetosphere | has definition The extent of a planet's magnetic field. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The region of space surrounding a rotating, magnetized sphere. Specifically, the outer region of earth's ionosphere, starting at about 1000 km above earth's surface, and extending to about 60,000 km (or considerably farther, on the side away from the sun). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has shape teardrop-like, with the point opposite the Sun; due to the effect of the solar wind | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| magnitude | has definition A logarithmic brightness scale for astronomical objects. See Appendix. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A measure. on a logarithmic scale, used to indicate the brightness of a celestial object. A 1-magnitude difference in brightness between two stars corresponds to a difference in luminosity by 100.4 or 2.51; 5 magnitudes corresponds to factor of 100 in luminosity. | ![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An arbitrary number, measured on a logarithmic scale, used to indicate the brightness of an object. Two stars differing by 5 mag differ in luminosity by 100. 1 magnitude is the fifth root of 100, or about 2.512. The brighter the star, the lower the numerical value of the magnitude (see also Pogson's ratio). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The brightness of a star or planet, expressed on a scale in which lower numbers mean greater brightness. Apparent magnitude indicates the brightness of objects as we see them from earth, regardless of their distance. Absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude a star would have if viewed from a distance of ten parsecs, or 32.6 light-years. each step in magnitude equals a difference of 2.5 times in brightness: the brightest stars in the sky are apparent magnitude 1; the dimmest, 6. The magnitudes of extremely bright objects are expressed in negative values - e.g., the apparent magnitude of the Sun is about -26. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The measure of a star's brightness. apparent magnitude measures a star's apparent brightness - that is, how bright a star looks from Earth. absolute magnitude measures a star's intrinsic brightness - that is, how much light the star actually emits. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The measured brightness of a celestial body. dim objects have magnitudes of high numbers, bright objects have magnitudes of low or even negative numbers. Seen from earth, stars of (apparent) magnitude 6 or higher cannot be detected with the naked eye. The Full Moon has a magnitude of -11, and the Sun one of -26.8. in order to standardize measurements of the brightness of more distant objects, the system of absolute magnitude is used. A measure of the radiation at all wavelengths emitted by a star is known as the bolometric magnitude. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation measurement |  |
| main lines | has definition The transitions that emit radiation at 1665 and 1667 mhz of an OH source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| Maksutov telescope | has definition A reflector whose primary mirror is spheroidal instead of parabolic. The light initially passes through a large concave lens to remove the spherical aberration. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has primary mirror shape concave spheroid |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| MAMA | has definition Multi-Anode Microchannel Analyzer. A detection system used with microchannel plates to detect events. Used as an imaging system in the ultraviolet. See microchannel plates. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of microchannel plate |  |
| manganese | has abundance 0.4 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.96 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.0 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.0 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 2.63 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 950 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 257.610 nm for Mn I |  |
| has atomic emission line 279.482 nm for Mn I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 279.827 nm for Mn I |  |
| has atomic emission line 403.307 nm for Mn I |  |
| has atomic emission line 403.449 nm for Mn I |  |
| has atomic emission line 403.076 nm for Mn I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 25 |  |
| has atomic radii 124 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to all species |  |
| has boiling point 2235 K |  |
| has bulk modulus n.a. GPa |  |
| has chief source pyrolusite, romanechite (also known as psilomelane), manganite (useful but rare) |  |
| has covalent radii 117 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 891.39 pm for α-Mn |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. for α-Mn |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.4 - 10 mg |  |
| has definition hard, brittle, silvery metal |  |
| has density 6430 kg m-3 for liquid at 2235 K melting point |  |
| has density 7440 kg m-3 for α-Mn solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer J.G. Gahn |  |
| has discovery date 1774 (isolated) |  |
| has discovery location Stockholm, Sweden |  |
| has electrical resistivity 185.0 × 10-8 Ω m at 298 K |  |
| has electron affinity less than 0 kJ mol-1 from Mn to Mn- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d54s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.55 Pauling |  |
| has hazard compounds are experimental carcinogens and teratogens |  |
| has hazard exposure to dust or fumes should not exceed 5 mg m-3 |  |
| has heat capacity 20.79 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 26.32 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 14.4 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 219.7 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 52 pm for Mn4+ |  |
| has ionic radii 70 pm for Mn3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 91 pm for Mn2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 49 to 62 |  |
| has lethal intake 1715 mg kg-1 for chloride in mouse |  |
| has level in humans 0.0016 - 0.075 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.2 - 100 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 0.2 - 2.3 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 3.6 - 9.6 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 22 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope manganese 55 |  |
| has main mining area South Africa, Russia, Gabon, Australia, Brazil |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 285 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 34.7 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +1.21 × 10-7 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 12 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1517 K |  |
| has mineral bixbyite, managanite, pyrolusite, rhodochrosite, rhodonite (jewelry), romanechite |  |
| has molar volume 7.38 cm3 |  |
| has name origin magnes = magnet from Latin or magnesia nigri = black magnesia (MnO2) |  |
| has neutron scattering length -0.373 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 15 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 25 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 50 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.24 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation man-gan-eez |  |
has registry number 7439-96-5 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 54.93805 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 3.6 × 109 tonnes (plus ocean floor nodules which are 24% Mn) |  |
| has rigidity modulus 79.5 GPa |  |
| has space group I-43m for α-Mn |  |
| has specimen chips, flake or powder. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Mn |  |
| has term symbol 6S5/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 7.82 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 13.3 barns |  |
| has toxic intake slighly toxic by ingestion |  |
| has uses steel production, ceramics, feed supplements and fertilizer additives |  |
| has world production 6.22 × 106 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 191 GPa |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with dilute acids by dissolving |  |
| reacts with oxygen by burning |  |
| reacts with water |  |
| manganese 52 | has atomic mass 51.945568 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.712 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 5.591 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.063 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 6+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 27 |  |
| has number of nucleons 52 |  |
| has symbol 52Mn |  |
is an instance of manganese  |  |
| manganese 53 | has atomic mass 52.941291 |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.596 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 3.7 × 106 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 5.024 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 53 |  |
| has symbol 53Mn |  |
is an instance of manganese  |  |
| manganese 54 | has atomic mass 53.940361 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (1.377 Mev) |  |
| has half life 312.2 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.282 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 54 |  |
| has symbol 54Mn |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of manganese  |  |
| manganese 55 | has atomic mass 54.938047 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 6.6195 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 24.664 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 994 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.4532 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +0.330 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/5- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 30 |  |
| has number of nucleons 55 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.18 where 1H = 1.00 for KMnO4 (aq) |  |
| has symbol 55Mn |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of manganese  |  |
| manganese 56 | has atomic mass 55.938906 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.696 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.578 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.2266 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 31 |  |
| has number of nucleons 56 |  |
| has symbol 56Mn |  |
is an instance of manganese  |  |
| manganese star | has definition Star with an anomalously high Mn-Fe ratio, which show deviations from the odd-even effect for phosphorus, gallium, and yttrium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| manned spacecraft | has crew one or more |  |
| is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| is disjoint from unmanned spacecraft |  |
| many-worlds interpretation | has author Everett and Wheeler |  |
| has competing theory Copenhagen interpretation | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The view of quantum mechanics holding that a physical system simultaneously exists in all of its possible states prior to and after a measurement of the system. In the many-worlds interpretation, each of these simultaneous existences is part of a separate universe. Every time we make a measurement of a physical system and find it to be in a particular one of its possible states, our universe branches off to one of the universes in which the system is in that particular state at that moment. The system, however, continues to exist in its other possible states, in parallel universes. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum mechanics interpretation |  |
| mare | has definition An area on the moon that appears darker and smoother than its surroundings. Lunar maria are scattered basaltic flows. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has plural maria |  |
| is a part of Moon |  |
| Markarian galaxy | has definition A galaxy in Markarian's list of galaxies with abnormally strong ultraviolet continua. They have broad emission lines arising in a bright, semi-stellar nucleus. Markarian 231 is the most luminous galaxy known if it is at its Hubble distance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line galaxy |  |
| Mars | has albedo 0.16 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition more than 90% CO2, traces of O2, CO, H2O. |  |
| has atmospheric pressure 3.5 millibars (data from mariner 7) |  |
| has core composition liquid Ni - Fe | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fourth major planet out from the Sun. Its tiny satellites are locked in synchronous rotation with mars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0934 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity 5.1 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 1°.85 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 6.45 × 1026< sup> g (0.11 MEarth) |  |
| has mean density 4.0 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from sun 1.5237 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean orbital velocity 24.2 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of satellites 2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has oblateness 0.0092 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 23°59' | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius (1974) 3394 km -has source: [H76] |  |
| has rotational period 24h37m22s.6 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has sidereal period 687 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 0.38 that of Earth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 248 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 779.9 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of naked eye planet |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of terrestrial planet |  |
| mascons | has definition Abbreviated form of mass concentrations: apparent regions on the lunar surface where gravity is somehow stronger. The effect is presumed to be due to localized areas of denser rock strata. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition gravity anomalies found on the moon. As of 1971, 12 mascons were known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Moon |  |
| is an acronym for mass concentrations |  |
| mass | has definition Measure of the amount of matter in an object. Inertial mass indicates the object's resistance to changes in its state of motion. Gravitational mass indicates its response to the gravitational force. In the general theory of relativity, gravitational and inertial mass are revealed to be aspects of the same quantity. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The measure of the inertia of an object, determined by observing the acceleration when a known force is applied. The gravitational force acting on an object is found to be proportional to its mass, as is the gravitational force that it exerts on other objects. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The quantitative property of an object due to the matter it contains. (Weight, in contrast, describes a force with which a body is attracted towards a gravitational focus.) Units of mass are grams and kilograms. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit mass unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| mass density unit | has definition kilogram per cubic meter |  |
| has symbol kg m-3 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| mass fraction unit | has definition kilogram per kilogram, which may be represented by the number one |  |
| has symbol kg·kg-1 = 1 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| mass motion | has definition A non-uniform matter flow | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| mass of the Galaxy | has definition The mass of the Milky Way. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 1.8 × 1011 MSun | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| mass unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of mass |  |
| massive black hole | has definition Utilized in a theoretical model for quasars and active galactic nuclei, according to which the energy source is due to infall (and resultant heating) of gas and stars onto a supermassive central black hole. | ![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| massive compact halo object | has acronym MACHO | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition These are black holes, neutron stars and brown dwarfs, none of which are luminous and all of which are postulated to exist in the halos of galaxies. They are a form of dark matter. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dark matter |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| massless black hole | has definition In string theory, a particular kind of black hole that may have large mass initially, but that becomes ever lighter as a piece of the Calabi-Yau portion of space shrinks. When the portion of space has shrunk down to a point, the initially massive black hole has no remaining mass - it is massless. In this state, it no longer manifests such usual black hole properties as an event horizon. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| massless particle | has definition A particle with zero mass | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 0 |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| materialism | has antonym spiritualism |  |
| has definition Belief that material objects and their interactions constitute the complete reality of all phenomena, including such seemingly insubstantial phenomena as thoughts and dreams. Compare spiritualism. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| mathematical concept | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| mathematical constant | is a kind of constant |  |
| matter era | has definition A cosmic epoch during which the matter content of the Universe ceased to be ionized. This led to a decrease in the optical depth of the Universe, and the photons of radiation (which we now observe as the cosmic microwave background) became able to travel large distances without interacting with matter. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Separation of classes of particles from regular interaction with one another, as in the decoupling of photons from particles of matter that produced the cosmic background radiation. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The Big Bang era when the temperature had dropped to 3000 K, at which time the recombination of hydrogen became possible. The plasma of free electrons and nuclei condensed to form a neutral gas. Matter and radiation consequently decouple from one another because no further scattering of the radiation occurs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The epoch at t ≈ 1013 s after the big bang (T ≈ 3000 K) when matter and radiation decoupled. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The era some 3 × 105 years after the Big Bang when the cosmic blackbody radiation was last scattered by the matter. At this era, at a redshift of about 1,000 and a temperature of about 3,000 K, the protons and electrons combined to form hydrogen atoms, which are effectively transparent to the radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The rapid transition from an ionized state at a redshift of 1000, when the blackbody radiation is scattered by the free electrons, to an unionized state, when the matter is predominantly in the form of hydrogen atoms that do not scatter the radiation appreciably. Radiation subsequently does not interact with matter unless the matter becomes reionized at a later epoch by radiation from quasars or forming galaxies. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The release of photons from constant collisions with massive particles as the universe expanded and its matter density diminished. See decoupling. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration > 1010 years |  |
| has start time 1012 s |  |
| has synonym decoupling era |  |
| has synonym recombination era |  |
| has temperature 3 K to 3000 K |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is preceded by radiation era |  |
| maxwell | has definition Unit of magnetic flux through 1 cm2 normal to a field of 1 gauss. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-8 Wb | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux unit |  |
| Maxwell distribution | has definition An expression for the statistical distribution of velocities among the molecules of a gas at a given temperature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distribution function that any species of particle will have if it is in thermodynamic equilibrium. This distribution function describes both the equilibrium in velocity space or kinetic energy, and the equilibrium in potential energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of statistical distribution |  |
| Mayall | has name Nick Mayall |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| is associated with Humason |  |
| McCormick Refractor | has altitude 264 m |  |
| has aperture 0.667 m |  |
| has creation date 1883 |  |
| has focal ratio f/14.9 |  |
| has latitude 38° 02' N |  |
| has lens maker Alvan Clark & Sons |  |
| has location Charlottesville, VA, US |  |
| has longitude 78° 31' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Warner and Swasey |  |
| has owner Leander McCormick Observatory |  |
| has synonym 26 inch |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| Me star | has definition Star of spectral type M with emission lines in their spectra. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of M star |  |
| mean element | has definition One of several elements of an adopted reference orbit (see elements, orbital) that approximates the actual, perturbed orbit. Mean elements may serve as the basis for calculating perturbations. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of orbital quantity |  |
| mean free path | has definition Mean length of the path of a particle between collisions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The mean distance traversed by a particle before undergoing a significant deflection or collision. | ![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of length |  |
| mean solar day | has definition The mean length of time between two successive culminations of the Sun (i.e., the mean period from apparent noon to apparent noon). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 24h00m00s |  |
| is an instance of day |  |
| mean solar second | has definition 1/86400 of a mean solar day (cf. ephemeris second). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 1/86400 mean solar day | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of second unit |  |
| mechanics | has definition The study, in physics, of the influence of forces. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| median | has definition Literally the middle value in a sequence of values arranged in increasing size order. A useful mathematical estimator of the true value from a set of values when one of these values is contaminated, i.e. known to be much larger than the average. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| mega | has symbol M |  |
| has value 106 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| Meinel band | has species N2+ radical | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 8000 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| meitnerium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| melting | has final phase liquid |  |
| has initial phase solid |  |
| has inverse process solidification |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| mendelevium | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| meniscus mirror | has definition A very thin mirror with a high curvature. A method of constructing very large mirrors which assumes from the outset that the mirror is too thin to hold its shape against gravity and will require an active control system. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| Mensa | has acronym Men |  |
| has genitive Mensae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin named after the table mountain near de Lacaille's observatory in Cape Town |  |
| has synonym Mons Mensa |  |
| has synonym Table Mountain |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Mercury | has advance of perihelion 476" per century | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has albedo 0.06 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition He and Ar | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere pressure < 2 × 10-9 millibars (data from Mariner 10) |  |
| has core composition iron rich | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Innermost planet of the Solar System. Transits of the Sun occur either 7 or 13 years apart - last transit 1973 November 10. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.206 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has equatorial radius 2446 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity Vesc 4.2 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| mercury | has image  |  |
| Mercury | has inclination i = 7°.0 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field inclination < 10° to the pole | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field offset 0.47 RM from the core | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field strength 200-300 gammas (data from Mariner 10) |  |
| has mass 3.15 × 1026 g (0.054 MEarth) (data from Mariner 10) |  |
| has maximum elongation 28° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 5.44 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 0.387 AU -has source: [H76] |  |
| has oblateness < 0.001 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| mercury | has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| Mercury | has orbital period 88 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity Vorb 47.9 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has relativistic advance of perihelion 42".6 per century | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 58.646 days exactly 2/3 of its orbital period |  |
| has subsolar point temperature 700 K (data from Mariner 10) |  |
| has surface gravity 360 cm s-2< sup> -has source: [H76] |  |
| has surface spectrum similar to lunar maria and uplands , probably lunar-like soil of low-density silicates |  |
| has synodic period 116 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| mercury | is a kind of liquid element |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| Mercury | is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of terrestrial planet |  |
| merger | is a kind of mass motion |  |
| meridian | has definition A great circle passing through the celestial poles and through the zenith of any location on Earth. For planetary observations a meridian is half the great circle passing through the planet's poles and through any location on the planet. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The great circle on the celestial sphere which passes through the celestial poles and the zenith of the observer. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The great circle passing through the zenith of the observer and the north and south points on his horizon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theoretical north-south line on the Earth's surface, or an extension of that line onto the night sky, connecting the observer's zenith with the celestial pole and the horizon. The meridian is used to state directional bearings. Devices and structures - such as meridian arcs - marking the meridian were once common in observatories. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of great circle |  |
| meridional flow | has definition Flow between the poles, or between the equator and the poles. A positive value indicates flow away from the equator: a negative value, flow toward the equator. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| MERLIN | has image   |  |
has reference MERLIN/VLBI National Facility  |  |
| is an instance of radio interferometer |  |
| meson | has definition A strongly interacting particle consisting of a quark and an antiquark. Its mass is intermediate between that of a proton and an electron, which is believed to be responsible for the strong nuclear force. In contrast to the case of baryons or leptons, meson number is not conserved: like photons, mesons can be created or destroyed in arbitrary numbers. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of quarks 2 |  |
| has spin 0 | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of boson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hadron |  |
| mesosphere | has definition The part of Earth's atmosphere immediately above the stratosphere, where the temperature drops from about 270 K to 180 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 270 K to 180 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| mesozoic era | has duration 167 million years |  |
| has start time 230 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of geological era |  |
| Messier catalog | has definition Designation of objects in the Messier Catalog of nebulae, star clusters, and galaxies, published in the Eighteenth Century. | ![has source: [f88], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition is an instance of nebula catalog |  |
| has definition List of the locations in the sky of more than 100 galaxies and nebulae, compiled by Charles Messier between 1760 and 1784. Some designations he originated are still used in identification; M1 is the Crab Nebula (in Taurus). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the earliest catalogues of nebulous-appearing astronomical objects, compiled in 1781 by the French astronomer Charles Messier. Messier's catalogue included many objects that were later realized to be galaxies. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nebula catalog |  |
| Messier object | has apparent dimension |  |
| has apparent magnitude |  |
| has catalog Messier catalog |  |
has definition an object assigned a number by Charles Messier  |  |
| has distance from Earth |  |
| has Messier number |  |
| has purpose originally to catalog all objects which could be confused with a comet |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| metal | has definition As used in stellar spectroscopy, any element heavier than helium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition To an astronomer, a metal is any element heavier than hydrogen and helium; thus, not only are iron and copper metals, but so are elements like oxygen and neon. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of solid |  |
| metal-poor star | has metallic line strength weak |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| metal-rich star | has definition A small subgroup of A-type stars in which the lines of Mg II are very strong. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star having metal-to-hydrogen ratios greater than those of the Hyades. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has metallic line strength strong |  |
| has synonym CN-strong star |  |
| has synonym metal-strong star |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| metallic element | is a kind of element |  |
| metallic hydrogen | has definition A hypothetical form of hydrogen in which the molecules have been forced by extremely high pressures to assume the lattice structure typical of metals. It is estimated that as much as 40% of Jupiter's mass (but not more than 3% of Saturn's) may be in the form of metallic hydrogen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solid |  |
| metallic metalloid | is a kind of metalloid element |  |
| metalloid element | is a kind of element |  |
| meteor | has average interval time one per hour from a given location on Earth, higher during meteorite shower |  |
| has definition A "shooting star" - the streak of light in the sky produced by the transit of a meteoroid through the Earth's atmosphere; also the glowing meteoroid itself. The term "fireball" is sometimes used for a meteor approaching the brightness of Venus; the term "bolide" for one approaching the brightness of the full Moon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fragment or particle that enters the Earth's atmosphere and is then destroyed through friction, becoming visible as this occurs as a momentary streak of light. At certain times of the year, meteors apparently emanating from a single area of the sky (a radiant) form meteor showers. They are thought to originate within the Solar System. See also meteorite. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition when a meteoroid collides with the atmosphere or surface of a celestial body, kinetic energy is converted to heat, light and sound | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has product meteorite (if meteoroid does not burn up) |  |
| has synonym shooting star |  |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| is a kind of naked eye object |  |
| can produce sonic boom |  |
| meteor event | has definition The event in a sequence of the events during the passage of a meteor. They are in order : - incandescent flight
- fireball
- smoke trail
- meteoroid break up
- retardation point
- dark flight
- meteorite impact
| ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| meteor shower | has definition A profusion of meteors that fall within a period of a few hours and that appear to radiate from a common point in the sky. Shower meteors are usually low-density material and have high eccentricities. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition temporary increase in the rate at which meteors are observed when the target runs into a swarm of meteoroids that share a common orbit | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration a few hours | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has location which depends on the observer's location on the planet, is it facing the correct direction |  |
| has parent object the object from which the meteroids originate |  |
| has period one year |  |
| has radiant a location on the sky from which meteor showers seem to originate |  |
| has rate the number of meteors observed in a given interval from the observers location |  |
| is a kind of periodic celestial event |  |
| meteorite impact | is a kind of meteor event |  |
can produce - crater
- blinding white light like a nuclear detonation
- ejecta blanket
- tektites and impact melt glass
- seismic disturbances like Earthquakes
| ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:06.0](facet.gif) |
| can shatter meteoroid |  |
| meteoroid break up | is a kind of meteor event |  |
| meteorological satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| Meteosat satellite | has creator EUMETSAT |  |
| has ground communication station Bracknell |  |
| has ground communication station Fucino, Italy |  |
| has ground communication station Rome |  |
| has ground communication station Toulouse |  |
| is a kind of EUMETSAT satellite |  |
| is a kind of geosynchronous satellite |  |
| Meteosat-7 | has launch date 2 Sept 1997 |  |
| is an instance of Meteosat satellite |  |
| meter | has approval agency 11th CGPM | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1960 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has consequence fixes the speed of light in vacuum at exactly 299792458 m·s-1 |  |
| has definition A unit of length. The meter is the length equal to 1650763.73 wavelengths in vacuum of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the levels 2p10 and 5d5 of the Krypton-86 atom. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second |  |
| has historical origin chosen in 1791 by the French Academy of Sciences as 10-7 of the length of the meridian through Paris from pole to the equator |  |
| has symbol m |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| methanimine | has symbol H2CNH |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| methanol | has definition More rotational lines have been observed astronomically for it than for any other molecule. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery in space date 1970 |  |
| has symbol CH3OH |  |
| has synonym methyl alcohol |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| methyl acetylene | has symbol CH3C2H |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| methyl cyanide | has symbol CH3CN |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| methyl formate | has symbol HCOOCH3 |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| methylamine | has definition A molecule discovered in interstellar apace in 1974, in Sgr B2, at a frequency of 87.77 GHz. Methylamine can react with formic acid to produce glycine, the simplest amino acid. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol CH3NH2 |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| methylidyne | has symbol CH |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| metric ton | has symbol t |  |
| has value in SI unit 103 kg |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| Meudon Refractor | has altitude 162 m |  |
| has aperture 0.83 m |  |
| has creation date 1889 |  |
| has focal ratio f/19.5 |  |
| has latitude 48° 48' N |  |
| has lens maker Henry brothers |  |
| has location Meudon, France |  |
| has longitude 2° 14' E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer P Gautier |  |
| has owner Observatoire de Paris |  |
| has synonym 33 inch |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| MF band | has frequency 300 kHz to 3 MHz |  |
| has wavelength 100 m to 1 km |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| micro | has symbol μ |  |
| has value 10-6 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| microchannel plate | has definition A compact electrostatic high-voltage electron multiplier with a very large number of narrow pores or channels. A photoelectron generated at the entrance face (photocathode) stimulates a cascade of secondary electrons down the nearest channel to produce a huge cloud of charge at the output face. The output pulse can be used in many different ways to record the event. If it impacts a phosphor screen then light emission can be detected with a CCD. Direct electrical detection can be obtained using a Multi Anode Microchannel Analyzer. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of imager |  |
| micron | has definition A unit of length. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-4 cm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 104 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol μ | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif) |
| microphotometer | has definition A device for measuring the variations in density in a photographic emulsion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| Microscopium | has acronym Mic |  |
| has genitive Microscopii |  |
| has synonym Microscope |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| microwave | has definition An electromagnetic wave (in the radio region just beyond the infrared) with a wavelength of from about 1 mm to 30 cm (about 109-1011 Hz). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength between one millimeter and 30 centimeters, or sometimes one meter. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum between infrared and radio waves. This range has wavelengths of between about 20 cm and about 1 mm. Radiation of this type was detected as background radiation. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Radio radiation with wavelengths of about 10-4 to 1 meter, equal to 109 to 1013 hertz. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| mid infrared | has acronym MIR |  |
| is a kind of infrared |  |
| MIDAS 1 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 2 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 3 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 4 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 5 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 6 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS 7 | is an instance of MIDAS satellite |  |
| MIDAS satellite | is a kind of reconnaissance spacecraft |  |
| middle precambrian period | has duration million years |  |
| has start time million years ago |  |
| is a kind of precambrian era |  |
| Mie diffraction | has definition The diffraction of light by small spherical particles. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction |  |
| Mie scattering | has definition Scattering of light (without regard to wavelength) by larger particles, such as those of dust or fog in Earth's atmosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| mile | has definition The mile employed in this book is the statute mile, equal to 5280 feet. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| military spacecraft | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| Milky Way | has definition A softly glowing band of light that bisects the skies of Earth, produced by light from stars and nebulae in the galactic disk. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Our own galaxy, the second largest in the local group. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition System of approximately 100000 million stars, of which our Sun is one. It is a normal spiral galaxy of class Sb, with a diameter now reckoned to be probably less than 100,000 light-years, and a strong but obscure energy source at the center (emitting infrared radiation). It is undergoing galactic rotation. Possibly one tenth of the galaxy's total mass - estimated at 1.8 × 1011 solar masses - comprises interstellar gas and dust. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The galaxy to which the Sun belongs. Our Galaxy is about 1010 years old and contains about 1011 stars. Its mass is at least 1011 Msun, about 5-10 percent of which is in the form of gas and dust. Diameter ~ 30 kpc; thickness of nuclear bulge about 4 kpc; thickness of disk about 700-800 pc; distance between spiral arms about 1.4 kpc. Mv = - 20.5. Mean density about 0.1 Msun per cubic parsec. Magnetic field about 3-5 × 10-6 gauss. Total luminosity about 1044 ergs s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids |  |
| is an instance of hypergalaxy | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| is an instance of spiral galaxy |  |
| milli | has symbol m |  |
| has value 10-3 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| Mimas | has albedo 0.49 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The second innermost satellite of Saturn. The perturbations of Mimas and Janus produce the divisions in Saturn's rings. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has dicovery date 1789 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Herschel | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 0d.94 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R ≈ 250 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| mini black hole | has definition In a chaotic early universe, black holes may form at eras as early as the Planck time. The characteristic size of these mini black holes is 10-6 gram, the minimum mass of a collapsing inhomogeneity at that time. Larger mini black holes may form at later eras. Since conventional theories of stellar evolution show that only very massive stars can form black holes, the possible formation of mini black holes is a unique characteristic of the very early universe. | ![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| Mintaka | has definition One of the three stars in Orion's belt, and the star along whose line of sight interstellar gas was first spectroscopically detected. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O9.5II |  |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| minute (angle) | has symbol ' |  |
| has synonym arc minute |  |
| has value in SI unit (1/60)° = (π/10800) rad |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| minute (time) | has symbol min |  |
| has value in SI unit 60 s |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| miocene epoch | has duration 12 million years |  |
| has start time 25 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of tertiary period |  |
| MIR space station | is an instance of space station |  |
| Mira | has amplitude 5 mag | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A irregular long-period intrinsic variable. It was named Mira ("wonderful") in 1596 by Fabricius, who made the first recorded observations of its brightness fluctuations. Mira is a double star with a faint B companion which is itself variable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A red giant that varies in brightness as it pulsates. When brightest, Mira is visible to the naked eye; when dimmest, Mira can be viewed only with optical aid. Mira is the prototype of all pulsating red giants, which are called Miras in its honor. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer David Fabricius |  |
| has discovery date 1596 |  |
| has distance 70 pc |  |
has image   |  |
| has period 331 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym omicron Cet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cetus | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of long-period variable |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of red giant |  |
| M6e-M9e III -has source: [H76] |  |
| Miranda | has definition The innermost satellite of Uranus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Kuiper | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1948 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 1d10h | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Uranus |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| mirror | has reflective coating |  |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| missing mass problem | has definition Poses the question: why does the Universe seem to have much more mass in it than can be seen with a telescope? Dynamical and theoretical constraints place the proportion of missing mass to be somewhere between 90-99 per cent of the total mass of the Universe. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The cosmic mass that some scientists hypothesize so that the universe will have the critical density of matter, with an exact balance between gravitational energy and kinetic energy of expansion. Such mass is called missing because it represents about 10 times as much mass as has actually been detected. (See closed universe; critical mass density; dark matter.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of problem |  |
| mississippian period | has duration 35 million years |  |
| has start time 345 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| MMT Telescope | has altitude 2608 m |  |
| has aperture 6.5 m |  |
| has creation date (1999) |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.25, 5.4, 9, 15 |  |
| has latitude 31° 41' N |  |
| has location Mount Hopkins, Arizona, US |  |
| has longitude 110° 53' W |  |
| has mirror maker R. Angel, B. Martin |  |
| has mirror type Spin-cast borosilicate honey-comb |  |
| has mounting manufacturer de Bartolomeis |  |
| has operator Smithsonian Institution and Univ. of Arizona |  |
| has owner MMT Observatory |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| molar gas constant | has symbol R |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000015 J mol-1 K-1 |  |
has value 8.314472 J mol-1 K-1  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| molar volume of ideal gas | has equation  |  |
| has pressure 101.325 kPa |  |
| has symbol Vm |  |
| has temperature 273.15 K |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000039 × 10-3 m3 mol-1 |  |
has value 22.413996 × 10-3 m3 mol-1  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| mole | has approval agency 14th CGPM | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1971 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon 12 |  |
| has definition The SI unit of the amount of substance, defined as the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon 12. One mole, which is equal to gram multiplied by the molecular weight, contains 6.02 × 1023 molecules (see Avogadro's number). In general, 1 mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 liters. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol mol |  |
| is an instance of amount of substance unit |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit |  |
| requires qualification elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles |  |
| molecular band | has definition A series of closely spaced, often unresolved, emission or absorption lines found in the spectra of molecules. Each line represents an increment of energy due to a change in the rotational state of the molecule. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of molecular lines |  |
| molecular hydrogen | has definition A molecule consisting of two hydrogen atoms (H2) and the most common molecule in space. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A molecule of hydrogen, discovered in interstellar space in 1970. H2 is a very hard molecule to detect. None of its transitions lie in the visible part of the spectrum. Second, being a symmetric homonuclear molecule, it does not have an electric-dipole rotation-vibration spectrum, and detection must be based on the weak quadrupole spectrum. Third, ultraviolet radiation is a very efficient dissociator of H2, so any H2 that survived would presumably be located inside very dense interstellar clouds. So far observations have borne out this supposition. Measurements of the region within about 1 kpc of the Sun suggest that H2 is about twice as abundant as atomic H. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol H2 |  |
| is a kind of interstellar molecule |  |
| is a kind of neutral particle |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| molecular oxygen | has symbol O2 |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| molecule | has definition The smallest unit of a chemical compound. A molecule is composed of two or more atoms, linked by interactions of their electrons. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| molybdenum | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI |  |
| has ocean residence time 600000 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| Monoceros | has acronym Mon |  |
| has genitive Monocerotis |  |
| has synonym Unicorn |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Monoceros Loop | has age 300000 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A filamentary supernova remnant resembling a loop. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 1 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Monoceros |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| month | has definition The period of one complete synodic or sidereal revolution of the Moon around the Earth; also a calendrical unit that approximates the period of revolution. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time unit |  |
| Moon | has V< i>esc 2.38 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has albedo 0.07 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has center of mass location displaced about 2 km from geometrical center towards the direction of Earth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has core temperature 1500 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has crust thickness 60 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Natural satellite of Earth. Studies of lunar rocks have shown that melting and separation must have begun at least 4.5 × 109 years ago,so the crust of the Moon was beginning to form a very short time after the solar system itself. It would have taken only 107 years to slow the Moon's rotation into its present lock with its orbital period. The Moon's orbit is always concave toward the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0549 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination of orbital plane to ecliptic 5°8'43" | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mantle thickness 1000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 7.35 × 1025 g = 0.0123 MEarth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 3.34 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Earth 384404.377 ± 0.001 km (1.28 lt-sec) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean radius 1738 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 6°41' | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity Vorb = 1.02 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has sidereal period 27d7h43m11s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 162.2 cm s-2 = 0.165 Earth's | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 29d12h44m2s.9 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Earth |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Moon orbital event | has participants satellite, Moon |  |
| is a kind of orbital event |  |
| moonrise | has antonym moonset |  |
| has definition The time at which the apparent upper limb of the Moon is on the astronomical horizon just before it rises; i.e., when the true zenith distance, referred to the center of the Earth, of the central point of the disk is 90°34' + s - π, where s is the Moon's semidiameter, π is the horizontal parallax, and 34' is the adopted value of horizontal refraction. | ![has source: [S92]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical horizon event |  |
| moonset | has antonym moonrise |  |
| has definition The times at which the apparent upper limb of the Moon is on the astronomical horizon just as it sets; i.e., when the true zenith distance, referred to the center of the Earth, of the central point of the disk is 90°34' + s - π, where s is the Moon's semidiameter, π is the horizontal parallax, and 34' is the adopted value of horizontal refraction. | ![has source: [S92]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical horizon event |  |
| motion | has definition Process of passing through space or changing position |  |
| is a kind of physical process |  |
| Mount Stromlo 2.3-meter | has altitude 1149 m |  |
| has aperture 2.3 m |  |
| has creation date 1984 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.09, 18 |  |
| has latitude 31 ° 16' S |  |
| has location Siding Spring Mtn., Australia |  |
| has longitude 149° 03' E |  |
| has mirror maker Norman Cole |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Australian National Univ., Newcastle Dockyard |  |
| has owner Mt. Stromlo and Siding Spring Obs. |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| MS star | has definition M-type stars with ZrO bands. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star sharing the M and S characteristics. They thus exhibit bands of both TiO and SrO. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of M star |  |
| Mt. Wilson | has altitude 1600 m |  |
| has definition The location, in California, of the 100-inch diameter telescope used by Edwin Hubble and others. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has director Hale (1904-19??) |  |
| has location 13 km from Pasadena, California, USA. |  |
| has telescope 1.5 m (1907) - largest in the world at that time |  |
| has telescope 2.5 m (1910) - largest in the world at that time |  |
| has telescope solar observatory (1904) |  |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| Mu Columbae | has definition Runaway star which diverges from a comparatively small area in Orion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Columba | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of runaway star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| Mulliken band | has species C2 radical | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| multiplet | has definition A group of spectral lines arising from transitions having a common lower energy level. The group of lines have the same values of L and S but different values of J. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of lines |  |
| Munich Image Data Analysis System | A suite of programs and a software environment developed at the European Southern Observatory for astronomy applications. -has source: [McL97] |  |
| has acronym MIDAS |  |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| muon | has charge -1 |  |
| has definition A second-generation lepton. It is essentially a more massive electron. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An elementary particle, formerly called a mu-meson but now classified with the leptons because it seems to be identical with the electron except for its much greater mass (207 times that of an electron). The muon family includes the muons and their neutrinos (and their antiparticles). Muons may have a positive or a negative charge. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Elementary particles produced when cosmic rays enter the upper atmosphere. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Short-lived elementary particle with negative electrical charge. Muons are leptons. They resemble electrons, but are 207 times more massive. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol μ |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of lepton |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| muon Compton wavelength | applies to particle muon |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol λC,μ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000035 × 10-15 m |  |
has value 11.73444197 × 10-15 m  |  |
| is an instance of particle Compton wavelength |  |
| muon magnetic moment anomaly | applies to particle muon |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol aμ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000064 × 10-3 |  |
has value 1.16591602 × 10-3  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment anomaly |  |
| muon mass | applies to particle muon |  |
| has symbol mμ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000016 × 10-28 kg |  |
has value 1.88353109 × 10-28 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| Musca | has acronym Mus |  |
| has genitive Muscae |  |
has synonym Fly  |  |
| has synonym Musca Australis |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| N 159 | has distance 170000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| N galaxy | has definition A galaxy with a small, bright, blue nucleus superposed on a considerably fainter red background. (In the Yerkes 1974 system, a galaxy with a small nucleus containing a considerable fraction of the luminosity; N-, less pronounced N galaxies; N+, extreme examples of N galaxies.) Also, a type of radio galaxy having a brilliant, starlike nucleus containing most of the luminosity of the system. N galaxies are compact galaxies, and as a class are intermediate between Seyfert galaxies and quasars in properties of form, color, spectra, redshift, and optical and radio variability. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| N magnitude | has band 10 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 10 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| N star | has definition In the old terminology, the cooler C-type stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Red star similar to M stars except that bands of C2, CN, and CH are present instead of those of TiO. N stars are strongly concentrated toward the Galactic plane. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C star |  |
| N1 line | has definition Green forbidden line of doubly ionized oxygen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has species [O III] |  |
| has wavelength 5007 Å |  |
| is an instance of [O III] line |  |
| N2 line | has definition Green forbidden line of doubly ionized oxygen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has species [O III] |  |
| has wavelength 4959 Å |  |
| is an instance of [O III] line |  |
| nadir | has antonym zenith |  |
| has azimuth 0 |  |
| has definition The point on the celestial sphere diametrically opposite to the zenith in the direction of gravity. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has elevation -90 |  |
| has synonym downward |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate |  |
| is opposite of zenith |  |
| naked eye object | has definition a physical object visible to the unnaided human eye |  |
| is a kind of physical object |  |
| naked eye planet | has apparent magnitude brighter than 5 |  |
| has been observed for many centuries |  |
| has definition a planet in our solar system visible to the unaided eye |  |
| has motion relative to stars epicycloidal |  |
| is a kind of planet |  |
| naked eye star | has apparent magnitude brighter than 5 |  |
| has been observed for many centuries |  |
| has definition A star visible without visual aids | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of naked eye object |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| is usually part of asterism |  |
| naked singularity | has definition A singularity that will be visible and communicable to the outside world. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of singularity |  |
| named derived SI unit | is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| nano | has symbol n |  |
| has value 10-9 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| narrow emission line galaxy | has acronym NELG |  |
| is a kind of emission line galaxy |  |
| narrow emission line X-ray galaxy | has acronym NLXG |  |
| is a kind of emission line galaxy |  |
| Narrow-line radio galaxy | has acronym NLRG |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| NASA Extragalactic Database | has acronym NED |  |
| is an instance of database |  |
| NASA Infrared Telescope Facility | has acronym NASA IRTF |  |
| has altitude 4208 m |  |
| has aperture 3.00 m |  |
| has creation date 1979 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.5, 35, 120 IR |  |
| has latitude 19° 50' N |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
| has mirror maker KPNO Optical Shop |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer de Bartolomeis |  |
| has owner Mauna Kea Observatory |  |
| has purpose infrared work |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of English equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| NASA satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| NASDA satellite | has creator NASDA |  |
is a kind of artificial satellite  |  |
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | has acronym NASA |  |
| has definition US government body set up in 1958, under which the Space Center at Houston, Texas, and the Space Center at Cape Canaveral, Florida, are responsible for manned and unmanned space flights. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| National Air and Space Development Agency | has acronym NASDA | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition National Air and Space Development Agency. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Japan |  |
| is an instance of space science institution |  |
| National Bureau of Standards | has acronym NBS | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| National Optical Astronomy Observatory | has acronym NOAO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
is an instance of astronomical institution  |  |
| National Radioastronomy Observatory | has acronym NRAO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| National Science Foundation | has acronym NSF | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| natural line broadening | has definition Line broadening resulting from the fact that excited levels have certain mean lives, and these mean lives, by virtue of the uncertainty principle, imply a spread in the energy values. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| natural logarithm e | has value 2.71828182 |  |
| is an instance of mathematical constant |  |
| natural object | has definition an object occurring naturally, not constructed by humans |  |
| is a kind of physical object |  |
| natural satellite | has definition Body orbiting a planet. Since 1957 the term has also been applied to man-made (artificial) satellites; many astronomers make the distinction by calling natural satellites moons (and the Earth's natural satellite the Moon). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a kind of satellite |  |
| natural unit | has definition Unit of length, time, mass, etc. in which the fundamental constants c (the speed of light), h bar (Planck's constant) and kB (Boltzmann's constant) are equal to unity. That is, c, h bar and kB have the numerical value 1. (For example, if we measure length in light-years and time in years, then c = 1 light-year per year.) The use of natural units allows these constants to be omitted from mathematical equations, leading to less-cluttered calculations. In natural units, E = mc2 becomes E = m and E = kBT becomes E = T, so that both mass and temperature can be expressed in units of energy. (Of course, the correct factors of c, h bar and kB must be inserted at the end of a calculation to obtain measurable quantities.) | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unit |  |
| nautical mile | has definition A unit of length. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1.15 statute miles | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| navigation satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| near infrared | has acronym NIR |  |
| has source atomic transitions, vibrational transitions in molecules | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of infrared |  |
| nebula | has catalog nebula catalog |  |
| has definition An irregularly shaped cloud of interstellar gas or dust whose spectrum may contain emission lines (emission nebula) or absorption lines characteristic of the spectrum of nearby illuminating stars (reflection nebula). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Indistinct, nonterrestrial objects visible in the night sky. "Bright" nebulae glow with light emitted by the gas of which they are composed ("emission" nebulae) or by reflected starlight ("reflection" nebulae) or both. "Dark" nebulae consist of clouds of gas and dust that are not so illuminated. "Planetary" nebulae are shells of gas ejected by stars. Spiral nebulae are galaxies. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The term "nebula" was previously applied to all kinds of hazy patches in the sky, many of which are now recognized to be clusters or galaxies. (See also diffuse nebula, gaseous nebula, dark nebula.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of gas |  |
| nebula catalog | has object type nebula |  |
| is a kind of astronomical catalog |  |
| nebular hypothesis | has definition Hypothesis, maintained in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, that the spiral nebulae are not galaxies but are instead whirlpools of gas from which new systems of stars and planets are condensing. Compare island universe theory. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| see also island universe hypothesis |  |
| neodymium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 500 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| neon | has abundance 2 × 10-4 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 3.72 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 7 × 10-5 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 837.761 nm for Ne I |  |
| has atomic emission line 878.062 nm for Ne I |  |
| has atomic emission line 878.375 nm for Ne I |  |
| has atomic emission line 885.387 nm for Be I |  |
| has atomic emission line 865.438 nm for Ne I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 10 |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 27.10 K |  |
| has chief source liquid air |  |
| has critical pressure 2721 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 44.5 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 445.462 pm |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c |  |
| has daily dietary intake low |  |
| has definition colourless, odourless gas |  |
| has density 0.89994 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 1207.3 kg m-3 for liquid at 27.10 K boiling point |  |
| has density 1444 kg m-3 for solid at 24.48 K melting point |  |
| has discoverer Sir William Ramsay and M.W. Travers |  |
| has discovery date 1898 |  |
| has discovery location London, England |  |
| has electron affinity -29 kJ mol-1 from Ne to Ne- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p6 in ground state |  |
| has hazard harmless gas, although it could asphyxiate if it excluded oxygen from the lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 0.324 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 1.736 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has isotope mass range 17 to 25 |  |
| has level in humans nil in bone |  |
| has level in humans nil in liver |  |
| has level in humans nil in muscle |  |
| has level in humans trace mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has longest lived isotope neon 20 |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -4.2 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person tiny for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 24.48 K |  |
| has mineral none |  |
| has molar volume 13.97 cm3 |  |
| has name origin neon = new from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 9 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 10 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| has pronunciation nee-on |  |
has registry number 7440-01-9 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 20.1797 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 6.5 × 1010 tonnes in atmosphere |  |
| has space group Fm3m |  |
| has specimen small pressurized canisters. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Ne |  |
| has synthesis mechanism liquid air |  |
| has term symbol 1S0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.0493 W m-1 K-1 for gas at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.040 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has uses ornamental lighting, neon signs |  |
| has van der Waals radii 160 pm |  |
| has world production 1 ton year-1 |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with nothing |  |
| neon 20 | has atomic mass 19.992435 |  |
| has natural abundance 90.48 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 10 |  |
| has number of nucleons 20 |  |
| has symbol 20Ne |  |
is an instance of neon  |  |
| neon 21 | has atomic mass 20.993843 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -2.1118 × × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.27 |  |
| has NMR frequency 7.894 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.0359 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.661796 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.10155 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 11 |  |
| has number of nucleons 21 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 2.50 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 21Ne |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of neon  |  |
| neon 22 | has atomic mass 21.991383 |  |
| has natural abundance 9.25 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 12 |  |
| has number of nucleons 22 |  |
| has symbol 22Ne |  |
is an instance of neon  |  |
| neon 23 | has atomic mass 22.994465 |  |
| has decay mode β- (4.376 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 37.2 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.08 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 13 |  |
| has number of nucleons 23 |  |
| has symbol 23Ne |  |
| has uses |  |
is an instance of neon  |  |
| neon 24 | has atomic mass 23.993613 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.468 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 3.38 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 14 |  |
| has number of nucleons 24 |  |
| has symbol 24Ne |  |
is an instance of neon  |  |
| neon burning | has definition The stage in which a star burns neon into oxygen and magnesium. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 1 year |  |
| has location center of star heavier than 9 solar masses |  |
| has optimum density 4 × 106 g cm-3 |  |
| has optimum temperature 1.2 × 109 K |  |
| has part product oxygen, magnesium |  |
| has reactant neon |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| neper | has symbol Np |  |
| has value in SI unit 1 |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| Neptune | has albedo 0.62 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition hydrogen and methane | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Eighth major planet out from the Sun. Discovered in by following predictions calculated by Urbain Le Verrier. Similar predictions had been made earlier by John Couch Adams but were not followed up. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Johann Galle and Louis d'Arrest | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1846 | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.009 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 25 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination 1°.8 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1.03 × 1029 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has maximum apparent brightness 7.6 mag | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 1.7 g cm-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 30.07 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has oblateness 0.02 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 28°.8 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 164.8 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity Vorb = 5.43 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 24500 ± 500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 15h49m30s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has satellites Triton and Nereid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 1.3 that of Earth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 367.49 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of gas giant |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| neptunium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| Nereid | has definition The outer satellite of Neptune. It has the most eccentric orbit of any natural satellite. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Kuiper |  |
| has discovery date 1950 |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.76 |  |
| has orbital period about 360 days direct |  |
| has radius 150-250 km |  |
| is a part of Neptune |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| neutral particle | has charge 0 |  |
| has definition A particle with zero charge | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| is not accelerated by electric or magnetic fields |  |
| neutrino | has antiparticle antineutrino |  |
