What
is Current Density?
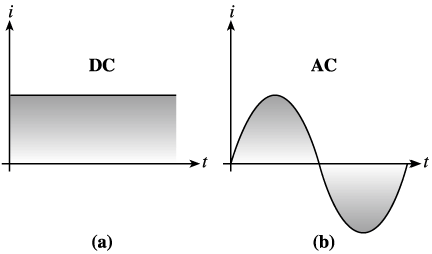
Figure
2.3 a. Direct current (DC) b. Sinusoidal
or alternating current (AC)
The
current density (J)
is the measure of the amount of current
flowing through a unit area perpendicular
to the direction of current flow.
The boldfaced J
is a vector whose magnitude is the
current per unit area (A/m2)
and whose direction is the direction
of current flow.
Range
of Currents
Can
you think of some of the currents
we encounter in our daily life?
Type
your answer in the box below:
Currents
in Our Daily Life
We encounter a wide range of currents
in our daily life. Table 2.1 shows some
examples of current ranging from high
currents to very small currents. In
the electrical power industry, for example,
an ampere is a small unit. In an electronic
circuit it is big unit for measuring
current. Therefore, the milliampere
(mA),
one-thousandth of an ampere (0.001 A),
or the microampere (µA),
one-millionth of an ampere (0.000001
A),
is used.
Table 2.1 Range of Currents

|