| has definition A fundamental elementary particle with no electric charge and very small if any rest mass. Believed to be exceedingly abundant in the universe. The neutrino has a very low cross-section for interaction with matter and is almost impossible to detect, hence the uncertainty over its rest mass. The Sun produces neutrinos from thermonuclear reactions in its core, and a large flux of neutrinos carries away most of the energy, of a supernova. Neutrinos are one candidate for Dark Matter. Experiments to detect cosmic neutrinos involve large masses of "stopping" material and indirect detection of the effects of neutrino absorption. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A stable particle with no charge, a rest mass of zero, and a spin of 1/2, that carries away energy in the course of nuclear reactions. Its main characteristic is the weakness of its interactions with all other particles. Since the wavelengths of neutrinos at the energies at which they are normally emitted from unstable nuclei are only a few thousandths of an angstrom (compared with the wavelength of a light photon which is several thousand angstroms), they have negligible probability (10-19 that of a light photon) of interacting with matter and escape at the speed of light. Neutrinos arise only in the energy-producing regions of stars and therefore, unlike light photons, provide direct evidence of conditions in stellar cores. There are two types of neutrinos, those associated with electrons (ve) and those associated with muons (vµ). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An electrically neutral, massless particle of spin-1/2, which interacts only by the weak force and gravity. It was first postulated by Pauli in 1930 to ensure conservation of energy and angular momentum in nuclear β decay. Three different types of neutrinos are known to exist corresponding to the three massive leptons: νe, νµ and ν τ. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An electrically neutral, very weakly interacting particle, with a rest energy which is either zero or very small. The particle was predicted in 1931 as a means of reconciling the measurements of beta decays with the conservation of energy, but it was not directly detected until 1956. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Chargeless species of particle, subject only to the weak force. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of lepton |  |
| is a kind of massless particle |  |
| is a kind of neutral particle |  |
| neutrino telescope | has definition telescope designed to detect neutrinos and determine their origin, type and energy |  |
| is a kind of telescope |  |
| neutron | has composition two down quarks and one up quark |  |
| has decay product proton, electron |  |
| has definition A neutral baryon. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A nuclear particle with a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. A free neutron decays, after a half-life of about 10.6 minutes, into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The neutron is probably made up of still more fundamental particles having both positive and negative charges. The charges balance to give a net charge of zero, but the motions of the charges are such that their magnetic contributions do not cancel and consequently the neutron is magnetic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the constituents of the atomic nucleus discovered in 1932. It is bound into atomic nuclei by the strong nuclear force. Free neutrons decay slowly via the weak nuclear force. Despite being electrically neutral, the neutron possesses both an electric dipole moment (as if it were made of positive and negative charges separated a minute distance) and a magnetic moment, indicating some internal substructure. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle in the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen. Through beta decay, a neutron may become a proton and an electron; the process occurs in reverse during the formation of a neutron star. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Stable within the nucleus, the neutron if isolated decays, with a ha half-life of fifteen minutes. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition typically found in the nucleus of an atom. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime 15 minutes | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1.6749 × 10-24 g |  |
| is a part of nucleus |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| is an instance of nucleon |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| neutron Compton wavelength | applies to particle neutron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol λC,n |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000010 × 10-15 m |  |
has value 1.319590898 × 10-15 m  |  |
| is an instance of particle Compton wavelength |  |
| neutron g factor | applies to particle neutron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol gn |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000090 |  |
has value -3.82608545  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| neutron gyromagnetic ratio | applies to particle neutron |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol γn |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000044 × 108 s-1 T-1 |  |
has value 1.83247188 × 108 s-1 T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| neutron induced fission | is a kind of fission |  |
| neutron magnetic moment | applies to particle neutron |  |
| has symbol μn |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000023 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value -0.96623640 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment |  |
| neutron mass | applies to particle neutron |  |
| has symbol mn |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000013 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 1.67492716 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| neutron star | has definition A dead, collapsed star that consists mostly of neutrons and is only about 20 kilometers across. Neutron stars are much denser than white dwarfs. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A star whose core is composed primarily of neutrons, as is expected to occur when the mean density is in the range 1013-1015 g cm-3. Under current theories pulsars are assumed to be rotating magnetic neutron stars. A neutron star would probably be only 10-15 km in diameter with a magnetic field of about 1012 gauss, a density of 1013-1015 g cm-3 (compared with a white dwarf's maximum density of about 108 g cm-3) and a central temperature of about 109 K and thus would be both bluer and dimmer than a white dwarf. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Remnant of a star after it has exploded as a supernova. Usually optically dim, a neutron star sends out regular or irregular radio emissions and is therefore also called a pulsar. The density of such a star may be unimaginably great although the diameter is generally around only 10 km; the gravitational and magnetic forces are correspondingly vast. It is called a neutron star because in such density, protons fuse with electrons to form neutrons, of which the star is almost entirely composed. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of massive compact halo object |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| New General Catalogue | has acronym NGC | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A catalogue of 7840 nebulae, star clusters, and galaxies that was published in 1888 by John Dreyer. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nebula catalog |  |
| New Technology Telescope | has acronym NTT |  |
| has altitude 2353 m |  |
| has aperture 3.50 m |  |
| has comment mirror figure controlled by 78 active supports |  |
| has creation date 1989 |  |
| has focal ratio U2.2, 11 |  |
| has latitude 29° 16' S |  |
| has location La Silla, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 44' W |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss |  |
| has mirror type thin Zerodur |  |
| has owner European Southern Observatory |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| newton | has base unit m·kg·s-2 |  |
| has definition The SI derived unit of force, equal to the force necessary to give an acceleration of 1 meter per second2 to a mass of 1 kg. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 105 dynes | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol N |  |
| is an instance of force unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| Newton's first law | has definition Newton's law which states that a body remains in a state of rest or uniform motion when left to itself. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Newton's law of motion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| Newton's law of motion | has definition One of three laws describing the motion of bodies based on the conception of an absolute and immutable space and time; these laws held sway until Einstein's discovery of special relativity. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Sir Isaac Newton |  |
| has domain mechanics |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| Newton's second law | has definition Newton's law which states that the net force on a body is equal to the product of its mass and its acceleration. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Newton's law of motion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| Newton's theory of gravity | has definition A force law that applies to the gravitational and electromagnetic forces in which the magnitude of the force decreases in proportion to the inverse of the square of the distance. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gravitational force decreases as one over distance squared (1/r2), where r is the distance from the source. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory of gravity declaring that the force of attraction between two bodies is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Subsequently supplanted by Einstein's general relativity. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Sir Isaac Newton |  |
| has synonym inverse square law |  |
| is an instance of gravity law |  |
| Newton's third law | has definition Newton's law which states that when two bodies interact, the force on the first due to the second is equal and opposite to the force on the second due to the first. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Newton's law of motion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| Newtonian | has definition A class of reflecting telescope developed by Sir Issac Newton with a paraboloidal primary mirror and a small, plane secondary mirror at 45°; to deflect the focus of the primary to a position outside the tube near the top of the telescope. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has primary mirror shape concave paraboloidal |  |
| has secondary mirror shape plane |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| Newtonian constant of gravitation | has definition The universal constant of proportionality in the attraction between two unit masses a unit distance apart. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect on other constants none, increases in the accuracy of its measurement have made no difference to the values of the other physical constants. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has equation F = G × m1 × m2/r2, where F is the gravitational force of attraction, m1 and m2 are the masses for two bodies separated by r. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has relationship no direct connection has, as yet, been established between G and any other physical quantities |  |
| has symbol G | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has uncertainty 0.010 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 |  |
has value 6.673 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2  |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| NGC 1275 | has definition The strongest known extragalactic X-ray source. Also a strong radio source. Optically it is a Seyfert galaxy with a huge amount (about 108 Msun) of ionized gas receding from it. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has recession velocity 5000 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has redshift z = 0.0183 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3C 84 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 0316+41 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Abell 426 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Perseus A | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Perseus X-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radio galaxy |  |
| is an instance of Seyfert galaxy |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| NGC 1326A | has distance 18.7 ± 1.5 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 1365 | has distance 18.3 ± 1.7 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 1425 | has distance 22.2 ± 1.0 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 147 | is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical galaxy |  |
| NGC 1818 | has distance 164000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of open cluster |  |
| NGC 185 | is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical galaxy |  |
| NGC 1850 | has distance 66000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of open cluster |  |
| NGC 1999 | has image   |  |
| is a part of dust |  |
| is an instance of reflection nebula |  |
| NGC 205 | has definition An elliptical galaxy that orbits the Andromeda galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Andromeda galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| NGC 2346 | has distance 2000 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| has orbit period 16 days |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Monoceros |  |
| NGC 2392 | has image   |  |
| has synonym Eskimo Nebula |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| NGC 3132 | has distance 2000 light years |  |
| has expansion rate 9 miles per second |  |
| has extent 0.5 light year |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym Eight-Burst Nebula |  |
| has synonym Southern Ring Nebula |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| NGC 3198 | has distance 14.5 ± 1.2 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 3319 | has distance 14.3 ± 0.9 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 3603 | has image   |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| NGC 3627 | has distance ? |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 3918 | has distance 3000 light years |  |
| has extent 0.3 light years |  |
has image   |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Centaurus |  |
| NGC 4214 | has distance 13 million light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of irregular galaxy |  |
| NGC 4535 | has distance 16.0 ± 1.9 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 4548 | has distance 15.9 ± 2.0 Mpc |  |
is an instance of galaxy containing Cepheids  |  |
| NGC 5195 | has declination +47d16m05s |  |
| has diameter 5.8 × 4.6 arcminutes |  |
has image   |  |
| has magnitude 10.45 |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has right ascension 13h29m58.7s |  |
| has synonym M51b |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
is an instance of irregular galaxy  |  |
| is part of Canes Venatici |  |
| NGC 5307 | has distance 10000 light years |  |
| has extent 0.6 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Centaurus |  |
| NGC 604 | has image   |  |
| is a part of Pinwheel galaxy |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| NGC 6210 | has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| NGC 6751 | has distance 6500 light years |  |
| has extent 0.8 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| NGC 6818 | has distance 6000 light years |  |
| has extent 0.5 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Sagittarius |  |
| NGC 6822 | has declination -14d48m05s |  |
| has diameter 2 kpc |  |
| has distance 600 kpc from Milky Way galaxy |  |
has image   |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has right ascension 19h44m56.1s |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of irregular galaxy |  |
| NGC 6826 | has distance 2200 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Cygnus |  |
| NGC 7009 | has distance 1400 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Aquarius |  |
| NGC 7027 | has distance 3000 light years |  |
has image     |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Cygnus |  |
| NGC 7635 | has distance 7100 light years |  |
| has extent 6 light-years |  |
has image   |  |
| has stellar wind speed 2000 kilometers per second |  |
| has synonym Bubble nebula |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Cassiopeia |  |
| NGC object | has catalog New General Catalogue |  |
| has definition an object assigned a number in the New General Catalog of non-stellar objects |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| Nicholas U. Mayall Reflector | has altitude 2120 m |  |
| has aperture 3.81 m |  |
| has creation date 1973 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.7, 8, 15.7 IR, 190 |  |
| has latitude 31° 58' N |  |
| has location Kitt Peak, Arizona, US |  |
| has longitude 111° 36' W |  |
| has mirror maker KPNO Optical Shop |  |
| has mirror type Fused-quartz |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Western Gear Corp. |  |
has owner Kitt Peak National Observatory  |  |
| has synonym Kitt Peak 4 m |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| nickel | has abundance 1 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1 × 10-4 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.91 × 106 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 4.0 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 5.7 × 10-4 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 80 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 232.003 nm for Ni I |  |
| has atomic emission line 349.296 nm for Ni I |  |
| has atomic emission line 351.505 nm for Ni I |  |
| has atomic emission line 361.939 nm for Ni I |  |
| has atomic emission line 341.476 nm for Ni I (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 352.454 nm for Ni I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 28 |  |
| has atomic radii 125 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to some species, and can act to stimulate metabolism |  |
| has boiling point 3005 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 177.3 GPa |  |
| has chief source garnierite, pentlandite |  |
| has covalent radii 115 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 352.38 pm |  |
| has crystal type f.c.c. |  |
| has Curie temperature 633 K |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.3 - 0.5 mg |  |
| has definition corrosion resistant, silvery-white, lustrous, malleable and ductile metal |  |
| has density 7780 kg m-3 for liquid at 1726 K boiling point |  |
| has density 8902 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer A.F. Cronstedt |  |
| has discovery date 1751 |  |
| has discovery location Stockholm, Sweden |  |
| has electrical resistivity 6.84 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 156 kJ mol-1 from Ni to Ni- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d84s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.91 Pauling |  |
| has hazard element and its compounds are poisonous, carcinogenic, and teratogenic |  |
| has hazard nickel carbonyl is extremely toxic |  |
| has heat capacity 23.359 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 26.07 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 17.6 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 371.8 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 62 pm for Ni3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 78 pm for Ni2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 53 to 67 |  |
| has lethal intake 350 mg kg-1 in rat for nickel acetate |  |
| has level in humans < 0.7 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 0.01 - 0.05 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.02 - 1.8 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 1 - 2 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 13.3 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope nickel 58 |  |
| has main mining area garnierite in Russia, South Africa, USA; pentlandite in Canada, South Africa |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 45.7 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 46.6 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility ferromagnetic |  |
| has mass of element in person 15 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1726 K |  |
| has mineral garnierite, millerite, nickeline, pentlandite, nickel-iron meteorites |  |
| has molar volume 6.59 cm3 |  |
| has name origin kupfernickel = Devil's copper or St Nicholas's copper from German |  |
| has neutron scattering length 1.03 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 14 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 28 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 80000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.312 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation nik-el |  |
has registry number 7440-02-0 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 58.6934 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 70 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 76.0 GPa |  |
| has space group Fm3m |  |
| has specimen foil, powder, rod, slugs, spheres and wire. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Ni |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| has term symbol 3F4 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 90.7 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 4.49 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 1 - 3 mg kg-1 |  |
| has uses alloys, especially stainless steel, coins, metal plating and catalysts |  |
| has world production 510000 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 199.5 GPa |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with acids by disolving except for concentrated HNO3 |  |
| nickel 56 | has atomic mass 55.943124 |  |
| has decay mode EC (2.14 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 6.10 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 56 |  |
| has symbol 56Ni |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 57 | has atomic mass 56.93799 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (3.265 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 35.6 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.88 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 29 |  |
| has number of nucleons 57 |  |
| has symbol 57Ni |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 58 | has atomic mass 57.935346 |  |
| has natural abundance 68.27% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 30 |  |
| has number of nucleons 58 |  |
| has symbol 58Ni |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 59 | has atomic mass 58.934349 |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 76000 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 31 |  |
| has number of nucleons 59 |  |
| has symbol 59Ni |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 60 | has atomic mass 59.930788 |  |
| has natural abundance 26.10% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 32 |  |
| has number of nucleons 60 |  |
| has symbol 60Ni |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 61 | has atomic mass 60.931057 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -2.3948 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 1.13% |  |
| has NMR frequency 8.936 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.242 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.7502 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +0.162 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 33 |  |
| has number of nucleons 61 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 3.57 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 61Ni |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 62 | has atomic mass 61.928346 |  |
| has natural abundance 3.59% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 34 |  |
| has number of nucleons 62 |  |
| has symbol 62Ni |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 63 | has atomic mass 62.929669 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.065 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 100 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 35 |  |
| has number of nucleons 63 |  |
| has symbol 63Ni |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 64 | has atomic mass 63.927967 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.91% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 36 |  |
| has number of nucleons 64 |  |
| has symbol 64Ni |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 65 | has atomic mass 64.930086 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.134 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.57 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.69 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 37 |  |
| has number of nucleons 65 |  |
| has symbol 65Ni |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| nickel 66 | has atomic mass 65.929116 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.24 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 54.6 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 38 |  |
| has number of nucleons 66 |  |
| has symbol 66Ni |  |
is an instance of nickel  |  |
| NICMOS | has definition Near Infrared Camera for Multi-Object Spectrography. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| Nicol prism | has definition A device made from a split crystal of Iceland spar with which plane-polarized light can be detected. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification polarization |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| Niels Bohr | is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of physicist |  |
| niobium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| nitrogen | has abundance 25 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 780900 p.p.m. by volume in Earth's atmosphere |  |
| has abundance 8.71 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 1246.962 nm for N I |  |
| has atomic emission line 463.054 nm for N II |  |
| has atomic emission line 500.515 nm for N II |  |
| has atomic emission line 567.956 nm for N II |  |
| has atomic emission line 746.831 nm for N I |  |
| has atomic emission line 399.500 nm for N II (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 7 |  |
| has atomic radii 71 pm |  |
| has biological role constituent element of DNA and amino acids; nitrogen cycle in nature |  |
| has boiling point 77.4 K |  |
| has chief source liquified air |  |
| has covalent radii 70 pm for single bond |  |
| has critical pressure 3394 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 126.05 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = pm |  |
| has crystal type |  |
| has daily dietary intake high |  |
| has definition colourless, odourless gas (N2) |  |
| has density 1.2506 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 1026 kg m-3 for solid at 21 K |  |
| has density 880 kg m-3 for liquid at 77.4 K boiling point |  |
| has discoverer D. Rutherford |  |
| has discovery date 1772 |  |
| has discovery location Edinburgh, Scotland, UK |  |
| has electron affinity -7 kJ mol-1 from N to N- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p3 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 3.04 Pauling |  |
| has hazard harmless gas, but it could asphyxiate if it excluded oxygen from the lungs |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for atomic gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 29.125 J K-1 mol-1 for molecular gas (N2) at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 0.720 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 5.577 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has isotope mass range 12 to 18 |  |
| has level in humans 34300 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 43000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 72000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 72000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has longest lived isotope nitrogen 14 |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 0.916 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 7.52 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -5.4 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person 1.8 kg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 63.29 K |  |
| has mineral nitratine, nitrammite, nitrobarite, nitrocalcite and nitromagnesite |  |
| has molar volume 12.65 cm3 |  |
| has name origin nitron genes = nitre forming (potassium nitrate) from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.936 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 8 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 7 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| has ocean residence time 6000 years |  |
| has pronunciation niy-troh-jen |  |
has registry number 7727-37-9 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 14.00674 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves × 10 tonnes |  |
| has space group |  |
| has specimen small pressurized canisters. Safe. |  |
| has symbol N |  |
| has synthesis mechanism liquifaction of air |  |
| has term symbol 4S3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.02598 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K for gas |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 1.91 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic as N2 gas but NO2, HCN and NH3 are toxic |  |
| has uses fertilizers, acids (HNO3), explosives, plastics and dyes |  |
| has van der Waals radii 154 pm |  |
| has world production 44 × 106 tonnes year-1 |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of group V element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| reacts with generaly unreactive at normal temperatures |  |
| nitrogen 13 | has atomic mass 13.005738 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.2205 Mev) % |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 9.97 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.3222 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2 |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 13 |  |
| has symbol 13N |  |
is an instance of nitrogen  |  |
| nitrogen 14 | has atomic mass 14.003074002 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.9331 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.634% |  |
| has NMR frequency 7.224 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 5.69 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.4037607 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.0202 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 7 |  |
| has number of nucleons 14 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 1.01 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 14N |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of nitrogen  |  |
| nitrogen 15 | has atomic mass 15.00010897 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -2.7116 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.366 |  |
| has NMR frequency 10.133 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.0219 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.2831892 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 15 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 1.04 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 15N |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of nitrogen  |  |
| nitrogen 16 | has atomic mass 16.006099 |  |
| has decay mode β- |  |
| has decay mode β-α(10.4187 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 7.13 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 9 |  |
| has number of nucleons 16 |  |
| has symbol 16N |  |
is an instance of nitrogen  |  |
| nitrogen 17 | has atomic mass 17.008450 |  |
| has decay mode β+ |  |
| has decay mode β-n (8.680 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 4.17 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 10 |  |
| has number of nucleons 17 |  |
| has symbol 17N |  |
is an instance of nitrogen  |  |
| NML Cygnus | has definition An infrared star. Its surface temperature is about the same as the surface temperature of Venus. It is a strong OH emitter, and CO has been identified in its spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Neugebauer, Martz, and Leighton | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 200 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has heliocentric radial velocity -43 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type M6 III | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 700 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym IRC+40448 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of M star |  |
| NOAA satellite | is a kind of meteorological satellite |  |
| nobelium | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| nodical month | has definition The interval of time between two successive transits of the Moon through its ascending node. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Draconic month | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 27.2122 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of month |  |
| non SI unit | has definition not an SI unit, but an important and widely used unit |  |
| has value in SI unit |  |
| is a kind of unit |  |
| non-coherent scattering | has definition Absorption of a photon and reemission at a different frequency (as seen by an observer) by scattering atoms. The natural width of the lines, Doppler broadening, and pressure broadening are the main processes that give rise to noncoherent scattering. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| nonaccelerating reference frame | has acceleration 0 |  |
| is a kind of frame of reference | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| nonmetal | is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| nonmetallic element | is a kind of element |  |
| nonmetallic metalloid | is a kind of metalloid element |  |
| nonrotating reference frame | has rotation rate 0 |  |
| is a kind of frame of reference |  |
| Nordic Optical Telescope | has acronym NOT |  |
| has altitude 2382 m |  |
| has aperture 2.56 m |  |
| has creation date 1989 |  |
| has focal ratio (f/2.0), 11.0 |  |
| has latitude 28° 45' N |  |
| has location La Palma, Canary Islands |  |
| has longitude 17° 53'W |  |
| has mirror maker Optics Labs (Tartu) |  |
| has mirror type Zerodur |  |
| has mounting altazimuth in rotating building |  |
| has owner Obs. del Roque de Ins Muchachos |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| Norma | has acronym Nor |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Normae |  |
| has historical origin as 'Norma et Regula' (appeared as the Level and the Square to de Lacaille) |  |
| has synonym Level (Square) |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Norma arm | is a part of Sagittarius arm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| North America Nebula | has definition An emission nebula in Cygnus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 7000 |  |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| North American continent | is a part of Earth's lithosphere |  |
| north celestial pole | has acronym NCP |  |
| has declination +90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Ursa Minor |  |
| is an instance of celestial pole |  |
| is opposite of south celestial pole |  |
| north galactic pole | has acronym NGP |  |
| has definition A point in the constellation Coma Berenices where we look perpendicular to and above the Galactic Plane. The nearest bright star to the North Galactic Pole is Arcturus, in the neighboring constellation Bootes. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic latitude 90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Coma Berenices |  |
| is an instance of galactic pole |  |
| is opposite of south galactic pole |  |
| north point | has azimuth 0 |  |
| has definition The point at which the meridian intersects the horizon below the north celestial pole. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has elevation 0 |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate |  |
| North Polar Spur | has definition A radio continuum feature extending from the galactic plane to the vicinity of the North Galactic Pole. It is believed to be a supernova remnant. It is also an X-ray source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 50-200 pc |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| north pole | has definition The astronomical coordinate which coincides with the northern intersection of Earth's axis with the geoid. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has terrestrial latitude +90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Earth |  |
| is an instance of pole |  |
| is opposite of south pole |  |
| nova | has definition A star that brightens suddenly and to an unprecedented degree, creating the impression that a new star has appeared where none was before. Hence the name, from nova for "new". See supernova. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A star that exhibits a sudden surge of energy, temporarily increasing its luminosity by as much as 14 mag. (Since 1925 novae have been given variable star designations.) Novae are old disk-population stars. Unlike supernovae, novae retain their stellar form and most of their substance after the outburst. All known common novae are found in close binary systems with one component a cool red giant and the other a hot, less massive object which is the seat of the instability. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A stars that undergoes an explosion during which its brightness increases by up to ten magnitudes. Usually the following phases are distinguished (in order of time): pre-maximum, principal, diffuse enhanced, Orion, nebular and post-nova. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy release 1044 ergs | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has use nova peak brightness distance determination |  |
| is a kind of cataclysmic variable |  |
| is a kind of close binary |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| can become naked eye star |  |
| Nova Cygni 1975 | has initial rise of light curve 19 magnitudes |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| is an instance of classical nova |  |
| Nova Cygni 1978 | has initial rise of light curve 11 magnitudes |  |
| is an instance of classical nova |  |
| nova remnant | has definition an expanding emission nebula produced by a nova |  |
| has expansion velocity typically 1000 km/s |  |
| has lifetime a few centuries |  |
| has mass much lower than planetary nebula |  |
| is a kind of expanding emission nebula |  |
| can be used to measure distance |  |
| Nu Octantis | has B-V magnitude 1.00 |  |
| has declination -77 23 24 |  |
| has right ascension 21 41 28.6 |  |
| has spectral type K0III |  |
| has synonym HR 8254 |  |
| has V magnitude 3.76 |  |
is a part of Octans  |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| nuclear decay | is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| nuclear density | has definition The density of an atomic nucleus (about 1014 g cm-3). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of density |  |
| nuclear disk | has definition A rotating disk of about 106 Msun of neutral hydrogen in the inner 800 pc of our Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| nuclear magneton | has equation  |  |
| has symbol μN |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000020 × 10-27 J T-1 |  |
has value 5.05078317 × 10-27 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| nuclear physics | has definition That branch of physics that attempts to understand the physics of the nucleus. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy physics |  |
| nuclear process | is a kind of physical process |  |
| nuclear time scale | has definition Time required for a star to evolve a significant distance off the main sequence; the time it takes a star to convert all its available hydrogen into helium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time |  |
| see also Kelvin timescale |  |
| nucleon | has definition The generic name for the proton and the neutron. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 939 MeV |  |
| has spin 1/2 |  |
| is a kind of baryon |  |
| is a kind of charge multiplet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of nucleus |  |
| nucleosynthesis | has definition The production of heavy nuclei from the fusion of lighter ones. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fusion |  |
| nucleosynthetic era | has definition The Big Bang era when neutrons were produced and helium and deuterium were synthesized. At t = 200 sec, nucleosynthesis began rather abruptly and virtually all deuterium was synthesized to helium. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 1000 s |  |
| has start time 1 s after the Big Bang |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is followed by radiation era |  |
| is preceded by lepton era |  |
| nucleosynthetic reaction | is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| nucleus | has definition The central part of an atom, composed of protons and neutrons (which are made of quarks) and containing nearly all of each atom's mass. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The massive, positively charged central part of an atom, composed mainly of protons and neutrons, around which the electrons revolve. The radius of an atomic nucleus is directly proportional to the cube root of its mass. Density at least 1014 g cm-3. Radius 10-12-10-13 cm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charged particle |  |
| is a part of element |  |
| nuclide | has definition A species of atomic nucleus, analogous to the word "isotope" for a species of atom. The word is also used to distinguish between atomic nuclei that are in different energy states. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleus |  |
| number | has value |  |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| nutation | has definition A small, irregular oscillation in the precessional motion of Earth's rotational axis, caused primarily by lunar perturbations. It has a principal period of 18.6 years, and moves the equinox as much as 17" ahead of or behind its mean position. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Slight but recurrent oscillation of the axis of the Earth, caused by the Moon's minutely greater gravitational effect on the Earth's equatorial "bulge". | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of axis motion |  |
| O magnitude | has band 11 microns | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The magnitude derived from observations at 11 microns. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of infrared magnitude |  |
| O star | has absorption line He II | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has color blue-white | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Very hot blue star, whose spectra is dominated by the lines of singly ionized helium (see Pickering series). (Most other lines are from at least doubly ionized elements, though H and He I lines are also present.) O stars are useful because they are found in dust clouds and virtually define the spiral arms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime 3 to 6 million years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has relative abundance rare | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation velocity very high | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 35000 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| O((f)) | has definition O-type stars in which N III is present in emission and He is strong in absorption. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line N III |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| O(f) | has definition O-type stars in which N III is present in emission and He II is weakly present in absorption or emission. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line N III and sometimes He II |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| OB association | has definition A loose gathering of O and B stars that typically stretches over hundreds of light-years and contains a few dozen OB stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of association |  |
| Oberon | has definition Outermost satellite of Uranus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Herschel | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1787 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 13.46 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R ≥ 500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotational period 13.46 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Uranus |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| objective | has definition The primary mirror of a reflecting telescope (or the primary lens of a refractor). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| objective grating | has definition A coarse grating placed in front of the telescope objective. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of diffraction grating |  |
| objective prism | has definition A small-angle prism placed in front of a telescope objective to transform each star image in a field of stars into an image of its spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph dispersing element |  |
| observatory | has address |  |
| has altitude |  |
| has definition a place on earth which has one or more telescopes |  |
| has location |  |
| has telescope |  |
| is a kind of artifact |  |
| Occam's Razor | has author William of Ockham |  |
| has definition Any hypothesis should be shorn of all unnecessary assumptions; if two hypotheses fit the observations equally well, the one that makes the fewest assumptions should be chosen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has formulation date fourteenth century |  |
| has name origin Entia non sunt multiplicanda ("Entities are not to be multiplied") | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| occultation | has definition The cutoff of the light from a celestial body caused by its passage behind another object. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conjunction |  |
| occultation phase | has definition A phase during the occultation of a celestial body | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of conjunction |  |
| oceanic element | has definition an element contained in the ocean |  |
| has occurrence ocean |  |
| has ocean concentration |  |
| has ocean oxidation state |  |
| has ocean residence time |  |
| is a kind of planetary element |  |
| Octans | has acronym Oct |  |
| has genitive Octantis |  |
| has historical origin the instrument used to measure the position of Polaris |  |
has synonym Octant  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Oe | has definition O star with emissions in the Balmer lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line Balmer lines |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| Oef | has definition Early O stars that show double emission lines in He II λ4686. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line He II λ4686 (double) |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| oersted | has definition Unit of magnetic field strength. 1 Oe corresponds to 1000/4π amperes per meter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Oe |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux density unit |  |
| Of star | has definition Peculiar O stars in which emission features at λλ4634-4641 from N III and 4686 from He II are present. They have a well-developed absorption spectrum, which implies that the excitation mechanism of the emission lines is selective, unlike that of Wolf-Rayet stars. The spectra of Of stars are usually variable, and the intensities of their emission lines vary in an irregular manner. Of stars belong to extreme Population I. All O stars earlier than 05 are Of. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line N III 4634-4641 and He II 4686 |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| is a kind of peculiar star |  |
| ohm | has base unit m2·kg·s-3·A-2 |  |
| has symbol Ω |  |
| has unit V·A-1 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of resistance unit |  |
| Olber's paradox | has definition A paradox formulated by the German astronomer Heinrich Olbers in 1826 that can be traced back to the writings of others, such as de Cheseaux, a century or more earlier. The paradox is: Why is the sky dark at night, if the universe is infinite? We now know that several of the assumptions made by Olbers (explicitly or implicitly) are incorrect. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A paradox formulated by the German astronomer Heinrich Olbers in 1826: Why is the sky dark at night? The amount of light we receive from a star decreases as the square of the distance from us. On the other hand, if we assume a uniform distribution of stars in space, the number of stars increases as the square of their distance from us, so the two factors should cancel out. In theory, then, the night sky should be a blazing mass of light, and obviously it is not. This self-contradictory statement is Olbers' paradox. In seeking to resolve it, astronomers noted that, besides the assumption of uniformity or homogeneity, Olbers made four other assumptions: (1) space is Euclidean; (2) the laws of physics that apply on Earth apply to the Universe as a whole; (3) the Universe is static (i.e., neither expanding nor contracting); (4) the Universe is spatially and temporally infinite. It is now known that all four of these assumptions are either incorrect or inaccurate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The puzzle of why the sky is dark at night. If the universe extends infinitely in space, as it might, then the accumulated light from an infinite number of distant stars should seemingly cause the sky to be bright at all times, whether our sun is visible or not. This paradox, first posed in the eighteenth century, has been resolved by the big bang theory. In a universe with a beginning, we can receive light only from that part of the universe close enough so that light has had time to travel from there to here since the big bang (about 10 billion years ago). Thus, even if space extends infinitely far, only a limited region, and a limited number of stars, are visible to us. And the accumulated light from this limited number of stars is not sufficient to spoil the darkness of the night sky. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of paradox |  |
| old star | has definition Star that, according to contemporary stellar evolution theory, have an age comparable to that of the galaxy to which they belong. This is not an observational definition. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| old thin disk | has definition The older part of the thin-disk population, ranging in age from about 1 to 10 billion years. The Sun and most other nearby stars belong to the old thin disk. The scale height of the old thin disk is about 1000 light-years. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has star age 1 to about 10 billion years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of thin disk |  |
| oligocene epoch | has duration 11 million years |  |
| has start time 36 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of tertiary period |  |
| omega | has definition Heavy short-lived baryon. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The ratio of the average density of mass in the universe to the critical mass density, the latter being the density of mass needed to eventually halt the outward expansion of the universe. In an open universe, omega is always less than 1; in a closed universe, it is always greater than 1; in a flat universe it is always exactly equal to 1. Unless omega is exactly equal to 1, it changes in time, constantly decreasing in an open universe and constantly increasing in a closed universe. Omega has been measured to be about 0.1, although such measurements are difficult and uncertain. (See critical mass density; closed universe; flat universe; open universe.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical constant |  |
| is an instance of hyperon | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| Omega Centauri | has definition A bright globular cluster. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of unclassified globular cluster |  |
| Omega Nebula | has definition A bright H II region. It is a double radio source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Philippe Loys de Cheseaux |  |
| has discoverery date 1745 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 17 |  |
| has synonym M 17 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 6618 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Swan Nebula | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| Omicron2 Eridani | has definition A triple star that was the first white dwarf ever discovered. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 16 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Eridanus |  |
| is an instance of white dwarf |  |
| Oort cloud | has definition H I region extending to more than 100000 AU from the Sun, barely gravitationally bound, postulated as the birthplace of comets. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has location < 100000 AU from the Sun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of dust |  |
| Oosterhoff Group globular cluster | has definition Globular cluster which differs in the period of transition between Bailey type ab and type c variables, the ratio of type c to type ab stars, in the metallicity of RR Lyrae stars, and in the mean period of the ab variables. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| Oosterhoff group I globular cluster | has metal line strength slightly weak | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Oosterhoff Group globular cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| Oosterhoff group II globular cluster | has metal line strength very weak | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Oosterhoff Group globular cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif) |
| open cluster | has age varies widely | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has catalog open cluster catalog |  |
| has definition A comparatively loose grouping (mass range 102-103 M)sun of Population I stars, strongly concentrated in the spiral arms or the disk of the Galaxy (in fact, open clusters give a good indication of where the spiral arms are). Unlike associations, open clusters are dynamically stable. Depending on their age, stars in open clusters "peel off" from the main sequence at different points (the higher the turnoff point, the younger the cluster). (Sometimes called Galactic cluster; NGC 188 is the oldest known open cluster.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A small, loose cluster of stars that typically contains several hundred members. The best examples are the Hyades and the Pleiades, both in the constellation Taurus. Open clusters line the Galactic plane, in contrast with globular clusters, which are members of the Galaxy's halo or thick disk. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star cluster |  |
| is a part of disk | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| open cluster catalog | has object type open cluster |  |
| is a kind of catalog about star systems |  |
| open string | has definition A type of string with two free ends. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of string theory |  |
| open universe | has definition A homogeneous, isotropic Universe is said to be temporally open if gravity is not strong enough to eventually reverse the expansion, so the universe goes on expanding forever. It is said to be spatially open if it curves the opposite way from a closed universe, so that triangles would contain less than 180°, the circumference of a circle would be more than π times the diameter, and the volume would be infinite. If Einstein's Cosmological Constant is zero, as is frequently assumed, then a universe which is temporally open is also spatially open, and vice versa. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Any model of the Universe which does not contain enough matter to halt its expansion. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Big Bang model that was formulated by Friedmann and Lemaitre which has a negative curvature, like a saddle-shaped surface, in which case the universe is infinite, open, and will expand forever. This space is unbounded. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Cosmological model in which the universe continues to expand forever; its space-time geometry is hyperbolic, or "open". | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has geometry of space negative curvature |  |
| is a kind of big bang |  |
| Ophiuchus | has acronym Oph |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Ophiuchi |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Serpent Bearer |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| opposition | has definition A configuration of the Sun, Earth and a planet in which the apparent geocentric longitude of the planet differs by 180 degrees from the apparent geocentric longitude of the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Occurs when the Earth comes directly between that planet and the Sun; it can thus only happen in relation to the superior planets and the asteroids. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has elongation 180° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planetary elongation event |  |
| optical | has definition Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths of or close to those detectable by the eye. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 430 to 750 THz |  |
| has synonym light | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 400 to 700 nm |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| optical device | is a kind of instrument |  |
| optical fibre | has definition A long, thin strand of glass capable of excellent transmission of light over large distances. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Glass and transparent plastics can be made into a very thin wire or fiber. Typical dimensions are 10-50 µm. If a ray enters one end of a fiber at the appropriate angle, it will undergo total internal reflection and travel down the fiber without much loss through the sides. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| optical law | has domain optics |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| optical matching | has definition The use of lenses or other optical devices to match the size of the image of the seeing disk, as it appears in the focal plane of the telescope, to the physical size of the CCD pixels. If the telescope yields 10 arcseconds per millimeter and the seeing is 1 arcsecond then the image is 0.1 mm in size. But a typical CCD pixel is 0.022 mm, five times smaller. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| optical process | has domain optics |  |
| is a kind of physical process |  |
| optical space telescope | has wavelength sensitivity 300 to 1000 nanometers |  |
| is a kind of optical telescope |  |
| is a kind of space telescope |  |
| optical telescope | has optical design |  |
has reference astroweb  |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| Optical Very Large Array | has acronym OVLA | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of array telescope |  |
| Optically Violent Variable galaxy | has acronym OVV |  |
| is a kind of blazar |  |
| optics | has definition The science of light. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| orange | is a kind of optical |  |
| orbit | has definition The path in space followed by a celestial body. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has parameters orbital element |  |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| orbital element | has definition One of seven quantities that must be established from observations in order to define the size, shape, and orientation of an orbit in space. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of orbital quantity |  |
| is required to define the size, shape, and orientation of an orbit in space | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| see also mean element | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| see also osculating element | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| orbital event | has definition Periodic celestial event in the orbit of a celestial body | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 orbital period |  |
| is a kind of periodic celestial event |  |
| orbital quantity | has definition A quantity used for calculating orbits | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| orbital velocity | has definition Velocity required by a body to achieve a circular orbit around its primary: Vorb = (GM / r)1/2. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| orbiting collision | has definition A collision in which an ion and an atom approach each other very closely and spend a long time (several orbits of the atomic electrons) in close proximity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Coulomb collision |  |
| ordovician period | has duration 75 million years |  |
| has start time 500 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| Orion | has acronym Ori |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Orionis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the hunter accompanied his dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor hunt Lepus and Taurus near the river Eridanus |  |
| has synonym Hunter |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Orion A | has definition A radio continuum feature (an H II region) centered on the Trapezium, and excited by θ1 Ori C. The Orion A molecular cloud, which lies beyond it, is a rich source of molecules CO, OH, HCN, and probably NO, HCO, and H2CO have been observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| Orion arm | has definition The spiral arm of the Milky Way in which the Sun is located. It lies between the Sagittarius arm and the Perseus arm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has density of interstellar gas 1.5 atoms cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 10.4 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has H I density 0.6 atoms cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym local arm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has width 600 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| Orion B | has definition A radio continuum source. |  |
| has synonym NGC 2024 |  |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| Orion Nebula | has age 20000 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A large cloud of gas and dust giving birth to young stars in the constellation Orion and visible to the naked eye. It is an HII region 1500 light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An HII region about 500 pc distant, barely visible to the naked eye in the center of Orion's sword. It is undoubtedly a region where stars are being born; young O stars and many T Tauri variables are associated with it, and its members are extreme Population I. Probably no more than 20000 years old. It is also an X-ray source (3U 0527-05 and M42, NGC 1976). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The Orion Nebula, a star-forming region in the constellation Orion. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 500 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has illuminating star(s) trapezium |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 42 |  |
| has synonym M 42 |  |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| Orion spur | has definition That part of the local spiral arm in which the Sun is embedded. The Sun is on an inner edge of the Orion spur. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion arm |  |
| Orionid | has duration 2 days |  |
| has parent object Comet Halley |  |
| has radiant Orion |  |
| has rate 30 per hour |  |
| has start time 21 October |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| ortho-hydrogen | has definition Molecular hydrogen in which the two protons of the diatomic molecule have the same direction of spin. It is a higher energy state than the para form. Terrestrial H2 is 75% ortho-hydrogen, 25% para-hydrogen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of molecular hydrogen |  |
| ortho-spectrum | has definition Spectrum of triplet (l = 1). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of lines |  |
| Oschin 48-inch Telescope | has altitude 1706 m |  |
| has aperture 1.24 m |  |
| has comment a new achromatic corrector plate (Grubb-Parsons) was installed in about 1984 |  |
| has creation date 1948 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.47 |  |
| has latitude 33° 21' N |  |
| has location Palomar Mountain, Calif., US |  |
| has longitude 116° 51' W |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.83 m |  |
| has mirror maker Don O. Hendrix |  |
| has mounting manufacturer California Institute of Technology |  |
| has owner Palomar Observatory |  |
| has synonym Oschin Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
is an instance of Schmidt  |  |
| Oscillating Universe | has definition Cosmological model in which the Universe is "closed" and its expansion is destined to stop, to be succeeded by collapse and "then" (if ordinary temporal terms may be said to apply) by a rebound into a new expansion phase. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of closed universe |  |
| osculating element | has definition One of several parameters that specifies the instantaneous position and velocity of a celestial body in its perturbed orbit. Osculating elements describe the unperturbed (two-body) orbit that the body would follow if perturbations were to cease instantaneously. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of orbital quantity |  |
| see also orbital element | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| osmium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| Otto Struve | has birth date 12 August 1897  |  |
| has career |  |
| has death date 6 April 1963 |  |
has image   |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| our solar system | has definition The Sun and all objects gravitationally bound to it. The solar system is roughly a sphere with a radius greater than 100,000 AU, with the Sun at the center. The Sun is overwhelmingly the dominant object. Planets, satellites, and all interplanetary material together comprise only about 1/750 of the total mass. Geochemical dating methods show that the solar system chemically isolated itself from the rest of the Galaxy (4.7 ± 0.1) × 109years ago. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solar system |  |
| is a part of local bubble | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| outdated belief | is a kind of belief |  |
| outer Van Allen belt | has altitude 18000 to 20000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has composition mostly electrons | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has particle energy lower than the inner Van Allen belt | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Van Allen belt |  |
| Owl Nebula | has definition A planetary nebula. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 600 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 97 |  |
| has synonym M 97 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 3587 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Ursa Major | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| oxygen | has abundance 474000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust (most abundant element on surface) |  |
| has abundance 6.92 × 108 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance constituent element of water |  |
| has atomic emission line 777.194 nm for O I |  |
| has atomic emission line 777.417 nm for O I |  |
| has atomic emission line 844.625 nm for O I |  |
| has atomic emission line 844.636 nm for O I |  |
| has atomic emission line 844.676 nm for O I |  |
| has atomic number 8 |  |
| has atomic radii pm |  |
| has biological role constituent element of DNA and of most other biologically important compounds |  |
| has boiling point 90.188 K |  |
| has chief source liquid air |  |
| has covalent radii 66 pm for single bond |  |
| has critical pressure 5043 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 154.58 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = pm |  |
| has crystal type |  |
| has daily dietary intake mainly as water |  |
| has definition colourless, odourless gas (O2) which is very reactive |  |
| has density 1.429 kg m-3 for gas at 273 K |  |
| has density 1140 kg m-3 for liquid at 90.188 K boiling point |  |
| has density 2000 kg m-3 for solid at 54.8 K melting point |  |
| has discoverer J. Priestley, C.W. Sheele |  |
| has discovery date 1774 |  |
| has discovery location Leeds, England and Uppsala, Sweeden |  |
| has electron affinity 141 kJ mol-1 from O to O- |  |
| has electron configuration [He]2s22p4 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 3.44 Pauling |  |
| has hazard O2 within a few percent of its natural concentration in air is harmless, but too little and it cannot sustain life, too much and it can cause pulmonary changes and teratogenic effects and is a fire hazard. |  |
| has heat capacity 21.912 J K-1 mol-1 for atomic gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 29.355 J K-1 mol-1 for molecular gas (O2 at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 0.444 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of sublimation kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 6.82 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 132 pm for O2- |  |
| has ionic radii 22 pm for O+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 13 to 20 |  |
| has lethal intake 4800 p.p.m. for 4 hours inhaled ozone (O3) |  |
| has level in humans 160000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 160000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 285000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans constitutent of water |  |
| has longest lived isotope oxygen 16 |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 1.31 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 11.5 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +1.355 × 10-6 kg-1 m3 for gas |  |
| has mass of element in person 43 kg for a 70 kg average person, mainly as water |  |
| has melting point 54.8 K |  |
| has mineral oxides, silicates, carbonates, phosphates, sulfates also occurs as gas in atmosphere and as water |  |
| has molar volume 8.00 cm3 at 54 K |  |
| has name origin oxy genes = acid forming from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.5803 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 8 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 8 |  |
| has pronunciation oksi-jen |  |
has registry number 7782-44-7 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 15.9994 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 1.2 × 1015 tonnes in atmosphere |  |
| has space group |  |
| has specimen small pressurized canisters. Safe, but be aware of possible dangers. |  |
| has symbol O |  |
| has term symbol 3P2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.2674 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.00019 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic as O2, but toxic as ozone (O3) |  |
| has uses steel-making, metal-cutting, the chemical industry and in medical treatment |  |
| has van der Waals radii 140 pm |  |
| has world production 1 × 108 |  |
| is a kind of atmophile element |  |
| is a kind of gaseous element |  |
| is a kind of group VI element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with all other elements except He, Ne, Ar and Kr |  |
| oxygen 14 | has atomic mass 14.008595 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (5.1430 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 70.60 seconds |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 6 |  |
| has number of nucleons 14 |  |
| has symbol 14O |  |
is an instance of oxygen  |  |
| oxygen 15 | has atomic mass 15.003065 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.754 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 122.2 seconds |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.719 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2- |  |
| has number of neutrons 7 |  |
| has number of nucleons 15 |  |
| has symbol 15O |  |
is an instance of oxygen  |  |
| oxygen 16 | has atomic mass 15.99491463 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.762% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 8 |  |
| has number of nucleons 16 |  |
| has symbol 16O |  |
is an instance of oxygen  |  |
| oxygen 17 | has atomic mass 16.9991312 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -3.6264 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 using H2O reference |  |
| has natural abundance 0.038% |  |
| has NMR frequency 13.557 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T using H2O reference |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.061 where 13C = 1.00 with H2O reference |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.89380 |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.02558 × 10-28 m2 using H2O reference |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 9 |  |
| has number of nucleons 17 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0291 where 1H = 1.00 using H2O reference |  |
| has symbol 17O |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of oxygen  |  |
| oxygen 18 | has atomic mass 17.9991603 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.200% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 10 |  |
| has number of nucleons 18 |  |
| has symbol 18O |  |
is an instance of oxygen  |  |
| oxygen burning | has definition The stage when a star fuses oxygen into silicon and sulfur. It occurs only in stars born with over eight solar masses. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 6 months |  |
| has optimum density 107 g cm-3 |  |
| has optimum temperature 1.5 × 109 K |  |
| has product silicon, sulfur |  |
| has reactant oxygen |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| requires minimum mass at star birth 8 solar masses |  |
| oxygen-rich giant | has definition A collective designation for a giant showing metal oxide molecules - thus M, MS and S stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| ozone layer | has altitude 20 to 60 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has composition higher than normal concentration of ozone (03) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A layer in the lower part of Earth's stratosphere where the greatest concentration of ozone (03) appears. This is the layer responsible for the absorption of ultraviolet radiation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of stratosphere | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| P Cygni | has distance 1200 pc |  |
| has magnitude 5 |  |
| has spectral type B1e |  |
| is a part of Cygnus |  |
| is an instance of P Cygni star |  |
| P Cygni star | has definition A type of star whose spectrum shows strong emission lines, like those of the Be and Wolf-Rayet stars, with blueshifted absorption components which are presumed to come from an expanding shell of low-density matter. A P Cygni profile is taken as an indication of mass loss. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition High-luminosity, early-type star, in which all lines have a P Cyg type profile (an emission component on the red side of the absorption line). | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype P Cygni |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| P-branch | has definition A set of lines in the spectra of molecules corresponding to unit increases in rotational energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of molecular lines |  |
| p-electron | has definition An orbital electron whose l quantum number is 1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital quantum number 1 |  |
| is a kind of bound electron |  |
| p-process | has definition The name of the hypothetical nucleosynthetic process thought to be responsible for the synthesis of the rare heavy proton-rich nuclei which are bypassed by the r-process and s-processes. It is manifestly less efficient (and therefore rarer) than the s- or r-process, since protons must overcome the Coulomb barrier, and may in fact work as a secondary process on the r-process and s-process nuclei. It seems to involve primarily (p, γ) reactions below cerium (where neutron separation energies are high) and the (γ, n) reactions above cerium (where neutron separation energies are low). The p-process is assumed to occur in supernova envelopes at a temperature greater than about 109 K and at densities less than about 104 g cm-3. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| p-spot | is a kind of sunspot |  |
| P-strong star | has definition A small subgroup of B-type stars in which P lines are very strong. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| Pa alpha | has upper energy level 4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 18751 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Paschen line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| Pacific ocean | is a part of Earth's lithosphere |  |
| PAH | has definition Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon |  |
| is a kind of molecule |  |
| pairing energy | has definition A quantity which expresses the fact that nuclei with odd numbers of neutrons and protons have less energy and are less stable than those with even numbers of neutrons and protons. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol δ |  |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| paleocene epoch | has duration 63 million years |  |
| has start time 5 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of tertiary period |  |
| paleozoic era | has duration 370 million years |  |
| has start time 600 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of geological era |  |
| palladium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 50000 years |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| Pallas | has albedo 0.05 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The second asteroid to be discovered. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter about 560 km -has source: [H76] |  |
| has discoverer Olbers |  |
| has discovery date 1802 |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.235 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has has surface spectrum resembles meteorites of either low-grade carbonaceous chondrite or enstatite achondrite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 34°.8 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 2.6 × 1023 g (1972 estimate) |  |
| has orbital period 1686 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 9-12 hours | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 2.77 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif) |
| Palomar | has definition The mountain in California upon which sits what was the largest telescope in the United States, 200 inches in diameter. The telescope itself is sometimes referred to as the Mt. Palomar telescope. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of observatory |  |
| Palomar Sky Survey | has acronym PSS |  |
| is a kind of sky survey | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| Pan | has definition Unofficial name for Jupiter XI. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has dicoverer Nicholson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1938 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 163° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 692d | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter XI | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif) |
| pancake model | has definition A model of galaxy formation in which the first structures to condense out of the smooth background of primordial gas were very large in size. These large masses then collapsed into thin sheets (pancakes) and fragmented into many smaller pieces the size of galaxies. A competing theory, sometimes called the hierarchical clustering model, proposes that the first structures to form were the size of galaxies. As galaxies clustered together, due to gravity, larger and larger structures were formed. (See hierarchical clustering model.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of contraction |  |
| PAPA | has definition Precision Analogue Photon Address. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of imager |  |
| para-hydrogen | has definition Molecular hydrogen in which the two protons of the diatomic molecule have opposite directions of spin. It is a lower energy state than ortho-hydrogen. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of molecular hydrogen |  |
| parabola | is a kind of conic section |  |
| paradox | has definition A self-contradictory proposition. Paradoxes are most useful when they seem most likely to be true, for it is then that they best serve to expose flaws in the data or reasoning that led to their appearance. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of problem |  |
| parallax | has definition Angle subtended by the apparent difference in a star's position when viewed from the Earth either simultaneously from opposite sides of the planet, or half such an angle, measured after a gap of six months from opposite sides of the planet's orbit; the nearer the celestial body, the greater the parallax. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The apparent displacement in the position of a star or planet occasioned by its being viewed from two different locations - e.g., by observing it from two widely separated stations on Earth, or at intervals of six months, when the earth is at either extreme of its orbit around the sun. The resulting angle can be used, by triangulation, to determine the distance of the star or planet. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The difference in apparent direction of an object as seen from two different locations; conversely, the angle at the object that is subtended by the line joining two designated points. Geocentric (diurnal) parallax is the difference in direction between a topocentric observation and a hypothetical geocentric observation. Heliocentric or annual parallax is the difference between hypothetical geocentric and heliocentric observations; it is the angle subtended at the observed object by the semi-major axis of the Earth's orbit. First trigonometric parallax was obtained in 1838. (eee also horizontal parallax.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The tiny shift in a star's apparent position that occurs when the star is viewed from slightly different perspectives as the Earth revolves around the Sun. The larger a star's parallax, the closer the star is to Earth. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym distance |  |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| parity | has definition The operation which reverses the signs of the coordinate axes used to describe a system, i.e. (x, y, z) -> (-x, -y, -z). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle of space-inversion invariance; i.e., no experiment can differentiate between the behavior of a system and that of its mirror image. Parity is conserved in strong interactions, but not in weak ones. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of symmetry |  |
| parsec | has approval agency International Astronomical Union | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has approval date 1922 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A unit used by astronomers to describe stellar distance. It is the distance from which the radius of the earth's orbit would subtend an angle of one second of arc. Alternatively one parsec is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends one second of arc. The name was proposed by Professor H. H. Turner (1861-1930), Savilian Professor of Astronomy at Oxford. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Astronomical unit of distance, equal to 3.26 light-years. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of 1 second of arc. 1 pc = 206,265 AU = 3.086 × 1013 km = 3.26 light-years. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc; equivalently, the distance to an object having an annual parallax of one second of arc. (abbreviation for parallax second) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 2.062648 × 105 astronomical units | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 3.08572 × 1016 m | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 3.26168 light years | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has name origin parallax second | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1840 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposer Bessel and Meadows | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| partial lunar eclipse | has definition An eclipse in which the Moon passes through the shadow cast by the Earth, the Moon passing partially through the Earth's umbra at maximum eclipse. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of lunar eclipse |  |
| particle | has charge |  |
has definition Fundamental unit of matter and energy. All may be classed as fermions, which have half-integral spin and obey the exclusion principle, and bosons, which have integral spin and do not obey the exclusion principle. The term particle is metaphoric, in that all subatomic particles also evince aspects of wave-like behavior.  | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency inversely proportional to the wavelength |  |
| has mass |  |
| has wavelength inversely proportional to its momentum |  |
| is a kind of natural object |  |
| obeys uncertainty principle |  |
| particle accelerator | has definition A device using electric and magnetic fields to accelerate beams of particles-usually electrons, positrons, protons, or antiprotons-to high energies for experimental purposes. Modern accelerators are often very large: the main ring at Fermilab, for example, is 4 miles in circumference. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A machine for speeding subatomic particles to high velocity, then colliding them with a stationary target or with another beam of particles moving in the opposite direction. (In the latter instance, the machine may be called a collider.) At velocities approaching that of light the mass of the particles increases dramatically, adding greatly to the energy released on impact. The resulting explosion promotes the production of exotic particles, which are analyzed according to their behavior as they fly away through a particle detector. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of instrument |  |
| particle Compton wavelength | has definition The wavelength of a photon containing the rest energy of a particular particle. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has equation h bar / mc, where h bar is Plancks constant, c is the speed of light, and m is the particle mass. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit m |  |
| is a kind of length |  |
| is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle constant | applies to particle |  |
| has definition a fundamental physical constant quantifying a particle property |  |
| is a kind of fundamental physical constant |  |
| particle g factor | is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle gyromagnetic ratio | has unit s-1 T-1 |  |
| is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle magnetic moment | has unit J T-1 |  |
| is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle magnetic moment anomaly | is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle mass | has unit kg |  |
| is a kind of mass |  |
| is a kind of particle constant |  |
| particle physics | has definition That branch of physics that attempts to understand the fundamental particles and forces of nature. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The branch of science that deals with the smallest known structures of matter and energy. As their experimental investigation usually involves the application of considerable energy, particle physics overlaps with high-energy physics. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym high-energy physics | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy physics |  |
| parton | has definition A generic term used to describe any particle which may be present inside nucleons. It includes quarks, antiquarks and gluons. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A hypothetical pointlike constituent of a nucleon, which contains all the charge of the nucleon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| pascal | has base unit m-1·kg·s-2 |  |
| has definition The derived SI unit of pressure. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 N m-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 10-5 bars | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Pa | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit N·m-2 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of pressure unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of SI unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| Paschen line | has lower energy level 3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has series limit 8204 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif) |
| Paschen-Back effect | has definition An effect on spectral lines obtained when the light source is located in a strong magnetic field, so that the magnetic splitting becomes greater than the multiplet splitting. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| Patroclus | has asteroid number 617 |  |
| has definition Trojan asteroid (60°) behind Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.14 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 22°.1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 11.82 yr | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 5.19 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Trojan asteroid |  |
| is an instance of Trojan asteroid |  |
| Pavo | has acronym Pav |  |
| has genitive Pavonis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin the mythological peacock sacred to Hera |  |
| has synonym Peacock |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| PDA | has definition Photodiode array. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| peculiar star | has definition Star with spectra that cannot be conveniently fitted into any of the standard spectral classifications. Denoted by a p after spectral type. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| peculiar velocity | has definition Velocity with respect to the Local Standard of Rest. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| Pegasus | has acronym Peg |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Pegasi |  |
| has historical origin son of Medusa, flew Bellerophon up to Mount Olympus, this impudence angered Zeus, who sent an insect to sting Pegasus |  |
| has synonym Winged Horse |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| pennsylvanian period | has duration 30 million years |  |
| has start time 310 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| penumbral lunar eclipse | has definition An eclipse in which the Moon passes through the shadow cast by the Earth, the Moon passing only through the Earth's penumbra. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym appulse | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of lunar eclipse |  |
| pep reaction | has definition A reaction occurring in the proton-proton chain which occurs only once in 400 p-p reactions but produces far more energetic neutrinos (1.44 MeV as against 0.42 MeV). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has reaction probability once in 400 p-p reactions | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of proton-proton chain | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| periapsis | has definition The point in the orbit of a satellite where it is closest to its primary. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of orbital event |  |
| periastron | has antonym apastron |  |
| has definition The point in the orbit of one component of a binary system where it is nearest the other component. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has participants binary star |  |
| is an instance of binary star orbital event |  |
| pericenter | has antonym apocenter |  |
| has definition The point in the orbit of one component of a binary system which is closest to the center of mass of the system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has participants binary star |  |
| is an instance of binary star orbital event |  |
| pericynthion | has definition The point in the orbit of a satellite around the Moon closest to the Moon. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Moon orbital event |  |
| perigalacticon | has antonym apogalacticon |  |
| has definition The point in a star's orbit around the Galaxy when the star lies closest to the Galactic center. The Sun is near perigalacticon now. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of galaxy orbital event |  |
| perigee | has antonym apogee |  |
| has definition The point at which a body in orbit around the Earth most closely approaches the Earth. Perigee is sometimes used with reference to the apparent orbit of the Sun around the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Earth orbital event |  |
| perihelion | has antonym aphelion |  |
| has definition The point in the orbit of an object orbiting the Sun where it is closest to the Sun's center of mass. Earth's perihelion occurs early in January. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Sun orbital event |  |
| period | has definition An orbital element representing the time required to complete an orbit. This parameter is required when determining the orbit of a binary star system in which the mass is not known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol P | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of orbital element | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| periodic celestial event | has definition Celestial event which occurs with a very regular period | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period |  |
| is a kind of celestial event |  |
| periodic variable | has period |  |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| permian period | has duration 50 million years |  |
| has start time 280 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| Perseid | has duration 3 days |  |
| has parent object Comet Swift-Tuttle |  |
| has radiant Perseus |  |
| has rate 100 per hour |  |
| has start time 12 August |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| Perseus | has acronym Per |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Persei |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin slew Medusa, mother of Pegasus, rescued Andromeda, daughter of Cepheus and Cassiopeia, from the sea monster Cetus |  |
| has synonym Hero |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Perseus arm | has definition The spiral arm that lies next out from the arm containing the Sun. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| Perseus cluster | has brightest member NGC 1275 |  |
| has definition A diffuse, irregular cluster (richness class 2) dominated by and centered on the Seyfert galaxy NGC 1275 (Perseus A). Mass required to bind the cluster, greater than 1015 Msun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 2 × 1015 Msun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 500 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has redshift z = 0.0183 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is a part of Perseus |  |
| is an instance of galaxy cluster |  |
| Perseus OB2 | has definition A young association of OB stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 350 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of OB association |  |
| Perseus-Pisces region | has definition A region of space containing a huge congregation of galaxies called a supercluster. The galaxies in this supercluster appear to be distributed in a long chain. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Universe |  |
| is an instance of supercluster |  |
| person | has birth date |  |
| has definition a human living or dead |  |
| is a kind of physical object |  |
| peta | has symbol P |  |
| has value 1015 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| Pfund line | has lower energy level 5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength far-infrared | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| PG 1159 star | has definition Very hot star with strong O VI and C IV lines, which is an X-ray emitter. Probably these stars are the central stars of planetary nebulae that have dissipated their envelopes. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym pre-degenerate |  |
| is a kind of central star of planetary nebula |  |
| phase angle | has definition The angle measured at the center of an illuminated body between the light source and the observer. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| phase of matter | has definition When used in reference to matter, describes its possible states: solid phase, liquid phase, gas phase. More generally, refers to the possible descriptions of a physical system as features on which it depends (temperature, string coupling constant values, form of spacetime, etc.) are varied. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of particles |  |
| phase transition | has definition An abrupt change in the equilibrium state of a system. A sudden transition between one state of matter or energy and another state. For example, when hot water turns to steam or when ice crystallizes out of a liquid that has been cooled to below freezing, a phase transition has occurred. According to the grand unified theories of particle physics, the infant universe may have undergone one or more overall phase transitions. In this case, the energy uniformly filling all space corresponded to the supercooled liquid. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has inverse process |  |
| is a kind of physical process |  |
| Phillips band | has wavelength 1.207 μ (transition 0-0) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C2 band |  |
| Phobos | has albedo 0.06 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The potato-shaped inner satellite of Mars. Phobos lies just outside the Martian Roche limit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer A. Hall | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1877 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.021 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 1°.1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 7h39m14s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius about 18 × 22 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 7h39m14s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface composition dust (from Infrared observations) |  |
| is a part of Mars |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Phoebe | has definition The outermost satellite of Saturn. Has retrograde orbit. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Pickering |  |
| has discovery date 1898 |  |
| has orbital period 550 days |  |
| has radius 100 km |  |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Phoenix | has acronym Phe |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Phoenicis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin a bird of incredible beauty who would live for 500 years and be reborn after being consumed fire |  |
| has synonym Phoenix (Bird) |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| phosphorus | has abundance 0.0015 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.0015 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.042 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.084 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 1000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 3.16 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 1648.292 nm for P I |  |
| has atomic emission line 213.618 nm for P I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 979.685 nm for P I |  |
| has atomic emission line 952.573 nm for P I (strong) |  |
| has atomic emission line 956.344 nm for P I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 15 |  |
| has atomic radii 115 pm for red form |  |
| has atomic radii 93 pm for white form |  |
| has biological role constituent of DNA, ATP and many other biochemical molecules. Phosphate cycle. |  |
| has boiling point 553 K for P4 |  |
| has chief source apatite, turquoise (ornamental stone) |  |
| has covalent radii 110 pm for single bond |  |
| has critical temperature 994 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 1131 pm for red phosphorus |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 1851 pm for white &alpha-P4 |  |
| has crystal type cubic for red phosphorus |  |
| has crystal type cubic for white &alpha-P4 |  |
| has daily dietary intake 900 - 1900 mg |  |
| has definition soft and flammable white solid, the red form is usually non-flammable |  |
| has density 1820 kg m-3 for P4 solid at 293 K |  |
| has density 2200 kg m-3 for red phosphorus solid at 293 K |  |
| has density 2690 kg m-3 for black phosphorus solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Hennig Brandt |  |
| has discovery date 1669 |  |
| has discovery location Hamburg, Germany |  |
| has electrical resistivity 1 × 109 Ω m for P4 solid at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 44 kJ mol-1 from to - |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p3 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.19 Pauling |  |
| has hazard white phosphorus chronic poisoning leads to necrosis of the jaw (phossy-jaw) |  |
| has hazard white phosphorus is much more toxic than red phosphorus |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 21.21 J K-1 mol-1 for red phosphorus solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 23.840 J K-1 mol-1 for P4 solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 2.51 kJ mol-1 for P4 solid |  |
| has heat of vaporization 51.9 kJ mol-1 for P4 solid |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 212 pm for P3- |  |
| has isotope mass range 26 to 36 |  |
| has lethal intake 100 mg for white phosphorus in humans |  |
| has level in humans 3 - 8.5 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 3000 - 8500 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 345 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 67000 - 71000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 124.5 × 10-6 K-1 for P4 solid |  |
| has longest lived isotope phosphorus 31 |  |
| has main mining area Russia, USA, Morocco, Tunisia, Togo, Nauru |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 7.89 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 74.1 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -1.1 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for P4 solid |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -8.4 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for red phosphorus solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 780 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 317.3 K for P4 solid |  |
| has melting point 683 K for red phosphorus solid under pressure |  |
| has mineral apatite, phosphophyllite, turquoise, vivianite |  |
| has molar volume 17.02 cm3 |  |
| has name origin phosphoros = bringer of light from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.513 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 10 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 15 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| has ocean residence time 100000 years |  |
| has pronunciation fos-for-us |  |
has registry number 7723-14-0 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 30.973762 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 5.7 × 109 tonnes |  |
| has space group I-43m for white &alpha-P4 |  |
| has space group Pm3m or P-43 for red phosphorus |  |
| has specimen white sticks (Danger!), red lumps or powder (Care!) |  |
| has symbol P |  |
| has term symbol 4S3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.235 W m-1 K-1 for P4 solid at 300 K |  |
| has thermal conductivity 12.1 W m-1 K-1 for black phosphorus solid at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.172 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 11 μg kg-1 for white phosphorus in rat |  |
| has uses fertilizers, insecticides, metal treatment, detergents and foods |  |
| has van der Waals radii 190 pm |  |
| has world production 153 × 106 tonnes year-1 |  |
| is a kind of group V element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| reacts with air by bursting into flames (white phosphorus) |  |
| reacts with alkalis to form phosphine gas |  |
| phosphorus 30 | has atomic mass 29.978307 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.226 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 2.50 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 15 |  |
| has number of nucleons 30 |  |
| has symbol 30P |  |
is an instance of phosphorus  |  |
| phosphorus 31 | has atomic mass 30.973762 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 10.8289 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 40.481 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 377 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.13160 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 16 |  |
| has number of nucleons 31 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0663 where 1H = 1.00 for 85% H3PO4 |  |
| has symbol 31P |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of phosphorus  |  |
| phosphorus 32 | has atomic mass 31.973907 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.710 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 14.28 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.2524 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 17 |  |
| has number of nucleons 32 |  |
| has symbol 32P |  |
| has uses medical diagnostic |  |
| has uses medical therapy |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of phosphorus  |  |
| phosphorus 33 | has atomic mass 32.971725 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.249 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 25.3 days |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 18 |  |
| has number of nucleons 33 |  |
| has symbol 33P |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of phosphorus  |  |
| photo reconnaissance spacecraft | is a kind of reconnaissance spacecraft |  |
| photocathode | has definition A thin metallic plate housed inside an evacuated tube capable of releasing electrons through the "photoelectric effect" when illuminated by light. These surfaces are best for optical and ultraviolet light. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of photoelectric device |  |
| photodiode | has definition A light-sensitive device made from the junction of two differently doped species of a semiconductor such as silicon. Also known as a pn junction. An internal electric field is generated at the junction of p and n type material. Photons absorbed in the junction create electron-hole pairs which are separated by the field and create a current. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| photoelectric device | has definition Any detector which uses the photoelectric effect to convert photons to electrons. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| photoelectric magnitude | has definition The magnitude of an object as measured with a photoelectric photometer. (mpe) (antiquated term) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of apparent magnitude |  |
| photographic magnitude | has definition The magnitude of an object as measured on the traditional photographic emulsions, which are sensitive to a slightly bluer region of the spectrum than is the human eye. (mph)(antiquated term) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of apparent magnitude |  |
| photoionization | has definition The ionization of an atom or molecule by the absorption of a high-energy photon by the particle. It is an important source of opacity in stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ionization |  |
| photomultiplier | has definition A vacuum encapsulated photocathode from which electrons are ejected by the photoelectric effect followed by multiple cathodes from which many additional electrons are emitted in a cascade. When finally collected, the original single electron may have generated a pulse of over one million electrons. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Device used in photometry for the amplification of light by the release and acceleration of electrons from a sensitive surface. The result is a measurable electric current that is proportional to the intensity of received radiation. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of photoelectric device |  |
| photon | carries the force electromagnetism |  |
| has definition A transverse wave of electric and magnetic fields which can propagate through empty space. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Smallest packet of the electromagnetic force field; messenger particle of the electromagnetic force; smallest bundle of light. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The quantum of the electromagnetic field. It is the massless spin-1 gauge boson of QED. Virtual photons mediate the electromagnetic force between charged particles. Virtual photons can also adopt a mass for a short period, in accordance with Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 1 |  |
| has synonym electromagnetic radiation |  |
| is a kind of carrier boson |  |
| is a kind of massless particle |  |
| is a kind of neutral particle |  |
| is a kind of transverse wave | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| photonics | has definition The technology of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is the photon for a range of applications ranging from detection to laser energy production to communications and information processing. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| photosphere | has definition The region of a star which gives rise to the continuum radiation emitted by the star. The visible surface of the Sun (temperature about 6000K), just below the chromosphere and just above the convective zone. The photosphere ends (and the chromosphere begins) at about the place where the density of negative hydrogen ions has dropped to too low a value to result in appreciable opacity. The spectrum of the photosphere consists of absorption lines (unlike that of the chromosphere, which consists of emission lines). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The visible surface of the Sun, or more generally, the layer of a star that gives rise to the continuum (as opposed to spectral-line) radiation emitted by the star. photosphere of the Sun has definition |  |
| is a part of solar atmosphere |  |
| photosynthesis | has definition a biochemical process operating in green plants in which carbohydrates are formed under the influence of light with chlorophyl serving as a catalyst |  |
| is a kind of biochemical process |  |
| photovisual magnitude | has definition The magnitude of an object as measured photographically by filters and emulsions that are sensitive to the same region of the spectrum as the human eye. (antiquated) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of apparent magnitude |  |
| physical object | has angular momentum |  |
| has definition Anything tangible having existence (living or nonliving) |  |
| has extent |  |
| has location or center of gravity |  |
| has mass |  |
| has material |  |
| has momentum |  |
| has temperature |  |
| has velocity |  |
| has volume |  |
| is a kind of kbTop |  |
| physical phenomena | is a kind of kbTop |  |
| physical process | has domain physics |  |
| is a kind of process |  |
| physicist | has definition a scientist specializing in physics |  |
| has domain physics |  |
| is a kind of scientist |  |
| physico chemical constant | is a kind of fundamental physical constant |  |
| physics | has definition The scientific study of the interactions of matter and energy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of science |  |
| physics theory | is a kind of theory |  |
| Pi alpha | has wavelength 10124 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Pickering line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| Pi beta | has wavelength 6560 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Pickering line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| pi+ | has charge 1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has decay product muon, neutrino | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 273 me | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of charged particle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of pion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| pi- | has charge -1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has decay product muon, neutrino | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 273 me | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of charged particle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of pion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| pi0 | has decay product two γ-rays | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 264 me | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| is an instance of pion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| Pickering | has career Havard College Observatory  |  |
has greatest achievement the Henry Draper Catalog of spectral types  |  |
has image   |  |
| has name Edward C. Pickering |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
is an instance of astronomer  |  |
| Pickering line | has lower energy level 4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has series limit 3644 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym ionized helium Brackett line |  |
| is a kind of ionized helium line |  |
| is a kind of spectral series line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif) |
| occurs in O star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| pico | has symbol p |  |
| has value 10-12 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif) |
| Pictor | has acronym Pic |  |
| has genitive Pictoris |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Easel |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| pinch machine | has definition A fusion device containing a plasma heated by a shock wave generated within the plasma as it is constricted by the rapidly increasing magnetic field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fusion device |  |
| Pinwheel galaxy | has definition A Sc II-III spiral galaxy, a satellite of the Andromeda galaxy, about 700 kpc distant. Mv = - 18.9. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A spiral galaxy that lies 2.6 million light-years away and is the third largest member of the Local Group, after Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The third largest member of the Local Group, after Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way. It is a spiral galaxy that lies 2.6 million light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Hodierna |  |
| has discovery date 1654 |  |
| has distance 800 kpc from Milky Way galaxy |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 33 |  |
| has synonym M 33 |  |
| has synonym NGC 598 |  |
| has synonym Triangulum galaxy |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Triangulum |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
is an instance of Sc spiral  |  |
| pion | has definition An unstable nuclear particle of mass intermediate between that of a proton and an electron. The pions are believed to be the particles exchanged by nucleons, resulting in the strong nuclear force; they play a role in the strong interactions analogous to that of the photons in electromagnetic interactions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 270 me |  |
| has synonym π-meson | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge multiplet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of meson |  |
| Pisces | has acronym Psc |  |
has boundary 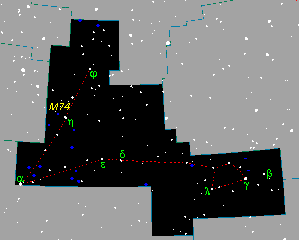  |  |
| has genitive Piscium |  |
| has synonym Fishes |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Pisces Australis | has acronym PsA |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Southern Fish |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of constellation |  |
| pitch angle | has definition Angle specifying the direction of electron velocity; or the angle between a tangent to a spiral arm and the perpendicular to the direction of the galactic center. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of angle |  |
| plage | has definition The bright rim of a sunspot, observed in emission in monochromatic light of some spectral line (H | ![has source: [alpha] or Ca II). It is a chromospheric phenomenon associated with and often confused with a facula. (sometimes called flocculus), 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym flocculus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of sunspot |  |
| Planck constant | has definition A universal constant of nature that measures the magnitude of quantum mechanical effects. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Planck's constant is a fundamental parameter in quantum mechanics. It determines the size of the discrete units of energy, mass, spin, etc. into which the microscopic world is partitioned. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The universal constant of proportionality relating the frequency of a photon to its quantum of energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol h |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000052 × 10-34 J s |  |
has value 6.62606876 × 10-34 J s  |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| Planck energy | has definition About 1000 kilowatt hours. The energy necessary to probe to distances as small as the Planck length. The typical energy of a vibrating string in string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An energy of 1.22 × 1019 GeV (billion electron volts), at which the strength of the gravitational interactions of fundamental particles becomes comparable to that of the other interactions. It is believed that the quantum effects of gravity become important at approximately this energy. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| Planck era | has definition The Big Bang era, prior to which Einstein's theory of gravitation breaks down and a quantized theory of gravity is needed. Density was so high that gravitational force acted as strongly as the other fundamental forces on the sub-atomic scale. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 10-43 s or the time at which the size of the universe was roughly the Planck length (the time it takes light to travel the Planck length; G h bar / c5)1/2 where G is Newton's constant of gravitation, h bar is Planck's constant, and c is the speed of light | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has start time 0 s after Big Bang |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is followed by hadron era, inflation era |  |
| is preceded by Big Bang |  |
| Planck length | has definition The dimension at which space is predicted to become "foamlike" and at which Einstein's theory is supposed to break down. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The scale below which quantum fluctuations in the fabric of spacetime would become enormous. The size of a typical string in string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The size limit at which normal notions of space-time are supposed to break down. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol lP |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0012 × 10-35 m |  |
has value 1.6160 × 10-35 m  |  |
| is an instance of length |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| Planck mass | has definition About ten billion billion times the mass of a proton; about one-hundredth of a thousandth of a gram; about the mass of a small grain of dust. The typical mass equivalent of a vibrating string in string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol mP |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0016 × 10-8 kg |  |
has value 2.1767 × 10-8 kg  |  |
| is an instance of mass |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| Planck time | has equation  |  |
| has symbol tP |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0040 × 10-44 s |  |
has value 5.3906 × 10-44 s  |  |
| is an instance of time |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| plane | has dimensions 2 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| planet | has composition various elements |  |
| has definition An object that formed in the disk surrounding a star. Unlike stars, planets do not produce light of their own but merely reflect that of the star(s) they orbit. Planets can have natural satellites. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass greater than Pluto's mass and less massive than ten times Jupiter's mass | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbit |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of solar system |  |
| planetary element | has definition an element which occurs in certain parts of planets with varying concentration |  |
| has occurrence in certain parts of planets |  |
| is a kind of element |  |
| planetary elongation | has definition The angle planet-Earth-Sun. Eastern elongations appear east of the Sun in the evening; western elongations, west of the Sun in the morning. An elongation of 0° is called conjunction; one of 180° is called opposition: and one of 90° is called quadrature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The geocentric angle between a planet and the Sun, measured in the plane of the planet, Earth and Sun. Planetary elongations are measured from 0° to 180°, east or west of the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elongation |  |
| planetary elongation event | has definition A point in the orbit of a celestial body with a specific planetary elongation such as 0°, 90° or 180° | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial event |  |
| is a kind of planetary elongation |  |
| planetary nebula | has catalog planetary nebula catalog |  |
| has definition A bubble of gas surrounding a hot, dying star. The star is so hot that it makes the planetary nebula glow, which allows astronomers to see it. The star was once the core of a red giant, which ejected its outer atmosphere and created the planetary. A planetary nebula has nothing to do with a planet, but through a small telescope, it looks like a planet's disk, hence the misleading name. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An expanding envelope of rarefied ionized gas surrounding a hot white dwarf. The envelope receives ultraviolet radiation from the central star and reemits it as visible light by the process of fluorescence. The planetary nebula stage lasts for less than 50,000 years. During the core contraction that terminates the red-giant stage, the helium-burning shell is ejected at a velocity so high that it becomes separated from the core. Under current theories, a star with a carbon core and a mass greater than 0.6 Msun (but less than 4 Msun) will become a planetary nebula and leave behind a white dwarf. Planetary nebulae are now known to occur in stars less than 4 Msun whose envelope becomes unstable during the hydrogen shell burning stage. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has expansion velocity typically 10 km/s |  |
| is a kind of expanding emission nebula |  |
| planetary nebula catalog | has object type planetary nebula |  |
| is a kind of nebula catalog |  |
| planetary precession | has definition The component of general precession caused by the gravitational coupling between the center of mass of the Earth and that of the other planets. The effect of planetary precession is to move the equinox eastward by ≈ 0".11 / year and to diminish the angle between the ecliptic and the equator by about 0".47 / year. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has rate 0".11 per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| planetary theory | has domain planet |  |
| is a kind of astronomy theory |  |
| planetocentric coordinate | has definition Coordinates for general use, where the z-axis is the mean axis of rotation; the x-axis is the intersection of the planetary equator (normal to the z-axis through the center of mass) and an arbitrary prime meridian; and the y-axis completes a right-hand coordinate system. Longitude (see longitude, celestial) of a point is measured positive to the prime meridian as defined by rotational elements. Latitude (see latitude, celestial) of a point is the angle between the planetary equator and a line to the center of mass. The radius is measured from the center of mass to the surface point. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| planetographic coordinate | has definition Coordinates for cartographic purposes dependent on an equipotential surface as a reference surface. Longitude (see longitude, celestial) of a point is measured in the direction opposite to the rotation (positive to the west for direct rotation) from the cartographic position of the prime meridian defined by a clearly observable surface feature. Latitude (see latitude, celestial) of a point is the angle between the planetary equator (normal to the z-axis and through the center of mass) and normal to the reference surface at the point. The height of a point is specified as the distance above a point with the same longitude and latitude on the reference surface. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| Plaskett's star | has definition A very massive O-type giant with known anomalies in its spectrum. It is a spectroscopic binary in which mass exchange is occurring. Its spectrum can be interpreted to mean that each component has a mass of 75 Msun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HD 47129 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Monoceros |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| is an instance of spectroscopic binary |  |
| plasma | has definition A completely ionized gas; the so-called fourth state of matter (besides solid, liquid, and gas) in which the temperature is too high for atoms as such to exist and which consists of free electrons and free atomic nuclei. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gas |  |
| plasmapause | has altitude 4 to 7 Earth radii |  |
| has definition The region in Earth's ionosphere where the particle density (100 particles per cm3 just below the plasmapause) drops off very rapidly. It marks the transition from high to low density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has density 100 particles per cm3 |  |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| platinum | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| is a kind of siderophile element |  |
| is a kind of supernova produced element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Pleiades | has age very young | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has composition B star, late star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 125 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 45 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars several hundred | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym M 45 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 1432 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Taurus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye object | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of open cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| Pleione | has definition A B8pe star, one of the brightest stars in the Pleiades, which developed an envelope or shell first observed in 1938. The shell increased in strength and attained its maximum intensity in 1945; thereafter it weakened and was scarcely visible by 1954. In 1972 it developed another shell. It is rotating so fast that it is unstable. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 28 Tau | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Taurus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of shell star |  |
| pleistocene epoch | has duration 1 million years |  |
| has start time 1 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of quaternary period |  |
| pliocene epoch | has duration 13 million years |  |
| has start time 13 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of tertiary period |  |
| Pluto | has albedo < 0.25 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The most distant known planet from the Sun. Its orbit has the highest eccentricity and highest inclination to the ecliptic of any planet and some astronomers suggest that it may be an escaped satellite of Neptune. In the mid-1970s Pluto crosses Neptune's orbit on its way in, and for the rest of this century Pluto will be closer to the Sun than Neptune (Pluto and Neptune, however, are never less than 2.6 AU apart). Its mass and radius have not been determined with any great certainty. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Clyde Tombaugh | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1930 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from Sun 39.44 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity 0.249 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination to the ecliptic 17°.17 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 6 × 1026 g, 0.1 to 0.2 MEarth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 248.43 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity Vorb 4.7 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has perhelion date 1989 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius < 2900 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 6d9h17m49s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 366.7 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 50-60 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of terrestrial planet |  |
| plutonium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| Pockels cell | has definition An electro-optic crystal used as a reversible waveplate by applying alternately high positive and negative voltage. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification polarization |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| point | has definition A geometrical object with zero dimensions, a location and possibly a time | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has dimensions 0 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| Poisson distribution | has definition An approximation to the binomial distribution used when the probability of success in a single trial is very small and the number of trials is very large. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of statistical distribution |  |
| polar motion | has definition The irregularly varying motion of the Earth's pole of rotation with respect to the Earth's crust. (See celestial ephemeris pole.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of axis motion |  |
| Polar-disk equatorial telescope | has mounting equatorial with polar-disk | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| Polaris | has B-V magnitude 0.60 |  |
| has declination +89 15 51 |  |
| has definition A supergiant F8 Ib, F3 V visual binary, with an orbital period of thousands of years. The primary (a Cepheid with a pulsation period of 3.97 days) is itself a single-lined spectroscopic double with a period of 29.6 years. There are at least two more faint (12th mag) components of the system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 330 light-years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 3.97 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has primary F8 Ib |  |
| has right ascension 2 31 50.5 |  |
| has spectral type F7:Ib-IIv |  |
| has synonym alpha UMi | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 424 |  |
| has synonym North Star | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Pole star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has use The star that lies near the direction in the sky toward which the North Pole of the Earth points. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has V magnitude 2.02 |  |
is a part of Ursa Minor  |  |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of Population I Cepheid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of supergiant |  |
| pole | has definition One of two points at which the Earth's axis of rotation intersects the geoid. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has height 0 |  |
| has terrestrial longitude 0 |  |
| is a kind of geocentric coordinate |  |
| Pollux | has B-V magnitude 1.00 |  |
| has declination +28 1 34 |  |
| has definition A K0 III star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 11 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 7 45 18.9 |  |
| has spectral type K0IIIb |  |
| has synonym beta Gem | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 2990 |  |
| has V magnitude 1.14 |  |
is a part of Gemini  |  |
| is an instance of bright giant |  |
| is an instance of K star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| polonium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of group VI element |  |
| is a kind of metallic metalloid |  |
| Population I Cepheid | has absolute magnitude <Mv> = -0.5 to -6 |  |
| has definition A Cepheid which is about 4 times more luminous than Population II Cepheids, probably because of their higher metal content (although mass may also be a factor). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 5-10 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym classical Cepheid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym young disk Cepheid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Cepheid |  |
| is a kind of Population I star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| Population I star | has author Baade (1944) |  |
| has definition Young star typical of those found in galaxy spiral arms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Young star with relatively high abundances of metals, and are usually found in the disk of a galaxy, especially the spiral arms, in dense regions of interstellar gas. |  |
| has definition Younger stars, generally formed towards the edge of a galaxy, of the dusty material in the spiral arms, including the heavy elements. The brightest of this Population are hot, white stars. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Youngest observed stars, like our sun, formed from hydrogen, helium, and a large range of heavier elements (like carbon and oxygen) believed to have been created in the interiors of earlier Population II stars and Population III stars and then blown out into space. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym arm population |  |
| has synonym disk star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| is a part of disk |  |
| Population II Cepheid | has absolute magnitude <Mv> = 0 to -3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A bright yellow star that pulsates like a Cepheid but is older and fainter. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 10 to 30 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym W Virginis star | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Cepheid |  |
| is a kind of Population II star |  |
| occur in globular clusters | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| Population II star | has author Baade (1944) |  |
| has definition Old stars typical of those found in the halo of the Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Older observed stars formed mostly from hydrogen and helium. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Older star with relatively low abundances of metals, usually found in the nucleus of a galaxy or in globular clusters. The Sun is a rather old Population I star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Older stars, generally formed towards the centre of a galaxy, containing few heavier elements. The brightest of this Population are red giants. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star that has high spatial velocity and low metallicity. This is not an observational definition. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym halo star |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| is a part of halo |  |
| Population III star | has author Baade (1944) |  |
| has definition Star older than Population II stars. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| Poseidon | has definition Unofficial name for J VIII, the next outermost satellite of Jupiter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Melotte | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1908 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 147° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 737d | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Jupiter VIII | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of natural satellite | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif) |
| positive muon g factor | applies to particle positive muon |  |
| has symbol gμ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000000013 |  |
has value 2.0023318320  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| positive muon magnetic moment | applies to particle positive muon |  |
| has symbol μμ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000022 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value 4.49044813 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment |  |
| positron | has antiparticle electron |  |
| has charge 1 |  |
| has definition The antiparticle of the electron, discovered by Anderson in 1934. It has the same mass and spin as the electron, but opposite charge and magnetic moment. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Anderson |  |
| has discovery date 1934 |  |
| has synonym antielectron |  |
| is an instance of antiparticle |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of lepton |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| positronium | has definition A positron and electron bound together electrostaticaly. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of boson |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| post-asymptotic branch star | has definition F-type supergiant with strong sulfur lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of F star |  |
| is a kind of supergiant |  |
| potassium | has abundance 1.45 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 21000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 5 × 106 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 404.414 nm for K I |  |
| has atomic emission line 691.108 nm for K I |  |
| has atomic emission line 693.877 nm for K I |  |
| has atomic emission line 769.896 nm for K I |  |
| has atomic emission line 766.491 nm for K I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 19 |  |
| has atomic radii 227 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to all living things |  |
| has boiling point 1047 K |  |
| has chief source sylvite, carnalite, alunite |  |
| has covalent radii 203 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 533.4 pm |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c |  |
| has daily dietary intake 1.4 - 7.4 g |  |
| has definition soft white metal which is silvery when first cut but oxidizes rapidly in air |  |
| has density 828 kg m-3 for liquid at 336.80 K melting point |  |
| has density 862 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Sir Humphry Davy |  |
| has discovery date 1807 (isolated) |  |
| has discovery location London, England |  |
| has electrical resistivity 6.15 × 10-8 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 48.4 kJ mol-1 from K to K- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]4s1 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 0.82 Pauling |  |
| has hazard excess ingestion of KCl (dietary supplement) can be fatal |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 29.58 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 2.40 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 77.53 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 133 pm for K+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 35 to 51 |  |
| has lethal intake 2600 mg kg-1 |  |
| has level in humans 16000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 16000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 1620 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 2100 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 83 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope potassium 39 |  |
| has main mining area Germany, Spain, Canada, USA, Italy |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 143 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 15.8 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +6.7 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 140 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 336.80 K |  |
| has mineral alunite, carnalite, orthoclase (mined for porcelain, ceramics and glass), sylvite |  |
| has molar volume 45.36 cm3 |  |
| has name origin potash from English |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.367 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 18 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 19 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 21000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.35 GPa at 83 K |  |
| has pronunciation poh-tass-ium |  |
has registry number 7440-09-7 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 39.0983 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves > 1 × 1010 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 1.30 GPa |  |
| has space group Im3m |  |
| has specimen metal chunks (in mineral oil) or ingots. Warning! |  |
| has symbol K |  |
| has symbol name origin kalium from Greek |  |
| has synthesis mechanism combine sodium metal with potassium chloride |  |
| has term symbol 2S1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 102.4 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 2.1 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 4 g of KCl |  |
| has uses compounds are used in fertilizers, chemicals and glass |  |
| has van der Waals radii 231 pm |  |
| has world production 200 tonnes year-1 for metal form |  |
| has world production 51 × 106 tonnes year-1 for salts |  |
| has young's modulus 3.53 GPa at 83 K |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| reacts with water violently |  |
| potassium 38 | has atomic mass 37.969080 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (5.913 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 7.63 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.37 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 19 |  |
| has number of nucleons 38 |  |
| has symbol 38K |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 39 | has atomic mass 38.963707 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.2483 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 93.2581% |  |
| has NMR frequency 4.667 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 2.69 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.391465 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.0601 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 20 |  |
| has number of nucleons 39 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 5.08 × 10-4 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 39K |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 40 | has atomic mass 39.963999 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.32 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has half life 1.25 × 109 years |  |
| has natural abundance 0.0117 % |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.298009 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.0749 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 4- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 21 |  |
| has number of nucleons 40 |  |
| has symbol 40K |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 41 | has atomic mass 40.961825 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 0.6851 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 6.7302% |  |
| has NMR frequency 2.561 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.0328 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.214869 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.0733 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 41 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 8.40 × 10-4 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 41K |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 42 | has atomic mass 41.962402 |  |
| has decay mode β- (3.523 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 12.36 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.1425 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 42 |  |
| has symbol 42K |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 43 | has atomic mass 42.960717 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.82 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 22.3 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.163 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 24 |  |
| has number of nucleons 43 |  |
| has symbol 43K |  |
| has uses medical diagnosis |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 44 | has atomic mass 43.96156 |  |
| has decay mode β- (5.66 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 22.1 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.856 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 25 |  |
| has number of nucleons 44 |  |
| has symbol 44K |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potassium 45 | has atomic mass 44.960696 |  |
| has decay mode β- (4.20 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 17.8 minutes |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.1734 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 45 |  |
| has symbol 45K |  |
is an instance of potassium  |  |
| potential energy | is a kind of energy |  |
| Potsdam Refractor | has altitude 107 m |  |
| has aperture 0.80 m |  |
| has creation date 1899 |  |
| has focal ratio f/15.0 |  |
| has latitude 52° 23' N |  |
| has lens maker C.A. Steinheil |  |
| has location Telegrafenberg, Potsdam, Germany |  |
| has longitude 13°04'E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Repsold |  |
| has owner Zentralinstitut fur Astrophysik |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| power | is a kind of quantity |  |
| power unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of power |  |
| PP I | has definition A thermonuclear reaction in which hydrogen nuclei are transformed into helium nuclei producing 4 × 10-5 ergs of energy. Although the neutrinos from this reaction are detectable, they have not been observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has reaction 1H(p, β+v)2D(p, γ)3He(3He, 2p)4He | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of proton-proton chain |  |
| PP II | has definition A thermonuclear reaction in which hydrogen nuclei are transformed into helium nuclei. Although the neutrinos from this reaction are detectable, they have not been observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has reaction 1H(p, β+v)2D(p, γ)3He(4He, γ)7Be(β+v)7Li(p,α)4He | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of proton-proton chain |  |
| PP III | has definition A thermonuclear reaction in which hydrogen nuclei are transformed into helium nuclei. Occurs once in 1000 times. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has reaction 1H(p, β+v)2D(p, γ)3He(4He,γ)7Be(p,γ)8B (β+v)8Be → 2 4He | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has reaction probability once in 1000 times |  |
| is an instance of proton-proton chain |  |
| Praesepe | has distance 160 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 44 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Beehive Cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym M 44 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 2632 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Cancer | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of naked eye object | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of open cluster | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| praseodymium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| precambrian era | has duration 2500 million years |  |
| has start time 3100 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of geological era |  |
| precession | has definition A slow, periodic conical motion of the rotation axis of a spinning body. In the case of Earth's precession it is due to the fact that Earth's axis of rotation is not perpendicular to the ecliptic but is inclined about 23°.5 and is thus affected by gravitational perturbations from other bodies in the solar system. The Moon and Sun pull harder on that part of the Earth's equatorial bulge nearest them than on that farthest away; this causes a torque which precesses the Earth's rotational axis. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The slow (once per twenty-six thousand years) gyration of the Earth's axis. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The uniformly progressing motion of the pole of rotation of a freely rotating body undergoing torque from external gravitational forces. In the case of the Earth, the component of precession caused by the Sun and Moon acting on the Earth's equatorial bulge is called lunisolar precession; the component caused by the action of the planets is called planetary precession. The sum of lunisolar and planetary precession is called general precession. (See nutation.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has rate |  |
| is a kind of axis motion |  |
| prediction | is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| pressure | has definition The force exerted over a surface divided by its area. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit pressure unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| pressure broadening | has cause pressure which in turn is caused by the surface gravity of the star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Line broadening caused by pressure. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has example white dwarfs have very broad absorption lines | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| pressure ionization | has definition A state found in white dwarfs and other degenerate matter in which the atoms are packed so tightly that the electron orbits encroach on each other to the point where an electron can no longer be regarded as belonging to any particular nucleus and must be considered free. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ionization |  |
| pressure unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of pressure |  |
| primary mirror | has definition The first mirror encountered by incident light in a telescope system. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| prime focus | has definition The focal point of the large primary reflecting mirror in astronomical telescopes when the light source is extremely distant. This focus actually falls at a point just within the upper structure of the telescope itself and is therefore accessible to CCD cameras and other instruments; it provides a large field of view. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of focus |  |
| primordial black hole | has definition Small black hole hypothesized to have formed during the first 10-43 seconds of the universe, when quantum effects were very large. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| primordial nucleosynthesis | has definition Production of atomic nuclei occurring during the first three minutes after the big bang. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The creation of elements that occurred just minutes after the Big Bang. According to standard theory, primordial nucleosynthesis gave the universe only five nuclei, all lightweight: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2 (or deuterium), helium-3, helium-4, and lithium-7. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The process, which took place between one second and 3-4 minutes after the beginning, in which the protons and neutrons of the primordial soup condensed to form the lightest atomic nuclei: Deuterium, Helium-3, Helium-4, and Lithium-7. See isotope and Lithium. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The production of heavy nuclei from the fusion of lighter ones during the Big Bang. The infant universe consisted of only hydrogen, the lightest of all atomic nuclei, because any heavier nuclei would have come apart in the intense heat. All other elements would have to be formed later, in nucleosynthesis processes. It is believed that most of the helium, the next lightest element after hydrogen, was formed when the universe was a few minutes old | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym big-bang nucleosynthesis |  |
| is a kind of nucleosynthesis |  |
| primordial quark | has definition All baryons and mesons are believed to be composed of quarks, which are elementary particles of fractional charge. In the high-density, hot-temperature phase of the very early universe, prolific numbers of quarks would have been present in equilibrium with the other elementary particles. As the universe expanded and cooled, some of these quarks may have been frozen out. To what extent independent free quarks could survive is an unresolved issue of elementary particle physics. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quark |  |
| probable error | has acronym p.e. |  |
| has definition The error which will not be exceeded by 50 percent of the cases. The probable error is equal to 0.6745 times the standard error. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| problem | is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| process | is a kind of physical phenomena |  |
| Procyon | has B-V magnitude 0.42 |  |
| has declination +05 13 30 |  |
| has definition One of the nearest stars, it is the eighth brightest star. An F star. It is a visual binary; its companion is a DF8 white dwarf. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3.5 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 40 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has parallax 0.283 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 07 39 18.1 |  |
| has spectral type F5 IV-V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha CMi |  |
| has synonym HR 2943 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.38 |  |
is a part of Canis Minor  |  |
| is an instance of F star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of subgiant |  |
| is an instance of visual binary |  |
| prograde motion | has definition Motion in the same direction as the prevailing direction of motion. |  |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| program star | has definition The star being observed or measured, as contrasted with the comparison stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| promethium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of synthetic element |  |
| prominence | has definition A region of cool, high-density gas embedded in the hot (106 K), low-density solar corona. Prominences are the flamelike tongues of gas that appear above the limb of the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Mass of hot, hydrogen rising from the Sun's chromosphere, best observed indirectly during a total eclipse. There are two kinds of prominence : erruptive prominence and quiescent prominence. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 104 K | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| proper motion | has definition Apparent angular rate of motion of a star across the line of sight on the celestial sphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The apparent movement of a star, year after year, caused by the star's velocity across the line of sight. If the star's distance is known, this velocity-called the tangential velocity, can be computed. The star with the largest proper motion is Barnard's Star, whose proper motion is 10.3 arc-seconds per year. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The projection onto the celestial sphere of the space motion of a star relative to the solar system; thus the transverse component of the space motion of a star with respect to the solar system. Proper motion is usually tabulated in star catalogs as changes in right ascension and declination per year or century. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| protactinium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| is a kind of actinide |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| proto-planet | has definition Early stage in the formation of planets according to the theory by which planetary systems evolve through the condensation of gas clouds surrounding a young star. The theory is not, however, generally accepted. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planet |  |
| protogalaxy | has definition A galaxy during the early phase, before it has developed its present shape and mix of stars. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A galaxy in the process of formation. None are observed nearby, indicating that all or most galaxies formed long ago. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| proton | has charge 1 |  |
| has composition two up quarks and one down quark |  |
| has definition A baryon made of two up quarks and a down quark. It possesses a positive electromagnetic charge and can only be found in atomic nuclei. A single proton is a hydrogen nucleus. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A massive particle with positive electrical charge found in the nuclei of atoms. Composed of two up quarks and one down quark. The proton's mass is 938.3 MeV, slightly less than that of the neutron. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A positively charged elementary particle; the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Mass of proton 1.00728 amu = 1.6726 × 10-24 g = 1836.12 me. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A subatomic particle with positive electric charge. Every atom has at least one proton in its nucleus; the number of protons determines the element. For example, all atoms with one proton are hydrogen, all atoms with two protons are helium, and so on. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the constituents of the atomic nucleus. It is a spin-1/2 particle carrying positive electric charge. The proton is the lightest baryon and, as a result, is the particle into which all other baryons eventually decay. It is believed to be absolutely stable, but certain theories (GUTs) predict it will decay very, very slowly. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol p |  |
| is a part of nucleus |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of elementary particle |  |
| is an instance of nucleon |  |
| is an instance of nucleus |  |
| proton Compton wavelength | applies to particle proton |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol λC,p |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000010 × 10-15 m |  |
has value 1.321409847 × 10-15 m  |  |
| is an instance of particle Compton wavelength |  |
| proton decay | has definition Spontaneous disintegration of the proton, predicted by grand unified theory but never observed experimentally. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of prediction |  |
| proton g factor | applies to particle proton |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000057 |  |
has value 5.585694675  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| proton gyromagnetic ratio | applies to particle proton |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol γp |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000011 × 108 s-1 T-1 |  |
has value 2.67522212 × 108 s-1 T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle g factor |  |
| proton magnetic moment | applies to particle proton |  |
| has symbol μp |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000058 × 10-26 J T-1 |  |
has value 1.410606633 × 10-26 J T-1  |  |
| is an instance of particle magnetic moment |  |
| proton mass | applies to particle proton |  |
| has symbol mp |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00000013 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 1.67262158 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| proton-proton chain | has definition A series of thermonuclear reactions in which hydrogen nuclei are transformed into helium nuclei. The temperature and density required are about 107 K and 100 g cm-3. It is the main source of energy in the Sun, where 1038 of these reactions occur every second. All parts of this reaction have been observed in the laboratory, except for the first step 1H(p, β+v)2D, which occurs only a few times in 1012 collisions of protons. But the first two reactions provide about one-third of the Sun's total energy release. The p-p chain divides into three main branches: PP I, PP II and PP III. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An important nuclear fusion reaction that occurs in stars. It begins with the fusion of two hydrogen nuclei, each of which consists of a single proton. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Process of nuclear fusion by which relatively cooler stars produce and radiate energy; hotter stars commonly achieve the same result by means of the carbon-nitrogen cycle. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The nuclear sequence by which the Sun and all other main-sequence stars with less than 1.5 solar masses fuse hydrogen into helium. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition thermonuclear reaction in which two protons collide a very high velocities and combine to form deuteurium, the deuteurium can capture a proton to form tritium and tritium can capture a proton to form helium | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has location the center of the Sun an other stars |  |
| has minimum temperature 107 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has next higher temperature reaction carbon cycle |  |
| has optimum temperature 5 million Kelvin |  |
| has part intermediate product deuterium |  |
| has part intermediate product tritium |  |
| has part product helium |  |
| has part reactant proton |  |
| has required reactant concentration high |  |
| has synonym p-p chain |  |
| has temperature dependence E ∝ T4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hydrogen burning |  |
| is a kind of pycnonuclear reaction |  |
| Proxima Centauri | has bolometric magnitude M bol = 11.66 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An flare star probably associated with the alpha Centauri system. It is the closest star to the Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4.25 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass M = 0.1 Msun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has parallax 0'.765 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R = 1.3 × 1010 cm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type dM4e | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Centaurus |  |
| is an instance of flare star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| PSR B 1257+12 | has definition A pulsar in the constellation Virgo and the site of the first solar system to be discovered outside our own. The planets were detected in 1991. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of pulsar |  |
| pulsar | has acronym PSR | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A fast-spinning neutron star that emits radiation toward Earth every-time it rotates. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An object discovered at Cambridge University in 1967 which has the mass of a star and a radius no larger than that of Earth and which emits radio pulses with a very high degree of regularity (periods range from 0.03 s for the youngest to more than 3 s for the oldest). All pulsars are characterized by the general properties of dispersion, periodicity, and short duty cycle. Pulsars are believed to be rotating, magnetic (surface magnetic fields of 1010 to 1014 gauss are estimated) neutron stars which are the end products of supernovae. Type S pulsars have a simple pulse shape: Type C, complex: Type D have drifting subpulses. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Neutron stars that spin rapidly and have strong magnetic fields, which produce electromagnetic radiation. (See neutron star.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of neutron star |  |
| is a kind of radio star |  |
| pulsating nova | has definition A variable star, probably not a true nova, in which the change between more and less luminous stages is extreme. (also called recurrent novae) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cataclysmic variable |  |
| Puppis | has acronym Pup |  |
| has genitive Puppis |  |
| has synonym Ship's Stern |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation formerly part of Argo Navis  |  |
| Puppis A | has age 104 to 105 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A supernova remnant. It is an extended nonthermal radio source, and also a source of soft X-rays. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 1 to 2 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 2U 0821-42 |  |
| is a part of Puppis |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| pycnonuclear reaction | has definition Nuclear process that take place at relatively low temperatures and that are not strongly temperature-dependent. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has minimum temperature relatively low |  |
| has temperature dependence weak |  |
| is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| Pyrex | is a kind of mirror |  |
| Pyxis | has acronym Pyx |  |
| has genitive Pyxidis |  |
| has synonym Ship's Compass |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation formerly part of Argo Navis  |  |
| is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille |  |
| Q-branch | has definition A set of lines in the spectra of molecules corresponding to changes in vibrational energy with none in rotational energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of molecular lines |  |
| Quadrantid | has duration 0.4 days |  |
| has radiant ??? |  |
| has rate 80 per hour |  |
| has start time 3 January |  |
| is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| quadrature | has definition Elongation of a planet when it makes a 90° angle with the Sun as seen from Earth. (b) A configuration in which two celestial bodies have apparent longitudes (see longitude, celestial) that differ by 90° as viewed from a third body. Quadratures are usually tabulated with respect to the Sun as viewed from the center of the Earth. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has elongation 90° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planetary elongation event |  |
| quantity | has definition A number with specific units | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit |  |
| is a kind of number |  |
| quantum chromodynamics | has acronym QCD | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gauge theory describing the interactions of quarks through the strong color field. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has exchange quantum gluon | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has gauge symmetry SU(3)C (non-Abelian group) | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gauge theory | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| see also Yang-Mills theories | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| quantum electrodynamics | has acronym QED | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Gauge theory describing the interactions between electrically charged particles through the electro-magnetic field. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has exchange quantum photon | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has gauge symmetry U(1) (Abelian group) | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of gauge theory | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| quantum field theory | has applicability elementary particles | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Relativistically invariant version of quantum mechanics used to describe the physics of elementary particles. The action of forces is a result of the exchange of sub-atomic particles. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has exchange quantum |  |
| has implication quantum fields are the ultimate reality and particles are merely the localized quanta of these fields. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has symmetry relativistic invariance | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantum mechanics |  |
| quantum gravity | has definition A general term used to describe attempts to quantize gravity. The elementary particle of the gravitational field is the graviton. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A theory of gravity that would properly include quantum mechanics. To date, there is no complete and self-consistent theory of quantum gravity, although successful quantum theories have been found for all the forces of nature except gravity. (See quantum mechanics.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A theory that successfully mergers quantum mechanics and general relativity, possibly involving modifications of one or both. String theory is an example of a theory of quantum gravity. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| quantum law | has domain quantum mechanics |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| quantum mechanics | has applicability microscopic scales of atoms and subnuclear particles but not restricted to this | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has constraint certain quantities (e.g. energy, angular momentum, light) can only exist in certain discrete amounts, called quanta. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Physics theory that explains wave-particle duality, the uncertainty principle and the exclusion principle. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Planck |  |
| has equation Any physical system, such as an atom, may be viewed as existing as a combination of its possible states, each of which has a certain probability. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has implication physical systems must be described in terms of probabilities. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym quantum theory |  |
| is a kind of physics theory |  |
| quantum mechanics interpretation | is a kind of quantum mechanics |  |
| quantum of circulation | has equation  |  |
| has symbol h/2me |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000027 × 10-4 m2 s-1 |  |
has value 3.636947516 × 10-4 m2 s-1  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| quantum quantity | is a kind of quantity |  |
| quantum solid | has definition A degenerate gas in which the densities are so great that the nuclei are fixed with respect to each other so that they resemble a crystalline lattice. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solid |  |
| quark | has antiparticle antiquark |  |
| has definition A fermion with fractional electric charge. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A particle that is acted upon by the strong force. Quarks exist in six varieties: up, down, charm, strange, top, bottom and three "colors" (red, green, blue). | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A sub-atomic particle which is a fundamental building block of the hadrons. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fundamental particle of which protons, neutrons and electrons are now thought perhaps to be made up. There are possibly three or four types of quark. It is even possible that quarks themselves may be made up of still more fundamental particles. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fundamental particles from which all hadrons are made. According to the theory of quantum chromodynamics, protons, neutrons, and their higher-energy cousins are composed of trios of quarks, while the mesons are each made of one quark and one antiquark. Held together by the strong nuclear force, quarks are not found in isolation in nature today; see asymptotic freedom. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the fundamental, indestructible particles of nature, out of which many other subatomic particles are made. Five types of quarks have been discovered, and it is believed that a sixth also exists. Quarks interact mainly via the strong nuclear force and the electromagnetic force. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothetical constituent of the elementary particles that interacts via glue forces. Originally only three quarks were hypothesized; today it appears that six are required. For a variety of theoretical reasons, free quarks can never be seen. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has spin 1/2 | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charged particle |  |
| is a kind of fermion | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of parton | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of nucleon |  |
| quark color | has definition An attribute which distinguishes otherwise identical quarks of the same flavor. Three colors red, green and blue - are required to distinguish the three valence quarks of which baryons are composed. It must be stressed that these colors are just labels and have nothing to do with ordinary color. Color is the source of the strong force which binds quarks together inside baryons and mesons, and so the three colors (r, g, b) can be thought of as three different color charges analogous to electric charge. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Each flavor of quark can exist in three variations, called colors, usually labeled as red, green, and blue. The color of a quark has no relation to its visual appearance, but the word color is used because there are three variations, in analogy with the three primary colors. Measurable properties of the quarks, such as electric charge and mass, depend on the flavor but not the color, but the color is responsible for the interactions that bind the quarks together (see Yang-Mills theories). Individual quarks cannot exist independently, but are forever confined within baryons or mesons, each of which is colorless. Baryons achieve colorlessness by being composed of three quarks, one of each color, while mesons achieve colorlessness by pairing each colored quark with its corresponding antiquark. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Property of quarks that expresses their behavior under the strong force. Analogous to the concept of charge in electromagnetism, except that, whereas there are two electrical charges (plus and minus), the strong force involves three color charges - red, green, and blue. The term is whimsical, and has nothing to do with color in the conventional sense, any more than quark "flavor", which determines the weak force behavior of quarks, has anything to do with taste. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| quasar | has acronym QSO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has catalog quasar catalog |  |
| has definition An intensely bright extragalactic object which superficially resembles a star. Most exist at very high redshifts and are therefore thought to be the nuclei of active galaxies. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An object with a dominant starlike (i.e., diameter less than 1") component, with an emission line spectrum showing a large redshift - up to z = 3.53 (0.91c) for OQ 172. (The largest redshift known for a normal radio galaxy is z = 0.637 for 3C 123.) Many have multiple absorption redshifts; a few have multiple emission redshifts. (Bahcall system: class I, zabs ≈ zem; class II, zabs significantly less than zem.) The light of most if not all quasars is variable over time intervals between a few days and several years, so their diameters must not be much larger than the diameter of the solar system; yet they are the intrinsically brightest objects known (for 3C 273 (z = 0.158), Mv = -27.5 if its redshift is cosmological). The energy output of a typical quasar at "cosmological" distance is of the order of 1047 ergs per second - which would require a mass of 1010 Msun if it derives its energy solely from nuclear fusion. (Energy requirement under the "local" hypothesis is on the order of 1042 ergs per second.) The basic problem of quasars is that they emit too much radiation in too short a time from too small an area. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Compact-looking objects, often radio sources, with emission lines in their spectrum which are displaced by very large amounts towards the red. These redshifts correspond to velocities which are a large fraction of the speed of light, and hence these objects are believed to lie at great distances. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Extremely distant and luminous astronomical objects that are much smaller than a galaxy and much more luminous. Quasars may be the central regions of certain very energetic galaxies at an early stage of their evolution. It is believed that the power of a quasar derives from a massive black hole at its center. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The brightest objects in the universe, quasars can generate over a trillion times as much light as the Sun from a region little larger than the solar system. Most are extremely distant, which means that they existed long ago. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity very large |  |
| has redshift large | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of violent galaxy |  |
| quasar catalog | has object type quasar |  |
| is a kind of galaxy catalog |  |
| quaternary period | is a kind of cenozoic era |  |
| quiescent prominence | has definition A relatively pacific prominence which may last for months. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of prominence | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| R Coronae Borealis | has amplitude 6th magnitude to 14th magnitude | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star with a large infrared excess and a rather high 7Li abundance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has outburst spectra with many emission-lines |  |
| has outburst start time within a few weeks |  |
| has recovery time several months to a year |  |
has reference Clayton, G.C. : 1996, PASP 108. The R Coronae Borealis Stars  |  |
has reference Clayton, G.C., Whitney, B.A., Stanford, S. A., Drilling, J.S. : 1992, ApJ 397, 652. Observations of R Coronae Borealis stars in decline - Empirical arguments for dust formation near the stellar surface  |  |
has reference Whitney, B.A., Soker, N., Clayton, G.C. : 1991, AJ 102, 284. Model for R Coronae Borealis stars  |  |
| has spectral type F star (F8-G0 Ib) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Corona Borealis |  |
is an instance of R Coronae Borealis variable  |  |
| R Coronae Borealis variable | has amplitude 8 magnitudes | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A very luminous helium-rich, carbon-rich, hydrogen-poor eruptive variable supergiant whose light declines up to 8 magnitudes at irregular intervals. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype R Corona Borealis | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cataclysmic variable |  |
| is a kind of hydrogen-deficient C star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of supergiant | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif) |
| R star | has definition Star with spectral characteristics similar to those of K stars except that molecular bands of C2, CN, and CH are present instead of TiO bands. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C star |  |
| R zone | has definition Region in the solar corona in which short-lived radiofrequency variations are observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of corona |  |
| R-branch | has definition A set of lines in the spectra of molecules corresponding to unit decreases in rotational energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of set of molecular lines |  |
| r-process | has definition The capture of neutrons on a very rapid time scale (i.e., one in which a nucleus can absorb neutrons in rapid succession, so that regions of great nuclear instability are bridged), a theory advanced to account for the existence of all elements heavier than bismuth (up to A ≈ 298) as well as the neutron-rich isotopes heavier than iron. The essential feature of the r-process is the release of great numbers of neutrons in a very short time (less than 100 seconds). The presumed source for such a large flux of neutrons is a supernova, at the boundary between the collapsing neutron star and the ejected material. However, other proposed sources have included such things as supernova shocks and black-hole-neutron-star collisions. The heavier r-process elements are synthesized at a temperature of about 109 K and an assumed neutron density of 1020-1030 per cm3. The r-process is terminated by neutron-induced fission. The existence of 244Pu (half-life 82 million years) in the early solar system shows that at least one r-process event had occurred in the Galaxy just before the formation of the solar system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The creation of elements heavier than zinc through the rapid bombardment of other elements by neutrons. The r process occurs in supernovae. Examples of reprocess elements are gold, iodine, and europium. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| rad | has definition Unit of radiation, equal to 100 ergs of ionizing energy absorbed per gram of absorber. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| radial velocity | has definition The speed at which an object moves toward or away from us. It can be measured from a star's spectrum: a star moving toward us has a blueshifted spectrum, and a star moving away from us has a redshifted spectrum. The larger the blueshift or redshift, the larger the radial velocity. The present radial-velocity champion is a star in the constellation Lacerta named Giclas 233-27, which moves toward us at 583 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Velocity along the line of sight toward (-) or away from (+) the observer. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| radian | has base unit m·m-1 = 1 |  |
| has definition A measure of angular distance; 2π radians equals 360 degrees. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit of angular measure equal to the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc the length of which is equal to the radius. There are 2π radians in a circle. The angle π/4 is called an octant and a thousandth of a radian is sometimes called a mil, which is equal to 3 minutes 26.5 seconds of arc. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 57.29578° | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1873 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposer James Thomson | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol rad | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| radiation direction modification | changes property direction |  |
| is a kind of radiation modification |  |
| radiation era | has definition The Big Bang era when the temperature had dropped to 109K and the rate of electron-positron pair annihilation exceeded the rate of their production, leaving radiation the dominant constituent of the universe. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 1012 s |  |
| has start time 10 s after Big Bang |  |
| has temperature 109K |  |
| is a kind of Big Bang era |  |
| is followed by matter era |  |
| is preceded by nucleosynthetic era |  |
| radiation intensity modification | changes property intensity |  |
| is a kind of radiation modification |  |
| radiation measurement | has unit radiation unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| radiation modification | changes property some aspect of the incomming radiation |  |
| is a kind of optical process |  |
| radiation pressure | has definition The transfer of momentum by electromagnetic radiation incident on a surface: prad = (4/3)σT4 / c. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pressure |  |
| radiation temperature | has definition The temperature that a blackbody of similar dimensions would have that radiated the same intensity at the same frequency. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of temperature |  |
| radiative recombination | has definition See radiative capture. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission |  |
| is a kind of recombination |  |
| radiative zone | has definition Region in a stellar interior where conduction and radiation dominates the heat flow | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of solar interior |  |
| radio | has definition Electromagnetic radiation with the lowest energy and longest wavelength. Unlike visible light, radio waves penetrate dust and can be detected from throughout the Galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 3 GHz or less |  |
| has wavelength 10 cm or more |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| radio astronomy | has definition Study of the universe at the radio wavelengths of electromagnetic energy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomy |  |
| radio galaxy | has definition A galaxy that is extremely luminous at radio wavelengths. A radio galaxy is usually a giant elliptical - the largest galaxy in a cluster - and is a strong emitter of synchrotron radiation. M87 and M82 are examples. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| is a kind of radio source |  |
| radio interferometer | has definition Type of radio telescope that relies on the use of two or more aerials at a distance from each other to provide a combination of signals from one source which can be analyzed by computer. Such an analysis results in a resolution that is considerably better than that of a parabolic dish aerial by itself because of the greater effective diameter. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of array telescope |  |
| is a kind of radio telescope |  |
| requires signals from different antenna to be combined |  |
| radio lobes | has definition Extended regions of diffuse radio emission, often dumbbell shaped, that surround a radio galaxy. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| radio loud quasar | has definition A quasar with detectable radio emission. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quasar |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| radio recombination line | has definition Radio recombination lines are the result of electron transitions between high-n (n > 50) levels in an atom or ion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| radio source | has catalog radio source catalog |  |
| has definition A source of extraterrestrial radio radiation. The strongest known is Cassiopeia A, followed by Cyg A and the Crab Nebula (Tau A) (the capital letters following the name of a constellation refer to the radio sources of the constellation, A being the strongest source). Radio sources are divided into two main categories: Class I, those associated with our Galaxy (which is a weak radio source), and Class II, extragalactic sources. Most radio sources are galaxies, supernova remnants, or H II regions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength radio |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| radio source catalog | is a kind of astronomical catalog |  |
| radio star | has definition Star with detectable emission at radio wavelengths. They include pulsars, flare stars, some infrared stars, and some X-ray stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| radio telescope | has definition A device for gathering and amplifying radio energy typically by using a metallic dish antenna | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Non-optical telescope (of various types) which, instead of focusing light received from a distant object, focuses radio signals onto a receiver-amplifier. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Sensitive radio antennae employed to detect the radio energy emitted by nebulae, galaxies, pulsars, etc. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
has reference astroweb  |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| radioactive element | has definition an unstable radioactive element which has an excess or deficit of neutron relative to the stable element | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of element |  |
| is a kind of radioactive particle |  |
| radioactive particle | has decay products the products produced immediately after decay |  |
| has definition A particle which can produce harmful radioactivity directly through its decay or by interacting with other particles. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has desintegration energy the total energy produced when the particle decays |  |
| has lifetime The average time in which a particle decays |  |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| radioactivity unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of radioactivity |  |
| radium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| radius | is a kind of length |  |
| radon | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| ram pressure | has definition Motion of a blunt body at supersonic velocity through an ambient gaseous medium causes a strong drag or ram pressure to be exerted on the body. In the case of a galaxy moving through the intergalactic gas, the ram pressure is capable of stripping the galaxy of much of its interstellar gas. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pressure |  |
| Raman effect | has definition In spectroscopy, the change in the wavelength of light scattered by molecules. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The change of wavelength on scattering. It arises from radiation exciting (or de-exciting) atoms or molecules from their initial states. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| Rankine | has absolute zero 0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A temperature scale with the same division as the Fahrenheit scale and the zero point at 0° absolute. 0 °R = - 470 °F. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unit which is 5/9 of the Kelvin. Rankine temperatures have the same temperature interval as those on the Fahrenheit scale. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water 491.688 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is named after W. J. M. Rankine (1820-1872) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| to convert to Fahrenheit subtract 459.69 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| rare Earth | has definition Element with atomic number between 57 and 71 in the top row of the inner-transition elements of the periodic table |  |
| has filling orbital 4f |  |
| has synonym lanthanide |  |
| is a kind of inner transition metal |  |
| Rayleigh scattering | has definition Selective scattering (i.e., preferential scattering of shorter wavelengths) of light by very small particles suspended in the Earth's atmosphere, or by molecules of the air itself. The scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| Rayleigh-Jeans law | has definition An approximation of Planck's blackbody formula valid at long wavelengths (hv << kT). It is often used in radio astronomy; it gives the brightness temperature of a radio telescope. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| reaction | has duration |  |
| has location |  |
| has optimum density |  |
| has optimum pressure |  |
| has optimum temperature |  |
| has part catalyst |  |
| has part intermediate product |  |
| has part product |  |
| has part reactant |  |
| has reaction rate |  |
| has required reactant concentration |  |
| is a kind of physical process |  |
| reasoning process | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| Reaumur | has absolute zero -218.52 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has boiling point of water 80 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An arbitrary scale in which the freezing and boiling points of water are taken to be 0 and 80°R respectively. The scale is based on the thermal expansion of an alcohol and water mixture. If the 'length' is 1000 units at the ice point the length expands to 1080 units at the boiling point, hence the peculiar figure of 80 in this scale. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1730 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water 0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of temperature unit | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| is named after R. A. F. Reaumur (1683-1757) | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif) |
| recent quaternary epoch | is a kind of quaternary period |  |
| recession | has definition Motion (increasing distance) away. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| recombination | has antonym ionization |  |
| has definition The capture of an electron by a positive ion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of atomic process |  |
| recombination radiation | has definition See radiative capture. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of bound-free transition |  |
| is a kind of emission |  |
| reconnaissance spacecraft | is a kind of military spacecraft |  |
| recoverable spacecraft | has definition a spacecraft which returns to Earth intact |  |
| is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| recurrent nova | has initial rise of light curve typically 6 magnitudes |  |
| has prototype star |  |
| is a kind of nova |  |
| recycled oceanic element | has ocean concentration increasing with depth |  |
| has ocean residence time 103 to 105 years |  |
| is a kind of oceanic element |  |
| red | is a kind of optical |  |
| red dwarf | has abundance 70 percent of all stars | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A main-sequence star with spectral type M. Red dwarfs are much fainter, cooler, and smaller than the Sun but are the most common type of star in the Galaxy, accounting for 70 percent of all stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type M |  |
| is a kind of dwarf |  |
| red giant | has definition A giant star with spectral type M. Such stars are in a more advanced state of evolution than the Sun, for they do not burn hydrogen into helium at their cores. Instead, they may fuse hydrogen into helium in a layer surrounding their cores, or they may fuse helium into carbon and oxygen, or they may do both. Often, astronomers use "red giant" loosely, to include not only M giants but G and K giants, too. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A late-type (K or M) high-luminosity (brighter than Mv = 0) star that occupies the upper right portion of the H-R diagram. Red giants are post-main-sequence stars that have exhausted the nuclear fuel in their cores. The red-giant phase corresponds to the establishment of a deep convective envelope. Red giants in a globular cluster are about 3 times more luminous than RR Lyrae stars in the same cluster. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Large, highly luminous but relatively cool star that has reached a late stage in its "life". It is running out of nuclear "fuel" and has accordingly expanded greatly and become less dense. Many also become variable stars of long periodicity. Its next evolutionary stage is to become a white dwarf, in developing into which the star has to cross the main sequence on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| is a kind of M star |  |
| Red Spot | has definition An elliptical spot on Jupiter. Its color and intensity vary with time. It has been observed for at least a century, and an examination of earlier records shows that Cassini had sketched it in the seventeenth century. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has dimension 40000 × 15000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| has location southern hemisphere of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Jupiter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif) |
| red supergiant | has definition A supergiant with spectral type M. Red supergiants are the largest stars in the universe: if put in place of the Sun, some would touch Saturn. The two brightest red supergiants in Earth's sky are Betelgeuse and Antares. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supergiant |  |
| redshift | has definition The shift of spectral lines toward longer wavelengths in the spectrum of a receding source of radiation. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value z = Δλ/λ where λ is the laboratory wavelength of the spectral line and Δλ is the difference between the laboratory and the observed wavelengths |  |
| is a kind of Doppler shift |  |
| reduced proper motion | has definition The observed proper motion of a star (in seconds of arc per year) reduced to absolute proper motion (in kilometers per second). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of proper motion |  |
| reflection nebula | has definition A cloud of interstellar gas and dust whose spectrum contains absorption lines characteristic of the spectrum of nearby illuminating stars. The emission component of its spectrum is due to gas; the reflection component, to dust (see also diffuse nebula). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nebula |  |
| reflector | has aperture or primary mirror diameter |  |
| has definition A device for gathering and amplifying light or other energy by means of a mirror. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Telescope that uses mirrors to magnify and focus an image onto an eyepiece. (reflector) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has mirror diameter equal to aperture (except for Schmidt which has aperture smaller than mirror diameter) |  |
| has mirror maker the person, company or institution that created the mirror | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has mirror type material and other engineering details |  |
| has primary mirror shape |  |
| has secondary mirror shape |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| reflector with corrector plate | has primary mirror diameter |  |
| is a kind of optical telescope |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| refraction | has definition Deflection (or "bending") of light - or any ray as it passes from one medium into another of greater or lesser density, representing a change in overall speed of the ray. Refracting telescopes rely on the refraction of light through lenses. The refractive index of a medium (e.g., glass) is a measure of the medium's "bending" power. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation direction modification |  |
| obeys Snell's law | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| refractor | has definition A device for gathering and amplifying light by means of a lens. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A telescope in which the light is focused by a lens at the viewing side of the telescope. By contrast, a reflecting telescope is one in which light is focused by a mirror. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Telescope that uses lenses to magnify and focus an image onto an eyepiece. (refractor) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has lens maker the person, company or institution that created the lens | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has lens type doublet |  |
| has optical design visual refractor |  |
| is a kind of optical telescope |  |
| regolith | has definition The layer of fragmentary debris produced by meteoritic impact on the surface of the Moon or a planet. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Moon |  |
| regression of the nodes | has definition The slow (19°.35 per year, 360° in 18.6 years), westward motion of the nodes of the Moon's orbit due to perturbations of the Earth and Sun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| Regulus | has definition A visual triple B8 V star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 26 pc |  |
| has spectral type B8 V |  |
| has synonym alpha Leo |  |
| is a part of Leo |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| relativity process | is a kind of physical process |  |
| relativity theory | is a kind of physics theory |  |
| religious belief | is a kind of belief |  |
| resistance | has unit resistance unit |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic quantity |  |
| resistance unit | is a kind of electromagnetic unit |  |
| is a unit of resistance |  |
| resonance line | has definition The longest-wavelength line arising from the ground state. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| rest-mass energy | has definition The energy which a particle has even when it is at rest. According to the famous relation E = mc2 of special relativity, this rest energy is equal to the rest mass of the particle-the mass it has when a rest-times the square of the speed of light. If the mass is in grams and the speed of light in centimeters per second (c = 2.998 × 1010 centimeters per second), then the energy is given in ergs. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| retardation point | has altitude inversely proportional to the mass of the meteoroid |  |
| has definition the point in the flight of a meteoroid through the atmosphere where it loses its cosmic velocity and falls freely due to gravity |  |
| has duration zero (it is a point in time) |  |
| has start time shortly after the time of initial contact with atmosphere but before impact |  |
| is a kind of meteor event |  |
| does not occur for meteoroids heavier than 10 tons they impact with a significant fraction of their cosmic velocity |  |
| Reticulum | has acronym Ret |  |
| has genitive Reticuli |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Net |  |
| has synonym Reticle (crosshairs in telescope eyepiece) |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| retrograde motion | has definition Apparent motion of a planet in a direction opposite to its normal progress across the sky produced by the orbital motion of the earth. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In a backwards direction; in astronomy this means in a direction corresponding to east-to-west. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| Rhea | has albedo 0.57 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Sixth satellite of Saturn | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter about 1500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Cassini | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1672 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 4d12h25m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| rhenium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| rhodium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| rich cluster | has definition Galaxy cluster with 100 or more galaxies within a volume comparable to that of a loose group. Scale of cluster, about 1 Mpc. | ![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1 Mpc |  |
| has number of galaxies > 100 |  |
| is a kind of galaxy cluster |  |
| Rigel | has B-V magnitude -0.03 |  |
| has declination -08 12 06 |  |
| has definition A blue supergiant. It is a multiple star. The seventh brightest star in the night sky. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 900 light-years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 05 14 32.2 |  |
| has spectral type B8 Iae | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym beta Ori |  |
| has synonym HR 1713 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.12 |  |
is a part of Orion  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of blue supergiant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| right ascension | has definition Angular distance on the celestial sphere measured eastward along the celestial equator from the equinox to the hour circle passing through the celestial object. Right ascension is usually given in combination with declination. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol α |  |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate component |  |
| ring | has definition A system of four concentric rings, only about 2-4 km thick. The outermost ring is ring A, then comes Cassini's division, then ring B (also called the bright ring), then Lyot's division, then ring C (the crepe ring), then ring D (discovered in 1969). The rings are a swarm of solid particles, probably jagged rocks about 1 meter to 1 km across (1973), not ice as previously had been assumed, inside the Roche limit. Bobrov (1969) estimates the total mass of the rings to be about 0.01 the lunar mass. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has width |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| ring galaxy | has definition A galaxy with a ring-like appearance. The ring contains luminous blue stars, but relatively little luminous matter is present in the central regions. It is believed that such a system was an ordinary galaxy that recently suffered a head-on collision with another galaxy. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| ring gap | has definition A gap between the rings of Saturn. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has width |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of Saturn ring system |  |
| Ring Nebula | has definition A famous planetary nebula (M57, NGC 6720) in the constellation Lyra. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2000 light years |  |
| has illuminating star |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 57 |  |
| has progenitor star |  |
| has synonym M 57 |  |
| is a part of Lyra |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| rise time | has definition The time required for the vehicle to achieve its optimum height (in rocket or balloon astronomy). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of time |  |
| Ritchey-Chrétien | has definition A class of reflecting telescope with a hyperbolic primary and secondary. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A system of two mirrors, aspherized to give an image at the secondary (Cassegrain) focus free from spherical aberration and coma. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has optical design Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| has primary mirror shape concave hyperboloid |  |
| has secondary mirror shape convex hyperboloid |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| Rocard scattering | has definition Linearly anisotropic scattering. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| root mean square | has acronym rms | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The square root of the mean square value of a set of numbers (see also random walk). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| ROSAT | has definition ROentgen SATellite, was an X-ray observatory developed through a cooperative program between the Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom. The satellite was designed and operated by Germany, and was launched by the United States on June 1, 1990. It was turned off on February 12, 1999. |  |
is an instance of grazing-incidence telescope  |  |
| ROSAT PRC97-32 | has distance greater than 400 light years |  |
has image   |  |
| is a part of Corona Australis |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
| is an instance of neutron star |  |
| rotating coordinate | has frame of reference rotating reference frame |  |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| rotating reference frame | has definition A frame of reference which rotates with the same period as the system. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of frame of reference |  |
| rotation | has definition Of a single body in space: spinning on an axis. Of a planetary system, rotation is generally planar in relation to the parent star. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| Rotten Egg Nebula | has image   |  |
| has synonym OH231.8+4.2 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| Royal Greenwich Observatory | has definition Primary national Observatory in Great Britain, first sited at Greenwich in 1675, but in 1958 moved to Herstmonceux, Sussex. From the first, Directorship of the Observatory has entailed appointment as Astronomer Royal. In the 1980s the Observatory will lose its primary national status with the completion of the Northern Hemisphere Observatory in Las Palmas, the Canary Islands. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| Royal Society | has definition English organization founded in the seventeenth century and dedicated to the advancement of science. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of science institution |  |
| RR Lyr | has definition An old metal-poor white or yellow-white giant star that pulsates like a Cepheid and therefore varies in brightness. Most RR Lyrae stars have periods of under one day, which is shorter than periods for Cepheids. RR Lyrae stars are also fainter than Cepheids, with absolute magnitudes around +0.7, corresponding to a luminosity about 45 times the Sun's. RR Lyrae stars are excellent distance indicators because they all have nearly the same intrinsic brightness. They take their name from the star RR Lyrae, in the constellation Lyra. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of RR Lyrae star |  |
| RR Lyrae star | has definition A large class of pulsating (amplitude variation about 1 mag) blue giants of anomalous spectral type (A2-F6) with periods of less than 1 day. Their average absolute magnitude is about +0.8. which makes them almost 50 times more luminous than the Sun. They are Population II objects often (but not always) present in globular clusters. RR Lyrae stars are valid distance indicators out to more than 200 kpc. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Periodic variable with period less than one day, and of spectral types A to early F. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Type of short-period variable stars. Spectrally classified as A to F giants. They were once called cluster-cepheids. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym cluster variable |  |
| has synonym cluster variable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of horizontal branch star |  |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| RRab star | has amplitude larger than RRc star |  |
| has definition A sub-class of Bailey type RR Lyrae variables, having asymmetric light curves of large amplitude. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition RR Lyr star characterised by a sharp rise to maximum then a slow fall to minimum. Usually combined with RRb star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Bailey type |  |
| RRc star | has amplitude smaller than RRa star |  |
| has definition RR Lyr star characterised by equally long rise and fall time. This type has the smallest amplitude | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Bailey type |  |
| RS CVn star | has definition Close binary, which show the HK lines in emission. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of binary star |  |
| RS Ophiuchi | is an instance of recurrent nova  |  |
| rubidium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 800000 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| runaway star | has definition Early type star (O and early B) outside the Galactic plane, which reached large distances (from the Galactic plane) because of their high velocities. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star of spectral type O or early B with unusually high space velocities. Runaway stars are thought to be produced when there is a supernova explosion in a close binary system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O star, B star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| ruthenium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| rutherfordium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| RV Tau variable | has definition Periodic variable with periods 60-100 days, and of spectral types G and K. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 60 - 100 days | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type G star, K star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of periodic variable |  |
| RV Tauri star | has definition A class of about 100 semiregular variable yellow supergiants of late spectral type (G-K), similar to W Virginis stars but with longer periods. Their spectra often contain emission lines, and their light curves have alternating deep and shallow minima. They have a large infrared flux. RVa stars maintain an approximately constant mean brightness; RVb stars have long-term (on the order of 1000 days) periodicity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1000 days (order of magnitude) |  |
| is a kind of semiregular variable |  |
| RW Aurigae | has definition A T Tauri star with a strong ultraviolet excess. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type G5e V |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of T Tauri star |  |
| rydberg | has definition Unit of energy (R = h bar3c / me4) equal to 13.5978 eV (the ionization potential of hydrogen). Rydberg correction has definition |  |
| is an instance of energy unit |  |
| Rydberg constant | has equation  |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol R∞ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000083 m-1 |  |
has value 10973731.568549 m-1  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| S Andromedae | has definition A supernova seen in 1885 in the Andromeda galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of supernova |  |
| S Doradus | has definition A supergiant eclipsing binary (an Eta Carinae-type object) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 40 years |  |
| is a part of Dorado |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| S star | has definition Late type giant (K5 to M) showing distinct bands of ZrO. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Late type giants (K5 to M) showing distinct bands of ZrO. [JJ95] |  |
| has definition Red-giant star of spectral type S are similar to M stars except that the dominant oxides are those of the metals of the fifth period (Zr, Y, etc.) instead of the third (Ti, Sc, V). They also have strong CN bands and contain spectral lines of lithium and technetium. Pure S stars are those in which ZrO bands are very strong and TiO bands are either absent or only barely detectable. Almost all S stars are LPVs. (S1,0. The number following the comma is an abundance parameter.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Red-giant stars of spectral type S are similar to M stars except that the dominant oxides are those of the metals of the fifth period (Zr, Y, etc.) instead of the third (Ti, Sc, V). They also have strong CN bands and contain spectral lines of lithium and technetium. Pure S stars are those in which ZrO bands are very strong and TiO bands are either absent or only barely detectable. Almost all S stars are LPVs. (S1,0. The number following the comma is an abundance parameter.) [H76] |  |
| is a kind of heavy-metal star |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| s-electron | has definition An orbital electron whose l quantum number is zero. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital quantum number 0 |  |
| is a kind of bound electron |  |
| s-process | has definition The process by which elements heavier than copper are formed through a slow flux of neutrons. The s-process operates in red giant stars; prominent s-process elements include barium, zirconium, yttrium, and lanthanum. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthetic reaction |  |
| S0 galaxy | has definition Galaxy with nuclei surrounded by disklike structure without arms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| Sa spiral | has definition In Hubble's classification, a spiral with a large nuclear bulge and closely coiled arms. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Spiral galaxy with arms tightly wound around the nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym early-type spiral |  |
| is a kind of spiral galaxy |  |
| Sackur-Tetrode constant | has pressure 101.325 kPa |  |
| has symbol S0/R |  |
| has temperature 1 K |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000044 |  |
has value -1.1648678  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| Sagitta | has acronym Sge |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Sagittae |  |
| has synonym Arrow |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of constellation -has URL: http://www.seds.org/Maps/Stars_en/Fig/sagitta.html |  |
| Sagittarius | has acronym Sgr |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Sagittarii |  |
| has synonym Archer |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Sagittarius A | has definition A radio source (the galactic center). (Sgr A West is a thermal source; Sgr A East is a nonthermal source.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The very center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A* is a strong source of radio waves and probably a massive black hole. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 12 pc |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| Sagittarius arm | has definition One of the spiral arms of the Milky Way, lying between us and the center of the Galaxy in the direction of Sagittarius. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has density of interstellar gas 1.2 atoms cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 8.7 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from Sun 1.5 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| Sagittarius B2 | has definition A massive (3 × 106 Msun), dense (up to 108 particles per cm3) H II region and molecular cloud complex - the richest molecular source in the Galaxy. It is in the galactic plane, near the galactic center. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 10 kpc distant |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| samarium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 200 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| SAMOS | is a kind of reconnaissance spacecraft |  |
| satellite | has approximately elliptical orbit |  |
| has definition a physical object gravitationaly bound and in orbit around a larger physical object |  |
has orbital inclination    |  |
| has orbital period |  |
| is a kind of physical object |  |
| orbits a more massive physical object |  |
| satellite elongation | has definition The geocentric angle between a satellite and its primary, measured in the plane of the satellite, planet and Earth. Satellite elongations are measured from 0° east or west of the planet. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elongation |  |
| satellite galaxy | has definition A galaxy that orbits a larger one. The Milky Way has at least ten satellite galaxies. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf galaxy |  |
| orbits |  |
| Saturn | has albedo 0.50 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition hydrogen and helium | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Sixth major planet out from the Sun. The most spectacular of the Solar System, it is circled by a series of concentric rings. All the satellites of Saturn are locked in synchronous rotation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.056 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has equatorial diameter 116340 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 33.1 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 2°29'33" | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 5.7 × 1029 g = 95.2 MEarth | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 0.7 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 9.540 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of satellites 10 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has oblateness 0.1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 26°44' | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity Vorb = 9.65 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period at equator 10h14m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period at poles 10h38m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has sidereal period 29.458 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 11 m s-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 378 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature Teff ≈ 160 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of gas giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye planet |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif) |
| Saturn ring system | is a part of Saturn |  |
| Sb spiral | has definition Spiral galaxy with arms spread out from the nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spiral galaxy |  |
| SBa barred spiral | has definition Barred spiral galaxy with arms tightly wound around the nucleus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of barred spiral |  |
| SBb barred spiral | has definition Barred spiral galaxy with arms wound around the nucleus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of barred spiral |  |
| SBc barred spiral | has definition Barred spiral galaxy with arms widely spread out from the nucleus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of barred spiral |  |
| Sc spiral | has definition Spiral galaxy with arms widely spread out from the nucleus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spiral galaxy |  |
| SC star | has definition Star which appears to be intermediate in type between S stars and carbon stars (C/O ratio near unity). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of S star |  |
| scandium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III] |  |
| has ocean residence time 5000 years |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| scattering | has definition Collision between a photon and a particle | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The process whereby light is absorbed and reemitted in all directions, with essentially no change in frequency. Scattering by free electrons was the dominant source of opacity in the early universe. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collision |  |
| is a kind of radiation direction modification |  |
| scavenged oceanic element | has ocean concentration decreasing with depth |  |
| has ocean residence time 103 years or less |  |
| is a kind of oceanic element |  |
| Schmidt | has definition A telescope with a spherical primary mirror and a thin refractive corrector plate with a complex, non-spherical shape. Very wide-field performance for surveys. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A type of reflecting telescope (more accurately, a large camera) in which the coma produced by a spherical concave mirror is compensated for by a thin correcting lens placed at the opening of the telescope tube. The Schmidt has a usable field of 0°.6. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Telescopic camera incorporating an internal corrective lens or plate that compensates for optical defects and chromatic faults in the main mirror. The system was invented by Bernhard Schmidt. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif) |
| has optical design Schmidt |  |
| has primary mirror shape concave spheroid |  |
| has secondary mirror shape none |  |
| is a kind of equatorial telescope |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| Schmidt plate | has definition Photographic plate obtained with a Schmidt telescope, which is a type of telescope with a particularly large field of view. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of integrating detector |  |
| Schmidt Telescope | has altitude 75 m |  |
| has aperture 0.80 m |  |
| has creation date 1968 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.0 |  |
| has latitude 56° 47' N |  |
| has location Riga, Latvia |  |
| has longitude 24° 24' E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.2 m |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has operator Latvian Academy of Sciences |  |
| has owner Radioastrophysical Observatory |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| scholastics | has definition Adherents to the philosophy and cosmology of Aristotle. Their dominance in the universities, which had been founded largely to study Aristotle, constituted an obstacle to acceptance of the Copernican system advocated by Kepler and Galileo. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| Schwarzschild black hole | has definition A nonrotating, spherically symmetric black hole derived from Karl Schwarzchild's 1916 exact solution to Einstein's vacuum field equations. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of black hole |  |
| Schwarzschild singularity | has definition The center of a black hole. According to Einstein's theory of general relativity, the entire mass of a black hole is concentrated at a point at its center, the "singularity". It is believed that quantum mechanical effects, not included in the theory, would cause the mass to spread out over a tiny but nonzero region, thus preventing an infinite density of matter and doing away with the singularity. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of singularity |  |
| science | has definition Systematic study of Nature, based upon the presumption that the universe is based upon rationally intelligible principles and that its behavior can therefore be predicted by subjecting observational data to logical analysis. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of abstraction |  |
| science institution | is a kind of institution |  |
| scientist | has career |  |
| has greatest achievement |  |
| is a kind of person |  |
| scintillation counter | has definition A device used with a photomultiplier tube to detect or count charged particles or gamma rays. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy detector |  |
| scintillator | has definition A detector for high-energy photons such as gamma-rays. The impact of a gamma-ray causes a burst of light which can be observed with a PMT. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy detector |  |
| Sco-Cen association | has definition An association of very young stars. The most luminous member is a B star of Mv = - 4.9. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 200 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of association |  |
| is part a of Gould Belt | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| Scorpius | has acronym Sco |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Scorpii |  |
| has historical origin beast that killed the Great Hunter, Orion |  |
| has synonym Scorpion |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Scorpius OB1 | has definition An extremely young association of OB stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Scorpius | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of OB association |  |
| Scorpius X-1 | has apparent magnitude brightest X-ray source in the sky (besides the Sun) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A compact eclipsing X-ray source. It has day-to-day variations (period about 0.78 days?) of as much as 1 mag; it also has optical and radio counterparts but no correlation has been found among the flares observed at the three different wavelengths. It is a thermal X-ray source, probably associated with a rotating collapsed star surrounded by an extensive envelope. Tentative optical identification with the 13th mag blue variable V818 Sco. The spectrum of Sco X-1 is similar to that of an old nova. (3U 1617-15) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1962 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 250 to 500 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Scorpius |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| Sculptor | has acronym Scl |  |
| has genitive Sculptoris |  |
| has synonym Sculptor |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| Sculptor Dwarf | has definition A dwarf elliptical galaxy that orbits the Milky Way (Mv = - 11.28 mag), in the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1938 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 85 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 255000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 3 × 106 Msun | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Sculptor |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| Sculptor Group | has brightest member NGC 253 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The nearest group of galaxies to the Local Group. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4 to 10 million light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is a part of Sculptor |  |
| is an instance of galaxy cluster |  |
| Scutum | has acronym Sct |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Scuti |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Shield |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Scutum arm | is a part of Sagittarius arm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif) |
| sdB | has definition Subdwarf B star with very broad and shallow Balmer lines; fewer lines of the Balmer series are visible than for normal dwarfs. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of B star |  |
| is a kind of subdwarf |  |
| sdO | has definition Subdwarf O star showing few very broad and shallow Balmer lines and a very strong He II 4686 line. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of O star |  |
| is a kind of subdwarf |  |
| seaborgium | is a kind of transactinide |  |
| second | has definition A unit of time defined as the duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom. In 1967 the General Conference of Weights and Measures (CGPM) adopted this as the tentative definition of the second in SI units, replacing the ephemeris second, which remains in the IAU system of astronomical constants. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium 133 atom |  |
| has historical origin was defined originally as the fraction 1/86400 of the mean solar day |  |
| has symbol s |  |
| is an instance of base SI unit |  |
| is an instance of second unit |  |
| second (angle) | has symbol " |  |
| has synonym arc second |  |
| has value in SI unit (1/60)' = (π/648000) rad |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| second law of thermodynamics | has definition A physical law formulated in the nineteenth century and stating that any isolated system becomes more disordered in time. (See entropy.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Law stating that total entropy always increases. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of thermodynamics law |  |
| second order phase transition | A phase transition where one phase evolves into the other as the temperature changes, so the two phases never coexist. -has source: [G97] |  |
| is a kind of phase transition |  |
| second radiation constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol c2 |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000025 × 10-2 m K |  |
has value 1.4387752 × 10-2 m K  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| second unit | is a kind of time unit |  |
| secondary cosmic ray | has definition Atomic fragment - mainly muons - produced by collisions between primary cosmic rays and the molecules in Earth's atmosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| secondary mirror | has definition The second reflecting surface encountered by the light in a telescope. The secondary is usually suspended in the beam and therefore obstructs part of the primary. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| secular parallax | has definition A parallax based on solar motion; i.e., the baseline is the distance the Sun moves in a given interval of time with respect to the local standard of rest. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 4.09 AU per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of parallax |  |
| segmented mirror | has definition A large mirror construction technique in which many smaller elements are built and then actively controlled to conform to the shape of the required large mirror. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| segmented mirror telescope | has definition a reflecting telescope whose mirror is composed of multiple segments |  |
| has number of segments |  |
| is a kind of reflector |  |
| selective absorption | has definition The process by which light from an astronomical object grows red as the light travels through interstellar dust. Dust scatters blue light more than red, thus leaving predominantly red light transmitted. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The reddening of starlight in passing through fine particles of interstellar dust. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym reddening |  |
| is a kind of absorption |  |
| selenium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI some IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 3000 years |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of group VI element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| selenocentric coordinate | has coordinate origin Moon |  |
| has definition With reference to the center of the Moon. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| semi-forbidden line | has definition Spectral lines from "semiforbidden" transitions, i.e., those whose transition probabilities are perhaps 1 in 106 instead of about 1 in 109 for forbidden transitions. One bracket - e.g., [C III] - is used to indicate semiforbidden lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line |  |
| semimajor axis | has definition An orbital element representing half the length of the major axis of an ellipse. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol a | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length |  |
| is an instance of orbital element | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| semiminor axis | has definition Half the length of the minor axis of an ellipse; a standard element used to describe an elliptical orbit. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length |  |
| semiregular variable | has amplitude variable |  |
| has definition A class of giant and supergiant pulsating stars of spectral class M, K, N, R, or S with a periodic (or semiperiodic) light curve of varying amplitude. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| Serpens | has acronym Ser |  |
| has genitive Serpentis |  |
| has synonym Serpent |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| set of lines | has definition A set of absorption or emission lines in the spectra of a celestial object |  |
| is a kind of spectral feature |  |
| set of molecular lines | has species molecule |  |
| is a kind of set of lines |  |
| SETI | has definition The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence, by using radiotelescopes to listen for signals transmitted by intelligent alien beings. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| Sextans | has acronym Sex |  |
| has genitive Sextantis |  |
| has synonym Sextant |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Sextans Dwarf | has definition A dwarf companion to the Milky Way. Discovered by computer. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1990 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galaxy center 300 kpc |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Sextans |  |
| is an instance of satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| Seyfert galaxy | has definition A type of spiral galaxy first discovered by Karl Seyfert in the 1940s. The central region of a Seyfert galaxy is distinguished by powerful radiation, much of it focused into narrow frequencies. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of a small class of galaxies (many of which are spirals) of very high luminosity and very blue continuum radiation with small, intensely bright nuclei whose spectra show strong, broad, high-excitation emission lines probably caused by discrete clouds moving at velocities that are higher than the escape velocity. Seyferts possess many of the properties of QSOs, such as the ultraviolet excess of the continuum, the wide emission lines, and the strong infrared luminosity. The energy sources in their nuclei are unexplained; presumably the energy input can be associated with some process that liberates gravitational binding energy to accelerate relativistic particles. Seyferts comprise about 1 percent of the bright galaxies. The brightest Seyfert known is NGC 1068. Weedman-Khachikian classification: class 1 Seyferts have broad Balmer line wings; class 2 have no obvious Balmer line wings. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spiral galaxy |  |
| Seyfert's Sextet | has brightest member NGC 6027 |  |
| has definition A compact group of galaxies surrounding NGC 6027. It has both spiral and irregular members. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 6 |  |
| is a part of Serpens |  |
| is an instance of compact group |  |
| shadow matter | has definition Theoretical classes of particles, their existence intimated by supersymmetry, theory, that participate in few if any of the four known fundamental forces. Planets, stars, and galaxies made of shadow matter could conceivably exist in the same space and time we occupy without our sensing their presence. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| Shajn 2.6-m Reflector | has aperture 2.64 m |  |
| has creation date 1960 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.8, 15.7, 16.4, 40 |  |
| has latitude 44° 44' N |  |
| has location Nauchny, Ukraine |  |
| has longitude 34° 00' E |  |
| has owner Crimean Astrophysical Obs. |  |
| has synonym Crimean 102 inch |  |
| is an instance of Fork equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| Shane-Wirtanen catalog | has definition A catalog of all galaxies brighter than seventeenth magnitude (a measure of brightness). There are about a million galaxies in the Shane-Wirtanen catalogue. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy catalog |  |
| Shapley | has associate Hale as director of Mt. Wilson |  |
| has associate Russel as his mentor |  |
| has associate van Maanen as a collegue at Mt. Wilson |  |
| has birth date 2 November 1885 |  |
| has career |  |
| has death date 20 October 1972 |  |
| has degree |  |
| has greatest achievement structure and scale of our galaxy determined from accurate globular cluster distances |  |
| has greatest gaffe ignored Humason's observations of Cepheids in Andromeda galaxy |  |
has image  |  |
| has name Harlow Shapley |  |
| has orbituary Kopal, Z. : 1972, Nature 240, 429. |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
is an instance of astronomer  |  |
| Shapley-Ames catalog | has definition A catalog of galaxies brighter than thirteenth magnitude, completed in 1932. There are about 1200 galaxies in this catalogue. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy catalog |  |
| shell star | has definition A hot main-sequence star, usually of spectral class B-F, whose spectrum shows bright emission lines presumed to be due to a gaseous ring or shell surrounding the star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A star in which two different types of line profiles co-exist. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type B star, A star, F star |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| SHF band | has frequency 3 to 30.0 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 1 to 10 cm |  |
| is a kind of microwave |  |
| SHF-G band | has frequency 3.95 to 5.85 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 5.1 to 7.6 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-H band | has frequency 7.05 to 10.0 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 3.0 to 4.25 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-J band | has frequency 5.3 to 8.2 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 3.7 to 5.7 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-K band | has frequency 18.0 to 26.5 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 1.1 to 1.67 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-M band | has frequency 10.0 to 15.0 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 2.0 to 3.0 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-P band | has frequency 12.4 to 18.0 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 1.67 to 2.4 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-R band | has frequency 26.5 to 40.0 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 0.75 to 1.1 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-S band | has frequency 2.6 to 3.95 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 7.6 to 11.5 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| SHF-X band | has frequency 8.2 to 12.4 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 2.4 to 3.7 cm |  |
| is a kind of SHF band |  |
| Shoemaker-Levy 9 collision | has duration 7 days |  |
| has start time July 16, 1994 |  |
is an instance of comet impact  |  |
| shuttle | is a kind of recoverable spacecraft |  |
| SI unit | has definition International System of Units. A practical system of units of measurement adopted in 1969 by the 11th International General Conference of Weights and Measures (CGPM). The seven base units are the meter, the kilogram, the second, the ampere, the kelvin, the mole, and the candela. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unit |  |
| is an acronym for Syteme Internationale |  |
| sidereal day | has definition The length of time between two successive meridian transits of the vernal equinox (cf. mean solar day). Because of precession the sidereal day is about 0.0084 second shorter than the period of rotation of Earth relative to a fixed direction (23h56m4s.099). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 23h56m4s.091 |  |
| is an instance of day |  |
| sidereal year | has definition A period of time based on the revolution of the Earth around the Sun, where a year is defined as the mean period of revolution with respect to the background stars. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| siderophile element | has definition element that tend to concentrate in metallic iron |  |
| has occurrence in planet metallic core and associated with iron |  |
| is a kind of planetary element |  |
| siemens | has base unit m-2·kg-1·s3·A2 |  |
| has definition The SI unit of electrical conduction. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol S |  |
| has synonym reciprocal ohm |  |
| has unit A·V-1 |  |
| is an instance of conductance unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| represents electric conductance |  |
| sievert | has base unit m2·s-2 |  |
| has symbol Sv |  |
| has unit J·kg-1 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of radioactivity unit |  |
| represents dose equavalent |  |
| sigma | has definition Short-lived baryon. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Short-lived baryon. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of hyperon | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of hyperon | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif) |
| silicon | has abundance 0.03 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.03 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 0.82 p.p.m. in deep Atlantic seawater |  |
| has abundance 277100 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 4.09 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 4.47 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has atomic emission line 251.611 nm for Si I |  |
| has atomic emission line 288.156 nm for Si I |  |
| has atomic emission line 504.103 nm for Si II |  |
| has atomic emission line 505.598 nm for Si I |  |
| has atomic emission line 566.956 nm for Si I |  |
| has atomic emission line 634.710 nm for Si II |  |
| has atomic emission line 637.136 nm for Si II |  |
| has atomic number 14 |  |
| has atomic radii 117 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to some species and possibly to humans |  |
| has boiling point 2628 K |  |
| has chief source quartz, talc, mica |  |
| has covalent radii 117 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = pm |  |
| has crystal type |  |
| has daily dietary intake 18 - 1200 mg |  |
| has definition ultrapure crystals of silicon have a blue-grey metallic sheen |  |
| has density 2329 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has density 2525 kg m-3 for liquid at 1683 K melting point |  |
| has discoverer J.J. Berzelius |  |
| has discovery date 1824 |  |
| has discovery location Stockholm, Sweden |  |
| has electrical resistivity 0.001 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 133.3 kJ mol-1 from Si to Si- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.90 Pauling |  |
| has hazard some silicate fibres are carcinogenic such as asbestos |  |
| has heat capacity 20.00 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 22.251 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 39.6 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 383.3 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 26 pm for Si4+ |  |
| has ionic radii 271 pm for Si4- |  |
| has isotope mass range 24 to 34 |  |
| has lethal intake non-toxic |  |
| has level in humans 100 - 200 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 12 - 120 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 17 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 3.9 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 4.2 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope silicon 28 |  |
| has main mining area talc in Austria, Italy, India, South Africa, Australia, mica in Canada, USA, India, Brazil |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 6.44 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 60.6 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -1.8 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 1 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1683 K |  |
| has mineral silicates |  |
| has molar volume 12.06 cm3 |  |
| has name origin silicis = flint from Latin |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.41543 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 11 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 14 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 30000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.42 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation sil-i-kon |  |
has registry number 7440-21-3 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 28.0555 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves unlimited × 10 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 39.7 GPa |  |
| has space group |  |
| has specimen available as powder, pieces or lumps. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Si |  |
| has synthesis mechanism reduction of sand (SiO2) with carbon produces black amorphous silicon |  |
| has term symbol 3P0 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 148 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.171 barns |  |
| has toxic intake non-toxic |  |
| has uses semiconductors, alloys and polymers |  |
| has van der Waals radii 200 pm |  |
| has world production 3.4 × 106 tonnes year-1 for metallurgical grade |  |
| has world production 480000 tonnes year-1 for metallurgical grade |  |
| has world production 5000 tonnes year-1 for electronic grade (very pure) |  |
| has young's modulus 113 GPa |  |
| is a kind of group IV element |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic metalloid |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| reacts HF acid or hot alkali solutions by dissolving |  |
| silicon 28 | has atomic mass 27.9769271 |  |
| has natural abundance 92.23% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 14 |  |
| has number of nucleons 28 |  |
| has symbol 28Si |  |
| has uses experimental |  |
is an instance of silicon  |  |
| silicon 29 | has atomic mass 28.9764949 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio -5.3146 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 4.67% |  |
| has NMR frequency 19.865 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 2.09 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.55529 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 15 |  |
| has number of nucleons 29 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 7.84 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 29Si |  |
| has uses experimental, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of silicon  |  |
| silicon 30 | has atomic mass 29.9737707 |  |
| has natural abundance 3.10% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 16 |  |
| has number of nucleons 30 |  |
| has symbol 30Si |  |
| has uses experimental |  |
is an instance of silicon  |  |
| silicon 31 | has atomic mass 30.975362 |  |
| has decay mode β- (1.49 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.62 hours |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 17 |  |
| has number of nucleons 31 |  |
| has symbol 31Si |  |
is an instance of silicon  |  |
| silicon 32 | has atomic mass 31.974148 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.227 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 160 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ |  |
| has number of neutrons 18 |  |
| has number of nucleons 32 |  |
| has symbol 32Si |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of silicon  |  |
| silicon burning | has definition The end of the line for a high-mass star, silicon burning creates iron and other elements of similar mass and presages a supernova. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration 1 day |  |
| has optimum density 3 × 107 g cm-3 |  |
| has optimum temperature 2.7 × 109 K |  |
| has part product iron 56 |  |
| has reactant silicon |  |
| has reactant silicon involved in many hundreds of nuclear reactions |  |
| is a kind of exothermic fusion process |  |
| silicon | does not react oxygen, water or acids |  |
| silicon monosulfide | has symbol SiS |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| silicon monoxide | has symbol SiO |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| Silkworm nebula | has image   |  |
| has synonym IRAS 17441-2411 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| silurian period | has duration 20 million years |  |
| has start time 425 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of paleozoic era |  |
| silver | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 5000 years |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| SIMBAD | is an instance of database  |  |
| single line spectroscopic binary | has definition a spectroscopic binary in which periodic Doppler shift is detected in only one component of the binary star |  |
| is a kind of spectroscopic binary |  |
| singularity | has definition A place, either in space or in time at which some quantity, such as density, becomes infinite. The laws of physics cannot describe infinite quantities and, in fact, physicists believe that infinities do not exist in nature. All singularities, such as the Schwarzschild singularity, are therefore probably the artifacts of inadequate theories rather than real properties of nature. According to Einstein's theory of general relativity, the universe began in a singularity of infinite density, the big bang. Physicists believe that an improved and yet-to-be discovered modification of general relativity, incorporating quantum mechanics, will show that the universe did not begin as a singularity. (See Schwarzschild singularity.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A point in space-time at which the space-time curvature and other physical quantities become infinite and the laws of physics break down. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A point of infinite curvature of space where the equations of general relativity break down. A black hole represents a singularity; so, perhaps, did the universe at the first moment of time. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Anomaly in space-time at which a state not in accord with the classical laws of physics obtains. An example is a black hole; another is the moment of the big bang. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition If the standard big bang theory is extrapolated all the way back to time zero, one reaches an instant of infinite density, infinite pressure, and infinite temperature - an instant that is frequently called the initial singularity. This singularity is sometimes said to mark the beginning of time, but it is more realistic to recognize that an extrapolation to infinite density cannot be trusted. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Location where the fabric of space or spacetime suffers a devastating rupture. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theoretical celestial body |  |
| Sirius | has B-V magnitude 0.00 |  |
| has declination -16 42 58 |  |
| has definition The brightest star in the sky. Its companion (Sirius B) is a white dwarf of about 0.96 Msun but only about 0.03 Rsun, the nearest white dwarf to Earth. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 8.6 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 49.9 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 6 45 8.9 |  |
| has spectral type A1Vm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym alpha CMa | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Dog Star |  |
| has synonym HR 2491 |  |
| has V magnitude -1.46 |  |
is a part of Canis Major  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of binary star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Sirius B | has definition Companion of Sirius, a white dwarf. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1 solar mass | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 0.03 solar radii | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature Teff = 32000 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Canis Major |  |
| is an instance of white dwarf |  |
| sky survey | is a kind of database |  |
| Slipher | has birth date 11 November 1875 |  |
| has career |  |
| has death date 8 November 1969 |  |
| has degree Indiana Univ. |  |
has image  |  |
| has name Vesto Melvin Slipher |  |
| has publication 1918, PASP 30, 346.. Discussion about the spectra of 'spiral nebula' NGC 4449 and NGC 4214, but no spectra actually published (claims 200 km/s and 300 km/s recession velocities respectively) |  |
| has refererence Hall, J.S. : 1989, PASP 101, 887. : He discovered the high velocities and rotation of nebulous objects later identified as galaxies. He measured the velocities of 41 of these objects. In 1929 Hubble derived his important velocity-distance relationship using, as he later wrote Slipher, "your velocities and my distances" |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
is an instance of astronomer  |  |
| Sloan Digital Sky Survey Telescope | has acronym SDSS |  |
| has altitude 2800 m |  |
| has aperture 2.5 m |  |
| has comment To take CCD imagery of a quarter of sky in 5 colors (u, g, r, i, z) and measure redshifts of 1 million galaxies |  |
| has creation date (1998) |  |
| has latitude 32° 47' N |  |
| has location Apache Point, New Mexico, US |  |
| has longitude 105° 49' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer L & F Industries and University of Washington |  |
| has owner Astrophys. Res. Consortium Obs. |  |
| has synonym Sloan 2.5 m |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| slow nova | has definition A nova whose light curve shows a much more gradual development - i.e., rise time of several days, maximum of several weeks, slower decline, amplitude only about 10 mag. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nova |  |
| Small Magellanic Cloud | has acronym SMC |  |
| has declination -72d49m43s |  |
| has definition The second largest, and the second nearest, of the galaxies that orbit the Milky Way. It lies in the southern sky, 190000 light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 320 × 185 arcminutes |  |
| has distance from galaxy center 60 kpc |  |
| has magnitude 2.7 |  |
| has mass 1 billion solar masses |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has right ascension 00h52m44.8s |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Tucana |  |
| is an instance of Magellanic Cloud | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| SMC X-1 | has definition An X-ray source in the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is a binary system. Identified with Sanduleak No. 160, a B0 I supergiant (mv = + 13.6). Because no radial-velocity variations are apparent in Sk 160, the mass of the X-ray emitter must be small relative to Sk 160 (about 2 Msun if Sk 160 is 20 Msun), unlike the compact member of CygX-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 3.89-day |  |
| has synonym 2U 0115-73 |  |
| is a part of Small Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is a part of Tucana |  |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| Smithsonian Astronomical Observatory | has acronym SAO | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of astronomical institution |  |
| smoke trail | has composition tiny roughly spherical micrometeorites |  |
| has definition condensation of vaporized rock removed from the surface of a meteoroid by ablation |  |
| has destination surface of celestial body |  |
| has duration hours |  |
| has time of occurence when meteoroid collides with atmosphere |  |
| is a kind of meteor event |  |
| can produce produce light visible only at night |  |
| SN 1987A | has distance 167000 light years |  |
has image    |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of type II supernova |  |
| Snell's law | has definition For a refracted light beam, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. (also called the Law of Refraction) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of optical law |  |
| sodium | has abundance 1.91 × 106 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 10500 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 23000 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 313.548 nm for Na II |  |
| has atomic emission line 589.595 nm for Na I |  |
| has atomic emission line 818.326 nm for Na I |  |
| has atomic emission line 819.482 nm for Na I |  |
| has atomic emission line 588.995 nm for Na I (strong, used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic number 11 |  |
| has atomic radii 154 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to most species including humans |  |
| has boiling point 1156.1 K |  |
| has chief source halite, trona |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 376.7, c = 615.4 pm for α-Na |  |
| has crystal type hexagonal for α-Na |  |
| has daily dietary intake 2 - 15 g |  |
| has definition soft, silvery-white metal which oxidizes rapidly when cut |  |
| has density 928 kg m-3 for liquid at 370.96 K melting point |  |
| has density 971 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Sir Humphry Davy |  |
| has discovery date 1807 (isolated) |  |
| has discovery location Royal Institution, London, England |  |
| has electrical resistivity 4.2 × 10-8 Ω m at 273 K |  |
| has electron affinity 52.9 kJ mol-1 from to - |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 0.93 Pauling |  |
| has hazard compounds are not hazardous, but excess sodium chloride can be toxic by ingestion |  |
| has heat capacity 20.786 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 28.24 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 2.64 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 89.04 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 98 pm for Na+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 19 to 31 |  |
| has lethal intake 3000 mg kg-1 of chloride in rat |  |
| has level in humans 10000 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 1970 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 2000 - 4000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 2600 - 7800 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 70.6 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope sodium 23 |  |
| has main mining area halite in Germany, Poland, USA, UK; trona in Kenya, USA |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 3.21 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 30.1 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +8.8 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 100 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 370.96 K |  |
| has mineral halite, trona, occurs in many others but these are not mined as a source of sodium |  |
| has molar volume 23.68 cm3 |  |
| has name origin soda from English |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.358 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 14 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 11 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 1 × 108 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.34 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation so-dee-uhm |  |
has registry number 7440-23-5 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 22.989768 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves almost unlimited |  |
| has rigidity modulus 2.53 GPa |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for α-Na |  |
| has specimen ingots or lumps, in sealed ampoules under nitrogen, or spheres and sticks stored under mineral oil. Warning! |  |
| has symbol Na |  |
| has symbol name origin natrium from Latin |  |
| has synthesis mechanism electrolysis of molted sodium chloride |  |
| has term symbol 2S1/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 141 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.530 barns |  |
| has toxic intake 12 g kg-1 of chloride in humans |  |
| has uses manufacture of chemicals and metals |  |
| has uses nuclear reactor heat exchanger |  |
| has van der Waals radii 231 pm |  |
| has world production 168 × 106 tonnes year-1 as salt |  |
| has world production 200000 tonnes year-1 as sodium metal |  |
| has world production 29 × 106 tonnes year-1 as sodium carbonate |  |
| has young's modulus 6.80 GPa |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of alkali metal |  |
| is a kind of lithophile element |  |
| reacts with water by producing hydrogen gas |  |
| sodium 22 | has atomic mass 21.994434 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.842 Mev) 90% |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC 10% |  |
| has half life 2.605 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.746 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 11 |  |
| has number of nucleons 22 |  |
| has symbol 22Na |  |
| has uses research, medical diagnostic |  |
is an instance of sodium  |  |
| sodium 23 | has atomic mass 22.989767 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 7.0761 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 100% |  |
| has NMR frequency 26.451 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 525 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +2.217520 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.1089 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 12 |  |
| has number of nucleons 23 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0925 where 1H = 1.00 using NaCl (aq) reference |  |
| has symbol 23Na |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of sodium  |  |
| sodium 24 | has atomic mass 23.990961 |  |
| has decay mode β- (5.514 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 14.96 years |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.690 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 4+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 13 |  |
| has number of nucleons 24 |  |
| has symbol 24Na |  |
| has uses research, medical diagnostic |  |
is an instance of sodium  |  |
| soft ultraviolet | is a kind of ultraviolet |  |
| soft X-ray | is a kind of X-ray |  |
| solar apex | has definition A point on the celestial sphere toward which the Sun and the solar system are moving with respect to the local standard of rest at a rate of about 19.4 km per second (about 4.09 AU per year). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Hercules | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equatorial coordinate |  |
| is opposite of antapex |  |
| solar atmosphere | has definition The gaseous outer layers of the Sun, including, from the deeper layers outward, the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The atmosphere constitutes those layers of the Sun that can be observed directly. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Sun |  |
| solar burst | has definition Suddenly enhanced nonthermal radio emission from the high solar corona immediately following a solar flare, probably due to energetic electrons trapped in the coronal magnetic field. Bursts are divided into several types, depending on their time frequency characteristics (type III is the most common). They are classified on a scale of importance ranging from -1 (least important) to +3. Bursts are generally attributed to a sudden acceleration of some 1035-36 electrons to energies greater than 100 keV in less than 1 second. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solar event |  |
| is preceeded by solar flare | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| solar cycle | has definition The 11-year period between maxima (or minima) of solar activity. Every 11 years the magnetic field of the Sun reverses polarity; hence the more basic period may be 22 years. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 11 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of periodic celestial event |  |
| is an instance of solar event |  |
| solar eclipse | has definition An eclipse in which the Earth passes through the shadow cast by the Moon. It may be total (observer in the Moon's umbra), partial (observer in the Moon's penumbra), or annular. (See eclipse, annular.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of eclipse |  |
| solar event | is a kind of celestial event |  |
| occurs on Sun |  |
| solar flare | has cause sudden release of large amounts of energy in a relatively small volume above the solar surface. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has classification scale of importance ranging from 3+ (largest area) to 1- (smallest area). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Sudden and short-lived brightening of a region of the solar chromosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has duration as short as 300 s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect on Earth ionization in Earth's atmosphere may increase by several orders of magnitude producing aurorae, magnetic storms and radio interference. (electron density 1011 compared with 108 in solar quiet times). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has ejected mass up to 1016 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy up to 1032 ergs | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has location in the vicinity of a sunspot | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass ejection velocity up to 1500 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solar event |  |
| is followed by solar burst | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif) |
| solar interior | is a part of Sun |  |
| solar mass | has definition Unit of mass equal to the amount of mass in the Sun, and the unit in which stellar and galactic masses are expressed. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of mass unit |  |
| solar motion | has definition The velocity of the Sun through space, relative to the local standard of rest. The solar motion is U = -9 kilometers per second, V = +12 kilometers per second, and W = +7 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| is a kind of peculiar velocity |  |
| solar neutral region | has definition A region where the magnetic field strength approaches zero. Generally, neutral regions occur between regions of opposite polarity. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| solar parallax | has definition Angle subtended by the equatorial radius of the Earth at a distance of 1 AU. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 8.79 arcsecond |  |
| is a kind of parallax |  |
| solar radius | has definition A unit of length based on radius of Sun | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of length unit |  |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| solar rotation | has definition Differential rotation, the equatorial rotation taking less time than the polar by up to 9.4 Earth-days. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of differential rotation |  |
| is a kind of solar motion |  |
| solar system | has definition A star with planets | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| solar velocity | has definition Velocity of the Sun (19.4 km sin the direction lII = 51°, bII = 23°) with respect to the local standard of rest. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of space velocity |  |
| solar wind | has definition A radial outflow of hot plasma from the solar corona which carries both mass and angular momentum away from the sun. It is the effects of the solar wind that produce aurorae in the Earth's upper atmosphere, that cause the tails of comets to stream back from the Sun, and that distort the symmetry of planetary magnetospheres. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has electron temperature 20000 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has ion temperature 10000 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field 5 × 10-5 gauss | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass loss rate 10-13 Msun per year | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has number density 5 per cm3 (1971) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has velocity 600 km s-1 | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has velocity at Earth 400 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of solar atmosphere |  |
| solid | has definition a high density collection of particle which do not move relative to one another (except for thermal oscillations) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of phase of matter |  |
| solid angle | has definition A measure of the angular size of an extended object, equal to the area it subtends on the surface of a sphere of unit radius. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| solid angle unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of solid angle |  |
| solidification | has final phase solid |  |
| has initial phase liquid |  |
| has inverse process melting |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| solstice | has definition One of the two points on the ecliptic at which the Sun appears to be farthest away from the celestial equator (representing therefore mid-summer or mid-winter). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 year |  |
| is a kind of periodic celestial event |  |
| Sombrero galaxy | has definition A spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was the first galaxy whose rotation was detected. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has Messier number 104 |  |
| has synonym M 104 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 4594 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Virgo | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of spiral galaxy |  |
| sound wave in gas | has definition A longitudinal wave propagated through a gas as a pattern of alternating high and low pressure. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of longitudinal wave | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mass motion |  |
| South Atlantic Anomaly | discovered by Orbiting Atronomical Observatory |  |
| has acronym SAA |  |
| has definition A disturbance in the geomagnetic field (a region of intense charged-particle fluxes) over the south part of the Atlantic Ocean. It was discovered in early OAO (Orbiting Atronomical Observatory) flights that when the detector passed over that area, the data it collected were not valid. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has location south part of the Atlantic Ocean |  |
| is a part of magnetosphere |  |
| south celestial pole | has acronym SCP |  |
| has declination -90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Octans |  |
| is an instance of celestial pole |  |
| is opposite of north celestial pole |  |
| south galactic pole | has acronym SGP |  |
| has definition A point in the constellation Sculptor toward which our line of sight is perpendicular to and below the Galactic disk. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic latitude -90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Sculptor |  |
| is an instance of galactic pole |  |
| is opposite of north galactic pole |  |
| south pole | has definition The astronomical coordinate which coincides with the southern intersection of Earth's axis with the geoid. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has terrestrial latitude -90 degrees |  |
| is a part of Earth |  |
| is an instance of pole |  |
| is opposite of north pole |  |
| Southern African Large Telescope | has acronym SALT |  |
| has altitude 1798 m |  |
| has aperture 9.1 m |  |
| has comment A twin of the Hobby-Eberly Telescope |  |
| has creation date (2004) |  |
| has focal ratio (f/1.4) f/4.7 |  |
| has latitude 32° 23' S |  |
| has location Sutherland, South Africa |  |
| has longitude 20° 49'E |  |
| has mounting altazimuth fixed in altitude but rotates in azimuth |  |
| has optical design Spherical figure |  |
| has owner South African Astronomical Obs. |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of reflector |  |
| space motion | has definition Velocity of a star with respect to the Sun; hypotenuse of the right triangle formed by its radial and tangential velocities (cf. peculiar velocity). Space motion vectors are U (in the direction of the galactic anticenter), V (in the direction of galactic rotation), and W (in the direction of the galactic north pole). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| Space Physics Analysis Network | has acronym SPAN | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| space science institution | is a kind of institution |  |
| space station | is a kind of manned spacecraft |  |
| space station Freedom | is an instance of space station |  |
| space telescope | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| is a kind of electromagnetic telescope |  |
| space velocity | has definition A star's total velocity with respect to the local standard of rest. This is the combination of the star's U, V, and W velocities: space velocity = sqrt (U2 + V2 + W2). For example, the Sun (U = -9, V = +12, W = +7) has a space velocity of 17 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galactic velocity component |  |
| spallation | has definition The process in which an incoming beam of particles or energy collides with a substance, reacts with it, and knocks off pieces of it. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of ablation |  |
| spark chamber | has definition A means of detecting high energy particles by the trail of ionizations left as they pass through a chamber containing many charge plates. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of high energy detector |  |
| sparticle | has definition Hypothetical particle which is predicted by some Grand Unified Theories. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| special relativity | has author Einstein (1905) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Relativity theory that explains Lorentz contraction and time dilation for observers in relative motion. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has equation E = mc2 (where m is mass, E is energy and c is the speed of light) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has phenomena Lorentz contraction and time dilation | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
has proposition - A spaceship (or other enclosed vessel) traveling at uniform speed through space contains its own space-time continuum.
- A ray of light passes an observer at the speed of light no matter how (uniformly) fast nor in what direction the observer is travelling.
| ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of relativity theory |  |
| specific volume unit | has definition cubic meter per kilogram |  |
| has symbol m3·kg-1 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| spectral feature | has definition A feature in the spectra of a celestial object which occurs at a specific wavelength or range of wavelengths |  |
| has species |  |
| has wavelength |  |
| has width |  |
| is a kind of radiation measurement |  |
| occurs in |  |
| spectral line | has definition A line corresponding to an image of the entrance slit of the spectrometer, seen when light is either emitted by or interrupted by a hot rarefied gas such as hydrogen. The pattern is characteristic of the gas and the wavelength at which the features are observed to occur is indicative of the velocity of the object. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Dark lines visible in an absorption spectrum, or bright lines that make up an emission spectrum. They are caused by the transference of an electron in an atom from one energy level to another; strong lines are produced at levels at which such transference occurs easily, weak where it occurs with difficulty. Ionization of certain elements can affect such transferences and cause problems in spectral analysis. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Discrete emissions (or absorptions) in frequency, usually formed by atomic transitions. The essential difference between optical line spectra and X-ray spectra is that the former correspond to energy changes in the outer electrons in an atom, and the latter to energy changes in the inner electron orbitals. Gamma rays usually correspond to energy changes in the nucleus. Infrared radiation is produced by high-n transitions of atoms or by the vibration or rotation of molecules. Thermal radio emission is usually produced by still higher-n transitions (the notation 109α corresponds to a transition in a hydrogenic atom between the principal quantum number n = 109 and n' = Δn = n + 1 = 110; similarly, a β-transition indicates Δn = 2. etc.). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Emission or absorption at a discrete wavelength or frequency, caused by atomic or molecular transitions. In the case of atoms, the transitions involve the jump of an electron from one orbit to another; a quantum of light is emitted if the electron jumps toward the nucleus and absorbed if it jumps outward. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent width |  |
| has transition |  |
| is a kind of spectral feature |  |
| spectral series line | has definition A spectral line belonging to a series of lines of a given atom arising from transitions with a common lower energy level. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has lower energy level |  |
| has series limit |  |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| spectrograph | has definition A device, usually based on a finely etched grate that performs the function of a prism, for breaking up light into its constituent parts and making a photographic or electronic record of the resulting spectrum. When lacking a means for recording the spectrum, the device is called a spectroscope. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A spectroscope fitted with a device such as a photoelectric cell for measuring the spectra observed with it. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An instrument that records the amount of light in each range of wavelength, that is, in each range of color. In general, each type of astronomical object, such as a star or a galaxy, will emit a characteristic spectrum of light. (See spectrum.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym spectrometer |  |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| spectrograph dispersing element | has definition The part of a spectrograph which disperses the light into component colors |  |
| has dispersion |  |
| has wavefront modification wavelength |  |
| is a kind of wavefront modifier |  |
| spectroheliograph | has definition Device with which spectra of the various regions of the Sun are obtained and photographed. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| spectroscopic binary | has definition Star whose binary nature can be detected from the periodic Doppler shifts of their spectra, owing to their varying velocities in the line of sight. Double-lined spectroscopic binaries have two sets of spectral features, oscillating with opposite phases. Single-lined spectroscopic binaries have only one set of oscillating spectral lines, owing to the dimness of the secondary component. Spectroscopic binaries are typically of spectral type B, with almost circular orbits (whereas long-period M-type binaries have highly eccentric orbits). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of binary star |  |
| spectrum variable | has definition Main-sequence Am or Ap stars whose spectra show anomalously strong lines of metals and rare earths which vary in intensity by about 0.1 mag over periods of about 1-25 days. They are characterized by large magnetic fields (103-104 gauss) at the surface, small variations in light and color, and small projected rotational velocities. These peculiarities are sometimes interpreted in terms of an oblique rotator. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of star |  |
| speed of light in vacuum | has symbol c |  |
| has uncertainty 0 |  |
has value 299792458 m s-1  |  |
| is an instance of universal constant |  |
| sphere | has definition The outer surface of a ball. The surface of a familiar three-dimensional ball has two dimensions (which can be labeled by two numbers such as "latitude" and "longitude," as on the surface of the earth). The concept of a sphere, though, applies more generally to balls and hence their surfaces, in any number of dimensions. A one-dimensional sphere is a fancy name for a circle; a zero-dimensional sphere is two points (as explained in the text). A three-dimensional sphere is harder to picture; it is the surface of a four-dimensional ball. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has dimensions 3 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| spheres | has definition Concept probably older than the ancient Greeks, in which the Sun, Moon, planets and the stars were thought to orbit the Earth travelling on their own crystalline but - except for that of the stars - transparent spheres. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of outdated belief |  |
| spherical collapse | has definition Initial stage in the collapse of a star, followed by gravitational collapse and finally singularity. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has symmetry spherical |  |
| is a kind of collapse |  |
| is followed by gravitational collapse | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| Spica | has B-V magnitude -0.23 |  |
| has declination -11 9 41 |  |
| has definition A double-lined spectroscopic binary (B1.5 V, late B). Component A (10.9 Msun) is a beta Cephei star which seems to be near core hydrogen exhaustion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 80 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.146 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 65° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 4.01452 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has right ascension 13 25 11.5 |  |
| has spectral type B1III-IV+B2V |  |
| has synonym alpha Vir | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 5056 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.98 |  |
is a part of Virgo  |  |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of giant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of spectroscopic binary |  |
| spicule | has definition A short-lived, narrow jet of gas spouting out of the solar chromosphere. Spicules tend to cluster at the edges of supergranulation cells. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime 5 minutes |  |
| has location edge of supergranulation cell |  |
| has synonym mottle | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of chromosphere |  |
| spin | has definition A quantum property of all particles which denotes the intrinsic angular momentum of the particle. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A quantum-mechanical version of the familiar notion of the same name; particles have an intrinsic amount of spin that is either a whole number or half a whole number (in multiples of Plancks constant), and which never changes. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, as by the particle's spinning on its axis. Spin is quantized in units of Planck's constant of action, h, so that, e.g., "spin 1," means spin = 1h. Particles with integral spin (0, 1) are called bosons; those with half spin are fermions. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The intrinsic angular momentum possessed by many particles. It can be thought of as resulting from the particles spinning about an axis through their centers. In contrast to orbital angular momentum, spin is quantized in integer and half-integer units of h bar. Fundamentally, spin describes how quantum fields transform under the transformations of special relativity. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| spin-flip collision | has definition Collision between particles in which the direction of the spin angular momentum changes. Since the total angular momentum is conserved, the orbital angular momentum must be changed in magnitude or direction or both. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collision |  |
| see also 21-cm radiation | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| spiral density wave | has definition A wave, due to a local increase in the gravitational field, that produces a series of alternate compressions and rarefactions as it propagates with fixed angular velocity in a rotating galaxy. The compression also acts on interstellar gas in the galaxy, which is triggered to form stars on the leading edges of the spiral arms. The large-scale structure of spiral galaxies can be understood in this way. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| spiral galaxy | has classification criterion Subdivided according to the openness of the spiral arms as Sa spiral, Sb spiral or Sc spiral. |  |
| has definition A galaxy with a prominent nuclear bulge and luminous spiral arms of gas, dust, and young stars that wind out from the nucleus. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 1010 to 1012 Msun | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| spiritualism | has antonym materialism |  |
| has definition Belief that material interactions alone cannot account for all phenomena, and that some - e.g., thought - are due to the fundamentally insensible actions of intangibles. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of religious belief |  |
| spontaneous emission | has definition Radiation emitted by an isolated body. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of bound-bound transition |  |
| is an instance of emission |  |
| spontaneous fission | is a kind of energy source |  |
| is a kind of fission |  |
| spontaneous symmetry breaking | has definition Any situation in physics in which the ground state (i.e. the state of minimum energy) of a system has less symmetry than the system itself. For example, the state of minimum energy for an iron magnet is that in which the atomic spins are all aligned in the same direction, giving rise to a net macroscopic magnetic field. By selecting a particular direction in space. the magnetic field has broken the rotational symmetry of the system. However, if the energy of the system is raised, the symmetry may be restored (e.g. the application of heat to an iron magnet destroys the magnetic field and restores rotational symmetry). | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The breaking of an exact symmetry of the underlying laws of physics by the random formation of some object. For example, the rotational in variance of the laws of physics can be broken by the randomly chosen orientation of an orthorhombic crystal that condenses as the material is cooled. In the standard model of particle physics, the symmetry between electrons and neutrinos is spontaneously broken by the values that are randomly chosen by the Higgs fields. In grand unified theories, the symmetry between electrons, neutrinos, and quarks is spontaneously broken by the values chosen randomly by the Higgs fields. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of phase transition |  |
| Sporer's law of zones | has definition The equatorward drift of average sunspot latitudes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of solar motion |  |
| Sputnik 1 | has definition First artificial Earth satellite, launched by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957. (lit.: companion) | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of artificial satellite |  |
| SS Cygni star | has definition A subclass of dwarf nova. SS Cyg is a double-lined, noneclipsing spectroscopic binary (sdBe, dG5) with an orbital period of 6h38m. Mean time between eruptions, 54 days. It may be a sporadic source of soft X-rays. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of dwarf nova |  |
| SSPM | has definition Solid State Photomultiplier. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of detector |  |
| stable Lagrangian point | has equilibrium stable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| see also Trojan asteroid |  |
| standard deviation | has definition The root mean square deviation from the arithmetic mean. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol σ |  |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| standard error | has acronym s.e. |  |
| has definition The standard deviation of a distribution of means or any other statistical measure computed from samples. It is equal to 1.4826 times the probable error. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| standing wave | has definition A pattern of oscillations in space in which the regions of maximum displacement and of zero displacement (the nodes) remain fixed in position. This pattern is formed when two waves of the same amplitude and frequency move simultaneously through a medium in opposite directions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym stationary wave | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wave |  |
| Stanford Linear Accelerator Center | has acronym SLAC | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition It is distinguished by having a 2-mile-long linear accelerator in which electrons and positrons can be accelerated for subsequent injection into storage rings such as PEP, an e+e- collider which was commissioned in 1980. It was in the SPEAR rings at SLAC that the J / ψ meson and the τ lepton were first observed in the mid-1970s. However, the most fascinating of SLAC's facilities is the novel SLC (Stanford Linear Collider), consisting of the old linear accelerator together with two new collider arcs. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| has location Stanford University, California, USA. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of high energy physics institution |  |
| star | has absolute magnitude |  |
| has age |  |
| has apparent magnitude |  |
| has B magnitude |  |
| has catalog star catalog |  |
| has definition A celestial object that generates energy by means of nuclear fusion at its core. To do this it must have more than about 0.08 the sun's mass. If, for instance, the planet Jupiter were some fifty to one hundred times more massive than it is, fusion reactions would transpire in its core and it would be a star. See planet. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition a spinning ball of hot gases held together by gravity |  |
| has energy production which takes place primarily within the core |  |
| has energy source gravitational contraction and or fusion |  |
| has mass greater than 0.08 the sun's mass | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has material hydrogen, helium |  |
| has parallax from the point of view of Earth's orbit |  |
| has position on celestial sphere from the point of view of Earth |  |
| has proper motion |  |
| has radiation at surface which is diffused out from the hotter core |  |
| has spectral type |  |
| has star surface temperature |  |
| has surface density which depends on luminosity class |  |
| has surface temperature greater than 1000 Kelvin |  |
| has U magnitude |  |
| has V magnitude |  |
| has velocity determined from proper motion and radial velocity |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| star catalog | has object type star |  |
is a kind of astronomical catalog  |  |
| star cluster | has definition Gravitationally bound aggregations of stars, smaller and less massive than galaxies. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of stars |  |
| star gravitational contraction | is a kind of gravitational contraction |  |
| star merger | has definition The formation of a new star from the gradual merging of two stars which spiral into each other within a common envelope of gas. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of merger |  |
| star system | has abundance half the stars in the solar neighborhood are members of star systems |  |
| has definition A few stars that orbit each other. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of collection of stars |  |
| starburst galaxy | has definition Any galaxy in which an anomalously large rate of star formation is taking place. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy |  |
| Stark effect | has cause the influence of an electric field on a radiating atom or ion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Line broadening due to the influence of electric fields. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect splitting of a spectral line | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has use indicator of atmospheric pressure in a stellar atmosphere and hence of the star's luminosity | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| is proportional to the ion and electron density in a plasma | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| STARLINK | has acronym STARLINK | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A software environment and suite of programs for astronomical data analysis developed in the UK and supported by the Rutherford-Appleton Labs. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomical software |  |
| stat-coulomb | has definition Unit of charge in the cgs electrostatic system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 3.3 × 10-10 coulombs. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of CGS unit |  |
| is an instance of charge unit |  |
| static universe | has definition A universe whose radius of curvature is constant and independent of time, as in the Einstein universe. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| statistical concept | is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| statistical distribution | has definition The range of variation of some quantity in a population, obtained by sampling many members of the population. For example, the statistical distribution of the height of American males could be obtained by sampling 10,000 randomly chosen males and counting the number of them within each range of heights. In cosmology, the distance between pairs of galaxies, averaged over a large number of galaxies, would constitute a statistical distribution. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical concept |  |
| statistical error | has definition The uncertainty resulting from a measurement of purely random events. Such an uncertainty is defined as bracketing a range of values within which the correct value has a 66% chance of lying. For example, a value of (100 ± 10) obtained from a given measurement means that the true value has a 66% chance of lying between 90 and 110, and a 34% chance of being either above or below this range. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of statistical quantity |  |
| statistical quantity | is a kind of quantity |  |
| is a kind of statistical concept |  |
| statistical test | is a kind of statistical concept |  |
| Steady State Theory | has definition A cosmological theory propounded by Bondi, Gold, and Hoyle in which the Universe has no beginning and no end and maintains the same mean density, in the face of its observed expansion, by the continuous creation of matter at the current rate of 2.8 × 10-46 g cm-3 s-1 (or roughly one nucleon per cubic kilometer per year). Discovery of the microwave background has persuaded most astronomers to reject the steady-state theory. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory that the expanding universe was never in a state of appreciably higher density - i.e., that there was no "big bang" - and that matter is constantly being created out of empty space in order to maintain the cosmic matter density. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| Stefan's law | has definition The flux of radiation from a blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature: L = 4πR2σT4. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | has definition A constant relating the energy radiated by a black body to its absolute temperature and incorporated in the Stefan-Boltzmann radiation law which states that the energy radiated per unit time is given by σ(T4 - T40), where σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant and T and T0 are the absolute temperatures of the body and its surroundings expressed in kelvins. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The constant of proportionality relating the luminosity of a star to its absolute temperature: σ = 5.67 × 10-5 ergs cm-2 (deg-K)-4 s-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif) |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol σ | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has uncertainty 0.000040 × 10-8 W m-2 K-4 |  |
has value 5.670400 × 10-8 W m-2 K-4  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| stellar nucleosynthesis | has definition The production of heavy nuclei from the fusion of lighter ones within a star. The Sun presently converts hydrogen into helium. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthesis |  |
| stellar parallax | is a kind of parallax | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif) |
| stellar theory | has domain star |  |
| is a kind of astronomy theory |  |
| stellarator | has definition A type of plasma machine. It has a twisted-field configuration in the form of a figure 8 to fold the plasma back on itself; therefore, unlike a pinch machine, it has no ends where the plasma can leak out. Stellarators and tokomaks resemble each other in that both are toroidal devices that attain equilibrium and MHD stability through rotational transform and shear; they differ mainly in the way they attain these properties. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fusion device |  |
| Stephan's Quartet | has number of galaxies 4 |  |
| is an instance of compact group |  |
| Stephan's Quintet | has definition A highly disturbed cluster of five peculiar galaxies (NGC 7317, NGC 7318A, NGC 7318B, NGC 7319, NGC 7320) in Pegasus which seem to exhibit gaseous connecting bridges. Four have large redshifts (of the order of 5700-6700 km s-1), but the fifth member (NGC 7320) has a much smaller redshift (800 km s-1). Discovered in 1877 by M. E. Stephan. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of galaxies 5 |  |
| is a part of Pegasus |  |
| is an instance of compact group |  |
| steradian | has approval date 1900 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has base unit m2·m-2 = 1 |  |
| has definition Unit of solid (three-dimensional) angular measure. One steradian is equal to the angle subtended at the centre of a sphere by an area of surface equal to the square of the radius. The surface of a sphere subtends an angle of 4π steradians at its centre. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has proposal date 1880 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol sr |  |
| has symbol sr, Ω0 | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a unit of solid angle |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of solid angle unit |  |
| stimulated emission | has definition Radiation emitted by a body, such as an atom, when it is bombarded by radiation. The stimulated radiation has the same wavelength and direction as the bombarding radiation. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym induced emission | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of bound-bound transition |  |
| is an instance of emission |  |
| Stingray Nebula | has distance 18000 light years |  |
| has extent 130 solar systems |  |
has image   |  |
| has synonym Hen-1357 |  |
| is an instance of planetary nebula |  |
| is part of Ara |  |
| strange | has charge -1/3 |  |
| has definition A flavor of quark. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of light quark |  |
| strangeness | has definition A property ascribed to certain hyperons whose lifetimes before decay are abnormally long (about 10-8 to 10-10 seconds) relative to their rates of production (about one every 10-23 seconds). Like parity, strangeness is conserved in strong interactions but not in weak ones. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A quantum number associated with the strange quark. Strangeness is conserved by the strong nuclear force. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A quantum number used in quark theory. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum quantity |  |
| stratosphere | has altitude 15 to 50 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The region of Earth's atmosphere immediately above the troposphere. The temperature increases with altitude. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 240 to 270 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| Stratospheric Observatory for Far-Infrared Astronomy | has acronym SOFIA | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of airborne telescope | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| string theory | has definition A theory in which the fundamental constituents of matter are not particles but tiny one-dimensional objects, which we can think of as strings. These strings are so minute (only 10-33 cm long) that, even at current experimental energies, they seem to behave just like particles. So, according to string theory, what we call "elementary particles" are actually tiny strings. each of which is vibrating in a way characteristic of the particular "elementary particle". | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Fundamental one-dimensional object that is the essential ingredient in string theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Nambu's original idea that the elementary particles could be described as extended, one-dimensional objects was called string theory. Since the ends of Nambu's strings whipped around at the speed of light they were also called light strings. Later attempts to include the spin half fermions within a string theory led to the term spinning strings. Strings that possess supersymmetry are called superstrings. Heterotic strings combine spaces of two different dimensionalities. The term string is used in a generic way to describe all these different variations, including superstrings. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The hypothesized, basic constituents of matter, according to new theories of physics. In earlier theories of physics, the basic constituents of matter were point-like particles, such as electrons, which interacted with other particles at a point. According to the string theory, the basic constituents are 1-dimensional structures called strings. There are completely different strings, called cosmic strings, which can form according to some theories and which may extend for great distances in space. Postulated to have formed as a result of processes in the early universe, cosmic strings are 1-dimensional structures of enormous energy, extending for perhaps thousands or millions of light years in space. There is no good observational evidence that either kind of strings exist. (See superstring theory.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Theory that subatomic particles actually have extension along one axis, and that their properties are determined by the arrangement and vibration of the strings. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Unified theory of the universe postulating that fundamental ingredients of nature are not zero-dimensional point particles but tiny one-dimensional filaments called strings. String theory harmoniously unites quantum mechanics and general relativity the previously known laws of the small and the large, that are otherwise incompatible. Often short for superstring theory. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| strong force | has carrier boson gluon |  |
| has definition Fundamental force of nature that binds quarks together, and holds nucleons (which are comprised of quarks) together as the nuclei of atoms. Portrayed in quantum chromodynamics as conveyed by quanta called gluons. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of the four fundamental forces of nature. It governs the interaction between particles in atomic nuclei. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Strongest of the four fundamental forces, responsible for keeping quarks locked inside protons and neutrons and for keeping protons and neutrons crammed inside of atomic nuclei. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The interactions which bind quarks together to form rotons, neutrons, and other particles. The residual effects of these forces are responsible for the forces between protons and neutrons. See Yang-Mills theories. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The short-range nuclear force which is assumed to be responsible for binding the nucleus together. Strong interactions are so called because they occur in the extremely short time of about 10-23 seconds. Strong interactions can occur only when the particles involved are less than 3 fermis apart. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The short-range nuclear interactions responsible for holding nuclei together. The characteristic range of the strong interaction is 10-13 cm, and the time scale over which it operates is 10-33 second. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif) |
| has range |  |
| has strength (relative to electromagnetism) |  |
| has synonym nuclear force |  |
| is a kind of fundamental force |  |
| strong force symmetry | has definition Gauge symmetry underlying the strong force, associated with invariance of a physical system under shifts in the color charges of quarks. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gauge symmetry |  |
| strontium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 4 × 106 years |  |
| is a kind of alkali earth metal |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| SU Ursa Major | is a part of Milky Way |  |
is an instance of dwarf nova  |  |
| SU(2) | has definition The symmetry of the weak nuclear interaction. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle symmetry |  |
| SU(2) x U(1) | has definition The symmetry of the unified electroweak interaction. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle symmetry |  |
| SU(3) | has definition Symmetrical Unitary of Order 3: A symmetry found in sub-nuclear spectra. It is a concept in group theory, by which Gell-Mann and others, using eight quantum numbers, have been able to combine particles into family groups or supermultiplets, as the lowest-lying eightfold group of the nucleon doublet, the Λ singlet, the Σ triplet, and the Ξ doublet. The SU(3) theory applies only to the strongly interacting particles. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The symmetry corresponding to quark theory and the strong nuclear interaction. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle symmetry |  |
| SU(5) | has definition One of the suggested symmetries of the grand unified theory in which the gluon and electroweak forces are united. It includes the group SU(3) × SU(2) × U(1). | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Symmetrical Unitary of Order 5: The simplest type of grand unified theory, proposed in the 1970s. (See grand unified theories.) | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle symmetry |  |
| Subaru Telescope | has altitude 4215 m |  |
| has aperture 8.3 m |  |
| has comment Thin primary (Coming ULE) under active control |  |
| has creation date (1999) |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.8, 12.5, 35 |  |
| has latitude 19° 49' N |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Mitsubishi |  |
| has owner National Astronomy Obs. (Japan) |  |
| has synonym Subaru |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| subdwarf | has definition A metal-poor main-sequence star. On the H-R diagram, subdwarfs lie slightly below the metal-rich Main Sequence, because they are fainter than metal-rich main-sequence stars of the same color. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Late-type object whose observed color and absolute magnitude place it below the Main Sequence. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star whose luminosity is 1.5 to 2 magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same spectral type. Subdwarfs are primarily Population II and lie just below the Main Sequence on the H-R diagram. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class VI |  |
| has symbol sd |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| subgiant | has definition A star whose position on the H-R diagram is intermediate between that of main-sequence stars and normal giants of the same spectral type. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class IV |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| subgiant CH star | has definition Hot Ba star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type < G5 | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of barium star |  |
| sublimation | has final phase gas |  |
| has initial phase solid |  |
| has inverse process condensation |  |
| is a kind of first order phase transition |  |
| submillimeter | has frequency 300 GHz to 3 THz |  |
| has wavelength 100 μm to 1 mm |  |
| is a kind of microwave |  |
| Sudbury Neutrino Observatory | has acronym SNO |  |
| has component deuterium detector |  |
| is an instance of neutrino telescope |  |
| sulfur | has abundance 1.6 × 107 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 260 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has abundance 870 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has atomic emission line 545.38 nm for S II |  |
| has atomic emission line 547.36 nm for S II |  |
| has atomic emission line 550.97 nm for S II |  |
| has atomic emission line 560.61 nm for S II |  |
| has atomic emission line 565.99 nm for S II |  |
| has atomic emission line 792.40 nm for S I |  |
| has atomic emission line 964.99 nm for S I |  |
| has atomic number |  |
| has atomic radii 104 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to all living things; part of the amino acids methionine and cysteine |  |
| has boiling point 717.824 K |  |
| has chief source native sulfur, pyrite, H2S in natural gas |  |
| has covalent radii 104 pm |  |
| has critical pressure 20700 kPa |  |
| has critical temperature 1314 K |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 1046.46, b = 1286.60, c = 2448.60 pm for α form |  |
| has crystal type orthorhombic for α form |  |
| has daily dietary intake 850 - 930 mg |  |
| has definition the α-S8 orthorhombic form of sulfur is yellow |  |
| has density 1819 kg m-3 for liquid at 393 K |  |
| has density 1957 kg m-3 for β solid at 293 K |  |
| has density 2070 kg m-3 for α solid at 293 K |  |
| has discovery date prehistoric |  |
| has electrical resistivity 2 × 1015 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 200.4 kJ mol-1 from S to S- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ne]3s23p4 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 2.58 Pauling |  |
| has hazard elemental form is harmless unless ingested; ignited it emits highly toxic SO2 fumes |  |
| has heat capacity 22.64 J K-1 mol-1 for α solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 23.673 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 1.23 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 9.62 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 184 pm for S2- |  |
| has ionic radii 29 pm for S6+ |  |
| has ionic radii 37 pm for S4+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 29 to 39 |  |
| has lethal intake 175 mg kg-1 for rabbits |  |
| has level in humans 1800 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 500 - 2400 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 5000 - 11000 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 7000 - 12000 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 74.33 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope sulfur 32 |  |
| has main mining area USA (native sulfur), Spain |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 89.1 cm2 g-1 for CuKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 9.55 cm2 g-1 for MoKα X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -5.83 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for β solid |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility -6.09 × 10-9 kg-1 m3 for α solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 140 g for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 386.0 K for α form |  |
| has mineral occurs naturally as native sulfur deposits associated with oil-bearing strata |  |
| has molar volume 15.49 cm3 |  |
| has name origin sulvere = sulfur from Sanskrit (sulphurium from Latin) |  |
| has neutron scattering length 0.2847 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 11 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 16 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI |  |
| has ocean residence time 8 × 106 years |  |
| has pronunciation sul-fer |  |
has registry number 7704-34-9 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 32.066 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 2.5 × 109 tonnes |  |
| has space group Fddd for α form |  |
| has specimen powder and flakes. Safe. |  |
| has symbol S |  |
| has term symbol 3P2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 0.269 W m-1 K-1 for α at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 0.53 barns |  |
| has toxic intake elemental form is not very toxic, but simple derivatives are (SO2, H2S, etc.) |  |
| has uses key industrial chemical, starting point for sulfuric acid |  |
| has van der Waals radii 185 pm |  |
| has world production 54 × 106 |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of group VI element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic element |  |
| reacts with air when heated |  |
| reacts with oxidising acids |  |
| sulfur 32 | has atomic mass 31.97207070 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 2.0534 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 95.02% |  |
| has NMR frequency 24.664 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.0973 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.678 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 16 |  |
| has number of nucleons 32 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 2.26 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 32S |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 33 | has atomic mass 32.97145843 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.75% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +0.643821 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 17 |  |
| has number of nucleons 33 |  |
| has symbol 33S |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 34 | has atomic mass 33.96786665 |  |
| has natural abundance 4.21% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 18 |  |
| has number of nucleons 34 |  |
| has symbol 34S |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 35 | has atomic mass 34.969031 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.1674 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 87.2 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.00 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.0471 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 19 |  |
| has number of nucleons 35 |  |
| has symbol 35S |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 36 | has atomic mass 35.96708062 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.02% |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 20 |  |
| has number of nucleons 36 |  |
| has symbol 36S |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 37 | has atomic mass 36.971125 |  |
| has decay mode β- (4.865 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 5.05 minutes |  |
| has number of neutrons 21 |  |
| has number of nucleons 37 |  |
| has symbol S |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur 38 | has atomic mass 37.971162 |  |
| has decay mode β- (2.94 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 2.84 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +1.00 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 38 |  |
| has symbol 38S |  |
is an instance of sulfur  |  |
| sulfur monoxide | has symbol SO |  |
| is an instance of diatomic molecule |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| summer solstice | is an instance of solstice |  |
| Sun | has absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol = +4.67 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has absolute visual magnitude Mv = +4.85 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has age 4.6 billion years |  |
| has apparent magnitude -26.74 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has central density 155 g cm-3 (Bahcall 1973) |  |
| has central temperature 14-15 × 106 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star that Earth orbits. Central body of solar system. It takes about 1-10 million years for photons to diffuse from the Sun's interior to its surface. About 3% of the energy radiated is in the form of neutrinos. Every second about 655 million tons of H are being converted into 650 million tons of He. A grazing light ray is deflected 1".7 by the Sun. If the total angular momentum of the solar system were concentrated in the Sun, its equatorial rotation speed would be about 100 km s-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has density at surface 3 × 10-7 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galactic center 27000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance from galactic plane 35 light-years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy generating mass 0.35 Msun |  |
| has energy source proton-proton reaction |  |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 618 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has galactic orbital period 220 million years (e ≈ 0) |  |
| has galactic orbital velocity Vorb = 250-300 km s-1 |  |
| has inclination of rotational axis to pole of ecliptic 7°15' | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity 3.83 × 1033 ergs s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class V (main-sequence) | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has magnetic field 1-2 gauss as high as 10-1000 gauss in active regions |  |
| has mass 1.989 × 1033 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 1.409 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean rotation speed 1.9 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 695990 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotational period at equator 24d6h | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotational period at poles 35 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type G2 | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 27398 cm s-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 5785 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif) |
| has velocity relative to nearby stars 20 km s-1 toward R.A. 18h4m, declination +30° (towards in Hercules) |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of G star |  |
| is an instance of naked eye object |  |
| is an instance of Population I star |  |
| Sun Kelvin timescale | has definition The time it takes the Sun to contract gravitationally from infinite radius down to its present radius by radiating its thermal energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 2 to 3 × 107 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of Kelvin timescale | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| Sun nuclear time scale | has definition Time required for the Sun to evolve a significant distance off the main sequence; the time it takes the Sun to convert all its available hydrogen into helium. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 1010 years. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of nuclear time scale | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif) |
| Sun orbital event | has participants planet, Sun |  |
| is a kind of orbital event |  |
| sunrise | has definition The times at which the apparent upper limb of the Sun is on the astronomical horizon; i.e., when the true zenith distance, referred to the center of the Earth, of the central point of the disk is 90°50', based on adopted values of 34' for horizontal refraction and 16' for the Sun's semidiameter. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 day |  |
| is an instance of astronomical horizon event |  |
| sunset | has definition The times at which the apparent upper limb of the Sun is on the astronomical horizon; i.e., when the true zenith distance, referred to the center of the Earth, of the central point of the disk is 90°50', based on adopted values of 34' for horizontal refraction and 16' for the Sun's semidiameter. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has period 1 day |  |
| is an instance of astronomical horizon event |  |
| sunspot | has definition A temporary disturbed area in the solar photosphere that appears dark because it is cooler than the surrounding areas. Sunspots usually occur in pairs of opposite polarity about 30° N and S of the equator, and move in unison across the face of the Sun as it rotates. The leading (or preceding) spot is called the p-spot; the following, the f-spot. Some sunspots have magnetic fields as high as 1000 gauss (highest observed was 5000 gauss | ![has source: [Steshenko 1967]). Typical diameter, 10<sup>9</sup> cm., 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Comparatively dark spot on the Sun's photosphere, commonly one of a (not always obvious) group of two. The center of a vast electrostatic field and a magnetic field of a single polarity (up to 4000 gauss), a sunspot represents a comparatively cool depression (at a temperature of approximately 4500 °C). Sunspots occur in cycles of about 11 Earth-years in period although their individual duration - a matter of Earth-days only - is affected by the differential rotation of the Sun; they tend to form at high latitudes and drift towards the solar equator. They are also sources of strong ultra-shortwave radio emissions. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| sunspot radiation | has definition Intense, variable, circularly polarized radio waves in a noise storm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of sunspot |  |
| Sunyaev-Zel'dovich process | has definition Compton scattering between the photons of the cosmic microwave background radiation and electrons in galaxy clusters. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Compton scattering |  |
| super-metal-rich star | has definition Used in reference to stars, or stellar populations, which are richer in metals than the Hyades. |  |
| is a kind of metal-rich star |  |
| supercluster | has definition A cluster of clusters of galaxies. Superclusters are typically about one hundred million (108) light-years in diameter and contain tens of thousands of galaxies. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of clusters |  |
| is a kind of collection of galaxies |  |
| superconducting super collider | has definition A proposed accelerator of great size and high energy. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of collider |  |
| Supergalactic Plane | has definition An apparent plane of symmetry, passing through the Virgo cluster of galaxies, about which many of the brightest galaxies in the sky are concentrated. These galaxies form the Local Supercluster. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of plane |  |
| supergiant | has definition An extremely luminous star of large diameter and low density. No supergiants are near enough to establish a trigonometric parallax. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has luminosity class I |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| supergranulation cell | has definition Convective cell in the solar photosphere, distributed fairly uniformly over the solar disk, that last as long as a day. New sunspots develop in the intersections of adjacent supergranulation cells. Most of the magnetic flux through the photosphere is concentrated in the supergranule boundaries. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 15000 to 30000 km |  |
| has distribution uniform |  |
| has mean lifetime 1 day |  |
| is a part of photosphere |  |
| supergravity | has definition A supersymmetric theory of gravity in which the graviton is accompanied by a spin-3/2 particle called the "gravitino". In supergravity theories, supersymmetry has been promoted to the status of a local gauge symmetry. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Class of point-particle theories combining general relativity and supersymmetry | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supersymmetry |  |
| superior planet | has definition Planets farther from the Sun than the Earth is (i.e., Mars to Pluto). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of planet |  |
| supermultiplet | has definition A multiplet of multiplets. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of multiplet |  |
| supernova | has definition A gigantic stellar explosion in which the star's luminosity suddenly increases by as much as a billion times. Most of the star's substance is blown off, leaving behind, at least in some cases, an extremely dense core which may be a neutron star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has energy release 1049 to 1051 ergs | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has peak brightness 108 solar luminosity units |  |
| has use supernova peak brightness distance determination |  |
| is a kind of cataclysmic variable |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| supernova explosion | is a kind of gravitational collapse |  |
| supernova produced element | has definition element heavier than iron produced within the core of an exploding supernova | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has origin exploding core of a supernova | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of element |  |
| supernova produced radioactive element | has definition a radioactive element produced within the core of an exploding supernova | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radioactive element |  |
| is a kind of supernova produced element |  |
| supernova remnant | has acronym SNR | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A gaseous nebula, the expanding shell ejected by a supernova, and deriving its energy (at least in some cases) from the conversion by the remanent neutron star of its rotational energy into a stream of high-energy particles being continually accelerated in the SNR. About 100 SNRs are known in our Galaxy. Supernova remnants are usually powerful radio sources. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The expanding shell of gas ejected at high speed by a supernova explosion, observed as an expanding diffuse gaseous nebula, often with a shell-like structure. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| has ejection velocity 10000 km s-1 |  |
| is a kind of expanding emission nebula |  |
| is a kind of radio source | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif) |
| produces synchrotron radiation |  |
| superpartner | has definition Particle whose spins differ by 1/2 unit and that are paired by supersymmetry. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| superstring theory | has definition A new type of theory in physics that unifies all the forces of nature, including the gravitational force, and that may be capable of explaining all of the fundamental laws and particles of nature. In superstring theories, the basic constituent of matter is a 1-dimensional structure, called a string, rather than a point-particle structure. According to superstring theory, space has more than 3 dimensions. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A proposal for the ultimate laws of nature, a "theory of everything," stemming primarily from discoveries in the mid 1980's. The fundamental entity in this theory is an ultramicroscopic string-like object, with a length of typically 10-33 centimeters and effectively zero thickness. At present our understanding of string theory is very limited. The simplest predictions of superstring theory concern processes at the Planck energy, and so far very little is known about the consequences of string theory at lower energies. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition String theory that incorporates supersymmetry. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of string theory |  |
| supersymmetric quantum field theory | has definition Quantum field theory incorporating supersymmetry. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supersymmetry |  |
| supersymmetric standard model | has definition Generalization of the standard model of particle physics to incorporate supersymmetry. Entails a doubling of the known elementary particle species. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supersymmetry |  |
| supersymmetry | has definition A mathematical property of some theories of physics proposing that every particle of integer spin (intrinsic angular momentum) has a partner of half integer spin. For example, the photon, which is the particle of light, has a spin of 1 unit. Its hypothesized super symmetric partner is called the photino, which would have a spin of 1/2 units. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A symmetry principle that relates the properties of particles with a whole number amount of spin (bosons) to those with half a whole (odd) number amount of spin (fermions). | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A symmetry relating fermions and bosons. If supersymmetry is a true symmetry of nature, then every "ordinary" particle has a corresponding "superpartner" which differs in spin by half a unit. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A symmetry that relates the fermions (fractional spin particles) to the bosons (elementary particles with integral spin). | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Class of theories that seek to identify symmetrical relationships linking fermions and bosons - i.e., particles of half integer spin, like electrons, protoins, and neutrinos, with those of integral spin, like photons and gluons. If attainable, a fully realized supersymmetry theory would provide a unified account of all four fundamental forces, and might well shed light on the very early evolution of the universe as well. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| superunified theory | has definition Hypothetical theory that presumably would show how all four fundamental forces of nature functioned as a single force in the extremely early universe. The best current candidates for such a potential achievement are thought to be supersymmetry and string theory. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition While grand unified theories attempt to describe three of the four known interactions of nature - the weak, strong, and electromagnetic interactions - in a unified way, the fourth interaction, gravity, is omitted. Theories which attempt to include gravity as well, such as superstrings, are called superunified. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| supra-thermal proton bremsstrahlung | has definition Ordinary electron-proton bremsstrahlung viewed from the rest frame of the electron rather than the proton; in other words, the electron is at rest and the heavy particle (proton) is moving. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of bremsstrahlung |  |
| Swan band | has definition A C2 band which passes through a minimum between spectral types R4 and R6 and increase again toward N6. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer W. Swan | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1856 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of C2 band |  |
| occurs in carbon star | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| SX Phoenicis | has definition A dwarf Cepheid (spectral type A) with the shortest known period (1h19m). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Phoenix |  |
| is an instance of dwarf Cepheid |  |
| symbiotic star | has definition A term originally used by P. Merrill to describe stars of two essentially dissimilar kinds which seem to occur together and which seem to "need" each other. In practice, it has come to signify a peculiar group of objects (usually spectral type Me) that display a combination of low-temperature absorption spectra and high-temperature emission lines. These objects undergo semiperiodic nova-like outbursts and display the spectral changes of a slow nova superposed on the features of a late-type star. Their spectra are midway between those of planetary nebulae and true stellar objects. A symbiotic star is now usually taken to be a small, hot, blue star surrounded by an extensive variable envelope. As of 1973 about 30 were known. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Object exhibiting a spectrum corresponding to a low-temperature star (generally a giant) plus emission lines corresponding to a hot plasma. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym combination variable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of composite spectrum star |  |
| is a kind of variable |  |
| symmetry | has antonym symmetry breaking |  |
| has definition A property of a physical system that does not change when the system is transformed in some manner. For instance, a sphere is rotationally symmetrical since its appearance does not change if it is rotated. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition State of a system such that it has a significant quantity that remains invariant after a transformation. More generally, an apt or pleasing proportion based upon such a state. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The property of being unchanged after some transformation. A square, for example, has a 4-sided rotational symmetry. It appears the same after it is rotated by 90 degrees. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| symmetry breaking | has antonym symmetry |  |
| has definition A reduction in the amount of symmetry a system appears to have, usually associated with a phase transition. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A set of mathematical transformations that represent a symmetry. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A violation of symmetry. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In cosmology and particle physics, a state in which traces of an earlier symmetry may be discerned. A broken symmetry condition differs from chaos in that its parts can in theory be united in a symmetrical whole, like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. | ![has source: [F88]], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The process by which an intrinsic symmetry of a system is disrupted. For example, a compass, in the absence of any outside magnetic field, has rotational symmetry and is equally likely to point in any direction. The magnetic field of the earth breaks the symmetry and causes the compass to point in a particular direction, toward the earth's north magnetic pole. In some cosmological models, the infant universe was much more symmetric than it is today. As the universe aged and cooled, some of these symmetries were permanently broken. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym asymmetry | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| synchronous rotation | has definition Rotation whose period is equal to the orbital period. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has period equal to orbital period | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of rotation |  |
| synodic month | has definition The period of time between two successive identical phases of the Moon e.g., new Moon to new Moon or full Moon to full Moon (cf. lunation). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 29.53 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of month |  |
| synthetic element | has definition element which cannot be found as a mineral deposit | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has lifetime |  |
| has synthesis mechanism |  |
| is a kind of element |  |
| T association | has definition Association containing many T Tauri stars. About 20 are known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of association |  |
| T Pyxidis | has acronym T Pyx |  |
| has definition a recurrent nova |  |
| has distance from Earth 6000 light-years |  |
| has erupted in 1966, 1944, 1920, 1902, and 1890. |  |
has image   |  |
has reference Shara, M.M., Zurek, D.R., Williams, R.E., Prialnik, D., Roberto.G., Moffat, A.F.J. : 1997, AJ 114, 258. HST Imagery of the Non-Expanding, Clumped Shell of the Recurrent Nova T Pyxidis  |  |
| is an instance of recurrent nova |  |
| T Tauri star | has definition Also called T Tauri variable, a type of variable star of spectral classification F, G or K (giants above the main sequence on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram) that loses an appreciable proportion of its mass in its (irregular) more luminous periods, and is thus surrounded by volumes of gas and dust. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Eruptive variable subgiant star associated with interstellar matter and believed to be still in the process of gravitational contraction on their way to the main sequence. They are found only in nebulae or very young clusters. They have low-temperature (G-M) spectra with strong emission lines and broad absorption lines. Their absolute magnitudes are brighter than those of main-sequence stars of similar spectral types. They have a high lithium abundance. T Tau itself is dG5e. (sometimes called RW Aurigae stars) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Late type irregular variables associated with bright or dark nebulosity. The spectrum exhibits emission in both CaII and H lines. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Luminous variable stars with low effective temperatures and strong emission lines, associated with interstellar gas clouds and found in very young clusters. They are believed to be still in the process of gravitational contraction from their protostellar phase and have not yet arrived at the main sequence and begun to burn hydrogen. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym nebular variable | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| is a kind of irregular variable |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| tachyon | has definition Particle whose mass (squared) is negative; its presence in a theory generally yields inconsistencies. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| tangential velocity | has definition A star's velocity across an observer's line of sight. To calculate a star's tangential velocity, one must know the star's distance and proper motion. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym transverse velocity | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of velocity |  |
| tantalum | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Tarantula Nebula | has image   |  |
| is a part of Large Magellanic Cloud |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
| tau | has charge -1 |  |
| has symbol τ |  |
| is an instance of charged particle |  |
| is an instance of lepton |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| tau Compton wavelength | applies to particle tau |  |
has equation  |  |
| has symbol λC,τ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00011 × 10-15 m |  |
has value 0.69770 × 10-15 m  |  |
| is an instance of particle Compton wavelength |  |
| tau mass | applies to particle tau |  |
| has symbol mτ |  |
| has uncertainty 0.00052 × 10-27 kg |  |
has value 3.16788 × 10-27 kg  |  |
| is an instance of particle mass |  |
| Taurid | is an instance of meteor shower |  |
| Taurus | has acronym Tau |  |
| has genitive Tauri |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin beast hunted by Orion, also Zeus in a disguise used to elope with Europa |  |
| has synonym Bull |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| TDRSS | has definition Transmission Data and Relay Satellite System. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of geosynchronous satellite |  |
| technetium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of synthetic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| telescope | has angular resolving power |  |
| has aperture |  |
has definition A device for gathering and amplifying light or X rays, gamma rays, or other forms of energy.  | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif) |
| has effective diameter |  |
| has focal ratio |  |
| has location |  |
| has operator |  |
| has purpose observe celestial objects |  |
| has wavelength sensitivity |  |
| is a kind of instrument |  |
| Telescopio Nazionale Galileo | has altitude 2370 m |  |
| has aperture 3.58 m |  |
| has creation date (1998) |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.5, 6, 11 |  |
| has latitude 28° 45' N |  |
| has location La Palma, Canary Islands |  |
| has longitude 17° 54'W |  |
| has mirror maker Zeiss |  |
| has mirror type Zerodur |  |
| has owner Obs. del Roque de los Muchachos |  |
| has synonym Galileo |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien |  |
| Telescopium | has acronym Tel |  |
| has genitive Telescopii |  |
| has synonym Telescope |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by de Lacaille  |  |
| tellerium | has ocean oxidation state VI some IV |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| telluric lines | has definition Spectral lines or bands that originate from absorption by gases such as O2, H2O, or CO2 in the Earth's atmosphere. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has species O2, H2O, or CO2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| tellurium | has image  |  |
| is a kind of group VI element |  |
| is a kind of nonmetallic metalloid |  |
| temperature | has definition A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a system. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit temperature unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| temperature unit | has absolute zero -has source: [JM92] |  |
| has definition A temperature unit is a measure of the average kinetic energy per degree of freedom of the constituent molecules. | ![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has triple point of water -has source: [JM92] |  |
| is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of temperature |  |
| tera | has symbol T |  |
| has value 1012 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:50.0](facet.gif) |
| terbium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| terrestrial latitude | has definition Angular distance on the Earth measured north or south of the equator along the meridian of a geographic location. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition On Earth, distance north or south on the equator along a line connecting the poles. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of geocentric coordinate component |  |
| terrestrial longitude | has definition Angular distance measured along the Earth's equator from the Greenwich meridian to the meridian of a geographic location. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition On Earth, distance east or west of Greenwich, England, measured along lines drawn parallel to the equator. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of geocentric coordinate component |  |
| terrestrial planet | has composition mostly made of heavier non-volatile elements |  |
| has definition A planet having a compact rocky surface like Earth |  |
| has material silicates, oxides, water |  |
| is a kind of planet |  |
| tertiary mirror | has definition The third mirror to be encountered by the light in a telescope system. A tertiary mirror is required on alt-az telescopes to direct light to the stationary Nasmyth foci. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of mirror |  |
| tertiary period | is a kind of cenozoic era |  |
| tesla | has base unit kg·s-2·A-1 |  |
| has definition The derived SI unit of magnetic flux density. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 maxwell per square centimeter | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 Wb m-2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 104gauss | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol T |  |
| has unit Wb·m-2 |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux density unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| tethered satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| Tethys | has definition Fourth satellite of Saturn | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 1000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Cassini |  |
| has discovery date 1684 |  |
| has orbital period P = 1.87 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| tevatron | has definition A particle accelerator capable of attaining an energy of 1 TeV. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle accelerator |  |
| thallium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state I |  |
| has ocean residence time 10000 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of group III element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| The Thaw Refractor | has altitude 380 m |  |
| has aperture 0.76 m |  |
| has comment Originally had a Brashear visual objective (1914); present one is corrected for red light |  |
| has creation date 1985 |  |
| has focal ratio f/18.6 |  |
| has latitude 40° 29' N |  |
| has lens maker R.E. Sumner |  |
| has location Pittsburgh, PA, US |  |
| has longitude 80° 01' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Warner and Swasey |  |
| has optical design Red-light refractor |  |
| has owner Allegheny Observatory |  |
| has synonym 30 inch |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| Themis | has definition A satellite of Saturn discovered by Pickering in 1900, but since lost. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| theoretical celestial body | has definition natural object postulated by theory but not yet observed |  |
| is a kind of natural object |  |
| theory | has author or reasearch group |  |
| has date or a range of dates for which the theory was active |  |
| has definition A rationally coherent account of a wider range of phenomena than is customarily accounted for by a hypothesis. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has domain a field of research |  |
| has validity correct or incorrect with caveats |  |
| is a kind of hypothesis |  |
| theory of everything | has acronym TOE |  |
| has definition Theory of Everything. A quantum-mechanical theory that encompasses all forces and all matter. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of unified theory |  |
| theory related concept | is a kind of abstraction |  |
| thermal bremsstrahlung | has definition A mode of X-ray production by very energetic electrons accelerated in the field of a positive ion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of bremsstrahlung |  |
| thermal energy | has definition Energy associated with the motions of the molecules, atoms, or ions in a substance. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| thermodynamics | has definition Laws developed in the nineteenth century to describe aspects of heat, work, energy, entropy, and their mutual evolution in a physical system. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The area of physics that analyzes the behavior of a system with very many members, such as a gas with many individual molecules. In such a situation, the behavior of the whole system is obtained by averaging over the behavior of individual members. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The study of the behavior of heat (and, by implication, other forms of energy) in changing systems. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym statistical mechanics | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of physics |  |
| thermodynamics law | has domain thermodynamics |  |
| is a kind of law |  |
| thermohaline convection | has definition A type of hydrodynamic instability. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of convection | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| theta pinch | has definition A fusion device in which the magnetic field runs parallel to the plasma column. It is a long cylindrical tube enclosed in a one-turn magnet coil. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pinch machine |  |
| Theta2 Orionis | has definition A spectroscopic binary tentatively identified with 2U 0525-06. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 21.03 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O9.5 Vp | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 2U 0525-06 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| is an instance of spectroscopic binary |  |
| thick disk | has definition The stellar population that contains Arcturus and about 4 percent of the other stars near the Sun. It has a scale height of about 3500 light-years and consists of old stars. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has height 3500 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| thin disk | has definition The stellar population that contains the Sun and most other nearby stars. Most of its stars have a scale height of 1000 light-years and orbit the Galaxy on fairly circular orbits. The stars of the thin disk range in age from 0 to about 10 billion years. The thin disk breaks into two subpopulations, the young thin disk and the old thin disk. The young thin disk has a smaller scale height than the old thin disk, and the former's stars have more circular orbits. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has height 1000 light-years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has star age 0 to about 10 billion years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of disk |  |
| thioformaldehyde | has symbol H2CS |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| third law of thermodynamics | has definition All substances have zero entropy at 0 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Nernst theorem |  |
| is an instance of thermodynamics law |  |
| Thompson Refractor | has altitude 34 m |  |
| has aperture 0.66 m |  |
| has creation date 1897 |  |
| has focal ratio f/10.4 |  |
| has latitude 50° 52' N |  |
| has lens maker Grubb |  |
| has location Herstmonceux, Sussex, England |  |
| has longitude 0° 20' E |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb |  |
| has owner Royal Greenwich Observatory |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| Thomson cross section | has equation  |  |
| has symbol σe |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000000015 × 10-28 m2 |  |
has value 0.665245854 × 10-28 m2  |  |
| is an instance of area |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| Thomson scattering | has definition The limit of Compton scattering at low energies. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Compton scattering |  |
| thorium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 50 years |  |
| is a kind of actinide |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| thought experiment | has definition An experiment that cannot be or is not carried out in practice, but can, given sufficient imagination and rigor, be reasoned through by thought and intuition alone. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory related concept |  |
| three body recombination | has definition Capture of an electron by an ion with the binding energy absorbed by a third free electron | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of recombination |  |
| three-phase | has definition A CCD construction in which three overlapping metal electrodes are used to define a pixel and effect the transfer of charge, in either direction along a column, by the charge-coupling method. If only two electrodes are used then the device is two-phase. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of electrodes 3 | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| threshold energy | has definition Difference between the energy at the first excited level and that of the ground state. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| thulium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| tidal dwarf galaxy | has acronym TDG |  |
| has definition A self-gravitating entity of dwarf-galaxy mass, built from tidal material expelled during interactions (e.g. AM0547-244, AM1054-325 and AM1353-272) |  |
| is a kind of dwarf galaxy |  |
| time | has definition A dimension distinguishing past, present, and future. In relativity, time is portrayed as a geometrical dimension, analogous to the dimensions of space. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit time unit |  |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| time dilation | has definition The flow of time slows down for an observer in motion. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is a consequence of special relativity | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of relativity process |  |
| time unit | is a kind of unit |  |
| is a unit of time |  |
| tin | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| is a kind of group IV element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| is a kind of scavenged oceanic element |  |
| tired light | has definition The hypothesis that light may be degraded in energy, thereby increasing in wavelength and becoming redshifted, during its passage through intergalactic space. This would provide an alternative to the Big Bang model in accounting for the redshifts of distant galaxies. However, there is no evidence for any such tired-light effect. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| TIROS satellite | is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| Titan | has albedo 0.21 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition H2 and CH4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Seventh (known) moon out from Saturn, its largest and brightest. It is possibly also the largest satellite in the Solar System. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Huyghens | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1655 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 15d22h41m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R ≈ 2900 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 15d22h41m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym S VI | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Saturn |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Titania | has definition Fourth satellite of Uranus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Herschel | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1787 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 8d17h | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius R ≈ 850 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Uranus |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| titanium | has abundance 1.12 × 105 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 4.8 × 10-4 p.p.m. in seawater |  |
| has abundance 5600 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 323.452 nm for Ti II |  |
| has atomic emission line 336.121 nm for Ti II |  |
| has atomic emission line 364.268 nm for Ti I |  |
| has atomic emission line 365.350 nm for Ti I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 399.864 nm for Ti I |  |
| has atomic emission line 334.941 nm for Ti II (strong) |  |
| has atomic number 22 |  |
| has atomic radii 145 pm |  |
| has biological role none |  |
| has boiling point 3560 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 108.4 GPa |  |
| has chief source ilmenite; sometimes anatase |  |
| has covalent radii 132 pm |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 295.11, c = 468.43 pm for α-Ti |  |
| has crystal type h.c.p. for α-Ti |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.8 mg |  |
| has definition hard, lustrous, silvery metal which resists corrosion due to an oxide layer on its surface |  |
| has density 4110 kg m-3 for liquid at 1933 K melting point |  |
| has density 4540 kg m-3 for solid at 293 K |  |
| has discoverer Rev. W. Gregor |  |
| has discovery date 1791 |  |
| has discovery location Creed, Cornwall, England |  |
| has electrical resistivity 42.0 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 7.6 kJ mol-1 from Ti to Ti- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d24s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.54 Pauling |  |
| has hazard some compounds are dangerous to handle, such as TiCl3, which is corrosive. Suspected carcinogen. |  |
| has heat capacity 24.430 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 25.02 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 20.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 428.9 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 69 pm for Ti4+ |  |
| has ionic radii 80 pm for Ti2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 41 to 53 |  |
| has lethal intake non-lethal |  |
| has level in humans 0.054 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.9 - 2.2 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has level in humans 1.2 - 4.7 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 8.35 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope titanium 48 |  |
| has main mining area Norway, India, Brazil, Canada, USA, Russia |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 208 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 24.2 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +4.01 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 20 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 1933 K |  |
| has mineral anatase, brookite, ilmenite, perovskite, rutile, titanite |  |
| has molar volume 10.55 cm3 |  |
| has name origin Titans = the sons of the Earth goddess from Greek |  |
| has neutron scattering length -0.3438 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 13 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 22 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| has ocean residence time 50 |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.361 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation tit-ayn-iuhm |  |
has registry number 7440-32-6 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 47.867 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has reserves 440 × 106 tonnes |  |
| has rigidity modulus 45.6 GPa |  |
| has space group P63/mmc for α-Ti |  |
| has specimen crystals, foil, granules, powder, rod or wire. Safe. |  |
| has symbol Ti |  |
| has term symbol 3F2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 21.9 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 6.09 barns |  |
| has toxic intake low as metal, oxide (TiO2) and inorganic titanium (IV) salts |  |
| has uses chemical plants, lightweight alloys, hip replacement joints |  |
| has uses paint, because TiO2 has good covering power |  |
| has world production 3 × 106 tonnes year-1 TiO2 |  |
| has world production 99000 tonnes year-1 titanium metal |  |
| has young's modulus 120.2 GPa |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| reacts with air if powdered metal is ignited |  |
| titanium 44 | has atomic mass 43.959689 |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.265 Mev) |  |
| has half life 67 years |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 22 |  |
| has number of nucleons 44 |  |
| has symbol 44Ti |  |
| has uses research |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 45 | has atomic mass 44.958124 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.063 Mev) 86% |  |
| has decay mode EC 14% |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 3.078 hours |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 0.095 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 45 |  |
| has symbol 45Ti |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 46 | has atomic mass 45.952629 |  |
| has natural abundance 8.0% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 23 |  |
| has number of nucleons 46 |  |
| has symbol 46Ti |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 47 | has atomic mass 46.951764 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.5084 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 7.3% |  |
| has NMR frequency 5.637 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.864 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -0.78848 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +0.290 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 5/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 25 |  |
| has number of nucleons 47 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 2.09 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 47Ti |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 48 | has atomic mass 47.947947 |  |
| has natural abundance 73.8% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 26 |  |
| has number of nucleons 48 |  |
| has symbol 48Ti |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 49 | has atomic mass 48.947871 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 1.5080 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 5.5% |  |
| has NMR frequency 5.638 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 1.18 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = -1.10417 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment +0.240 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 27 |  |
| has number of nucleons 49 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 3.76 × 10-3 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 49Ti |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| titanium 50 | has atomic mass 49.944792 |  |
| has natural abundance 5.4% |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 0+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 50 |  |
| has symbol 50Ti |  |
is an instance of titanium  |  |
| Tokamak | has definition A type of "magnetic bottle" used in experiments on controlled nuclear fusion. (the name is a Russian acronym) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of fusion device |  |
| top | has charge 2/3 |  |
| has definition The sixth flavor of quark. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of heavy quark |  |
| top-down scenario | has definition A scenario of galaxy formation in which large structures form first and then fragment to become galaxies. | ![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| topocentric coordinate | has definition With reference to, or pertaining to, a point on the surface of the Earth, usually with reference to a coordinate system. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of coordinate |  |
| Torino scale 10 impact | has definition impact capable of causing a global climatic catastrophe  |  |
| has has average interval time 100000 years or longer |  |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| Torino scale 8 impact | has definition collision capable of causing localized destruction  |  |
| has has average interval time 50 to 1000 years |  |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| Torino scale 9 impact | has definition collision capable of causing regional devastation  |  |
| has has average interval time 1000 to 100000 years |  |
| is a kind of impact event |  |
| Toro | has albedo ≤ 0.15 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has aphelion distance 1.96 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has asteroid number 1685 |  |
| has closest distance to Earth 0.13 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Wirtanen | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1948 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.44 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 584.2 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has perihelion distance 0.77 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 5 × 3 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 10h11m | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 1.37 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface composition rocky, thinly covered with dust | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Earth-crossing asteroid |  |
| is an instance of Earth-crossing asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif) |
| torr | has definition A unit of pressure. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1 mm Hg | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 1/760 atmosphere | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of pressure unit |  |
| torus | has definition The topological name for the shape of a donut. While a donut is a two-dimensional surface in a three-dimensional space, the torus can be generalized to higher numbers of dimensions. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The two-dimensional surface of a doughnut. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has dimensions 3 |  |
| is a kind of geometrical object |  |
| total lunar eclipse | has definition An eclipse in which the Moon passes through the shadow cast by the Earth, the Moon passing completely through the Earth's umbra. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of lunar eclipse |  |
| total solar eclipse | has definition A solar eclipse in which the solar disk is completely covered at maximum eclipse. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of solar eclipse |  |
| toy theory | has definition A theory which is known to be too simple to describe reality, but which is nonetheless useful for theorists to study because it incorporates some important features of reality. For example, most of what is known about magnetic monopoles in grand unified theories was discovered first in a toy theory that includes only three Higgs fields, while the simplest realistic grand unified theory includes twenty-four of them. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory |  |
| transactinide | is a kind of transuranium element |  |
| transformation | is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| transient X-ray source | has definition As of early 1974, four had been detected: Cen X-2, Cen X-1, 2U 1543-47, and Cep X-4. They resemble slow novae. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of X-ray source |  |
| transit | has definition The passage of a smaller, nearer astronomical object across the face of a larger object in the background, as in a transit of Venus across the Sun. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of occultation phase |  |
| is followed by emersion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| is preceeded by immersion | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif) |
| transit telescope | has definition A stationary support structure for a telescope. Motion is allowed along the meridian from the zenith to the horizon, but stars cannot be tracked east/west. Measurements are only possible when the objects "transit" the meridian due to the Earth's rotation. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Earth based telescope |  |
| transition metal | is a kind of column grouped element |  |
| is a kind of metallic element |  |
| transuranium element | has atomic number greater than 92 |  |
| has definition A synthetic element with atomic number greater than 92 (uranium) | ![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:24.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of actinide |  |
| is a kind of synthetic element |  |
| transverse wave | has definition Wave vibrating at right angles to the direction of propagation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of wave |  |
| Triangulum | has acronym Tri |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Trianguli |  |
| has synonym Triangle |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Triangulum Australe | has acronym TrA |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Trianguli Australis |  |
has synonym Southern Triangle  |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| triassic period | has duration 49 million years |  |
| has start time 230 million years ago |  |
| is a kind of mesozoic era |  |
| Trifid Nebula | has definition An emission nebula in Sagittarius. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 1 kpc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 9000 light years |  |
has image    |  |
| has Messier number 20 |  |
| has synonym M 20 |  |
| has synonym NGC 6514 |  |
| is a part of Sagittarius |  |
| is an instance of gaseous nebula |  |
is an instance of Messier object  |  |
| trigonometric pi | has value 3.1415926535 |  |
| is an instance of mathematical constant |  |
| triple star | has definition A star system having three stars that revolve around one another. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of stars 3 |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| is a kind of star system |  |
| tritium | has atomic mass 3.016 |  |
| has decay mode β- (0.01861 Mev) 100% |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has definition A short-lived isotope of hydrogen. Tritium does not exist naturally on Earth. |  |
| has half life 12.26 years |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 28.5335 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has NMR frequency 106.663 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.97896 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 1/2 |  |
| has number of neutrons 2 |  |
| has number of nucleons 3 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 1.21 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 3H |  |
| has synonym hydrogen 3 |  |
| has uses research, diagnostic |  |
is an instance of hydrogen  |  |
| triton | has charge 1 |  |
| Triton | has definition The inner satellite of Neptune, discovered by Lassell in 1846. It is larger than the Moon (R ≈ 2900 km), with an almost circular retrograde orbit of 5 days 21 hours. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| triton | has definition The nucleus of the tritium atom. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol T |  |
| Triton | is a part of Neptune |  |
| triton | is an instance of charged particle |  |
| Triton | is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| triton | is an instance of nucleus |  |
| is an instance of radioactive particle |  |
| Trojan asteroid | has definition Asteroid located at the points of Jupiter's orbit around the Sun that are equidistant from the Sun and Jupiter. About 15 are now known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of asteroid |  |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| see also Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif) |
| tropical year | has definition The interval of time between two successive vernal equinoxes. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The period of one complete revolution of the mean longitude of the sun with respect to the dynamical equinox. The tropical year is longer than the Besselian year by 0s.148 T, where T is centuries from B1900.0. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 365.242 mean solar days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of year |  |
| tropopause | has altitude 5 km |  |
| has definition Upper boundary of the troposphere, where the temperature gradient goes to zero. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of troposphere |  |
| troposphere | has altitude 0 to 15 km |  |
| has definition Lowest level of Earth's atmosphere, from zero altitude to about 15 km above the surface. This is the region where most weather occurs. Its temperature decreases from about 290 K to 240 K. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 240 to 290 K |  |
| is a part of atmosphere |  |
| Tucana | has acronym Tuc |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Tucanae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin Kepler and Riccioli, called it Anser Americanus (the American Goose), |  |
| has synonym Toucan |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| Tully-Fisher relation | has definition An observed relation between the intrinsic luminosity of a spiral galaxy and the rotational speed of its stars. More luminous galaxies have stars that are moving faster. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| tungsten | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Tunguska meteorite | is a kind of comet impact  |  |
| twin-exhaust model | has definition A theoretical model for radio galaxies in which a compact source in the galactic nucleus is assumed to emit twin beams of rapidly moving plasma that traverse hundreds of thousands of light-years, eventually splattering to a halt in the ambient intergalactic gas, where the resulting dissipation energizes the radio lobes. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy theory |  |
| Twistor Theory | has definition Model of the Universe proposed by Roger Penrose, based on the application of complex numbers (involving (-1)1/2) used in calculations in the microscopic world of atoms and quantum theory to the macroscopic ordinary world of physical laws and relativity. The result is an eight-dimensional concept of reality that although complicated is possibly a more logical understanding of the constitution of the Universe. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| Two-Micron All-Sky Survey | has acronym 2MASS |  |
is an instance of sky survey  |  |
| Tycho's star | has definition Remnant of a Type I supernova (B Cas), 3-5 kpc distant, which Tycho observed and described in 1572. At its peak it was as bright as Venus and was visible in the daytime, reaching a magnitude of about -4. It is an X-ray source (2U 0022+63). (3C 10) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of type I supernova |  |
| Tycho-2 catalog | is a kind of star catalog |  |
| type I string theory | has definition One of the five superstring theories; involves both open and closed strings. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of superstring theory |  |
| type I supernova | has absolute magnitude Mv = -14 to -17 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A gigantic stellar explosion in which the star's luminosity suddenly increases by as much as a billion times. Most of the star's substance is blown off, leaving behind, at least in some cases, an extremely dense core which may be a neutron star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A supernova which may be produced by the thermonuclear detonation of a highly degenerate core produced by mass transfer from a companion star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has ejecta velocity 10000 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency less common than type II supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has location spiral and elliptical galaxies | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass lower than type II supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectra nonhydrogen lines | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| type II supernova | has absolute magnitude Mv = - 12 to - 13.5 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A gigantic stellar explosion in which the star's luminosity suddenly increases by as much as a billion times. Most of the star's substance is blown off, leaving behind, at least in some cases, an extremely dense core which may be a neutron star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has ejecta velocity 5000 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 0.01 to 0.05 per year (in our Galaxy) |  |
| has location young, massive stars near the edge of spiral arms | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass higher than type II supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectra hydrogen lines | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif) |
| type IIA string theory | has definition One of the five superstring theories; involves closed strings with left-right symmetric vibrational patterns. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of superstring theory |  |
| type IIB string theory | has definition One of the five superstring theories; involves closed strings with left-right asymmetric vibrational patterns. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of superstring theory |  |
| type III supernova | has definition A gigantic stellar explosion in which the star's luminosity suddenly increases by as much as a billion times. Most of the star's substance is blown off, leaving behind, at least in some cases, an extremely dense core which may be a neutron star. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Supernova similar to Type II | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass much higher than type II supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of supernova | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| Télescope Combiné de Schmidt | has altitude 105 m |  |
| has aperture 0.84 m |  |
| has creation date 1958 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.5 |  |
| has latitude 50° 48' N |  |
| has location Uccle, Bruxelles, Belgium |  |
| has longitude 4° 21'E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.2 m |  |
| has mirror maker Cox, Hargreaves, Thomson |  |
| has mirror type borosilicate |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Zeiss (Jena) |  |
| has owner Observatoire Royal de Belgique |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| Télescope de Schmidt | has altitude 1270 m |  |
| has aperture 0.90 m |  |
| has creation date 1981 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.5 |  |
| has latitude 43° 45' N |  |
| has location Calern, France |  |
| has longitude 6° 56'W |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.52 m |  |
| has mirror maker Jean Texereau |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer C.M.G-Paris |  |
| has owner Observatoire de Calem |  |
| has synonym Calem Schmidt |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| U Geminorum | has image   |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
is an instance of U Geminorum star  |  |
| U Geminorum star | has definition A type of dwarf nova. All U Geminorum stars are binaries containing a white dwarf and a red dwarf with total masses of roughly 1-2 Msun and with periods of less than 12 hours (period of U Gem, 1.5 × 104 seconds). About 150 are known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype U Geminorum |  |
| is a kind of dwarf nova |  |
| U line | has species sodium (Na I) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength 3302 Å | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectral line |  |
| U velocity | has definition The component of a star's motion away from the Galactic center. If a star moves away from the Galactic center, the star's U velocity is positive; if a star moves toward the Galactic center, the U velocity is negative; and if the star moves neither toward nor away from the Galactic center, the U velocity is zero. The Sun has a U velocity of -9 kilometers per second, so the Sun is moving toward the Galactic center at 9 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galactic velocity component |  |
| U(1) | has definition The symmetry of the electromagnetic field. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of elementary particle symmetry |  |
| UBC-Laval Telescope | has acronym LMT |  |
| has altitude 50 m |  |
| has aperture 2.7 m |  |
| has creation date 1992 |  |
| has focal ratio f/1.887 |  |
| has latitude 49° 07' N |  |
| has limitation views a 21' field at local zenith (centered on declination +49° 1) |  |
| has location Vancouver, BC, Canada |  |
| has longitude 122° 35' W |  |
| has mirror maker P Hickson |  |
| has mirror type rotating liquid mercury container |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Univ. of British Col. |  |
| has optical design Paraboloid, field corr. |  |
| has owner Univ. of B.C. and Laval Univ. |  |
| is an instance of fixed vertical mount telescope |  |
| is an instance of Newtonian |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| UHF band | has frequency 300 MHz to 3 GHz |  |
| has wavelength 10 cm to 1 m |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| ULF band | has frequency 30 Hz or less |  |
| has wavelength 10000 km and higher |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| ultra-luminous infrared galaxy | has acronym ULIRG |  |
| is a kind of infrared galaxy |  |
| ultraviolet | has acronym UV |  |
| has definition Electromagnetic radiation "beyond the violet" with wavelengths in the approximate range 100-4000 Å. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength slightly shorter than that of visible light. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Part of the electromagnetic spectrum immediately above visible light (but below gamma-rays and X-rays); it therefore comprises a range of radiation of shorter wavelength and higher frequency than those of visible light. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 750 THz to 30 PHz |  |
| has wavelength 10 to 400 nm |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| ultraviolet Ga star | has definition Bp star which exhibits a strong 1414 line of Ga II in the ultraviolet spectrum . | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Bp star |  |
| ultraviolet star | has definition Very hot prewhite-dwarf star; usually the hot central star of a planetary nebula which is contracting toward the white-dwarf state. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of central star of planetary nebula |  |
| ultraviolet-bright star | has definition Star that is brighter than horizontal-branch stars and bluer than giant-branch stars. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of central star of planetary nebula |  |
| Umbriel | has definition A satellite of Uranus. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Lassell | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1851 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 4.1 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 200 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Uranus |  |
| is an instance of natural satellite |  |
| Umklapp scattering | has definition The contribution to scattering caused when the exchange of momentum crosses the boundary of a Brillouin zone. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| uncertainty principle | has corollary it is impossible to measure an atomic or nuclear process without at the same time disturbing or altering the process. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The principle that the fundamental uncertainty in a variable times that in its canonical conjugate is of the order of Planck's constant. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Werner Heisenberg | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
has equation | Relation | Conjugates |
|---|
| ΔxΔp ≥ h | position, momentum | | ΔEΔt ≥ h | energy, time |
|  |
| has example the uncertainty in the measurement of the position of an electron varies inversely as the uncertainty in the measurement of its momentum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has implication the microscopic realm is a roiling frenzy, awash in a violent sea of quantum fluctuations. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym Heisenberg uncertainty principle | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| unclassified globular cluster | is a kind of globular cluster |  |
| unclassified oceanic element | has ocean concentration unknown |  |
| has ocean residence time unknown |  |
| is a kind of oceanic element |  |
| unified atomic mass unit | has symbol u |  |
| has value in SI unit 1.66054 × 10-27 kg, approximately |  |
| is an instance of non SI unit |  |
| unified theory | has definition Any theory that describes all four forces and all of matter within a single, all-encompassing framework. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition In particle physics, any theory exposing relationships between seemingly disparate classes of particles. More generally, a theory that gathers a wide range of fundamentally different phenomena under a single precept, as in Maxwell's discovery that light and magnetism are aspects of a single, electromagnetic force. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of theory |  |
| uniformitarianism | has antonym catastrophism |  |
| has definition The hypothesis that the extensive changes in the earth, as evinced in the geological record, have resulted, not from massive catastrophes, but from the slow operation of wind, weather, volcanism, and the like over many millions of years. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of doctrine |  |
| unit | has historical origin |  |
| is a kind of mathematical concept |  |
| represents |  |
| unit prefix | has rule - multiple prefixes may not be used
- any unit prefix can be used with any SI unit
|  |
| has value strictly represented by powers of 10 except for information technology units such as bits |  |
| is a kind of constant |  |
| unitary transformation | has definition A transformation whose reciprocal is equal to its Hermitian conjugate. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol U |  |
| is a kind of transformation |  |
| United Kingdom Infrared Telescope | has acronym UKIRT |  |
| has altitude 4194 m |  |
| has aperture 3.802 m |  |
| has creation date 1978 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.5, 36 IR |  |
| has latitude 19° 50' N |  |
| has location Mauna Kea, Hawaii, US |  |
| has longitude 155° 28' W |  |
| has mirror maker Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting English-yoke equatorial |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Hadfields Ltd. (Sheffield) |  |
has owner Joint Astronomy Centre  |  |
| has purpose infrared work only |  |
is an instance of Cassegrain  |  |
| is an instance of English equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
| United Kingdom Schmidt Telescope Unit | has acronym UKST |  |
| has altitude 1145 m |  |
| has aperture 1.24 m |  |
| has creation date 1973 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.5 |  |
| has latitude 31° 16' S |  |
| has location Siding Spring Mtn., Australia |  |
| has longitude 149° 04' E |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.83 m |  |
| has mirror maker Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb-Parsons |  |
has owner Anglo-Australian Observatory  |  |
| has synonym U.K. Schmidt |  |
is an instance of Schmidt  |  |
| universal constant | is a kind of fundamental physical constant |  |
| Universe | has definition The total celestial cosmos. According to Gott et al. the universe seems to be on a large scale isotropic, homogeneous, matter-dominated, and with negligible pressure. The total proper mass content of about 1023 Msun (Sandage derives 1056 g from his determination of the deceleration parameter q0) and radius of about 2 × 1028 cm are the order of magnitude that most cosmologists would accept if the universe is bounded. Total mass contributed by luminous matter, about 3 × 1053 g (see mass discrepancy). Age about 18 × 109 yr for a Hubble constant H0 = 55 km s-1 Mpc-1. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of kbTop |  |
| unmanned spacecraft | has crew none |  |
| has definition an artificial satellite without a crew |  |
| is a kind of artificial satellite |  |
| unstable Lagrangian point | has equilibrium unstable | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Lagrangian point | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif) |
| up | has charge 2/3 |  |
| has definition A flavor of quark |  |
| is an instance of light quark |  |
| upper chromosphere | has composition ionized hydrogen |  |
| has definition The upper part of the chromosphere and consists of hot, ionized hydrogen. It has an emission spectrum (see flash spectrum). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has density ρ ≈ 10-16 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has location 4000 to 12000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature 106 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of chromosphere |  |
| upper culmination | has definition Passage of a celestial object across the observer's meridian. The crossing closer to the observer's zenith. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym culmination above pole | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of culmination | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif) |
| upper precambrian period | has duration million years |  |
| has start time million years ago |  |
| is a kind of precambrian era |  |
| uranium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state VI |  |
| has ocean residence time 300000 years |  |
| is a kind of accumulating oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of actinide |  |
| uranium 235 decay | is an instance of spontaneous fission |  |
| uranium 235 splitting | is an instance of neutron induced fission |  |
| Uranus | has albedo 0.66 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition H2 and CH4 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Seventh planet from the Sun. Has retrograde rotation. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Herschel | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date March 13, 1781 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.04 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity 22 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 0°.8 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 8.78 × 1028 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has maximum brightness +5.7 mag | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 1.21 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 19.18 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has oblateness 0.07 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 97°.9 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 84.0 years | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity 6.8 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 25400 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 10h49m26s | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has satelites 5 major ones, all of which orbit in its equatorial plane | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 0.96 Earth's | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 110 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| has synodic period 369.66 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of gas giant |  |
| is an instance of superior planet | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif) |
| Urca process | has definition A series of nuclear reactions, primarily among the iron group of elements, accompanied by a high rate of neutrino formation and postulated as a cause of stellar collapse. Neutrinos carry away energy quickly and invisibly, so this process was named for the Urca casino in Rio de Janeiro, which carried away money the same way. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nuclear process |  |
| Ursa Major | has acronym UMa |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Ursae Majoris |  |
| has historical origin wagon or cart, a plow, a bull's thigh, and (to the Chinese) the government |  |
| has synonym Big Dipper |  |
| has synonym Great Bear |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Ursa Minor | has acronym UMi |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Ursae Minoris |  |
| has synonym Little Bear |  |
| has synonym Little Dipper |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| Ursa Minor Dwarf | has definition An intrinsically faint (Mv ≈ - 9) dwarf elliptical galaxy, a member of the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 70 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is a part of Ursa Minor |  |
| is a part of Ursa Minor |  |
| is an instance of dwarf elliptical satellite galaxy | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif) |
| orbits Milky Way |  |
| UV Ceti | has angular separation 1".0 |  |
| has apparent magnitude Mv = 15.3 and 15.8 |  |
| has definition Late-type dwarf with spectra showing hydrogen emission lines. Faint flare star of very low mass. Like other flare stars, it is a member of a binary system in which both components are of nearly equal brightness. Radio flares have also been observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 2.8 pc |  |
| has eccentricity e = 0.615 |  |
| has mass 0.15 Msun |  |
| has orbital period 26.5 years |  |
| has spectral type M6e V |  |
| has synonym Luyten 726-8 B |  |
| is a part of Cetus | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of binary star |  |
| is an instance of dMe star |  |
| is an instance of flare star |  |
| UV Ceti star | has definition Late-type dwarfs with spectra showing hydrogen emission lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line hydrogen |  |
| has prototype UV Ceti |  |
| has spectral type dKe star, dMe star |  |
| is a kind of dwarf |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| UVES | has definition Ultraviolet Echelle Spectrograph. | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of spectrograph |  |
| V velocity | has definition A star's velocity in the direction of Galactic rotation, as measured relative to a nearby star that has a circular orbit. If a star revolves faster than such a star, the V velocity is positive; if it revolves more slowly, the V velocity is negative; and if both revolve at the same rate, the V velocity is zero. The Sun has a V velocity of +12 kilometers per second, so it revolves 12 kilometers per second faster than it would if it had a circular orbit. Since a star on a circular orbit revolves around the Galaxy at 220 kilometers per second, a star with a V velocity of 0 is not stationary; rather, it revolves at 220 kilometers per second. The Sun therefore revolves around the Galaxy at 220 + 12 = 232 kilometers per second. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galactic velocity component |  |
| Van Allen belt | has definition One of two doughnut-shaped belts in the Earth's magnetosphere, where many energetic charged particles from the solar wind are trapped in Earth's magnetic field. The energy of the particles is highest in the inner belt. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition One of two toroidal zones of high radiation in Earth's upper atmosphere, above the equator, caused by the trapping of charged particles in the magnetosphere. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| has location above the equator | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| has shape toroidal | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of magnetosphere |  |
| van der Waals force | has definition The relatively weak attractive force operative between neutral atoms and molecules. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of force quantity |  |
| van Maanen | has career Mt. Wilson |  |
| has name Adrian van Maanen |  |
| is an instance of 19th century scientist |  |
| is an instance of astronomer |  |
| van Maanen's star | has density 4 × 105 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 4 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of white dwarf |  |
| vanadium | has abundance 1.05 × 104 in Sun relative to H = 1 × 1012 |  |
| has abundance 1.1 × 10-3 p.p.m. in Atlantic surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.6 × 10-3 p.p.m. in Pacific surface seawater |  |
| has abundance 1.8 × 10-3 p.p.m. in deep Pacific seawater |  |
| has abundance 160 p.p.m. in Earth's crust |  |
| has atomic emission line 318.398 nm for V I |  |
| has atomic emission line 318.540 nm for V I (used in atom absorption spectrometry) |  |
| has atomic emission line 399.864 nm for V I |  |
| has atomic emission line 411.178 nm for V I |  |
| has atomic emission line 438.472 nm for V I |  |
| has atomic emission line 437.924 nm for V I (strong) |  |
| has atomic number |  |
| has atomic radii 132 pm |  |
| has biological role essential to some species including humans; stimulates metabolism |  |
| has boiling point 3650 K |  |
| has bulk modulus 158 GPa |  |
| has chief source descloizite, patronite, vanadinite, carnotite |  |
| has crystal cell dimension a = 302.40 pm |  |
| has crystal type b.c.c. |  |
| has daily dietary intake 0.04 mg |  |
| has definition shiny, silvery metal, soft when pure. Resists corrosion due to a protective film of oxide |  |
| has density 5550 kg m-3 for liquid at 2160 K melting point |  |
| has density 6110 kg m-3 for solid at 292 K |  |
| has discoverer A.M. del Rio |  |
| has discovery date 1801 |  |
| has discovery location Mexico City, Mexico |  |
| has electrical resistivity 24.8 × 10-8 Ω m at 293 K |  |
| has electron affinity 50.7 kJ mol-1 from V to V- |  |
| has electron configuration [Ar]3d34s2 in ground state |  |
| has electronegativity 1.63 Pauling |  |
| has hazard irritates eyes and lungs; highly toxic fumes |  |
| has hazard mutagenic effect in some experimental compounds |  |
| has heat capacity 24.89 J K-1 mol-1 for solid at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat capacity 26.012 J K-1 mol-1 for gas at constant pressure 0.1 MPa at 298.15 K |  |
| has heat of fusion 17.6 kJ mol-1 |  |
| has heat of vaporization 458.6 kJ mol-1 |  |
has image  |  |
| has ionic radii 59 pm for V5+ |  |
| has ionic radii 61 pm for V4+ |  |
| has ionic radii 65 pm for V3+ |  |
| has ionic radii 72 pm for V2+ |  |
| has isotope mass range 44 to 55 |  |
| has lethal intake 10 mg kg-1 V2O5 ingested by rat |  |
| has level in humans < 0.0002 mg dm-3 in blood |  |
| has level in humans 0.0035 p.p.m. in bone |  |
| has level in humans 0.006 p.p.m. in liver |  |
| has level in humans 0.02 p.p.m. in muscle |  |
| has linear expansion coefficient 8.3 × 10-6 K-1 |  |
| has longest lived isotope vanadium 51 |  |
| has main mining area not mined as such, obtained as ore by-product and from Venezuelan oils |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 233 cm2 g-1 for CuKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass absorption coefficient 27.5 cm2 g-1 for MoKalpha X-ray diffraction |  |
| has mass magnetic susceptibility +6.28 × 10-8 kg-1 m3 for solid |  |
| has mass of element in person 0.11 mg for a 70 kg average person |  |
| has melting point 2160 K |  |
| has mineral carnotite, descloizite, patronite, vanadinite |  |
| has molar volume 8.34 cm3 |  |
| has name origin Vanadis = Scandinavian goddess from Scandinavian |  |
| has neutron scattering length -0.0382 × 10-12 cm |  |
| has number of isotopes 11 including nuclear isomers |  |
| has number of protons 23 |  |
| has ocean oxidation state V |  |
| has ocean residence time 50000 years |  |
| has poisson's ratio 0.365 GPa |  |
| has pronunciation van-ay-di-uhm |  |
has registry number 7440-62-2 for Chemical Abstracts System database  |  |
| has relative atomic mass 50.9415 in units of 12C = 12.000 |  |
| has rigidity modulus 46.7 GPa |  |
| has space group Im3m |  |
| has specimen foil, granules, powder, rod, turnings. Care ! |  |
| has symbol V |  |
| has term symbol 4F3/2 in ground state |  |
| has thermal conductivity 30.7 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K |  |
| has thermal neutron capture cross section 5.08 barns |  |
| has toxic intake varies |  |
| has uses alloys, especially in steel |  |
| has world production 7000 tonnes year-1 |  |
| has young's modulus 127.6 GPa |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| reacts with concentrated acids |  |
| vanadium 47 | has atomic mass 46.954906 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (2.927 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode EC |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 32.6 minutes |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 3/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons |  |
| has number of nucleons |  |
| has symbol V |  |
is an instance of vanadium  |  |
| vanadium 48 | has atomic mass 47.952257 |  |
| has decay mode β+ (4.015 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode γ |  |
| has half life 15.98 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 2.01 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 4+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons |  |
| has number of nucleons |  |
| has symbol V |  |
is an instance of vanadium  |  |
| vanadium 49 | has atomic mass 48.948517 |  |
| has decay mode EC (0.601 Mev) |  |
| has decay mode no γ |  |
| has half life 337 days |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = 4.47 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons |  |
| has number of nucleons |  |
| has symbol V |  |
is an instance of vanadium  |  |
| vanadium 50 | has atomic mass 49.947161 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 2.6491 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 0.25% |  |
| has NMR frequency 9.970 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 0.755 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +3.34745 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment 0.210 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 6+ h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 27 |  |
| has number of nucleons 50 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.0555 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 50V |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of vanadium  |  |
| vanadium 51 | has atomic mass 50.943962 |  |
| has magnetogyric ratio 7.0362 × 107 rad T-1 s-1 |  |
| has natural abundance 99.75% |  |
| has NMR frequency 26.289 MHz where 1H = 100 MHz; 2.3488 T |  |
| has NMR receptivity 2150 where 13C = 1.00 |  |
| has nuclear magnetic moment μ = +5.1574 nuclear magnetons with diamagnetic correction |  |
| has nuclear quadrupole moment -0.052 × 10-28 m2 |  |
| has nuclear spin I = 7/2- h/2π |  |
| has number of neutrons 28 |  |
| has number of nucleons 51 |  |
| has relative NMR sensitivity 0.38 where 1H = 1.00 |  |
| has symbol 51V |  |
| has uses isotopically enriched samples available for experimental purposes |  |
| has uses Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |  |
is an instance of vanadium  |  |
| variable | has amplitude |  |
| has definition A star that varies in luminosity. The first variable discovered in a given constellation has the letter R preceding the name of the constellation. Then S, . . . , Z. Then RR, RS, . . . , Rz, SS, . . . , Sz, . . . , ZZ. Then AA, . . . , AZ (the letter J is never used), BB, . . . , BZ, . . . , QQ, . . . QZ. The next variable (the 335th) is given the designation V335. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A star whose light varies. Some variables vary simply because they consist of two stars, one of which eclipses the other; Algol is the most famous example. Other variables, however, vary because the stars themselves actually change in brightness; the most famous are the Cepheids, RR Lyraes, and Miras, all of which pulsate. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star whose luminosity changes over periods of time; there are many reasons and many types. Periods vary widely in length and even regularity. Novae and supernovae are classed as variables. The present brightest variable star is Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis). | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition a star whose apparent magnitude varies by at least 0.1 magnitudes in the visible spectrum (a star whose optical brightness variations can be detected by the human eye) | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has light curve |  |
has name designated with - R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, or Z and the genitive of the latin constellation name
- RR, RS, RT, RU, RV, RW, RX, RY, or RZ and the genitive of the latin constellation name when the single letter designations are exhausted
- AA...AZ, BB...BZ, etc. (omitting J), which ends with QQ...QZ and the genitive of the latin constellation namewhen the RR...RZ designations are exhausted
- V 335, V 336, etc., when the double letter designations are exhausted
|  |
has observable variation time scale within a period of decades  |  |
| has observational problem some difficulty in distinguishing between various kinds |  |
| has optical brightness variation 0.2 magnitudes or greater |  |
| is a kind of star |  |
| variable-mass theory | has definition A theory of Hoyle and Narlikar in which the masses of fundamental particles are assumed to vary with time in a manner that precisely accounts for the Hubble redshift law. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cosmology theory |  |
| vector boson | carries the force electroweak |  |
| has acronym IVB |  |
| has definition A hypothetical elementary particle that acts as intermediary for the weak interaction, carrying its effect from one particle to another as the photon does for electromagnetic interactions and as various mesons do for the strong interactions. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Also called the intermediate vector boson. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Force-carrying particles of nature. Three vector bosons are responsible for the weak nuclear force. By admitting the photon on an equal footing it is possible to create a unified electroweak theory. As a result of symmetry-breaking processes, however, this photon remains massless while the three other vector bosons pick up mass. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of carrier boson |  |
| is a kind of hypothetical particle |  |
| see also Weinberg-Salam theory |  |
| vector translation | has definition The small theoretical precession of the axis of an orbiting body due to the gravitational influence of its primary. This effect is predicted by general relativity, but so far it has not been observed. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of precession |  |
| is an instance of prediction |  |
| Vega | has B-V magnitude 0.00 |  |
| has declination +38 47 01 |  |
| has definition The fifth brightest star in the night sky. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 25 light-years |  |
| has right ascension 18 36 56.2 |  |
| has spectral type A0Va |  |
| has synonym alpha Lyr | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HR 7001 |  |
| has V magnitude 0.03 |  |
is a part of Lyra  |  |
| is an instance of A star |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| Vela | has acronym Vel |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Velorum |  |
| has synonym Ship's Sail |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation formerly part of Argo Navis  |  |
| Vela pulsar | has definition A compact radio source about 400-500 pc distant associated with the Vela supernova remnant (q.v.). It has a nonthermal radio spectrum and is about 20 percent polarized. It is associated with the Gum Nebula, the Vela pulsar, and the X-ray source 2U 0832-45, although the pulsar and the X-ray source are displaced about 0°.7 from the center of the Vela X radio emission. Vela Y and Vela Z are outlying components, also nonthermal, but too weak to exhibit polarization. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A pulsar about 400-500 pc distant, probably associated with the Vela supernova remnant. Period 0.0892 seconds. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym PSR 0833-45 |  |
| has synonym Vela X |  |
| is a part of Vela |  |
| is an instance of pulsar |  |
| Vela satellite | has altitude 120000 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:28.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A sequence of satellites launched to monitor possible violations of the nuclear test ban treaties. The system consists of four satellites in a circular orbit around the Earth with a radius of 120000 km. The Vela satellites have detected cosmic gamma-ray bursts (q.v.). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:27.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of military spacecraft |  |
| Vela supernova remnant | has definition A gaseous nebula in the middle of the Gum Nebula, the remnant of a Type II supernova whose light reached Earth about 10000 to 30000 years ago. It consists of bright filaments that form a D-shaped ring in Hα and a rough circle in the ultraviolet. It includes the Vela X, Y, and Z radio complexes and is a strong X-ray source. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Vela |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| Vela X-1 | has apparent magnitude 7 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass of unseen companion 1.7 to 15 Msun, with a probable value of about 2.6 Msun. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 8.96 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type B0.5 Ib | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym 3U 0900-40 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym HD 77581 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of B star |  |
| is an instance of eclipsing binary |  |
| is an instance of single line spectroscopic binary |  |
| is an instance of supergiant |  |
| is an instance of X-ray source |  |
| velocity | has base unit length per unit time |  |
| has definition The speed and the direction of an object's motion. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of quantity |  |
| velocity unit | has definition meter per second |  |
| has symbol m·s-1 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| velocity-of-light radius | has definition The radius of a rotating neutron star at which the rotational velocity of the plasma approaches the velocity of light. (also called velocity-of-light cylinder) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of radius |  |
| Venezuela 1-meter Schmidt | has altitude 3610 m |  |
| has aperture 1.00 m |  |
| has comment has a 1-m objective prism |  |
| has creation date 1978 |  |
| has focal ratio f/3.0 |  |
| has latitude 8° 47' N |  |
| has location Llano del Hato, Merida, Venezuela |  |
| has longitude 70° 52' W |  |
| has mirror diameter 1.52 m |  |
| has mirror maker Askania |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Askania |  |
| has optical design Concentric Schmidt |  |
| has owner Centro "EJ. Duarte" |  |
| is an instance of Bent-yoke equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of Schmidt |  |
| Venus | has albedo 0.76 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has atmosphere composition 90-95% CO2, remainder primarily N2, traces of water vapor, oxygen, HF, HC1 (by volume) |  |
| has atmospheric pressure 92-95 atm | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has cloud altitude 44 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Second planet from the Sun. Has retrograde rotation. Mariner 10 has established that the cloud tops rotate every 4 hours retrograde. Radar experiments have established that the surface is somewhat smoother than the Moon, but there are mountains and there is extensive cratering. Last transit of Sun was in 1882; next one will be 2004. Venus's rotation period is in synchronism with Earth - that is, at inferior conjunction the same side is always toward the Earth. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.0068 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has escape velocity Vesc = 10.3 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 3°.39 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has mass 4.872 × 1027 g | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has maximum elongation 48° | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean density 5.16 g cm-3 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has mean distance from Sun 0.7233 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has obliquity 3° R | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period 224.7 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital velocity 35 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has radius 6056 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 243.09 ± 0.5 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface gravity 8 m s2 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has surface temperature 743 ± 8 K (from Venera 8) |  |
| has synodic period 583.9 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature of cloud tops 250 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of our solar system |  |
| is an instance of naked eye planet |  |
| is an instance of terrestrial planet |  |
| vernal equinox | has date on or around 21 March | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The ascending node of the ecliptic on the celestial equator; also the time at which the apparent longitude (see apparent place; longitude, celestial) of the Sun is 0°. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The point of intersection between the ecliptic and the celestial equator, where the Sun crosses from south to north. It is sometimes called the First Point of Aries because several thousand years ago it was in Aries. Because of precession it has now slid west into Pisces and in 200-300 years it will edge into Aquarius. By definition, the vernal equinox is at α = 0°, δ = 0°. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym First Point of Aries | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym spring equinox | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of equinox |  |
| Very Large Array | has acronym VLA |  |
| has angular resolving power 1 arcsecond | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A radio telescope distributed along three 13-mile-long arms of a Y-shaped track. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has element aperture 82 feet | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif) |
has image   |  |
| has number of elements 27 | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif) |
| has position near Socorro, Atacama desert, New Mexico, USA |  |
has reference NRAO Very Large Array  |  |
| is an instance of radio interferometer |  |
| Very Large Telescope | has acronym VLT |  |
| has altitude 2640 m |  |
| has aperture 16 m equivalent |  |
| has comment Four separate telescopes and domes, first unit became operational in 1998 |  |
| has creation date 2001 |  |
has diagram   |  |
| has element aperture 8.2 m |  |
| has focal ratio f/13.5, 15 (each mirror) |  |
has image   |  |
| has latitude 24° 51' S |  |
| has location Cerro Paranal, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 27' W |  |
| has mirror maker REOSC |  |
| has mirror type Schott Zerodur, active optics |  |
| has number of elements 4 |  |
| has owner European Southern Observatory |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of array telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| Very Large Telescope Interferometer | has acronym VLTI | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of array telescope |  |
| Vesta | has albedo 0.24 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An asteroid in diameter. It is the brightest of all minor planets, at times approaching naked-eye visibility. Its spectrum can also be interpreted to mean a rotation period of 10h40m58s.84. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 500 km | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has discoverer Olbers | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has discovery date 1807 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has eccentricity e = 0.09 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has inclination i = 7°.1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has orbital period P = 1325 days | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotation period 5h20m31s.665 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has semi-major axis a = 2.361 AU | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| has visual magnitude 5.5 (at mean opposition) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of asteroid belt |  |
| is an instance of asteroid | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif) |
| VF band | has frequency 30 to 300 Hz |  |
| has uses submarine communication |  |
| has wavelength 1000 to 10000 km |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| VHF band | has frequency 30 to 300 MHz |  |
| has wavelength 1 to 10 m |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| vibrational energy | has definition Motion of the pair of nuclei in a diatomic molecule along the direction of the internuclear axis (cf. rotational energy). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| Victor M. Blanco Telescope | has altitude 2215 m |  |
| has aperture 4.001 m |  |
| has creation date 1976 |  |
| has focal ratio f/2.8, 8.0 |  |
| has latitude 30° 10' S |  |
| has location Cerro Tololo, Chile |  |
| has longitude 70° 49' W |  |
| has mirror maker KPNO Optical Shop |  |
| has mirror type Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Western Gear Corp. |  |
has owner Cerro Tololo Inter-American Obs.  |  |
| has synonym CTIO 4 meter |  |
| is an instance of Horseshoe equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of Ritchey-Chrétien  |  |
| vidicon | has definition General name for the class of vacuum tube imaging devices which employ a scanning electron beam to read out the image. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of image tube |  |
| violent galaxy | has definition A type of galaxy differentiated only recently. Violent galaxies include QSOs and exploding galaxies like M82. About 1 percent of the galaxies are classified as violent. Violent galaxies release on the average 1058 ergs of energy, compared with a supernova release of 1049 ergs. Nearest violent galaxy is Cen A. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym eruptive galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym exploding galaxy | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of emission line galaxy |  |
| violet | is a kind of optical |  |
| Virgo | has acronym Vir |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Virginis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Virgin |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
is an instance of zodiacal constellation  |  |
| Virgo cluster | has definition An irregular cluster including the giant elliptical M87 (the galaxy of greatest known mass). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has members M87 |  |
| has number of galaxies 2500 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| has redshift z = 0.004 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Supercluster |  |
| is a part of Virgo |  |
| is an instance of rich cluster |  |
| Virgo infall | has definition The observed gravitational motion of nearby galaxies toward the Virgo cluster of galaxies, about 50 million light years away. The Virgo cluster represents a strong concentration of mass, a strong departure from a uniform distribution of matter, and it therefore causes galaxies in its vicinity to deviate from the Hubble flow. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galaxy motion |  |
| virial theorem | has definition For a bound gravitational system the long-term average of the kinetic energy is one-half of the potential energy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of thermodynamics law |  |
| virtual pair | has definition Particle and antiparticle that exist for an extremely short time, often as the intermediate stage of a nuclear transition. According to Dirac's theory, the vacuum can be visualized as consisting of a sea of virtual electron-positron pairs that can only be released or separated when sufficient energy is made available. | ![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of virtual particle |  |
| virtual particle | has definition A particle that exists for an extremely short time in an intermediate stage of a reaction or transition. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particles that erupt from the vacuum momentarily; they exist on borrowed energy, consistent with the uncertainty principle, and rapidly annihilate, thereby repaying the energy loan. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particles which take part in virtual processes. They are said to be "off mass-shell", meaning that the relation E2 = p2c2 + m02 c4 does not hold. | ![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Quantum uncertainties in energy make it possible for virtual particles to be constantly created and annihilated during elementary particle interactions. Elementary particles are able to make use of these virtual particles within their interactions. | ![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of particle |  |
| virtual phase | has definition A type of CCD in which only one electrode is physically outside the silicon and is such as to obscure only half of the pixel. A specially doped layer under the transparent part acts as another or virtual electrode. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| has number of electrodes 1 | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of charge-coupled device |  |
| visibility function | has definition The Fourier transformation of a distant radio source, normalized to its value at small antenna spacings. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Fourier transformation |  |
| visual binary | has definition A binary star which can be resolved into two components with current telescopes. | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of binary star |  |
| VLBA | has angular resolving power 15 microarcsecond |  |
| has effective diameter 12000 kilometers |  |
has image   |  |
has reference The Very Long Baseline Array  |  |
| is an acronym for Very Long Baseline Array |  |
| is an instance of radio interferometer |  |
| VLF band | has frequency 3 to 30 kHz |  |
| has wavelength 10 to 100 km |  |
| is a kind of radio |  |
| Volans | has acronym Vol |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Volantis |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has historical origin sailors in the south seas said they had seen schools of flying fish |  |
| has synonym Flying Fish |  |
| has synonym Piscis Volans |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation named by Bayer  |  |
| volt | has base unit m2·kg·s-3·A-1 |  |
| has symbol V |  |
| has unit W·A-1 |  |
| is an instance of electric potential unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| volume unit | has definition cubic meter |  |
| has symbol m3 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| von Klitzing constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol RK |  |
| has uncertainty 0.000095 Ω |  |
has value 25812.807572 Ω  |  |
| is an instance of electromagnetic constant |  |
| is an instance of resistance |  |
| Vulpecula | has acronym Vul |  |
has boundary   |  |
| has genitive Vulpeculae |  |
has historical image   |  |
| has synonym Little Fox |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
is an instance of constellation  |  |
| VV Cep | is a part of Cepheus |  |
| is an instance of VV Cep star |  |
| VV Cep star | has definition A composite spectrum star. One observes a spectrum of a K or M supergiant, showing emissions of hydrogen and [FeII] plus the spectrum of the secondary, which is generally of type B. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype VV Cep |  |
| is a kind of composite spectrum star |  |
| VV Cephei star | has definition Eclipsing binaries with M supergiant primaries and blue (usually B) supergiant or giant secondaries. They have a rich emission spectrum. Sandage (1974) suggests Mv = - 7.3 for the M2p component of VV Cep. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of eclipsing binary |  |
| VW Hydri | is a part of Milky Way |  |
is an instance of dwarf nova  |  |
| W particle | has definition Massive boson thought to have been abundant in the early universe, when the unified electroweak force was manifest. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle that transmits the unified electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces. These particles were predicted by the Weinberg-Salam theory of the 1960s and later discovered in the 1980s. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition See Intermediate Vector Boson. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of vector boson |  |
| W Ursae Majoris star | has definition A large class of double-lined eclipsing binaries with very short periods (a few hours) whose spectra indicate mass transfer. They are distinguished by the fact that their primary and secondary minima are equal. They are all F or G binaries on or near the main sequence. They may be the progenitors of dwarf novae. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of eclipsing binary |  |
| W velocity | has definition A star's velocity perpendicular to the Galactic plane. If a star is moving up, its W velocity is positive; if a star is moving down, its W velocity is negative; and if a star does neither, its W velocity is zero. The Sun has a W velocity of +7 kilometers per second, so it is moving up at 7 kilometers per second. In general, the greater a star's W velocity when it crosses the Galactic plane, the farther above and below the plane the star will travel. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of galactic velocity component |  |
| W3 | has definition A dense cloud of gas in the Perseus arm. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3 kpc |  |
| is a part of Perseus arm |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| W44 | has definition A radio source. It is a supernova remnant less than 0°.5 from the galactic plane. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 3 kpc |  |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| W49 | has definition A radio source (a giant H II region). It is the most powerful thermal radio source known in our Galaxy. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 14 kpc |  |
| is an instance of radio source |  |
| W51 | has definition A radio source, a supernova remnant. PSR 1919+14 lies within its radio contours. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of supernova remnant |  |
| water vapor | has symbol H2O |  |
| is an instance of interstellar molecule |  |
| is an instance of neutral particle |  |
| watt | has base unit m2·kg·s-3 |  |
| has definition Unit of power. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 107 ergs s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol W |  |
| has unit J·s-1 |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| is an instance of power unit |  |
| wave | has definition A propagating pattern of disturbance. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Propagation of energy by means of coherent vibration. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif) |
| has propagation direction |  |
| is a kind of harmonic motion |  |
| is a kind of motion |  |
| wave number unit | has definition reciprocal meter |  |
| has symbol m-1 |  |
| is a kind of derived SI unit |  |
| wave-particle duality | has definition Basic feature of quantum mechanics that objects manifest both wavelike and particle-like properties. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| wavefront modifier | has definition A device which modifies the wavefront shape, polarization or wavelength | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavefront modification shape, polarization or wavelength |  |
| is a kind of optical device |  |
| wavelength shift | changes property frequency (and wavelength) |  |
| has definition The alteration in frequency of electromagnetic radiation | ![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of radiation modification |  |
| WC star | has emission line He I, He II, C II, C III or C IV | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Wolf-Rayet |  |
| weak G-band star | has definition G-type giant (G5 to K5) with a very weak or absent G band of CH and weak CN bands. These stars are C-deficient. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of G star |  |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| weak gauge symmetry | has definition Gauge symmetry underlying the weak force. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of gauge symmetry |  |
| weak line star | has definition Late stars in which the lines of all metals are weakened when compared with normal stars of the same temperature. Also called metal-weak stars. | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif) |
| has metallic line strength small |  |
| is a kind of late star |  |
| weak mixing angle | has equation  |  |
| has symbol sin2θW |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0019 |  |
has value 0.2224  |  |
| is an instance of atomic constant |  |
| Weak-lined radio galaxy | has acronym WLRG |  |
| is a kind of radio galaxy |  |
| weakly interacting massive particle | has acronym WIMP | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A generic term for a class of hypothetical particle which may form the missing mass. A form of non-baryonic cold dark matter. | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Some astronomers believe that these exotic subatomic particles make up most of the mass of the universe. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of cold dark matter | ![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif) |
| weber | has base unit m2·kg·s-2·A-1 |  |
| has definition The derived SI unit of magnetic flux. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has equivalent 108 maxwells | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol Wb | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has unit V·s |  |
| is an instance of magnetic flux unit |  |
| is an instance of named derived SI unit |  |
| week | has definition An arbitrary period of days, usually seven days; approximately equal to the number of days counted between the four phases of the Moon. (See lunar phases.) | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif) |
| has value 7 days |  |
| is a kind of time unit |  |
| Werner line | has definition Spectral line of molecular hydrogen in the ultraviolet, in the same general region as the Lyman lines. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif) |
| has species H2 |  |
| has wavelength UV |  |
| is a kind of molecular band |  |
| Whirlpool galaxy | has discoverer Charles Messier |  |
| has discovery date 1773 |  |
has image   |  |
| has Messier number 51 |  |
| has synonym M 51 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym NGC 5194 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Canes Venatici | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
| is an instance of Messier object |  |
| is an instance of Sc spiral | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif) |
| whistlers | has definition Radio waves generated by a flash of lightning, which travel along Earth's magnetic field out beyond the ionosphere and back to Earth. They arrive back with a descending pitch because the high-frequency end of the wave train arrives first (see dispersion). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of ionosphere |  |
| white dwarf | has definition A small, faint, dense, dying star that has used up its nuclear fuel and is slowly fading from view. A typical white dwarf has 60 percent of the Sun's mass but is little larger than the Earth. White dwarfs are common, accounting for 10 percent of all stars in the Galaxy; the nearest is Sirius B, just 8.6 light-years away. But no white dwarf is visible to the naked eye. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Faint star lying five or more magnitudes below the main sequence. |  |
| has definition Faint very-compact stars at the end of their life. Also used as convenient photometric and flux standards. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Final stage of a star, at which the nuclear energy is exhausted. Cool, and becoming a dead, black body, it is nevertheless extremely dense. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Star of high surface temperature, low luminosity, and high density (105-108 g cm-3), with roughly the mass of the Sun and the radius of the Earth, that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel, believed to be a star near its final stage of evolution. When the Sun becomes a white dwarf, its radius will be about 0.01 of its present radius. DA white dwarfs are hydrogen-rich; DB white dwarfs are helium-rich; DC are carbon rich; DF are calcium-rich; DP are magnetic stars. White dwarfs have relatively low rotational velocities. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol D |  |
| has symbol wd |  |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| white giant | has definition A giant star of spectral type A. Some RR Lyrae stars are white giants. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| white hole | has antonym black hole |  |
| has definition The time-reversal of a black hole. A white hole is a singularity from which matter emerges unpredictably, but into which matter cannot enter. The initial singularity of the standard big bang theory is an example of a white hole. It can be shown that the creation of a new universe from a false vacuum bubble in the context of classical general relativity would require a white hole singularity, which means essentially that it cannot be done, even in principle. However, a false vacuum bubble could conceivably grow to become a new universe through a process of quantum tunneling. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of singularity |  |
| white supergiant | has definition A supergiant star with a spectral type of A. White supergiants are rare; the nearest is Deneb, which lies 1500 light-years away. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of A star |  |
| Wien displacement law constant | has equation  |  |
| has symbol b |  |
| has uncertainty 0.0000051 × 10-3 m K |  |
has value 2.8977686 × 10-3 m K  |  |
| is an instance of physico chemical constant |  |
| Wien's law | has definition The wavelength at which a blackbody emits the greatest amount of radiation is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of quantum law |  |
| William Herschel Telescope | has acronym WHT |  |
| has altitude 2332 m |  |
| has aperture 4.2 m |  |
| has creation date 1987 |  |
| has focal ratio 02.5, 11 |  |
| has latitude 28° 46' N |  |
| has location La Palma, Canary Islands |  |
| has longitude 17° 53' W |  |
| has mirror maker Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has mirror type Owens-Illinois Cer-Vit |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Grubb-Parsons |  |
| has operator Royal Greenwich Observatory |  |
| has owner Obs. del Roque de los Muchachos |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| winter solstice | is an instance of solstice |  |
| Wisconsin-Indiana-Yale-NOAO Telescope | has altitude 2089 m |  |
| has aperture 3.5 m |  |
| has comment mirror by Steward Observatory Mirror Lab (R. Angel) |  |
| has creation date 1994 |  |
| has focal ratio (f/1.75) f/6.3 |  |
| has latitude 31° 57' N |  |
| has location Kitt Peak, Arizona. US |  |
| has longitude 111° 36' W |  |
| has mirror maker Charles Harmer/NOAO |  |
| has mirror type spin-cast borosilicate honey-comb |  |
| has mounting manufacturer L & F Industries |  |
| has owner WIYN Observatory |  |
| has synonym WIYN 3.5 m |  |
| is an instance of altazimuth telescope |  |
| is an instance of optical telescope |  |
is an instance of reflector  |  |
| WN star | has emission line He I, He II, N III, N IV or N V | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Wolf-Rayet |  |
| WO star | has emission line He I, He II, O IV, O V or O VI | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of Wolf-Rayet |  |
| Wolf 359 | has definition A nearby flare star. |  |
| is a part of Leo |  |
| is an instance of flare star |  |
| Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte | has declination -15d27m51s |  |
| has definition A dwarf E5 elliptical galaxy, sometimes considered a member of the Local Group. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif) |
| has diameter 11.5 × 4.0 arcminute |  |
| has distance 4.2 million light years |  |
| has magnitude 11.03 |  |
has NED data  |  |
| has right ascension 00h01m57.9s |  |
| has synonym WLM |  |
| is a part of Local Group |  |
is an instance of irregular galaxy  |  |
| Wolf-Rayet | has definition Hot stars characterized by wide emission lines of highly ionized elements, standing out distinctly from the continuous spectrum. There exist three varieties: WN, WC and WO |  |
| has definition One of a class of very luminous, very hot (as high as 50000 K) stars whose spectra have broad emission lines (mainly He I and He II), which are presumed to originate from material ejected from the star at very high (~ 2000 km s-1 ) velocities. Some W-R spectra show emission lines due to carbon (WC stars); others show emission lines due to nitrogen (WN stars). (Hiltner and Schild classification: WN-A, narrow lines; WN-B, broad lines.) | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has ejection velocity 2000 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has emission line He I, He II | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| has temperature up to 50000 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of early star |  |
| is a kind of emission line star |  |
| work function | has definition The amount of energy needed to release an electron from the attraction of positive ions in a metal. It is different for different metals. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| has symbol W |  |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| wormhole | has definition A bridge to another universe created by a black hole. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition A tube-like region of space connecting one region of the universe to another. | ![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition An intriguing solution to the equations of general relativity which describes a neck that can connect two completely separate universes. Wormholes arise in the discussion of the creation of a universe in the laboratory, because the new universe disappears through a wormhole and completely detaches itself from the parent universe. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of singularity |  |
| WR 124 | has distance 15000 light-years |  |
has image emission nebula M1-67
  |  |
has reference Grosdidier, Y.; Moffat, A. F. J.; Blais-Ouellette, S.; Joncas, G.; Acker, A. : 1999, Proc. IAU Symp. 193, 356. M1-67, nebula ejected from the 200 km/s runaway WN8 star WR 124  |  |
| has spectral type WN 8 |  |
| has spectral type WN8 |  |
| has velocity 200 km/s |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
is an instance of WN star  |  |
| WZ Cassiopeiae | has definition A lithium star, the most super-rich carbon star known. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| has effective temperature 2420 K | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of lithium star |  |
| WZ Sagittae | has definition A recurrent DAe old nova (1913 and 1946) with the shortest known orbital period (about 80 minutes). It is almost certainly a close binary system in which mass is being transferred onto a white-dwarf primary. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of recurrent nova |  |
| X-process | has definition The unknown nucleosynthetic process that Burbidge, Burbidge, Fowler, and Hoyle said had formed the light nuclei deuterium, lithium, beryllium, and boron. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of nucleosynthesis |  |
| X-ray | has definition A large band of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than extreme ultraviolet light. A typical X-ray photon has over one thousand times as much energy as a photon of visible light. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Photon of wavelength between about 0.1 Å and 100 Å - more energetic than ultraviolet, but less energetic than a γ-ray. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has frequency 30 PHz to 3 EHz |  |
| has wavelength 100 pm to 10 nm |  |
| is a kind of photon |  |
| X-ray astronomy | has definition Detection of stellar and interstellar X-ray emission. Because X-rays are almost entirely filtered out by the Earth's upper atmosphere, the use of balloon- and rocket-borne equipment is essential. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of astronomy |  |
| X-ray pulsar | has definition Pulsar (q.v.) that radiates in the X-ray region of the spectrum. Best verified examples are Her X-1 and Cen X-3. They are thought to be rotating, strongly magnetic neutron stars of about 1 Msun in a grazing orbit around a more massive star from which they are accreting matter. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pulsar |  |
| X-ray selected BL Lac object | has acronym SBL |  |
| is a kind of BL Lacertae |  |
| X-ray source | has definition A class of celestial objects whose dominant mechanism of energy dissipation is through X-ray emission. Galactic X-ray sources appear optically as starlike objects, peculiar in their ultraviolet intensity, variability (on time scales ranging from milliseconds to weeks), and spectral features. All known compact X-ray sources are members of close binary systems; a current popular model is mass accretion onto a compact object from a massive companion. (Four X-ray sources - all variable - are known to be associated with globular clusters.) The 21 known extended X-ray sources associated with clusters of galaxies seem to be clouds of hot gas trapped in the cluster's gravitational field. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif) |
| has wavelength X-ray |  |
| is a kind of celestial body |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| X-ray space telescope | has wavelength sensitivity in gamma ray and X-rays |  |
| is a kind of space telescope |  |
| xenon | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state 0 |  |
| is a kind of inert gas |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| XMM | has definition X-ray Multi-mirror Mission | ![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif) |
| has owner ESA |  |
is an instance of X-ray space telescope  |  |
| year | has definition A period of time based on the revolution of the Earth around the Sun. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of time unit |  |
| yellow | is a kind of optical |  |
| yellow giant | has definition A giant star with a spectral type of G. The nearest and brightest yellow giants are the two composing the double star Capella. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of G star |  |
| is a kind of giant |  |
| yellow supergiant | has definition A supergiant star with a spectral type of G. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of G star |  |
| is a kind of supergiant |  |
| Yerkes 40-inch Refractor | has altitude 334 m |  |
| has aperture 1.016 m |  |
| has comment a focal reducer also provides an f/3 focus |  |
| has creation date 1897 |  |
| has focal ratio f/19.04 |  |
| has latitude 42° 34' N |  |
| has lens maker Alvan Clark & Sons |  |
| has location Williams Bay, Wisconsin, US |  |
| has longitude 88° 33' W |  |
| has mounting manufacturer Warner and Swasey |  |
| has operator University of Chicago |  |
| has owner Yerkes Observatory |  |
| has synonym 40 inch |  |
| is an instance of German equatorial telescope |  |
| is an instance of refractor |  |
| ylem | has definition Primordial state of matter - neutrons and their decay products (protons and electrons) - before the Big Bang. The term was taken from Aristotle and used for the α-β-γ theory. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The word used by Gamow and his collaborators for the primordial material of the Big Bang. In most of his work Gamow assumed that the ylem consisted entirely of neutrons. In inflationary cosmology, the role of the ylem is played by the false vacuum. | ![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of phase of matter |  |
| yocto | has symbol y |  |
| has value 10-24 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| yotta | has symbol Y |  |
| has value 1024 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| young thin disk | has definition A subPopulation In the thin disk whose stars range in age from 0 to 1 billion years old. The stars of the young thin disk have a scale height of 350 light-years and have very circular orbits around the Galaxy. | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| has star age 0 to 1 billion years | ![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of thin disk |  |
| ytterbium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| has ocean residence time 400 years |  |
| is a kind of rare Earth |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| yttrium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state III |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| YY Orionis | has definition An extremely young star (younger than T Tauri) in the Orion Nebula. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Orion |  |
| is an instance of YY Orionis star |  |
| YY Orionis star | has definition Very young, late-type, low-mass stars in the gravitationally contracting stage in which the star is still accreting matter from the protostellar cloud. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectra peculiarity inverse P Cyg type emission profiles in the Ca II HK lines | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of T Tauri star | ![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif) |
| Z Camelopardalis | has acronym Z Cam |  |
| has definition is a dwarf nova with standstills in the light curve |  |
has light curve from AAVSO  |  |
has reference Oppenheimer, B.D., Kenyon, S.J., Mattei, J.A.: 1998, AJ 115, 1175. An Analysis of AAVSO Observations of Z Camelopardalis  |  |
| is a part of Milky Way |  |
is an instance of Z Camelopardalis star  |  |
| Z Camelopardalis star | has definition A class of dwarf nova with standstills in their light curves. Z Cam itself is a semidetached binary (period 7h21m) consisting of a dG1 star and a hot white dwarf or a hot blue subdwarf which is probably degenerate. Mean time between eruptions, 20 days. Peak-to-peak amplitude, about 0.5 mag. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has prototype Z Camelopardalis |  |
| is a kind of dwarf nova |  |
| Z particle | has definition Massive boson thought to have been abundant in the early universe, when the unified electroweak force was manifest. | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Particle that transmits the unified electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces. These particles were predicted by the Weinberg-Salam theory of the 1960s and later discovered in the 1980s. | ![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of vector boson |  |
| z pinch | has definition A diffuse toroidal pinch in which the magnetic field runs around the plasma column. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pinch machine |  |
| Zeeman effect | has cause the influence of an magnetic field on a radiating atom or ion. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition Line broadening due to the influence of magnetic fields. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| has effect splitting of a spectral line into a multiplet of lines with distinct polarization characteristics. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of line broadening |  |
| is measured by measuring the difference between right-hand and left-hand polarization across a spectral line. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif) |
| zenith | has antonym nadir |  |
| has azimuth 0 |  |
| has definition The point in the sky directly overhead. | ![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has definition The point on the celestial sphere directly above the observer's head - i.e., opposite to the direction of gravity (nadir). | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif) |
| has elevation 90 |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate |  |
| is opposite of nadir |  |
| zenith distance | has definition Angular distance on the celestial sphere measured along the great circle from the zenith to the celestial object. Zenith distance is 90° minus altitude. | ![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of angle |  |
| is an instance of local coordinate component |  |
| zepto | has symbol z |  |
| has value 10-21 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| zero-point energy | has definition The energy of the lowest state of a quantum system. Amount of vibrational energy allowed by quantum mechanics to be associated with atomic particles at 0 K, whereas classical mechanics requires this to be zero. Also, the energy of an electron in its ground state. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of energy |  |
| zero-point pressure | has definition The pressure contributed by degenerate electrons, which do not come to rest even at absolute zero. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of pressure |  |
| Zerodur | is a kind of mirror |  |
| zeroth law of thermodynamics | has definition The temperature of a body in equilibrium is the same at all points. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| has synonym law of thermal equilibrium | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif) |
| is an instance of thermodynamics law |  |
| zeta Aurigae star | has definition Binary star with a K supergiant primary and a main-sequence secondary. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of binary star |  |
| Zeta Ophiuchi | has definition A reddened O star (a runaway star from the Sco-Cen association) with a high rotational velocity. It is well known for its strong interstellar absorption lines in the visible part of the spectrum. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has distance 170 pc | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has rotational velocity 396 km s-1 | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O9.5 V | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Ophiuchus |  |
| is an instance of dwarf |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| Zeta Pup | has definition The brightest Of star known, embedded in the Gum Nebula. It has an envelope which is rapidly accelerating outward. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| has spectral type O4f | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of Puppis |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| Zeta Puppis | has B-V magnitude -0.26 |  |
| has declination -40 0 11 |  |
| has right ascension 8 3 35.0 |  |
| has spectral type O5Iaf |  |
| has synonym HR 3165 |  |
| has V magnitude 2.25 |  |
is a part of Puppis  |  |
| is an instance of blue supergiant |  |
| is an instance of naked eye star |  |
| is an instance of O star |  |
| zetta | has symbol Z |  |
| has value 1021 |  |
| is an instance of unit prefix |  |
| zinc | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state II |  |
| has ocean residence time 5000 years |  |
| is a kind of chalcophile element |  |
| is a kind of recycled oceanic element |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| zirconium | has image  |  |
| has ocean oxidation state IV |  |
| is a kind of transition metal |  |
| is a kind of unclassified oceanic element |  |
| Zodiac | has definition A band about 8° wide on the celestial sphere, centered on the ecliptic. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has historical origin Contains twelve constellations which represent a calendar of the Sun's apparent progress across the celestial sphere. Naked eye planets are found along much the same path (the ecliptic) and caused these constellations to become a focus for astrology. | ![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif) |
| has purpose to facilitate planetary observations as most objects in solar orbit are found in this region |  |
| has synonym ecliptic region |  |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
| zodiacal constellation | has definition a constellation within the Zodiac region, each is a sign of the zodiac except for Ophiuchus |  |
| has historical origin a constellation which the Sun passes through |  |
| has historical purpose to approximately represent the month in which the Sun occupies this constellation |  |
| is a kind of constellation |  |
| is a part of Zodiac |  |
| Zodiacal Light | has definition A faint glow that extends away from the Sun in the ecliptic plane of the sky, visible to the naked eye in the western sky shortly after sunset or in the eastern sky shortly before sunrise. Its spectrum indicates it to be sunlight scattered by interplanetary dust. (Pioneer 10 has determined that its brightness varies inversely as the square of the distance out to 2.25 AU and then decreases more rapidly.) The zodiacal light contributes about a third of the total light in the sky on a moonless night. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif) |
| is a kind of scattering |  |
| Zone of Avoidance | has definition An irregular zone near the plane of the Milky Way where the absorption due to interstellar dust is so great that no external galaxies can be seen through it. | ![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| has name origin galaxies appear to "avoid" the Milky Way | ![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif) |
| is a part of celestial sphere |  |
| is an instance of equatorial sky area |  |
 Astronomy Glossary Help
Astronomy Glossary Help Astronomy Glossary Help
Astronomy Glossary Help








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)






































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:20.0](facet.gif)






























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:24.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:23.0](facet.gif)










































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)










































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:28.0](facet.gif)


















































































![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)












































































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)






































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:25.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)







































































































































![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)

































































































































































































![has source: [1946], Resolution 2, approved by the 9th CGPM 1948). A current of 1 A is equivalent to the passage along the filament of a light bulb of about 6 × 10<sup>18</sup> electronic charges per second., 2001-09-19 14:39:00.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)





















![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)





















































































































































































































![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:13.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)













































![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)










































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)































































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)






















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:44.0](facet.gif)




























![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:33.0](facet.gif)




















































































































































![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)













































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)



































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [adapted from B.M. Peterson <i>An Introduction to Active Galactic Nuclei</i>, Cambridge University Press, (1997)], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:02.0](facet.gif)
























![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:19.0](facet.gif)







































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [JJ95]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)




































































































































































































































![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)







































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)





































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:26.0](facet.gif)




























































































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)




































































































































































































































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)

























![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)


















































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)




















![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)

![has catalog: Radio source, has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:30.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [LB90][H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:49.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)





















![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)













































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
































![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)





































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:01.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [HH98], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)













































































































































![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:38.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)





















































![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

















































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)





































![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)























































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)

























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)
























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)

























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)





















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)
































![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:50.0](facet.gif)
































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)




















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:55.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)




















![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:48.0](facet.gif)



























































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
































































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)







































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)




























![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:16.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)



































![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:15.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76]*, 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:48.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)



























![has source: [A84][C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:32.0](facet.gif)





















































































































![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
















































































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)


























































































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:16.0](facet.gif)



























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)















































































































































































![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)






















































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:19.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [f88], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:05.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:06.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)

























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [SILK90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:36.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)


































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:47.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:52.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [S92]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92]*, 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:06.0](facet.gif)








































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)






























![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)




































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:04.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)










































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)

































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)









































































































































































































































































































































































![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)






















































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:44.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)




























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:16.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:34.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:18.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)






































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:58.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:01.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:37:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:57.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


























![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:56.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)

































































































































































![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:09.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:51.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:07.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [alpha] or Ca II). It is a chromospheric phenomenon associated with and often confused with a facula. (sometimes called flocculus), 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:53.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:54.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:10.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:35.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:22.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:26.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:59.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:14.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)













































































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:25.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:17.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)





























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:59.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:57.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:12.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:21.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:57.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:09.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], has author: Rood, 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:36.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:01.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:13.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:45.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)


























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:41.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:24.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:46.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:02.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)





































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:08.0](facet.gif)
















































































































































![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:43.0](facet.gif)

































![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:27.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)






























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)






























































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:01.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:20.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:23.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:15.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:37:33.0](facet.gif)



















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:49.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:56.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:24.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:36:14.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:39.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:37:20.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:24.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:36:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:22.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:43.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:21.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:34:56.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:29.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:51.0](facet.gif)














































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:49.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:18.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Steshenko 1967]). Typical diameter, 10<sup>9</sup> cm., 2001-09-19 14:38:59.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:36:08.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:37:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:12.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:39.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88]], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:33:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:55.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)









































![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:26.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:36.0](facet.gif)





























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JM92], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:50.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:24.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:48.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)






















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:58.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:34:38.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:03.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:06.0](facet.gif)




































































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:20.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [c97], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:32.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:37.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:38.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:23.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:00.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:43.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [NASA/SP-2000-7501/Vol1], 2001-09-19 14:33:24.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:53.0](facet.gif)























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:19.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)





















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:53.0](facet.gif)















![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:52.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)

































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:15.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)



























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:11.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:50.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:57.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)







































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:11.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:35.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:47.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:03.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:04.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:40.0](facet.gif)






















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:13.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:29.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:28.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:36:55.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:04.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)






















































































































































![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:38:53.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:09.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:50.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:36:35.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:35.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:35.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:28.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:27.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:38.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)
















![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:51.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:02.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:39.0](facet.gif)





























![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:42.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:09.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)


















![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:17.0](facet.gif)














![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:07.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:34:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [Silk90], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [CD99], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [P88], 2001-09-19 14:33:03.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:32:32.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:35:32.0](facet.gif)

























































![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:37.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:38:19.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:17.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:42.0](facet.gif)




![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:34:52.0](facet.gif)






![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:38:46.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:32:33.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [T01], 2001-09-19 14:34:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:48.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:37:28.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:47.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C97], 2001-09-19 14:33:18.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:44.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:46.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:11.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:21.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:20.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:54.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:53.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)








![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:47.0](facet.gif)




































![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:31.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:19.0](facet.gif)











![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:30.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G99], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:35:08.0](facet.gif)













![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:34:41.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:37:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:34.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:22.0](facet.gif)










![has source: [LLM96], 2001-09-19 14:32:38.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:37:45.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:52.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:35:50.0](facet.gif)

















![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [G97], 2001-09-19 14:33:34.0](facet.gif)







![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [C95], 2001-09-19 14:37:13.0](facet.gif)












![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [JJ95], 2001-09-19 14:35:40.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:43.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [LB90], 2001-09-19 14:33:10.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:32:25.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:44.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [McL97], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:37:34.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [S92], 2001-09-19 14:38:25.0](facet.gif)





![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:06.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:05.0](facet.gif)


![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:45.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:35:33.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:43.0](facet.gif)



![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:36:42.0](facet.gif)




























![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [A84], 2001-09-19 14:38:27.0](facet.gif)









![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:34:49.0](facet.gif)

![has source: [H76], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)
![has source: [F88], 2001-09-19 14:38:26.0](facet.gif)

